ADH2 Final: Liver, Pancreas, Varices
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Common causes of hepatitis: (3)
viruses (herpes, varicella-zoster)
drugs/toxins (tylenol)
alcohol
How does Hepatitis A (HAV) spread? (3)
fecal-oral route
eating contaminated food/water
shellfish common
contact w/ infected stool
Hepatitis B (HBV) spreads how? (4)
Blood/ body fluids
unprotected sex
sharing needles
infected mother → baby
How does hepatitis C spread? (3)
blood-to-blood (needles)
organ transplants
tattoo/piercings w/ dirty equipment
Facts abt Hepatitis D? (2)
can only infect someone who already has Hep B
Spreads the same way as hep B
body fluids
sex
Common symptoms of Hepatitis? (6)
flu-like findings (fatigue, fever, N)
jaundice
dark urine (bilirubin)
clay colored stool (decreased bile)
RUQ pain
joint pain
Lab changes in hepatitis? (4)
Increased ALT (liver injury)
Increased AST
Increased ALP
Increased Bilirubin → jaundice
Liver biopsy pre procedure care:
pt is fasting @ midnight day of procedure
incase they need surgery d/t complications
Liver biopsy During procedure: (2)
supine
pt holds breath for 10 secs to keep liver still
Liver biopsy post-procedure: (2)
right-side-lying to reduce bleeds
monitor VS, abd pain, bleeds, s/s pneumothorax
Nurse care hepatitis: (2)
rest liver
no alcohol!
no unnecessary meds!
limit physical activity
high carb, high cal diet
Hepatitis complications:(4)
Chronic hepatitis → cancer!
Fulminant Hepatitis (sudden + severe liver failure!!)
hepatic encephalopathy
liver failure
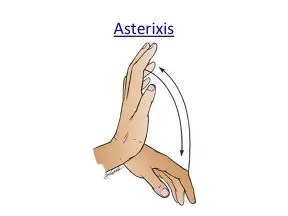
Symptoms Hepatic encephalopathy? *4)
ammonia levels build in brain
stupor
confused
asterixis (hand flapping)
fruity, musty “liver breath” (aka fetor hepaticus)
What exactly is cirrhosis?
what does it lead to? (3)
scarring of the liver (healthy cells replace w/ nonfunctioning scar tissue)
blocked blood flow
blocked bile flow
liver failure
Causes of cirrhosis? (5)
alcohol
hep B or C
toxins/meds
bile duct blockage (biliary cirrhosis)
autoimmune disease
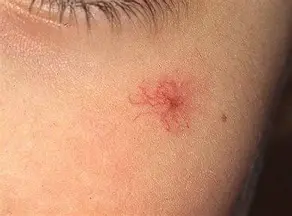
Symptoms of cirrhosis? (8)
RUQ pain
ascites
pruritus
confused
splenomegaly → thrombocytopenia
spider angiomas (spider-like blood vessels)
jaundice
GI bleed (esophageal varices)
Cirrhosis labs: (4)
Increased bilirubin
Increased ammonia
Decreased albumin → ascites
Decreased platelets
Care for Cirrhosis: (6)
HOB >30 degrees
Elevate feet
Low Na diet
Measure abd girth
Monitor mental status
Protect skin (fragile and itchy)
Meds for Cirrhosis? (3)
Diuretics
BB (reduce portal HTN and esophageal varices bleeds)
Lactulose
removes ammonia through stool
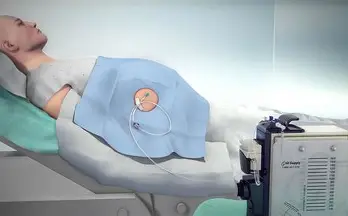
Whats paracentesis and Pre + Post (2) op care:
removes ascites fluid from belly
Pre: void bladder
Post:
measure fluid
weigh pta
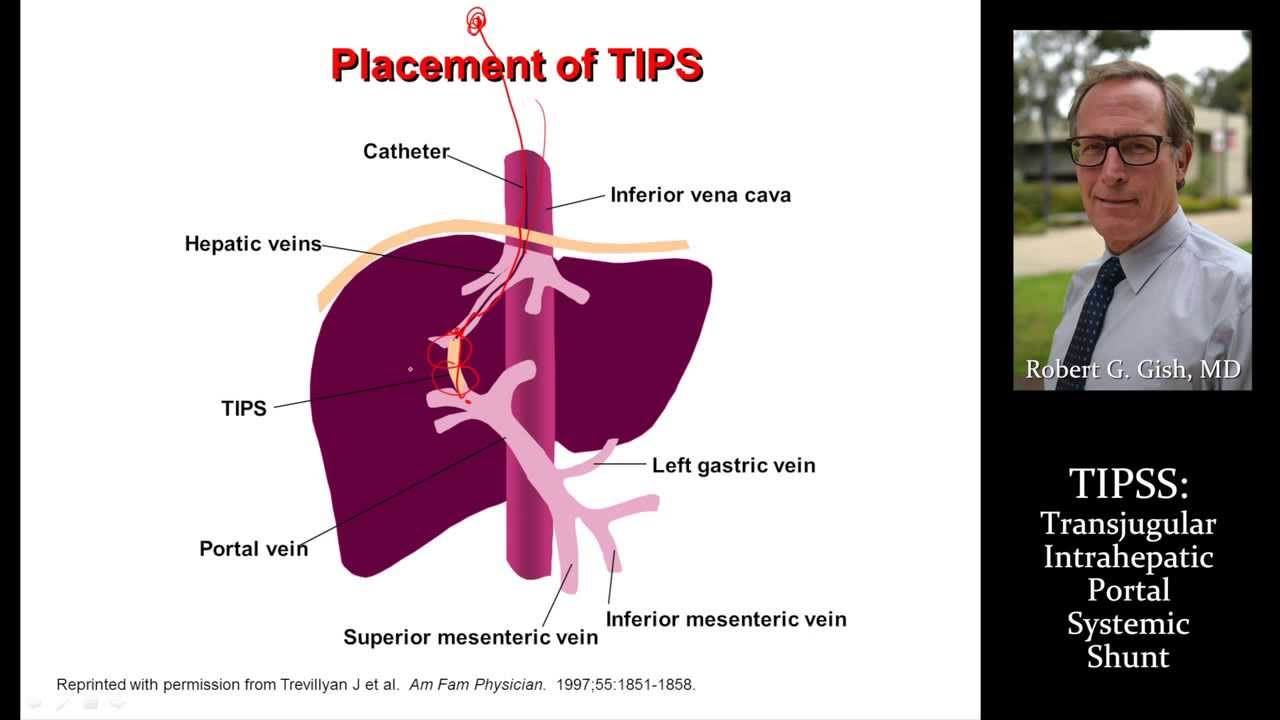
What procedure reduces Portal HTN?
TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic shunt)
shunt placed through liver to reduce Portal HTN
Complications of Cirrhosis?
Portal Systemic Encephalopathy
toxicity in brain bc liver cant filter blood (ammonia build-up)
Lactulose to clear up ammonia
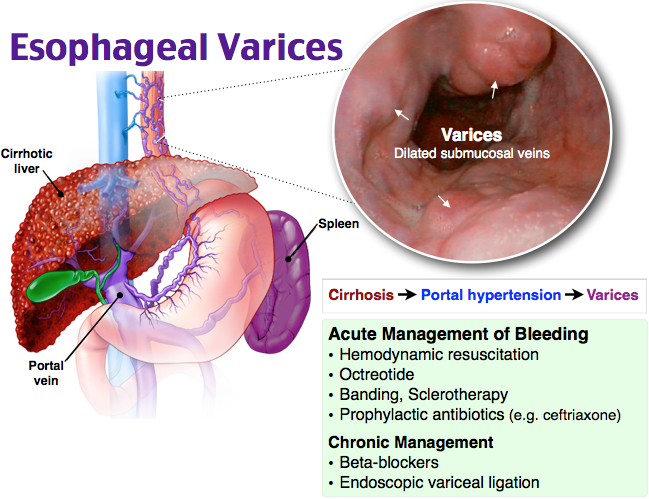
Esophageal Varices
What are Esophageal Varices?
huge, fragile veins in esophagus caused by portal HTN
bleeds easily → life threatening
Portal hypertension = elevated BP in veins carrying blood from intestines to liver
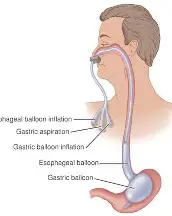
Tx for Esophageal Varices? (5)
Esophagogastric Balloon Tamponade
Sclerotherapy (inject to shrink)
Ice Saline lavage (to vasoconstrict)
Blood transfusions
Banding (ligation)
Classic signs of pancreatitis? (4)
severe, constant LUQ/ epigastric pain
pain radiates to back
worse when lying FLAT
better when lean forward or fetal position

2 Skin signs of pancreatitis:
Cullen’s sign:
bruise around belly button
Turner’s sign
bruising on flanks

What lab diagnoses pancreatitis? (2)
Elevate Serum Lipase!!
Elevated Serum Amylase!!
Nurse care pancreatitis? (6)
NPO until no pain
IV hydrate
NG tube if vomit
NO alc or smoking
Bland, low fat meals when able to eat
Monitor glucose
pancreas makes insuiln
Whats a pancreatic enzyme to treat pancreatitis?
what’s its function?
Pancrelipase!!
replaces pancreatic enzymes → helps digest fat and protein
Pancrelipase teachings: (5)
take w/ every meal and snack
can sprinkle capsule on food
drink water after taking
wipe lips after (can irritate skin)
take AFTER antacids/ H2 blockers

Complications of pancreatitis? (6)
Hypovolemia (fluid loss)
Pancreatic infx
Type 1 Diabetes
Lung issues (effusions/atelectasis)
Coagulation problems
Multi-organ failure
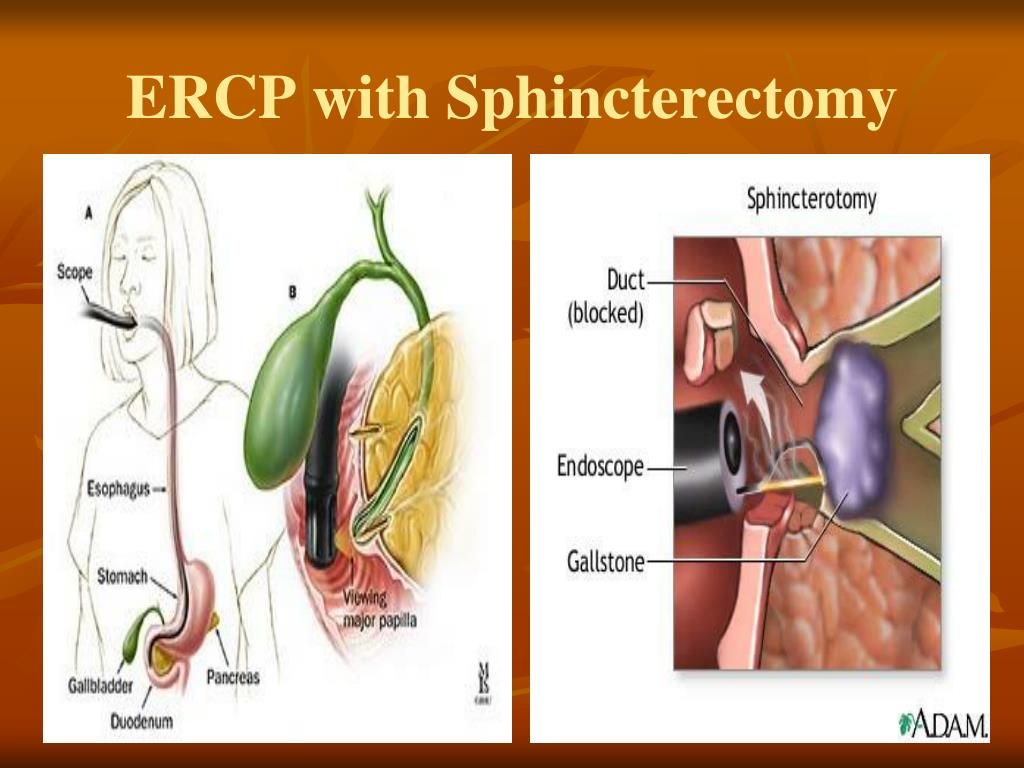
Surgeries for Pancreatitis: (4)
ERCP
removes gallstones blocking pancreatic duct
Cholecystectomy
if result of cholecystitis/gallstones
Sphincterotomy:
enlarges pancreatic duct
Pancreatojejunostomy:
reroutes pancreatic secretion to jejunum