Chemistry Chapter 1: Matter & Measurement
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is Chemistry?
The scientific study of matter, its properties, and its behavior
Matter
Anything that has mass and occupies space; everything that surrounds us
Includes things we can and can’t see
Can be classified according to composition and physical state
Composition
What is it made out of?
Element
Compound
Mixture
Physical State
Gas
Liquid
Solid
Properties
Characteristics used to describe matter, such as color, odor, and density
Behavior
The way matter reacts or changes under various conditions, including physical and chemical processes
What is the Importance of Chemistry?
Central to understand other sciences and the connections between them
Important practical applications (ex. energy, medicine, batteries in electronics) (chemical reactions are taking place)
A way of explaining our material world
What do the Properties of Matter relate to?
The kinds of atoms (composition)
The arrangement of atoms (structure) (how are they arranged?)
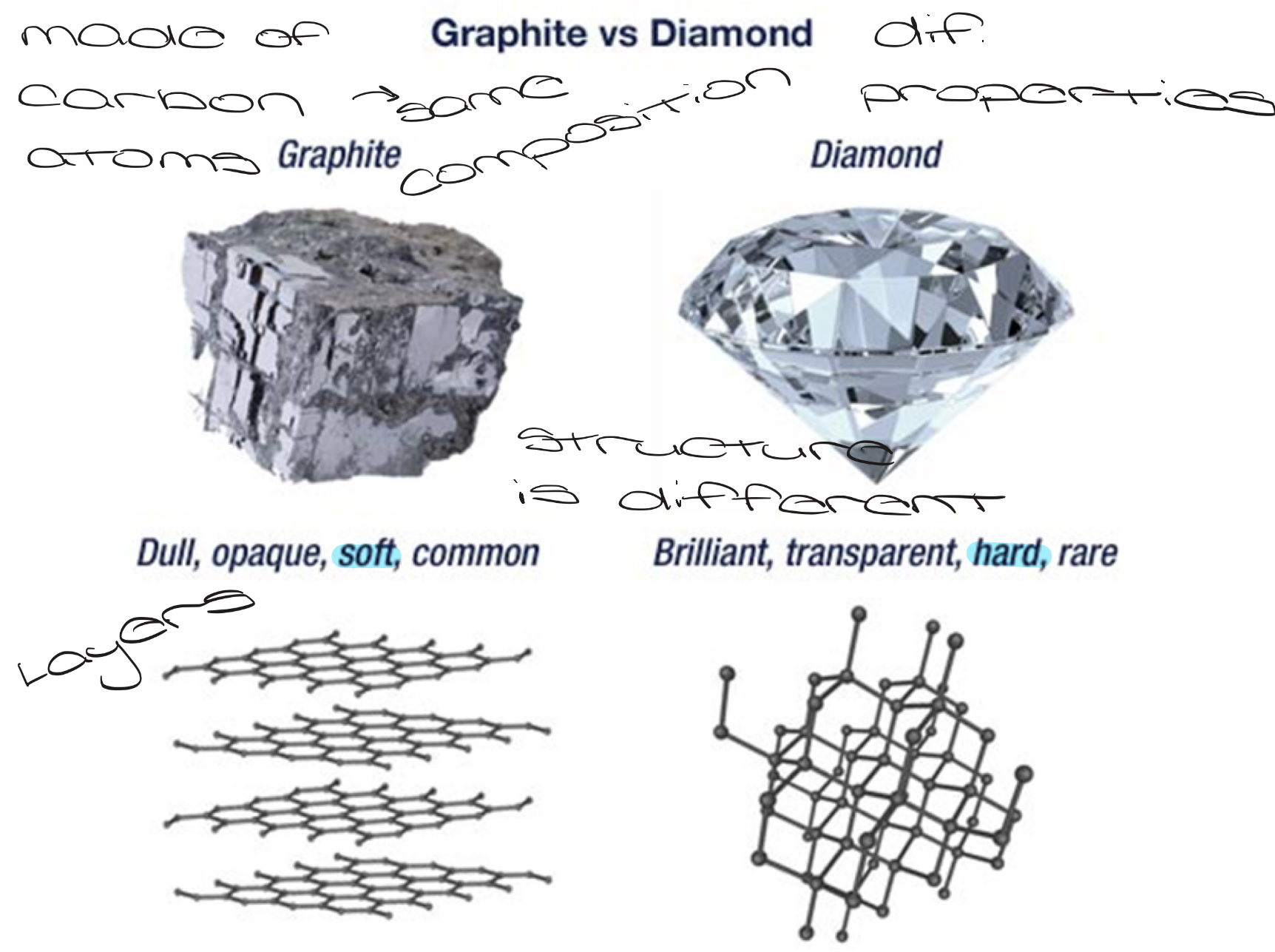
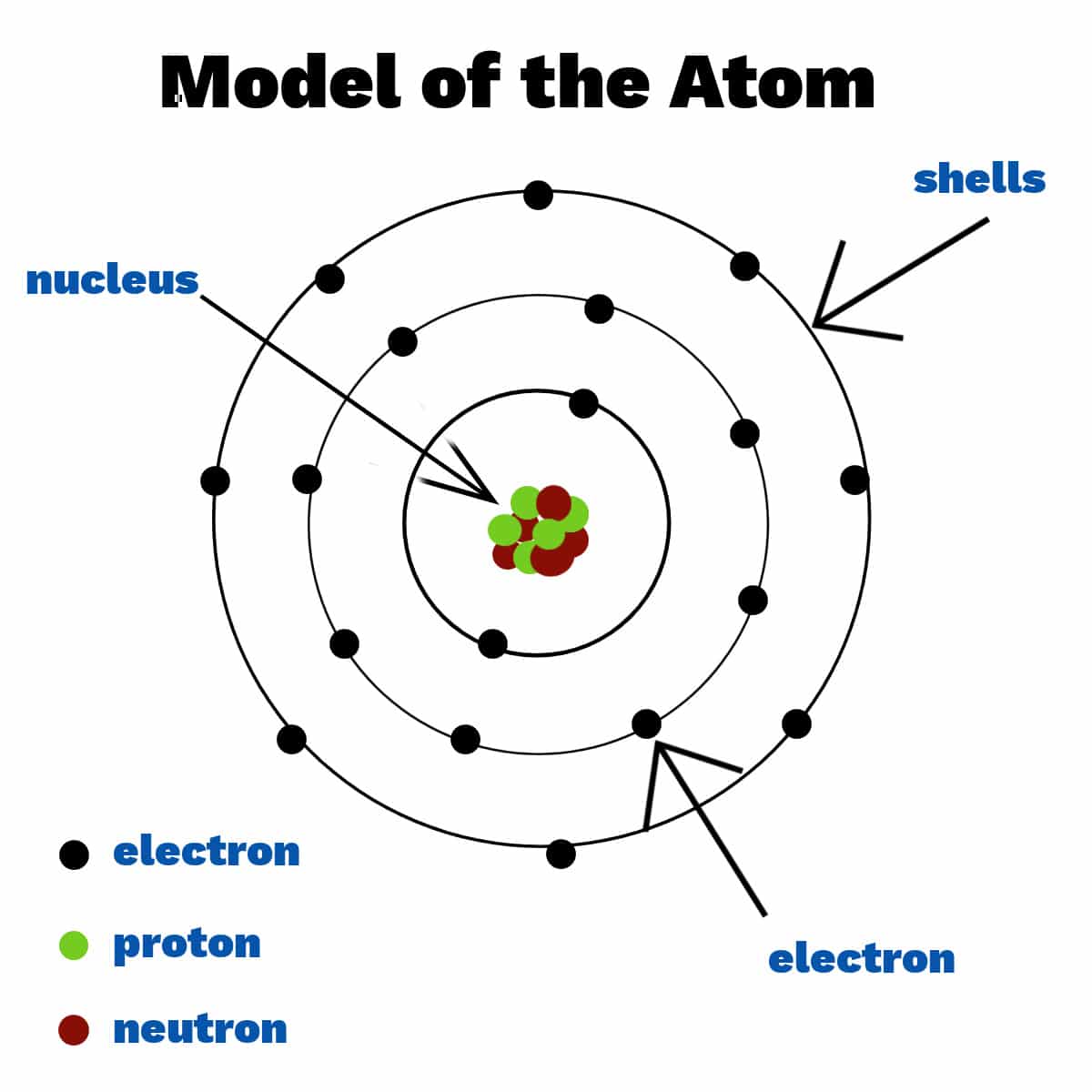
Atom
The building blocks of matter
Element
A pure substance that consists of only 1 type of atom
Cannot be decomposed into smaller substances
Compound
Made of 2 or more different kinds of elements held together by special forces (ex. Water - H₂0)
Constant ratio
Pure substance
Mixture
A physical combination/collection of 2 or more substances (elements and/or compounds)
Not chemically bonded
Not a pure substance; composition is never constant (ex. air in Albany is different from air in the Bronx)
Pure Substances
Elements & compounds
Diatomic Element
Must exist as a 2-atom element, can’t exist on its own
Hydrogen (H₂)
Nitrogen (N₂)
Oxygen (O₂)
Fluorine (F₂)
Chlorine (C₂)
Bromine (Br₂)
Iodine (I₂)
Scanning Tunneling Microscope
Image surfaces at the atomic level
1986 Nobel Prize awarded to E. Ruska, G Binning, & H. Rohrer
How many elements are in the Periodic Table? How many are non-radioactive?
118 elements in the Periodic Table, 92 are non-radioactive (others are too unstable to exist in regular conditions, rapidly decay to other elements)
What are 2 ways the Periodic Table is organized?
Into blocks & columns