Aging, Age-Related, Degenerative Disorders
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Macular Degeneration
Central portion of your retina (macula) becomes worn
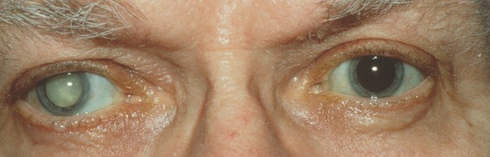
Cataracts
Clouding of the eye
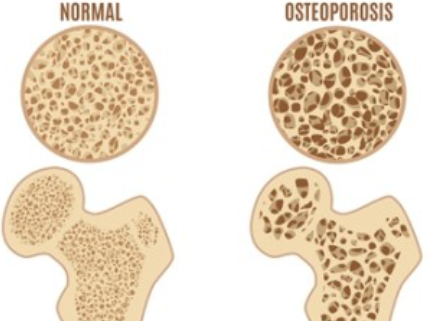
Osteoporosis
Bone disease that changes bone structure and strength through decreasing mineral density
Oestrogen: bone protection
More women affected by this due to menopause
Hyperkyphosis
Aka Dowager’s Hump caused by prolonged forward leaning posture (cane or walker)
Can be a result of advanced osteoporosis (vertebral collapse)
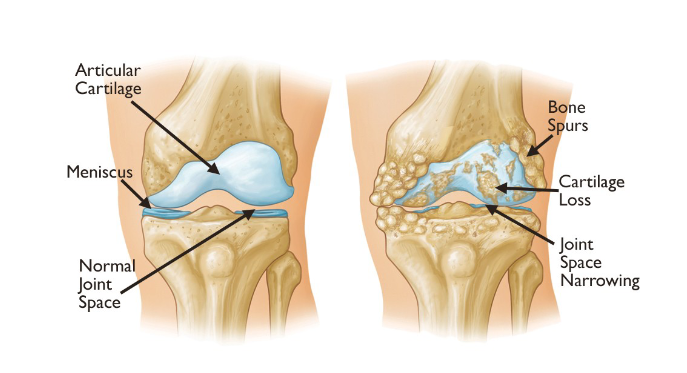
Osteoarthritis
Degenerations and breakdown of joints
Common in knees, hips and hands
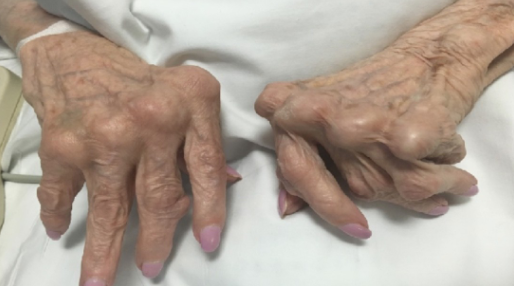
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Autoimmune and inflammatory disease
Common in hands, wrists and knees
Affects of Aging on Skin
Becomes thin, translucent and has less elasticity
More fragile, susceptible to bruising and tears
Loss of subcutaneous tissues (no padding or anchoring of veins)
Longer wound healing time
Diabetes (Type II)
Insulin resistance or impaired B-cell function
Can be not diagnosed, irritation in lining of blood vessels and damages peripheral nerves
Atherosclerosis
Fatty deposits causing damage, hardening and narrowing of blood vessels
Affects of Aging on Brain
Shrinks 5% per decade after 40yrs (frontal lobe)
More space to bleed and gain speed when hit head
Likely to bleed rather than bruise (ICP without symptoms)
Should be scanned at hospitals if they hit their head
Demyelination
Loss of myelin sheath (protective layer) around nerve cells
Causes delays, slower reactions, memory issues and struggle to learn new things
Brain Injuries
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) or Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)
Ischemic Stroke: Blocked blood vessel
Hemorrhagic Stroke: Ruptured blood vessel
Urinary Retention
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Enlarged prostate (need to go to hospital)
Compresses urethra blocking urine from being removed
Alzheimer’s Disease
Amyloid plaques in the brain, brain degeneration
Wandering: Getting lost or losing track of time due to increased confusion and disorientation
Vascular Dementia
Caused by impaired blood flow to parts of the brain
Abrupt Onset: Following a stroke
Lewy Body Dementia
Protein deposits (Lewy bodies) in the brain
Fluctuations between normal and abnormal behaviour
Parkinsonism: Motor/movement tremors or rigidity
Vivid visual hallucinations, may act out dreams in sleep
Frontotemporal Dementia
Damage to frontal and temporal areas, more significant
Mood/personality shifts (why is your belly big?)
Lack of social inhibition, apathy
Loses speech and language (nod and smile when they don’t understand what you’re saying)
Behaviour Variant FTD (BvFTD)
Frontal lobe affected first
Changes in behaviour and personality
Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA)
Temporal lobes affected first
Loss of language skills
Progressive Non-Fluent Aphasia and Semantic Dementia
Progressive Non-Fluent Aphasia
Speech becomes hesitant and lacks grammatical accuracy
Semantic Dementia
Lose ability to understand or formulate words in a spoken sentence
Wernicke’s Encephalopathy
Loss of mental activity
Vision change (twitching/ticking)
Similar to alcohol withdrawal
Muscle coordination loss
Feelings of apathy, confusion and unmotivated (don’t look after themselves)
Korsakoff’s Syndrome
Can’t form new memories
Confabulation (know enough to make up info to fill gaps)
Severe memory loss
Hallucinations (later stages)
Feelings of apathy, confusion and unmotivated (don’t look after themselves)
7 Stages of Progressive Dementia
Appears normal and can cover up lapses
Forgets certain things but can otherwise function normally
Difficulties at work, becomes anxious and family notices
Reduced ability to count, finds travel difficult, and can’t manage affairs
Needs help getting dressed
Help eating, using toilet, incontinent, disoriented, forgets who they are
Speech loss, motor stiffness, needs feeding, incontinence, total disorientation
Sundowning
Increased agitation in late afternoon/evening
Refusal to obey those trying to help
Delirium
Sudden change from their baseline (on and off switch)
PINCH ME (Pain, Infection, Constipation/Urinary Retention, Hydration, Medications/Substances and Environmental Triggers)
Reversible
Parkinson’s Disease
Loss of dopamine
Early stages retain good brain function, may develop dementia later
Masked face, stooped posture, parkinson’s shuffle, lots of tremors
Locked-In Syndrome
Rare neurological disorder, brainstem damage (pons)
Full consciousness and normal cognitive abilities
Paralysis of all voluntary muscles EXCEPT vertical movements of the eyes (up and down) and blinking
Causes: Stroke, TBI, Tumours, Demyelination, ALS, Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Progressive neurodegenerative disease affecting nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord
Muscle weakness/twitches and slurred speech
Unknown cause and cure but therapy and medications to manage symptoms
Life expectancy of 3-5 years
Motor Neurone Disease
Group of neurological disorders that affect cells that control voluntary muscle movement
Muscle weakness/wasting, difficulty speaking, breathing and swallowing
Unknown cause and cure but therapy and medications to manage symptoms
Affects men and women equally at any age
Myaesthenia Gravis
Immune system attacks nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in muscles, blocking nerve signals
Weakness in voluntary muscles (face, eyes, throat)
No cure but Rituxan can help manage symptoms
More common in women under 40 and men over 60
Huntington’s Chorea
Inherited condition that causes brain cells to lose function (voluntary muscles and memory)
Uncontrolled movement (chorea), ataxia (loss of coordination), dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
Causes can be genetic or TBI, new cure known as AMT-130, slows progression
Muscular Dystrophy
Duchene muscular dystrophy causes progressive muscle weakness
Muscle weakness, scoliosis, developmental delay
Genetic disorder with no cure, just managing symptoms
Affects younger men
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Immune systems attacks myelin causing inflammation, disrupts and damages nerves that control body functions
Vision, motor, sensory, cognitive, and bowel issues
Genetic disorder with no cure, just managing symptoms
Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Immune system attacks nerves causing weakness and paralysis
Tingling, loss of reflexes, abnormal hr and bp
Not curable but ability to recover with minor symptoms
Treatment includes plasma exchange and IV immunoglobulin