Science
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Now on 98
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
What is the scientific method
A process where scientists formulate hypotheses, conduct experiments, and analyze data to draw conclusions.
What is the first step of the Scientific method
Ask a question
What is the second step of the Scientific method
Form a hypothesis
What is the third step of the Scientific method
Design an experiment
What is the fourth step of the Scientific method
Do the experiment
What is the fifth step of the Scientific method
Analyze the data
What is the sixth step of the Scientific method
Draw a conclusion/graph
What are the 3 variables in a experiment
Manipulative, Control, and Responding
What is the Manipulative Variable
The variable that is intentionally changed or controlled in an experiment to test its effects on the responding variable.
What is the Controlled Variable
The variable that remains constant and unchanged throughout an experiment to ensure that the effects of the manipulative variable can be accurately measured.
What is the Responding variable
The variable that is measured and observed in an experiment to determine the effect of the manipulative variable.
What is the data with numbers and graphs
quantitative
What is the data with colors and drawings
qualitative
What measurement system do scientists use
metric
What is the base measurement for length
meter
What is the base measurement for liquid volume
liter
What is the base measurement for weight
Grams
What is the measurement for temperature
Celsius
What is the base word for 0.1
Deci
What is the base word for .01
Centi
What is the base word for .001
Milli
What is the base word for 10
Deca
What is the base word for 100
Hecto
What is the base word for 1,000
Kilo
All of Earths things are made of _____
Atoms
Matter is everything that has ______ and _____ __ _____
weight takes up space
_____ are the building blocks of all matter
Atoms
What are the 3 subatomic particles
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons
Where is the Electrons in an Atom
Outer shell
Where are the Neutrons in an atom
Nucleus
Where are the Protons in an atom
Nucleus
In an element what do you have to do to get the atomic
Add the atomic number and x to get the atomic mass
What charge does a Proton have
Positive
What charge does a Neutron have
No charge
What charge does an electron have
Negative
What do atoms combine to make
molecules
What are the 4 spheres
Hydrosphere, Geosphere, Hydrosphere, Atmosphere
What is the Atmosphere
Air
What is the Hydrosphere
Water
What is the Geosphere
Rocks/ Earth
What is the Biosphere
Life
What is an organism
A living thing
What are the 5 functions of life
Reproduce, made of cells, respond to environment, grow and develop, metabolize
What are the levels of orginization
Atoms
Compounds
Molecules/organelles
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ System
Organism
Population
Community
Ecosystem
Biome
Biosphere
The invention of what resulted in the beginning of microbiology
Compound Microscope
What are the building blocks for all living things
Cells
What does it mean to be Eukaryotic
Multicellular
What does it mean to be Prokaryotic
Unicellular
What does the cell membrane do
Like a gatekeeper regulates who enters and exits
What stores the “Blueprints” of a cell
Nucleus
What are the coded blueprints to a cell
DNA
What is the powerhouse of the cell
Mitocondria
What shape is a plant cell
Rectangle
What shape is an animal cell
circle
In plant cells what helps the plant stay up
Cell wall
What helps plants convert sunlight to energy/Photosynthsise
Chloroplasts
What does Photosynthesis convert sun energy to
Glucose
What is CO2
Carbon Dioxide
H2O
Water
C6H12O6
Glucose
O2
Oxygen
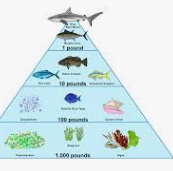
What percent of energy is lost on the energy pyramid
90%
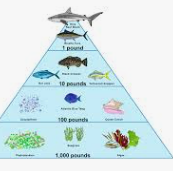
What is at the bottom of the pyramid
Producers
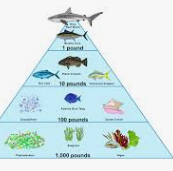
What is the 2nd level of the pyramid
Primary
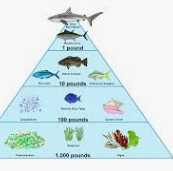
What is the 3rd level of the pyramid
Secondary
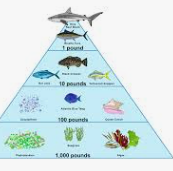
What is the top level of the pyramid
Consumers
What are decomposers called
FBI
How much energy do Producers have
1,000
How much energy do Primary have
100
How much energy do Secondary have
10
How much energy do Consumers have
1
What is MItosis
Asexual reproduction
What is MEiosis
Sexual reproduction
What is are the asexual reproduction letters
IPMATC
What is the I in IPMATC
Interphase
What is Interphase
The first phase in Mitosis where the cells aren’t doing anything besides growing and doing there jobs
What is Prophase
When the cell prepares to divide
What is Menaphase
When Chromosomes are created and start making the new cells
What is Anaphase
When the chromosomes are moved to opposite sides of the cell
What is Telophase
When the cell forms into 2
What is Cytokinesis
The end where the 2 cells are made
How many chromosomes are in a mitosis cell
46
How many daughter cells are there in mitosis
2
How many daughter cells are there in a meiosis cell
4
How many cell divisions are in mitosis
1
How many cell divisions are there in meiosis
3
How many chromosomes are there in a meiosis cell
23
What occurs when an egg and sperm come together
Fertilization
After fertilization what is left
A Zygote
What are the pros of Mitosis
Takes 1 to make a new cell
What are the Cons of Mitosis
No Variation
What are the Pros of Meiosis
Variation
What are the cons Meiosis
Takes 2 to make a cell
Chromosomes each control a different____
trait
What is a Homozygous allele
Both upper or lower case alleles
What is a heterozygous allele
1 upper and 1 lowercase allele
What are used to predict traits
Punnet Squares
What is the M in IPMATC
Metaphase
What is the P in IPMATC
Prophase
What is the T in IPMATC
Telophase