MGT 3320 Exam 3
5.0(1)Studied by 16 people
Card Sorting
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:59 AM on 4/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
1
New cards
Training
A planned effort to facilitate the learning of job-related knowledge, skills, and behavioral by employees.
2
New cards
Diversity Training
Change employee attitudes about diversity or to develop skills needed to work with a diverse workforce.
3
New cards
Unconscious Bias Training
Make employees aware of unconscious bias and reduce its impact by slowing down decision making and carefully considering the reasoning and language used in judgments.
4
New cards
Ally Training
Encourage employees to have conversations about difficult topics and perspectives without fear of blame or shame.
5
New cards
Continuous Learning
A learning system that requires unemployed to understand the entire work process and expects them to acquire new skills, apply them on the job and share what they have learned with other employees
6
New cards
Training Design Process
a systematic approach developing training programs
7
New cards
What are pressure points in a needs assessment?
Includes legislation, lack of basic skills, poor performance, new technology, customer requests, new products, higher performance standards, new jobs, business growth or contraction, global business expansion
8
New cards
Organizational Analysis
The process for determining the business appropriateness of training
9
New cards
Person Analysis
the process for determining whether employees need training, who needs training, and whether employees are ready for training
10
New cards
Task Analysis
The process of identifying the tasks, knowledge, skills, behaviors, and other factors (e.g. equipment, working conditions) that need to be emphasized in training.
11
New cards
What are the outcomes in a needs assessment?
What trainees need to learn, who receives training, what type of training, frequency of training, buy-versus-build training decisions, training versus other HR options such as selection or job design, how training should be evaluated
12
New cards
What is required for employee training readiness
* Self efficacy
* Understanding the benefits or consequences of training
* Awareness of training needs, career interest, and goals
* Enabling work environment characteristics
* Basic skills needed for learning
* Goal orientation
* Conscientiousness
\
* Understanding the benefits or consequences of training
* Awareness of training needs, career interest, and goals
* Enabling work environment characteristics
* Basic skills needed for learning
* Goal orientation
* Conscientiousness
\
13
New cards
What factors ensure that transfer of training takes place?
* Opportunity to use learned capability
* Self management skills
* Peer support
* Manager support
* Technological support
\
* Self management skills
* Peer support
* Manager support
* Technological support
\
14
New cards
What are the different training methods?
* Presentation Method
* Hands-On Method
* Group/Team Building
* Hands-On Method
* Group/Team Building
15
New cards
Presentation Training Method
Trainees are passive recipients of information
16
New cards
Hands-On Training Method
Trainees are actively involved in Learning
17
New cards
Group/Team Building Training Method
Improving team or group effectiveness by sharing ideas and experiences, building group identity, understanding the dynamics of interpersonal relationships, and getting to know each other’s strengths and weaknesses.
18
New cards
Training Evaluation Designs
\
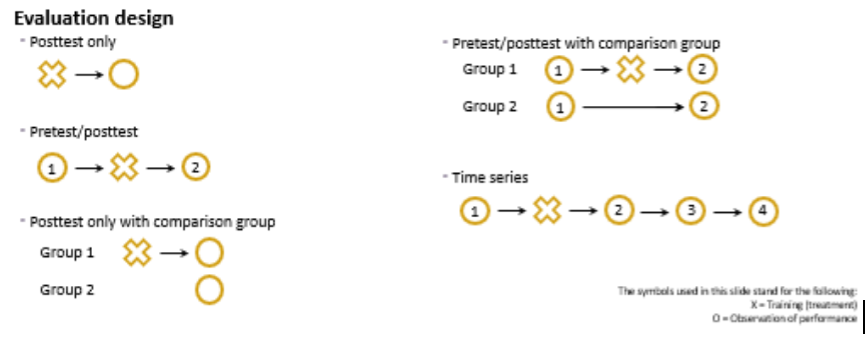
19
New cards
What is the difference between training and development?
Development as the acquisition of knowledge, skills, and behaviors that improve an employee’s ability to meet changes in job requirements and in client and customer demands
\
\
20
New cards
Understand the development planning system in terms of employer’s and employee’s roles
* Employer provides assessment information to identify the employee’s strengths, weaknesses, interests, and values
* Employee uses information to determine his/her career interests, values, aptitudes and behavioral tendencies and to identify needs and opportunities to improve \n
* Employee uses information to determine his/her career interests, values, aptitudes and behavioral tendencies and to identify needs and opportunities to improve \n
21
New cards
What are the different approaches to employee development
* Formal Education Programs
* Job Experiences
* Job Experiences
22
New cards
Formal Education Programs
Off-site and on-site programs designed for the company’s employees
23
New cards
Job Experiences
* Expose employees to new demands, tasks, problems and relationships to foster their professional growth
* Job Enlargement
* Job Rotation
* Transfer
* Promotions
* Downward Moves
* Sabbatical
* Volunteer Assignments
* Job Enlargement
* Job Rotation
* Transfer
* Promotions
* Downward Moves
* Sabbatical
* Volunteer Assignments
24
New cards
Job Enlargement
Adding challenges or new responsibilities to employee’s current job (special project assignments, switching roles within a work team)
25
New cards
Job Rotation
Involves the systematic movement of an individual from one job to another over the course of time
26
New cards
Transfer
The movement of an employee to a different in a different area of the company
27
New cards
Promotions
Advancements into positions with greater challenges, more responsibility, and more authority than in the previous job
28
New cards
Downward Moves
Seen as a punishment, give employees less responsibility and authority (helps in long-term development)
29
New cards
Temporary Assignments
Job tryouts such as employees taking on a position to help them determine if they are interested in working in a new role
\
\
30
New cards
Sabbatical
A leave of absence from the company to renew or develop skills
\
\
31
New cards
Volunteer Assignments
Gives employees opportunities to manage change, teach, have a high level of responsibility and be exposed to other job demands
\
\
32
New cards
Coaching
* A peer or manager who works with employees to motivate them, help them, develop skills, and provide reinforcement and feedback. They may even be fired professional from an outside company
* One-on-one coaching (e.g., motivating, giving feedback)
* Helping employees learn for themselves by helping them find experts and teaching them how to obtain feedback from others
* Providing resources such as mentors, courses, or job experiences
* One-on-one coaching (e.g., motivating, giving feedback)
* Helping employees learn for themselves by helping them find experts and teaching them how to obtain feedback from others
* Providing resources such as mentors, courses, or job experiences
33
New cards
Mentoring
* An experienced, productive senior employee who helps develop a less experienced employee ((the protégé or mentee).
* Mentoring can occur informally or be part of a formal mentoring program
* Mentors provide career support and psychological support
* Formal mentorship programs
\
* Mentoring can occur informally or be part of a formal mentoring program
* Mentors provide career support and psychological support
* Formal mentorship programs
\
34
New cards
Understand the 9-box-grid and be able to identify and development plans for different groups of employees
* Poor employees performance improvement in current position
* Technical/subject experts keeping knowledge, skills and competencies current and getting them experiences to continue to motivate them and facilitate creativity and innovation
* Potential may be misplaced moving them to a position that best matches their skill set, or ensuring that they get the training and development opportunities and resources necessary to help them attain high performance levels
* Core employees training and development to help ensure their solid performance continues; development experiences that can help grow their skills and determine their interest and ability to perform in positions requiring different skills and/or more responsibility
* Stars developing them for leadership positions in the organization
\
* Technical/subject experts keeping knowledge, skills and competencies current and getting them experiences to continue to motivate them and facilitate creativity and innovation
* Potential may be misplaced moving them to a position that best matches their skill set, or ensuring that they get the training and development opportunities and resources necessary to help them attain high performance levels
* Core employees training and development to help ensure their solid performance continues; development experiences that can help grow their skills and determine their interest and ability to perform in positions requiring different skills and/or more responsibility
* Stars developing them for leadership positions in the organization
\
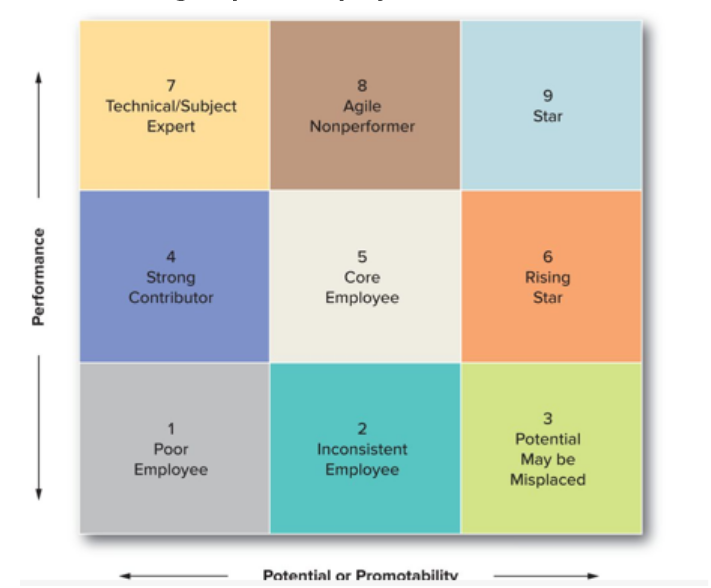
35
New cards
Parent Country
The Country that a company’s headquarters is located in.
36
New cards
Host Country
Parent-country organization seeks to locate or has already located a facility in this country
37
New cards
Third Country
A country other than the host or parent country
38
New cards
Parent-country nationals
Employees who were born and live in the parent country
39
New cards
Host-country nationals
Employees who were born and live in the host country.
40
New cards
Third-country nationals
Employees who were born and live in a third country.
41
New cards
In expatriate selection, which characteristics should HRM look for?
* Ability to communicate verbally and nonverbally in the host country (can be aided by training)
* Willingness to learn about the host country (can be aided by training)
* Adaptability and cultural sensitivity
* Family support and accommodations
* Motivation to succeed and ability to enjoy the challenge of working in another country
* Resourcefulness and initiative
* Willingness to learn about the host country (can be aided by training)
* Adaptability and cultural sensitivity
* Family support and accommodations
* Motivation to succeed and ability to enjoy the challenge of working in another country
* Resourcefulness and initiative
42
New cards
What are the goals of cross-cultural training and who should receive it?
* Goal: Educate expatriates and their families who are given an assignment in a foreign country
* Who should receive it?
* Value: fairness, professionalism, reliability, punctuality, and quality
* Strict separation of work and personal life
\
* Who should receive it?
* Value: fairness, professionalism, reliability, punctuality, and quality
* Strict separation of work and personal life
\
43
New cards
What do the different cross-cultural training phases entail?
* Pre-departure Phase
* On-site Phase
* Repatriation Phase
* On-site Phase
* Repatriation Phase
44
New cards
Pre-departure phase
Language training, orientation of country's culture, housing, schooling, health information, discussion of career plans and positions expected after return.
45
New cards
On-site Phase
Continuance of host country orientation, formal programs, mentorship and pairings, access to software for global assignment, development of relationships, maintenance of contact to the company.
46
New cards
Repatriation Phase
Provide company letters and mail, discussion of expectations, compensation, return assignments.
47
New cards
How can companies support expatriate compensation?
* Equalizes the purchasing power of the expatriate manager with that of employees in similar positions in the home country
* Provides incentives to offset the inconveniences incurred in the location
\
Balance sheet approach to compensation
Compensation components:
Base salary (+ incentivizing premium)
Tax equalization allowance
Benefits
Cost-of-living allowances (e.g., housing, education, relocation)
\
* Provides incentives to offset the inconveniences incurred in the location
\
Balance sheet approach to compensation
Compensation components:
Base salary (+ incentivizing premium)
Tax equalization allowance
Benefits
Cost-of-living allowances (e.g., housing, education, relocation)
\
48
New cards
How can companies support an expatriate's successful acculturation?
maintain close contact while abroad
\- provide recognition from peers and supervisors
\- management of work and nonwork expectations
\
\- provide recognition from peers and supervisors
\- management of work and nonwork expectations
\
49
New cards
Performance Management
The process or system through which managers ensure that employees’ behaviors and results are congruent with the organization’s goals
50
New cards
What are the steps in the performance management process?
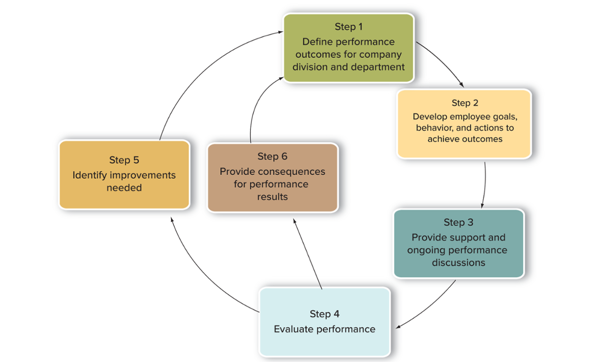
51
New cards
Understand the strategic, administrative, and developmental purposes of performance management

52
New cards
Which criteria should performance measures fulfill?
* Strategic Congruence
* Validity
* Reliability
* Acceptability
* Specificity
* Validity
* Reliability
* Acceptability
* Specificity
53
New cards
Strategic Congruence
Extent to which a performance management system elicits job performance that is congruent with the organization’s strategy, goals, and culture.
54
New cards
Validity
Extent to which a performance measure assesses all the relevant—and only the relevant—aspects of performance.
55
New cards
Reliability
Consistency of a performance measure.
56
New cards
Acceptability
Extent to which a performance measure is deemed to be satisfactory or adequate by those who use it.
57
New cards
Specificity
Extent to which a performance measure gives detailed guidance to employees about what is expected of them and how they can meet these expectations.
58
New cards
What is the behavioral approach to measuring performance, and what are their pros and cons?
* Defines behaviors an employee must exhibit to be effective in the job
* Can link company strategy to specific behavior necessary for implementing that strategy
* Provides specific guidance and feedback for employees
* Valid when based on job analysis
* Reliable when raters are trained
* Often high acceptability
* Behaviors and measures must be continually monitored and revised to ensure strategic congruence
* Assumes that there is “one best way” to do the job and that those behaviors can be identified more suitable for less complex jobs where the “best way” is more likely to be clear)
\
\
* Can link company strategy to specific behavior necessary for implementing that strategy
* Provides specific guidance and feedback for employees
* Valid when based on job analysis
* Reliable when raters are trained
* Often high acceptability
* Behaviors and measures must be continually monitored and revised to ensure strategic congruence
* Assumes that there is “one best way” to do the job and that those behaviors can be identified more suitable for less complex jobs where the “best way” is more likely to be clear)
\
\
59
New cards
What is the results approach to measuring performance, and what are their pros and cons?
* Manages objective, measurable results of a job or work group
* Subjectivity is minimized –Usually high acceptability
* Individual results are linked to organizational strategies and goals
* Objective measures can be contaminated because they are affected by things out of the employee’s control
* Objective measures can be deficient because not all important aspects of job performance are amenable to objective measures
* Individuals may focus only on measurable aspects of performance and ignore other aspects
* Feedback may not help employees identify ways to change their behavior to improve performance
\
* Subjectivity is minimized –Usually high acceptability
* Individual results are linked to organizational strategies and goals
* Objective measures can be contaminated because they are affected by things out of the employee’s control
* Objective measures can be deficient because not all important aspects of job performance are amenable to objective measures
* Individuals may focus only on measurable aspects of performance and ignore other aspects
* Feedback may not help employees identify ways to change their behavior to improve performance
\
60
New cards
What is the comparative approach to measuring performance, and what are their pros and cons?
* Compares an individual employee’s performance with the performance of other employees, usually based on an overall assessment of performance or worth
* Effective tool to differentiate employee performance, because problems of various rater errors (esp. leniency, central tendency, and strictness) are eliminated
* Easy to develop and typically easy to use
* Lack of strategic congruence
* Ratings are often subjective validity and reliability are modest at best
* Lack of specificity for feedback purposes
* Low acceptance of evaluations
\
* Effective tool to differentiate employee performance, because problems of various rater errors (esp. leniency, central tendency, and strictness) are eliminated
* Easy to develop and typically easy to use
* Lack of strategic congruence
* Ratings are often subjective validity and reliability are modest at best
* Lack of specificity for feedback purposes
* Low acceptance of evaluations
\
61
New cards
What are the sources of performance information?
* **360- degree appraisal**: multiple raters provide input into a manager's evaluation, minimizes bias in otherwise subjective evaluations
\
\
62
New cards
Unconscious Bias
A judgment outside of our consciousness that affects decisions based on background, culture, and personal experience.
\
\
63
New cards
Appraisal Politics
Refers to evaluators purposefully distorting a rating to achieve personal or company goals.
64
New cards
Rater Errors
* Similar to me
* Contrast
* Leniency
* Strictness
* Central Tendency
* Halo
* Horns
* Contrast
* Leniency
* Strictness
* Central Tendency
* Halo
* Horns
65
New cards
Similar to me
Individuals who are similar to us in race, gender, background, interest, beliefs, and the like receive higher ratings than those who are not.
66
New cards
Contrast
Ratings are influenced by comparison between individuals instead of objective standard
67
New cards
Leniency
Rater gives high ratings to all employees regardless of performance.
68
New cards
Strictness
Rater gives low ratings to all employees regardless of performance.
69
New cards
Central Tendency
Rater gives middle or average ratings to all employees regardless of performance.
70
New cards
Halo
Rater gives employee high ratings on all aspects of performance because of an overall positive impression of the employee.
71
New cards
Horns
Rater gives employee low ratings on all aspects of performance because of an overall negative impression of the employee.
72
New cards
How do you give performance feedback?
* Give feedback frequently, not just once a year in the annual appraisal
* Create the right context for the discussion
* Ask the employee to rate his or her performance before the session (self-appraisal)
* Have ongoing, collaborative performance conversations
* Recognize effective performance through praise
* Focus feedback on behavior or results, not on the person
* Minimize criticism
* Provide evidence for positive and negative feedback
* Focus on solving problems; provide suggestions to change or improve behavior
* Agree to specific goals and set a date to review progress
* Create the right context for the discussion
* Ask the employee to rate his or her performance before the session (self-appraisal)
* Have ongoing, collaborative performance conversations
* Recognize effective performance through praise
* Focus feedback on behavior or results, not on the person
* Minimize criticism
* Provide evidence for positive and negative feedback
* Focus on solving problems; provide suggestions to change or improve behavior
* Agree to specific goals and set a date to review progress
73
New cards
Involuntary Turnover
Turnover initiated by the organization (often among people who would prefer to stay).
74
New cards
Voluntary Turnover
Turnover initiated by employees (whom the company often would prefer to keep).
75
New cards
What are the different principles of justice?
* Distributive
* Procedural
* Interactional
* Procedural
* Interactional
76
New cards
Distributive Justice
Dismissal decisions must be justified by the individual’s actions and be consistent with how other individuals who engaged in the same offense were treated.
77
New cards
Procedural Justice
Dismissal decisions are more acceptable if they are perceived as consistent, unbiased, based on accurate information, correctable, representative of the concerns of all affected groups, and ethical.
78
New cards
Interactional (Interpersonal) Justice
Dismissal decisions are more acceptable if the decision is explained well and implemented with social sensitivity, consideration, and empathy
79
New cards
What does a progressive discipline program look like?
Progressive discipline involves a series of disciplinary actions that escalate in severity as an employee fails to improve their performance.
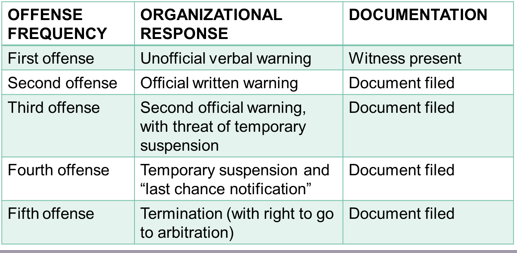
80
New cards
Employee Wellness Programs
Programs that take a proactive and preemptive focus on trying to prevent health-related problems.
81
New cards
Employee Assistance Programs (EAP)
Programs that attempt to ameliorate problems encountered by workers who are drug dependent, alcoholic, or psychologically troubled.
82
New cards
Outplacement Counseling
Counseling to help displaced employees manage the transition from one job to another.
83
New cards
Job Satisfaction
A pleasurable feeling that results from the perception that one’s job fulfills or allows for the fulfillment of one’s important job values.
84
New cards
How does job withdrawal manifest itself?
* Behavioral changes
* Supervisor-subordinate confrontation and conflict
* Whistle-blowing
* Counterproductive work behaviors
* Physical withdrawal
* Absenteeism
* Internal transfers
* Quits
* Psychological withdrawal
* Reduced job involvement
* Reduced organizational commitment
* Supervisor-subordinate confrontation and conflict
* Whistle-blowing
* Counterproductive work behaviors
* Physical withdrawal
* Absenteeism
* Internal transfers
* Quits
* Psychological withdrawal
* Reduced job involvement
* Reduced organizational commitment
85
New cards
What are the different causes of job dissatisfaction?
* Unsafe working conditions
* Personal Dispositions
* Task and Roles
* Supervisors and co-workers
* Pay and Benefits
* Personal Dispositions
* Task and Roles
* Supervisors and co-workers
* Pay and Benefits
86
New cards
How is job satisfaction measured and monitored?
* Pulse Surveys
* Employee survey research programs
* Employee survey research programs
87
New cards
Pulse Surveys
* Focus on a small set of specific questions
* Assessed every day or once a week
* Uncover issues as they develop
* Assessed every day or once a week
* Uncover issues as they develop
88
New cards
Employee survey research programs
* Monitor trends over time and prevent problems related to voluntary turnover
* Empirically assess the impact of policy and personnel changes
* Comparison with other firms in the industry
* Identify differences between units and benchmark best practices across business units
* Exit interviews to uncover systematic concerns driving retention problems
* Empirically assess the impact of policy and personnel changes
* Comparison with other firms in the industry
* Identify differences between units and benchmark best practices across business units
* Exit interviews to uncover systematic concerns driving retention problems
89
New cards
Job Descriptive Index (JDI)
* Assesses different aspects of the job, including:
* The work itself
* Pay
* Opportunities for promotion
* Coworkers
* Supervision
* The work itself
* Pay
* Opportunities for promotion
* Coworkers
* Supervision
90
New cards
Pay Satisfaction Questionnaire (PSQ)
Assesses satisfaction with pay and benefits
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
IB BIO - U1 L3 P2 - MICROSCOPES AND MICROSCOPE SKILLS (SCIENTIFIC DRAWINGS).
22Updated 900d ago0.0(0)
IB BIO - U1 L3 P2 - MICROSCOPES AND MICROSCOPE SKILLS (SCIENTIFIC DRAWINGS).
22Updated 900d ago0.0(0)