Unit 3: Atomic Emission Spectra and the Bohr Model
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is the visible spectrum?
The portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye
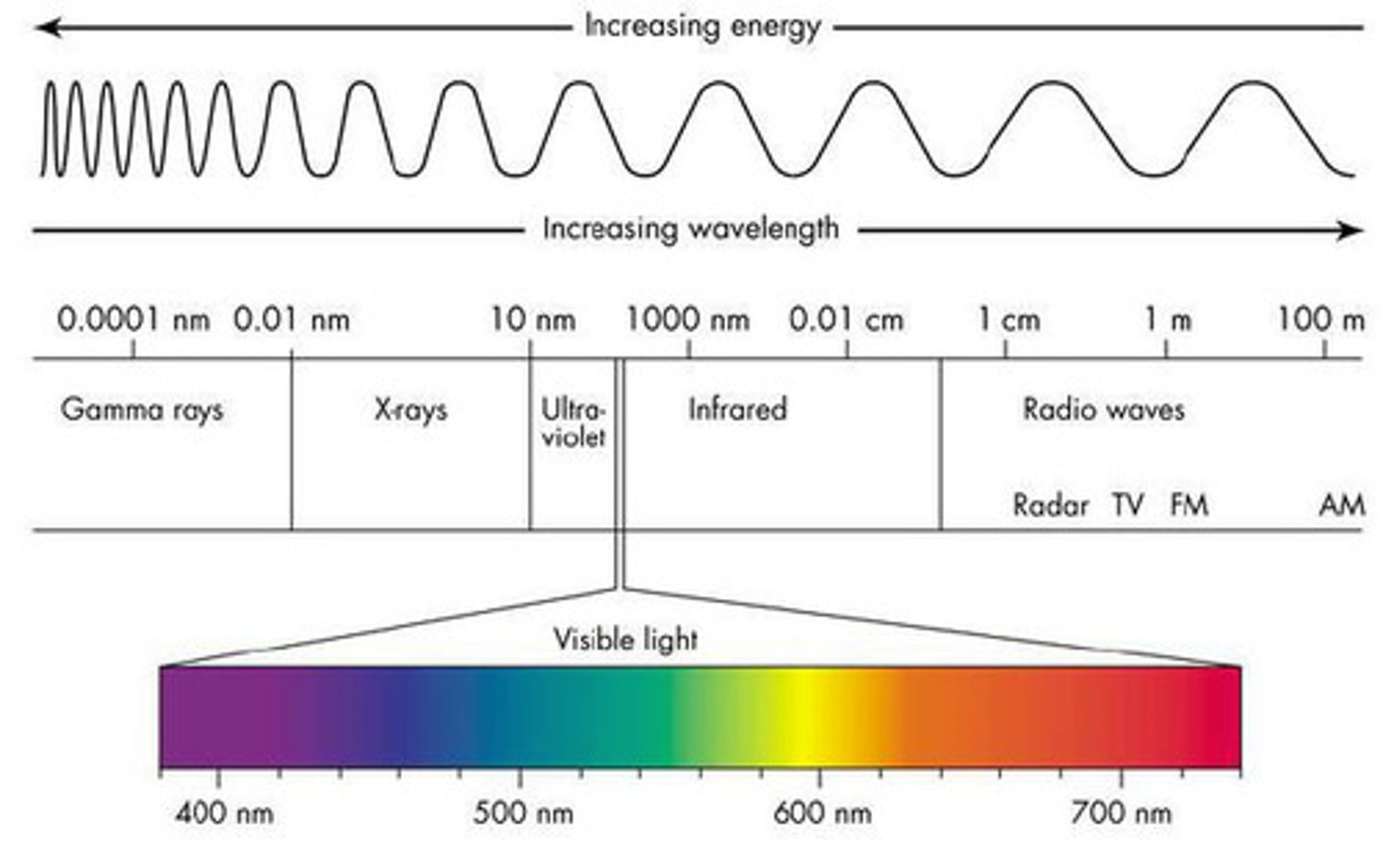
Electromagnetic waves are ______ waves(type)
Transverse
______ and _____ are inversely proportional
Wavelength and Frequency
Wavelengths with highest/lowest energies
Violet(highest); Red(lowest)
Continuous Spectrum
A spectrum that contains radiation distributed over all wavelengths
Emission Spectrum
A spectrum containing radiation of only specific wavelengths
Bohr Model Description
-Each circle represents an orbit
-Where electrons are located
-Larger circles indicate higher energy; Inner circles indicate lower energy
*How can we see light?
When something emits light we are actually seeing a photon. A photon is emitted when electrons lose energy.

Radiation
Radiation is absorbed or emitted when electrons change orbits. When radiation is emitted it is a photon.
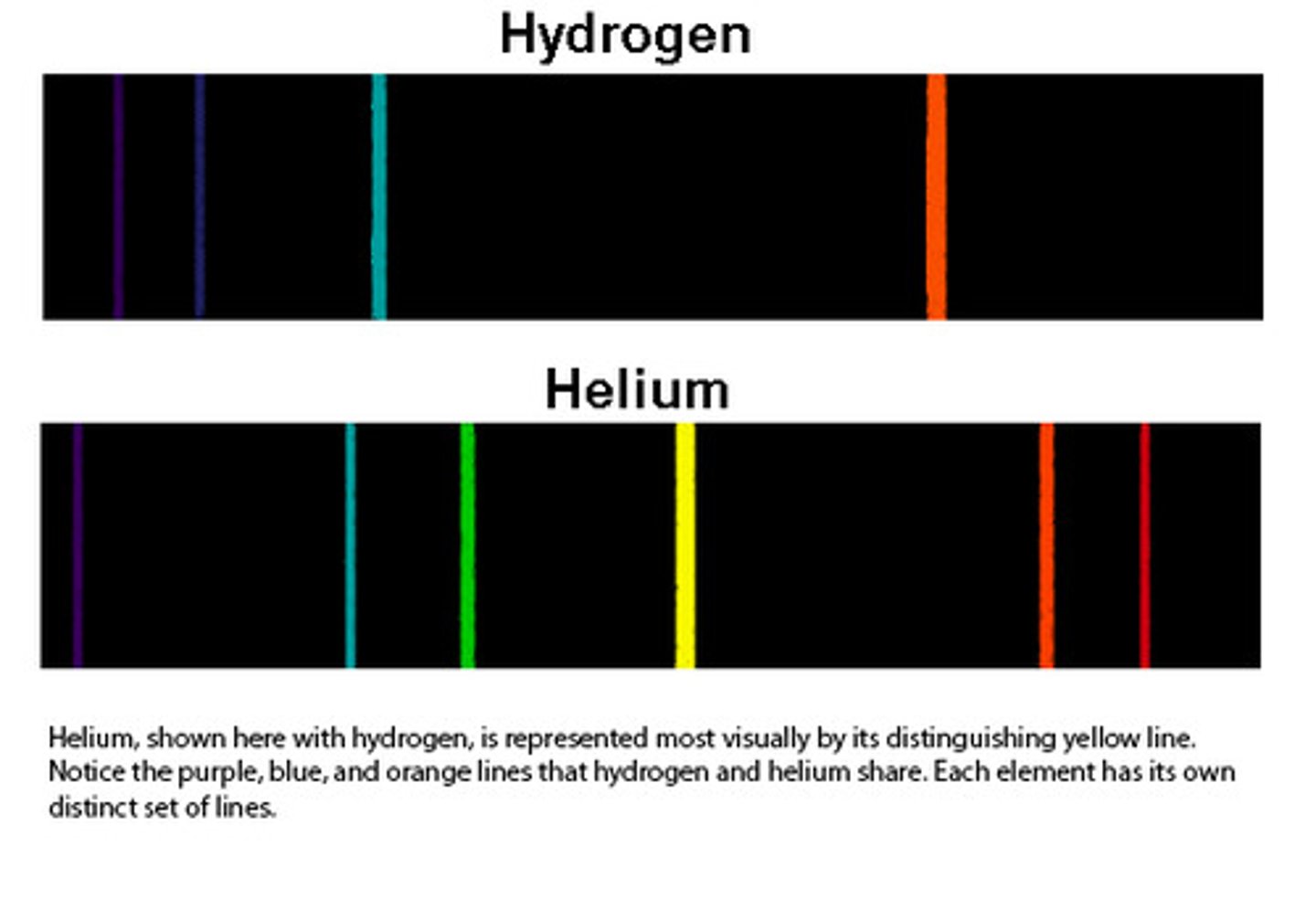
What determines the color that is emitted?
The distance travelled(wavelength) determine the color emitted
Quantum
The amount of energy needed to move an electron from one energy level to another
*How is a photon emitted?
1. Energy enters the Bohr Model
2. Electrons get excited and go into excited state
3. Electrons lose energy and go into ground state
4. Photon is emitted and color is determined by wavelength
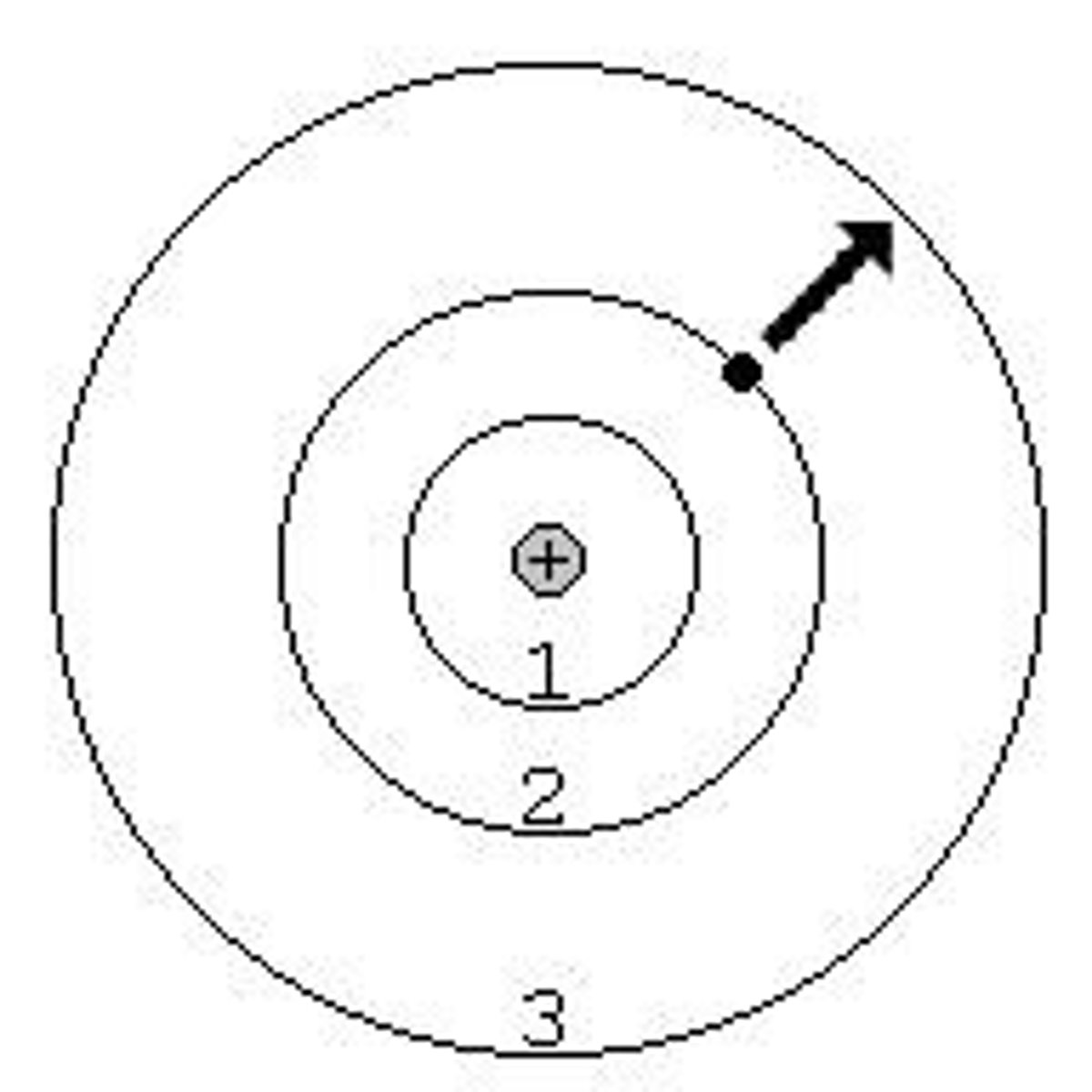
What is the lowest possible energy level that an electron can occupy?
Ground State
If the hydrogen atom emits red, blue-green, blue, and violet light, how many energy levels does it have in the visible region of the spectrum?
4
Element
Simplest form of matter that has properties(one type of atom)
Atom
Fundamental building blocks of matter
Isotope
Different form of an atom that only differs in the amount of neutrons
Atomic Mass
Number of protons and neutrons an atom has
Atomic Number
Number of protons an atoms has
Electrically Neutral
Equal number of protons and electrons in an atom(atoms in the periodic table are electrically neutral)
Energy
Capacity to move or change matter
Location, charge, and size of each subatomic particle
Protons: Nucleus, Positive, 1 AMU
Neutrons: Nucleus, No Charge, 1 AMU
Electrons: Electron Cloud, Negative, 1/1836 AMU