Memory | Chapter 6
1/11
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Memory
our ability to store and retrieve information
the basic for knowledge
knowing friends
knowing language
knowing ourselves
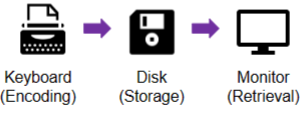
Three Stages of Memory
Encoding
inputting information into memory storage
Storage
the process of retaining information in memory
Retrieval
accessing stored information
Three Types of Encoding
Acoustically
encoding by forming recognizable sounds
Visually
encoding by making a mental picture
Semantically
encoding by meaning
Three Kinds of Storage
Sensory memory
brief sensory impressions
Short-term memory
retains and processes information for about 30 seconds
Long term memory
retains information for long periods of time, beyond that of short-term memory
Retrieval
We cannot retrieve information that was never stored
Claims
Forgetting is the failure to access stored information
This could happen due to (1) encoding failure or (2) retrieval cues
Retrival Process
Recall
Recognition
Semantic Network Model
Claims
information is retained within networks of interlinking concepts
we understand the meaning of information by linking it to related things
retrieval is facilitated by spreading activation - the rippling effect of remembering one concept from another
Retrieval Cues
Associations that help bring memories into awareness
Facilitators
Chunking
storing large amounts of information by breaking it down into smaller bits of information
Example: Instead of remembering the last 4 digits of your phone number as 4 separate pieces of information, you might encode them as 2 whole numbers
Context Effects
we recall better when in the same environment where encoding took place
Amnesia
There are two kinds of Memory Loss
Retrograde Amnesia
loss of memory of past events
Anterograde Amnesia
inability to form new memories
Constructionist Theory
Claims
memory is not a replica of the past, but a reconstruction or representation of the past
We filter or fill in missing information to make memory more coherent
Memories are vulnerable to misinformation and distortion
Misinformation Effect
memory distortion due to misinformation provided during retention
Elizabeth Loftus studies the effect on eye-witness testimony
Eye-Witness Study
In one study of the misinformation effect, Dr. Elizabeth Loftus randomly divided participants into two groups: A & B
Both groups viewed the same car-crash on tape and answered follow-up questions
Group A
How fast were the cars going when they hit each other?
Group B
How fast were the cars goign when they smashed into each other?
The results suggested their memory had been influenced by the framing of the questions
Compared to Group A, Group B reported the cars were traveling at a faster speed, on average
Compared to Group A, Group B was more likely to report seeing broken glass (of which there was none)
Indicators of Memory Accuracy
Ease of Recall
Hesitation indicates less accuracy
Degree of Confidence
highly confident witness tend to be accurate
General Knowledge
the general knowledge of a subject increases accuracy of memories about that subject
Types of Questions
Avoid subjectivity or leading questions