Week 11: non-avian and avianreptiles
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Reptilia characteristics
ectothermic, dry, scaly skin, amniotic egg, internal fertilization, terrestrial
reptilia
non-native reptiles (paraphyletic) - becomes monophyletic when you include birds
reptilia includes
tuataras, turtles, snakes, lizards, and crocodilians
reptilia land adaptations
tough protective skin, shelled eggs with amnion, internal fertilization, advanced respiratory mechanisms
reptile skin
tough scales (scutes) made from keratin, prevents dehydration and provides protection, ecdysis
reptile reproduction
internal fertilization, eggs laid on landa
amnion
fluid-filled sac surrounding the reptile embryo and often has leathery shell
reptile respiration
negative-pressure breathing, carrier’s constraint
carrier’s constraint
legs are to the side of the body-sideways flexing while walking - can’t fully expand ribcage while walking - leads to difficulty breathing and walking at the same time
ectothermy benefits
requires less energy, can survive in low-resource environments, resilient to temperature fluctuations
reptile circulation
reptiles and amphibians both have a 3-chambered heart
crocodilia
4 chambered heart, lung muscles attached to liver - as liver pulls down, lungs expand which allows for locomotion and respiration at the same time
anapsid amniotic skull
no temporal openings (turtles)
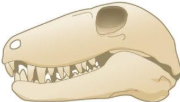
synapsid amniotic skull
one temporal opening (mammals)
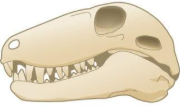
diaosid amniotic skull
two temporal openings (crocodiles, birds, lizards)
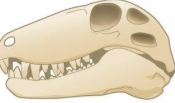
diapsid skull advantages
decreases skull weight, increased surface for muscle attachment, and increase space for jaw muscles when mouth is closed
turtles (testudines)
very different from other reptile groups (have anapsid skull and shell) - sister group of archosaurs
plastron (turtles)
bottom of shell
carapace (turtles)
top of shell
clade aves
birds descended from dinosaur ancestor av
aves characteristics
keratinous feathers, are endothermic, 4-chambered heart, no urinary bladder
bird evolution
descended from theropod dinosaurs, remnants from reptile ancestry
remnants from reptile ancestry
amniotic egg with hard shell, skeleton similar to other dinosaurs (diapsid skull), 4- chambered heart
evolution of feathers
initially evolved in non-avian dinosaurs due to thermoregulation with insulation, courtship displays, and species recognition - DID NOT INITIALLY EVOLVE FOR FLIGHT
flight adaptation
forelimbs modified into wings, large flight muscles, hollow, ridged bones, efficient respiratory system, high metabolic rate helps maintain constant body temp (endothermic), no urinary bladder
hollow bird bones
lighten skeleton
keel
attachment of pectoral muscles and lowers center of gravity
furcular
fused clavicles that strengthen thoracic cavity
bird respiration
air sacs are connected to longs, unidirectional air flow over lungs allows for efficient gas exchange
no bladder for birds
all nitrogenous wastes released as uric acid - only store as much as can fit in the ureters