lower motor neurons 2/4
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
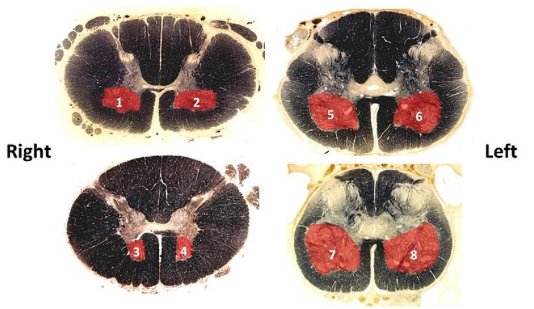
PI: a unilateral lesion of which of the following results in right upper limb flaccid paralysis?
1
two other terms for lower motor neuron
somatic efferent and alpha
flaccid paralysis
muscle paralysis (weakness) and hypotonicity (decreased tone)
PI: during a neurologic examination on a 7 year old boy, the physician taps the patellar tendon and elicits a simple knee-jerk reflex that is also called the quadriceps stretch reflex. this is one example of a myotatic reflex. which of the following is characteristic of this type of reflex?
Is a three-neuron reflex; the afferent receptor is the Golgi tendon organ, which is innervated by Ib nerve fibers, and the afferent endings are the neuromuscular junctions, which are innervated by lower motor neurons
Requires glutaminergic (excitatory) input to the extensor and flexor motor neurons
Relies on nociceptive input to the primary sensory ending
Causes withdrawal on the ipsilateral limb and extension on the contralateral limb
Is a two-neuron reflex; the afferent receptor is the muscle spindle, which is innervated by Ia and II nerve fibers, and the efferent endings are neuromuscular junctions, which are innervated by lower motor neurons
5
muscle spindle
detects muscle stretch and responds (myotatic reflex receptor)
encapsulated receptor within muscle
consists of small, encapsulated nuclear bag and nuclear chain intrafusal muscle fibers connected in parallel with large extrafusal fibers
what types of fibers innervate the nuclear bag and nuclear chain (intrafusal fibers)?
Is and II afferent and gamma motor neurons
PI: a 78 year old man presents with weakness of the muscles of mastication and of facial expression, both on the same side of the face. the examining physician concludes that the lesion involves the nuclei of cranial nerves V and VII. which of the following parts of the nervous system is the most likely site of this lesion?
medulla
pons
midbrain
thalamus
telencephalon
2
which cranial nerves don’t have LMNs?
olfactory, optic, vestibulocochlear
where would you find lower motor neurons?
brainstem and spinal cord
tract/fasiculus
bundle of axons in the CNS
PI: a 5 year old girl presents with medial deviation of her left eye. when asked to abduct her left eye, it doesn’t move. these signs are characteristic of which of the following?
oculomotor nerve palsy
trochlear nerve palsy
abducens nerve palsy
trigeminal nerve palsy
facial nerve palsy
3
exotropia
medial deviation of the eye
palsy
weakness or paralysis of a nerve
diplopia
double vision
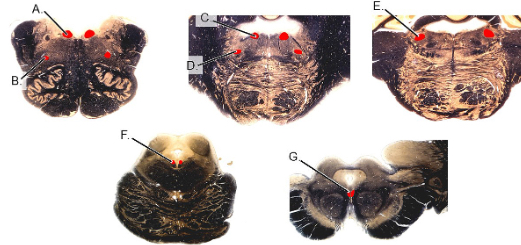
PI: a unilateral lesion of which of the following results in sagging of ipsilateral palatal arch and vocal muscle paralysis?
B
PI: a lesion of which of the following cranial nerves results in diplopia with an ipsilateral ptosis, down and out eye, and mydriasis?
5
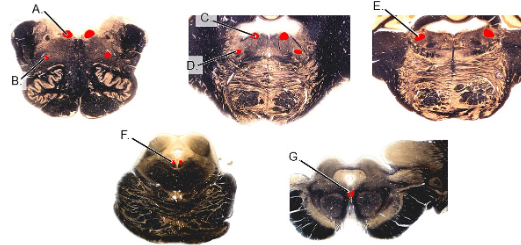
PI: a unilateral lesion of which of the following results in the ability to close ipsilateral eye and retract corner of mouth?
D
facial nerve lesions cause…
flaccid paralysis of muscles of facial expression around the eyes AND the mouth
which axons arch over the abducens nucleus?
facial
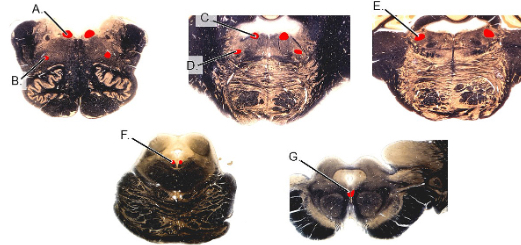
PI: a unilateral lesion of which of the following results in the inability to depress eye in the adducted position and compensatory tilting of the head?
F
PI: a lesion of which of the following cranial nerves results in paralysis and atrophy of ipsilateral muscles of the tongue and, when protruded, the tongue deviates to the side of lesion?
9
lower motor neurons
brainstem or spinal cord motor neurons whose axon carries impulses to skeletal muscle
aka somatic body efferent or alpha motor neuron
axons go directly into peripheral nerves (spinal or cranial) and synapse on skeletal muscles (extrafusal fibers)
what does a lesion of lower motor neurons or their axons result in?
lower motor neuron syndrome
lower motor neuron syndrome
flaccid paralysis
decreased or absent reflexes
severe muscle atrophy
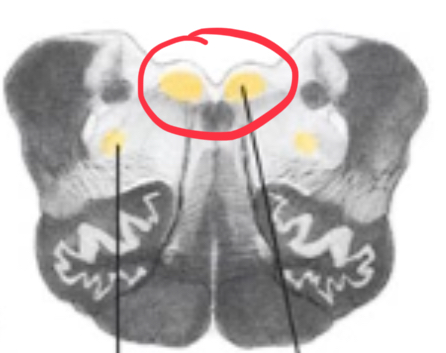
where are spinal LMN cell bodies?
ventral horn, specifically 2 main cell columns (medial and lateral) forming lamina IX
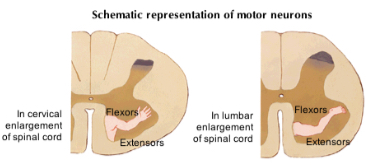
cell bodies of spinal LMNs are arranged
somatotopically
LMN organization
medial (proximal) to lateral (distal) and dorsal (flexors) to ventral (extensors)
efferent limbs of spinal reflexes
LMNs
3 types of spinal reflexes
stretch (myotatic) reflex—knee jerk
golgi tendon (inverse myotatic) reflex
flexor withdrawal reflex
stretch (myotatic) reflex
monosynaptic
muscle stretches→stretching stimulates Ia afferent fibers→synapse on alpha motor neurons→contraction in stretched muscle
nuclear bag and Ia afferents
detect the rate of change—beginning of stretch
nuclear chain and II afferents
detect static changes—maintained stretch
gamma motoneurons
keeps the muscle spindle taut and increases the sensitivity of the muscle spindle to contraction or stretching, innervate the ends of intrafusal fibers
golgi tendon (inverse myotatic) reflex
disynaptic
active muscle contraction (tension) stimulates the golgi tendon organs and Ib afferent fibers→stimulate inhibitory interneurons in spinal cord→inhibit alpha motoneurons→relax contracting muscle
Clasp-knife reflex (in spastic muscles)
flexor withdrawal reflex
polysynatic
pain afferents stimulate spinal interneurons (inhibitory and excitatory)→flexion on ipsilateral side and extension of contralateral side
examples of myotatic reflex
biceps reflex (musculocutaneous nerve)
triceps reflex (radial nerve)
patellar reflex (femoral nerve)
achilles tendon reflex (tibial & sciatic nerves)
where are spinal alpha motor neurons found?
more than one spinal cord segment for neurons innervating any muscle
extrafusal fibers
contract to allow movement to occur
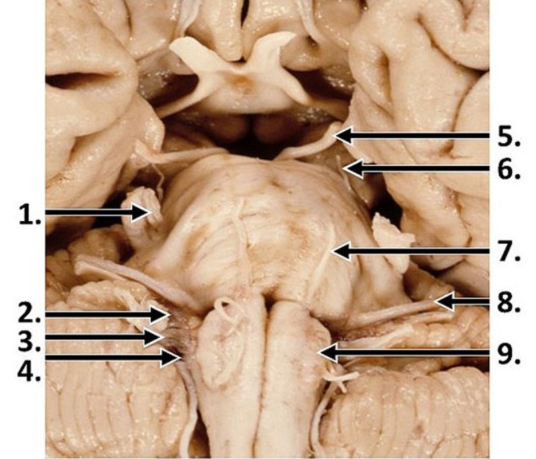
brainstem LMNs
found within medulla, pons, and midbrain
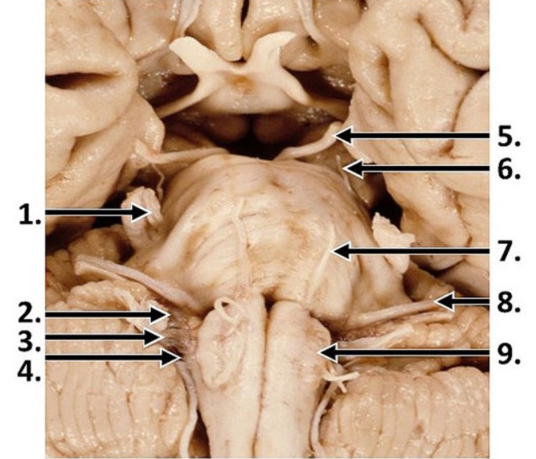
LMNs of the open medulla
hypoglossal and ambiguus
CNS nuclei
clusters of neuronal cell bodies
hypoglossal nuclei
originate just deep to the dorsal surface of the open medulla
intramedullary rootlets
axons from the hypoglossal nuclei coursing through the medulla to emerge on the ventral surface between the olive and the medullary pyramid as the hypoglossal nerve
nucleus ambiguus
ventral and lateral to hypoglossal nuclei
give rise to LMNs that enter 3 cranial nerves—majority to vagus n., caudal to cranial accessory n. (merges w/ vagus), rostral to glossopharangeal n.
nuclei of the caudal pons
abducens and facial
abducens nuclei
just deep to the facial colliculus
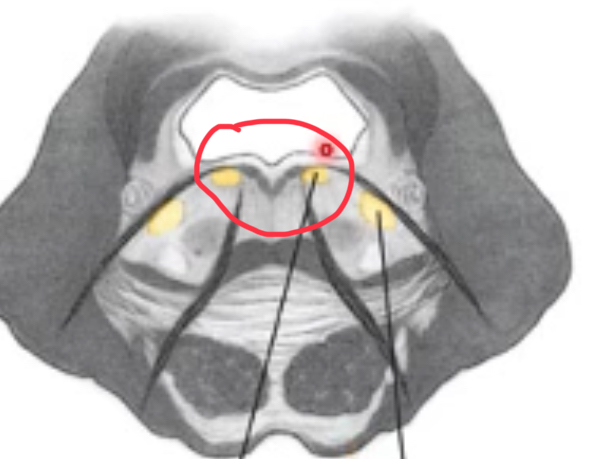
facial nuclei
ventral and lateral to abducens nuclei
axons course towards midline of pons, arch over abducens nuclei to form facial colliculus, then continue laterally and ventrally to emerge as nerves
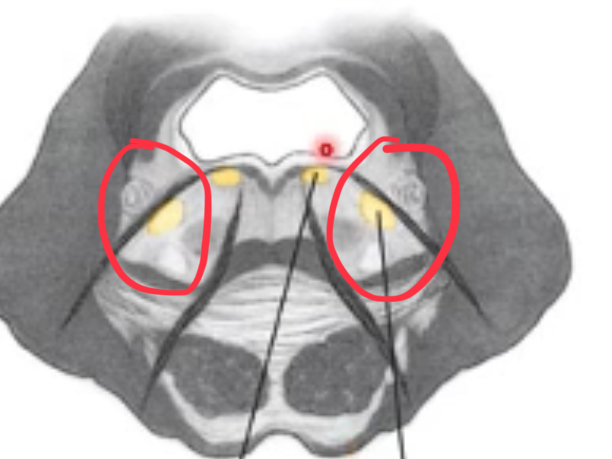
nuclei of the mid pons
motor trigeminal
motor trigeminal nuclei
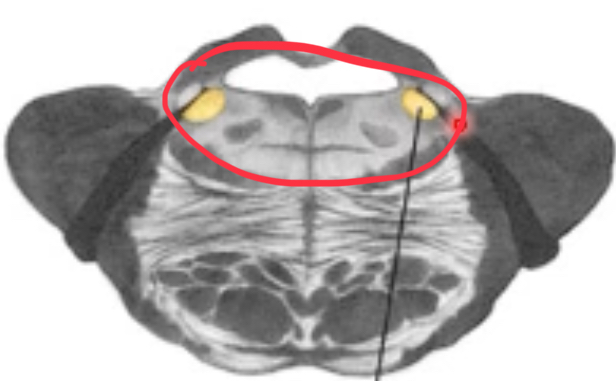
nuclei of the caudal midbrain
trochlear
trochlear nuclei
nerve emerges dorsally
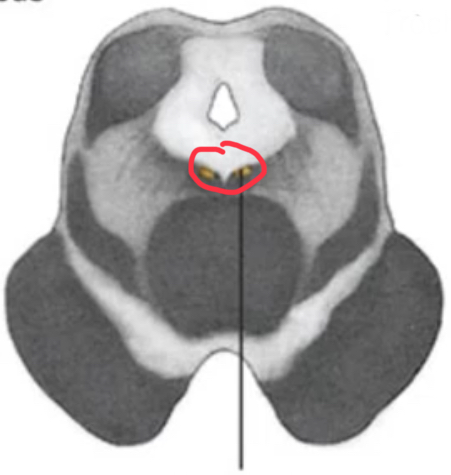
nuclei of the rostral midbrain
oculomotor
oculomotor nuclei
axons emerge as nerves from interpeduncular fossa
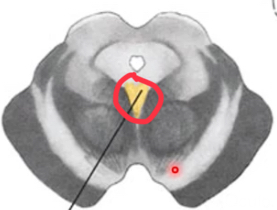
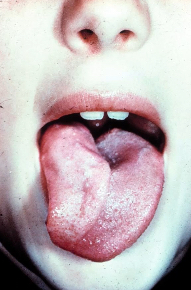
atrophy of one side of tongue, deviation to ipsilateral side
hypoglossal nucleus/rootlets/nerve
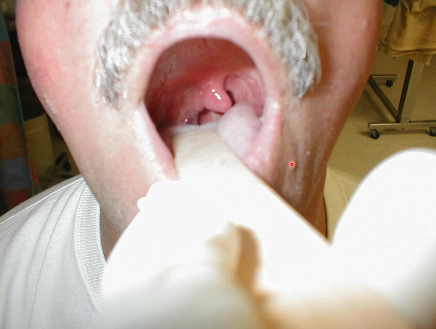
sagging of pharyngeal muscles on one side, uvula deviated to contralateral side, partial vocal muscle paralysis
vagus nerve or nucleus ambiguus, glossopharyngeal, cranial accessory rootlets & nerves
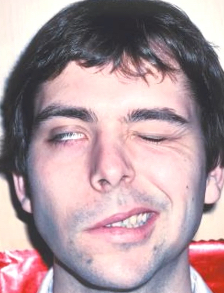
facial muscle paralysis on one side—no closing eye, no retraction of corner of mouth
facial nerve/nucleus/rootlets

medial deviation of eye, limited eye abduction, diplopia (double vision)
abducens nerve/nucleus/rootlets→flaccid paralysis of lateral rectus (isotropia)
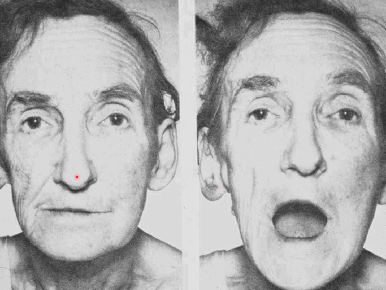
trouble chewing, atrophy of ipsilateral cheek, mandible deviated to atrophied side
motor trigeminal nucleus/rootlets/nerve
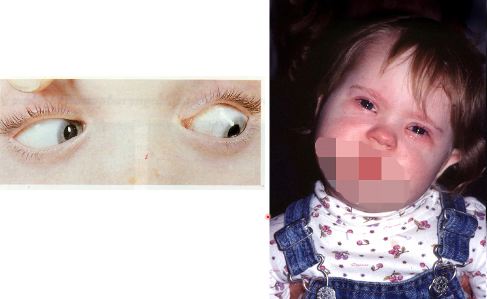
tilting head to contralateral side, diplopia in affected eye, cannot depress eye fully when adducted
trochlear nerve/nucleus/rootlet→flaccid paralysis of superior oblique
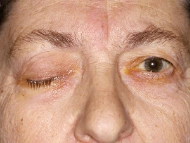
cannot open affected eye, pupil depressed and abducted and dilated
oculomotor nerve/nucleus/rootlets→flaccid paralysis of superior rectus, inferior rectus, inferior oblique, medial rectus, superior levator (causes ptosis) of upper eyelid—superior oblique and lateral rectus unaffected
dilation caused by preganglionic parasympathetics that go to ciliary ganglion and postganglionic parasympathetic dilates—lesion will cause constriction
Bell’s palsy
facial nerve lesion