All of skin lesions/tumors and autoimmune
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
patch
greater than 5 mm macule:
nodule
greater than 5 mm papule
bulla
vesicle greater than 5 mm
urticaria: what cells?
immediate type I hypersensitivity: IgE and mast cell degranulation
when do you get response in type I and type IV hypersensitivity?
second exposure
urticaria: what does this do to blood vessels
histamine from mast cells cause BV to dilate (red and purple skin), permeable (edema)
clinical term caused by urticaria
plaque (raised skin lesion)
mast cell releases histamine → _____ → itchy
unmyelinated C fibers
urticaria: what part of skin does it affect?
epidermis affected?
what makes skin red/purple
what raises the skin?
unaffected epidermis
dilated blood vessels
superficial dermis edema (space between collagen)
how fast do lesions appear in urticaria
a few minutes in pre-exposed individual
acute eczematous dermatitis: what cells? what hypersensitivity?
allergic contact dermatitis: delayed type IV hypersensitivity, T cells
two main things happen when T cells release cytokines in allergic contact dermititis
inflammation: redness, dermal edema, itchy
keratinocyte apoptosis and breakage of intracellular adhesion molecules → edema in epidermis: spongiosis
allergic contact dermatitis skin lesions (2): from where?
vesicle (smaller) or bulla (bigger), epidermis
allergic contact has __ edema, urticaria has _ edema
allergic has both dermal edema and epidermal edema, urticaria just has dermal
how fast do lesions occur in allergic contact dermitis
several hours to days
Erythema Muliforme is a __ manifestation of inflammatory dermatoses:
two kinds?
acute
without mucosal disease: EM minor
with mucosal involvement: EM major
what can cause erthema multiforme
appears to be type IV, cell mediated, hypersensitivity rxn to 90% infectious agents, 10% of time to drugs
two kinds that can cause erythema multiforme:
main: herpes, mycoplasma pneumoniae
Erythema multiforme pathogenesis
Reactivation of HSV infection →
viral antigens deposit in skin or mucosa
recruitment of cytotoxic T cells
inflammation (edema and redness)
apoptosis/necrosis of basal epithelial cells with subepidermal blister
clinical features of erythema multiforme
bright red ring
paler, raised area (edema)
dusky or dark red central area with blister or crust
*target looking lesion
erythema multiforme: lesions appear __, resolve in _
3-5 days, 2 weeks
psoriasis: pathogenesis
the cause is __: involves both _ and ?
__ mediated - possibly _
1 inciting __ _ →
2. Activated ___ home to the __ and accumulate in the _
3. Release ___
___: → ___ and _
___
multifactorial: genetic and enviornmental
T cell, autoimmune
1. antigens
2. T cells, dermis, epidermis
3. Cytokines
Inflammation: dilated BV, edema
keratinocyte hyperproliferation
Continuation of psoriasis: pathogenesis
Keratinocyte hyperproliferation →
excess and rapid growth of epidermis → migration time from basal layer to susrface goes from 14 days to 4-7 → nuclei retained in cells at skin surface: parakerotosis
parakeratosis
stratum corneum: nuclei retained in cells at skin surface
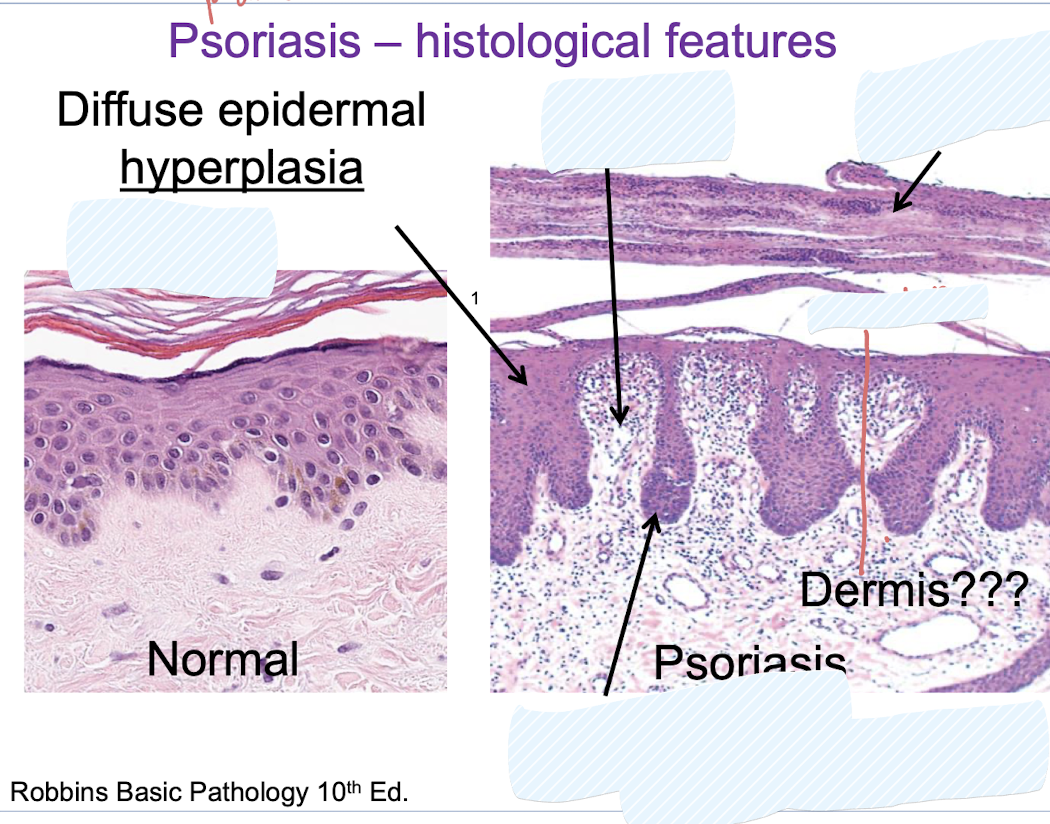
ancanthosis, t cells, parakaratosis, dilated BV, downward extension of rete ridges
Psoriasis causes ? what layer
due to keratinocyte proliferation:
parakaratosis: corneum
acanthosis: thickening of epithelium?
hyperkeratosis: corneum thickening
psoriasis clinical features: raised or flat? colors?
plaque (rasied), red + silver/white, purple/brown and gray
psoriasis causes what clinical feature: where commonly?
plaque on scalp, knees, elbow
auspitz sign
multiple, minute bleeding points clinical sign of psoriasis
lichen planus: pathogenesis
autoimmune: antigen on cells in basal layer
CD8 →
TNF/Fas: apoptosis of keratinocytes
Chemokines: inflammation
in lichen planus: lesions are concentrated at the?
epidermal-dermal interface
Lichen planus histololigically:
saw tooth interface: epidermal hyperplasia, hyperkeratinosis, hypergranulosis
wickham striae
white lacelike markings of lichen planus
lichen planus clinical features: why?
Purple papule (small, less than 5 mm raised): from melanin released from keratinocytes
wickham striae: (white lacelike markings)
Lichen planus: what shape? rounded or flat topped? Shiny or scaly?
flat topped, shiny
is there oral inovlement with lichen planus?
yes: wickham’s striae (often asymptomatic), erosive form (ulcers)
two kinds of blistering (bullous disorders): both are what?
pemphigus, bullous pemphigoid, both autoimmune
Pemphigus vulgaris or foliaceus pathogenesis
autoantibodies to desmoglein 1 and 3 (cadherins) → loss of keratinocyte to keratinocyte adhesion
cadherins
desmoglein 1 and 3: related to pemphigus
Bullous pemphigoid pahthogensis
autoantibody to type XVII collagen (or other BM proteins) → damages basement membrane
location of demoglein 1 and 3 in epidermis in pemphigus foliaceus vs. pemphigus vulgaris
upper part of epidermis: more desmogelin 1: Pemphigus foliaceus
lower part of epidermis: more desmoglein 3: pemphigus vulgaris
cleft positions:
pemphigus foliaceus
Pemphigus vulgaris
Bullous pemphigoid
subcorneal
suprabasal
subepidermal
pemphigus foliaceus clinical featuer
bullae or blister (more superficial)
pemphigus vulgaris clinical feature
flaccid blisters and skin erosions (more erosive as blister is deeper than foliaceous), gingival erosion
bullous pemphigoid clinical features
tense bullae with clear fluid (more difficult to break than pemphigus), blisters/erosions in mucosa
how does immunofluoresence work to diagnose blistering disorder?
anti-desmoglein IgG (auto-antibody) incubate section with fluorescently tagged anti IgG antibody on epithelial cells
tumors: two kinds of benign and premalignant epithelial lesions
seborrheic keratosis and actinic keratosis (solar)
seborrheic keratosis: occurs where?
occurs in people __
sun related?
trunk, extremities, head, neck
greater than 50
no
seborrheic keratosis pathogenesis
cause unknown:
somatic mutation in gene for fibroblast Growth factor receptor 3L (FGFR3)
receptor on basaloid keratinocytes: increased proliferation, greater production of keratin
seborrheic keratosis histological features
rete ridge pattern ablated (flat)
Horn cysts in epidermis (keratin filled cysts)
Acanthosis
seborrehic keratosis clinical features
tan to brown (melanin production in melaocytes), waxy, plaque
actinic keratosis: where does it occur? Why
balding scalp, face, lateral neck, distal or lower extremeties: sun related!
Actinic keratosis pathogenesis
uv light → DNA damage → mutates TP53 tumor suppressor → proliferation of atypical keratinocytes → intraepithelial dysplasia
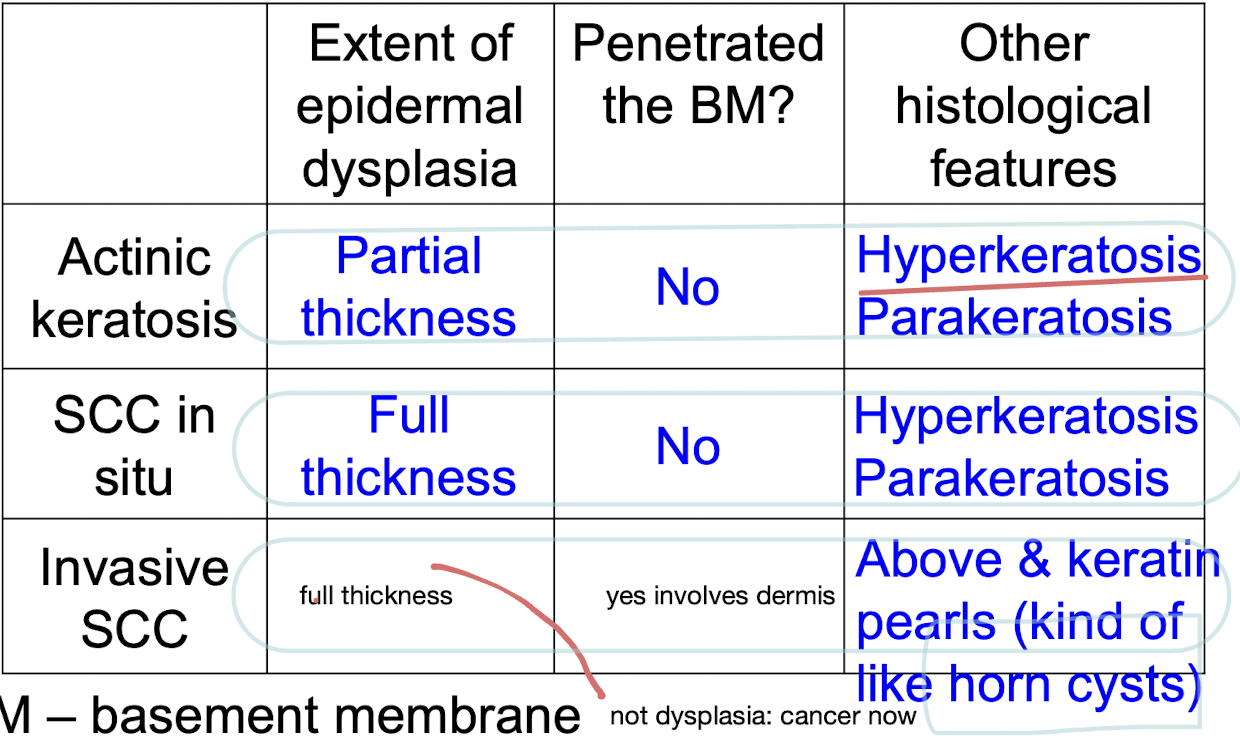
skin tumors on white skin: actinic keratosis, squamous cell carcinoma in situ (in place epithelial layer), invasive SCC, basal cell carinoma main causes
sun, invasive SCC is usually other carcinogens but can be sun
common mutations in the pathway of skin tumors and other
actinic keratosis: TP 53
SCC in situ: HRas
invasice SCC: HRas (proto-oncogenes)
Basal cell carcinoma: hedgehog pathway (oncogene)
dysplasia
atypical cells in epithelium
is dysplasia malignant? Why?
no: confined to epithelium: can progress to malignancy, persist, or regress
Sun exposed skin tumors: clinical features
actinic keratosis
SCC in situ
invasive SSC
Basal cell carinoma
macule or patch, scaly (hyperkeratosis)
patch or plaque
plaque or nodule
papule
why can you get oral squamous cell carninoma in mouth?
stratified squamous epithelium
is there basal cell carcinoma in mouth?
no only on skin
main cause of invasive SCC in skin of color and basal cell carcinoma
where?
not sun usually: ulcers, scar, radiation, carcinogens: non-sun exposed skin like legs
basal is both exposed and non-sun exposed skin
invasive SCC skin of color features vs basal cell
dark scaly, plaque
pigemented, pearly, papule
melanocyte proliferations (3) and their cause? which can metasize (which is cancer?)
common nevus (mole), dysplastic nevus (dysplasia mole), melanoma: cancer
BRAF or NRAS
risk factors for melanoma besides sun
genetics
main location of melanoma in people of color
sole, under nail, mucosa
ABCD of melanoma vs mole
Melanoma
Assymetrical: yes
border: bumpy/irregular
color: variable
Diameter: large than 6 mm
why important to recognize melanoma early? (3)
much less common, aggressive and metasize to any organ, high morality rate
what causes systemic lupus ertyhematosus
antibodies against nuclear components (like DNA, histones) → immune complex forms (antigen + antibody) → deposits in tissue and causes damage
SLE is a ___ disease: _ and ?
variable presentation: what 5 main things
multisystem, relapsing and remitting
butterfly rash (malar)
photosensitvity
mouth ulcers
swollen, painful joint (joint inflammation)
fatigue and fever
does age and gender matter in lupus?
occurs more often in younger women
What causes myasthenia gravis
autoantibodies to nicotinic acetylcholine receptor on skeletal muscle → degradation of the receptor
if myasthenia gravis continues you get fewer receptors: what happens?
muscle weakness → flaccid paralysis
symptoms of myasthenia gravis (3)
muscle weakness:
droopy eyelid
droopy mouth
difficulty chewing and swallowing
what is sjorgen syndrome
autoimmune destruction of Salivary and lacrimal glands
primary vs secondary forms of Sjogren
primary: just sjorgen (sicca)
secondary: associated with other autoimmune: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), lupus
what symptoms suggest Sjogren syndrome (6)
dry mouth, mouth sores/ulcerations, dental caries, lump in neck by salivary glands (due to infilitration of lymphocytes), dry eyes, rheumatoid arthritis (60% have Sjoren and another)
gender and age of sjoren
90% occurs in women 35-45