Comprehensive Bacterial and Eukaryotic DNA and Transcription Mechanisms
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Bacterial Genome
Chromosome + Plasmid
variable and related to lifestyle: free-living large, facultative pathogen intermediate, obligate symbiont pathogen is smallest
Plasmid
Smaller and multiple copies than chromosome
Chromosome
Larger and one copy
Eukaryote vs bacteria chromosome
bacteria more organized in operon, no introns, small number non-coding genes, more compact
Structure of DNA
Double helix, antiparallel 5' --> 3', proofreading and mismatch repair, use opposite strand as template for repair
Nucleotide
Sugar + phosphate + base
Nucleoside
pentose + base
Purines
A-G with double bond
Pyrimidines
C-G with triple bond
RNA OH group
on 2 carbon whereas DNA lack
Chargaff's Rule
%GC content differs among species but is constant in all cells of an organism within a species
Tm
Melting temperature which 1/2 dsDNA have denatured
Thermostability
Can be obtained through more GC, ex: thermophilic organisms higher GC to maintain integrity in hot environment
DNA Replication Components
template strand (semi-conservative), helicase (uses ATP), replication fork, DNA pol lll 5-->3, leading strand 5-->3, lagging strand make Okazaki fragments 3-->5, DNA ligase, Topoisomerase
Techniques Molecular Biology
microarray - protein, northern blot - RNA, southern blot - DNA
Time it takes replicate E coli genome
40 min, and division time 20 min, new DNA replication starts before prior one finishes, multiple replication forks going at once and daughter cells inherit partially replicated chromosomes
DNA pol 1
removes primers so polymerase can continue synthesis, using phosphate from NTP, then ligase reseals after exonuclease activity
OriC
Origin of replication and proceeds in multiple directions, multifork replication allows for 20 min generation time of E. coli
Termination Chromosome Replication
Ter sites act as roadblock for replication
Tus
Termination utilization substance, bind to ter sites and stop replication fork
Topoisomerase
Torsional stress transmit across replication fork, chromosomes between interlinked after replication, and this releases the stress created and decatenation (untangling)
Cis Elements
Elements on same molecule of DNA as gene they replicate
Trans Elements
Elements that can regulate genes distant from the gene they were transcribed on
E. coli partitioning
1 chromosome to each daughter cell
E. coli Segregation
Moving replication chromosome to daughter cells, starts soon after replication
ParA & ParB
Partitioning proteins encoded by Par genes, cis-acting sites, ParB binds pars sites around OriC and ParA binds nonspecific DNA
Central Dogma
DNA --> RNA --> proteins
Difference transcription and translation
Template same but only part of genome transcribed
Translation: RNA poly use ribonucleotides and Uracil, don't need primer, and no proofreading, 5-->3, produce single-strand DNA molecule compared to 1 strand DNA template
Polycistronic mRNA
1 RNA carries genetic info for various genes/ proteins allowing for coordinated expression, related genes in 1 operon
Transcription and Translation in bacteria
Coupled, since no nucleus
Polysome
Multiple ribosome acting on same RNA
Holoenzyme
Core enzyme (5 subunits with catalytic activity but can't bind and start transcription) + Sigma factor (recognize promoter sequence)
Alpha
Enzyme assembly and interaction with regulatory proteins
Beta
Catalytic activity of RNA synthesis
Beta Prime
Catalytic activity and essential DNA binding
Omega
Assembly and stability of RNA polymerase complex
Promoter
Site DNA where transcription initiates, recognized by sigma factors
Transcription start site is not start of coding region of gene, so what is?
5' UTR before coding region
A-subunit
Interact with UP element upstream to improve strength
Sigma 2 Domain
Interact with -10 element to open DNA
Sigma 4 Domain
Interact with-35 element for initial recognition
Promoter Strength
Determine frequency of transcription initiation, relates affinity of RNA polymerase for promoter region
Initiation Transcription
Promoter recognition
Isomerization - rearrangment to allow binding sigma 2 and open -10 element
2 outcome: abort or promoter escape and clearance to elongation
Elongation Transcription
5-->3 synthesis
Termination Transcription
2 types Rho-indep (intrinsic) or Rho dependent
Intrinsic Termination
signal is on same RNA molecule (cis-acting)
-GC rich hairpin loop followed by serine U residues
-hairpin cause RNA pol pause and poly U leads to dissociation with weak DNA-RNA hybrid
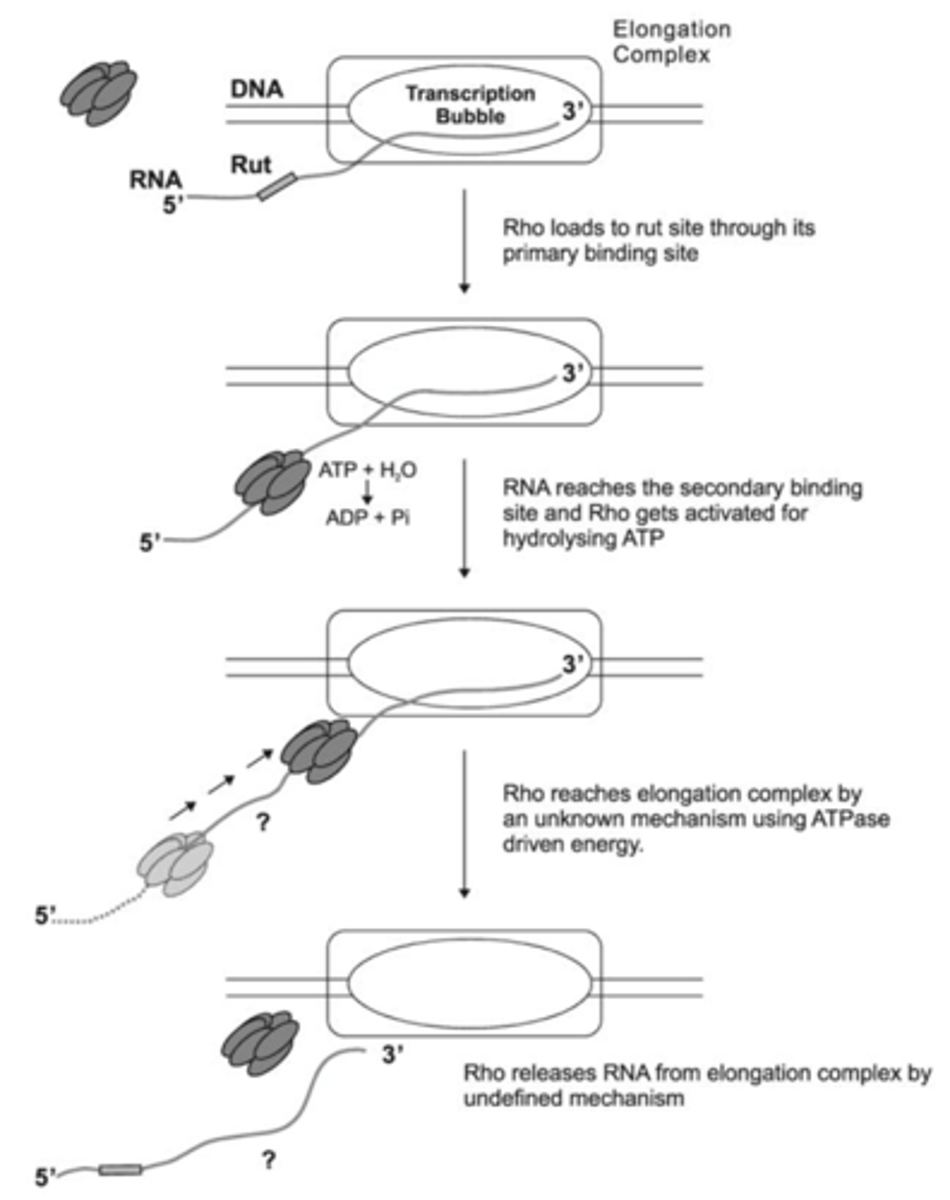
Factor-dependent
Requires RNA-DNA helicase, Rho protein (trans-acting)
Rho bind to rut
Rho termination site allow Rho to catch up with RNA polymerase
Rho is ATP-dependent
Rho can't bind rut sites if mRNA being translated so Rho help prevent transcription of mRNA
Sigma Factors E. coli
Diverse set relating to unique environment and stress
Extracytoplasmic Function (ECF) Sigma Factors
Crucial role in signal transduction
Respond to extracytoplasmic stress
Conjunction with membrane-bound anti-sigma factor for quick response
Highly diverse
Transcriptional Regulaton of T6SS by sigma factor
Xanthomonas T6SS transcribed only in presence of sigma factor ECFK, and T6SS prevent ameoba from eating bacteria
Polar effect on gene expression
Some mutation in polycistronic mRNA can effect downstream genes so important to use complement with plasmid to restore gene to prevent downstream effects, often causes premature stop in translation preventing downstream transcription of genes
Advantages to degenerate amino acids
1) Error tolerance: mitigate mutations
2) Translation efficiency tRNAs can recognize multiple codons due to wobble base pairing
3) Evolutionary flexibility: variation without altering protein function
Termination codons:
UAA, UGA, UAG - don't insert an amino acid but prompt the release of polypeptide from the ribosome
Initiation codon
AUG is main one in E. coli but also GUG and UUG
Wobble Base Pairing
Wobble position is anticodon base 34
Codon base 3 is wobble base of codon
Located here bc ribosome monitoring is relaxed at this position, allowing modified bases and nonstandard pairing
Support efficient decoding of the genetic code without compromising fidelity
Reading Frames
6, 3 forward, 3 backward
How ribosome distinguish between start codons
Shine-Dalgarno sequence/ribosome binding start, short region rich in purines that binds to the 3' end of 16S rRNA anti-Shine-Dalgarno sequence
5-10nt upstream of start codon
Polycistronic mRNA each internal ORF has own SD sequence
How is ribosome number determined (70S)
Subunit number is related to configuration and properties of particle (size, shape)
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
Attach an amino acid to a tRNA
Most cells have 20 different ones for each amino acid
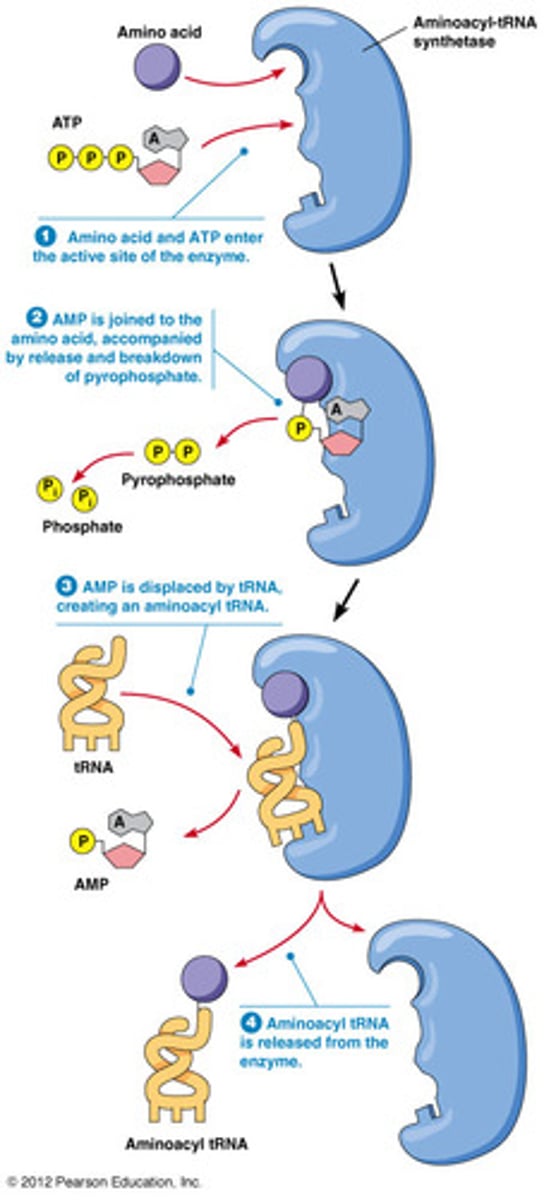
Steps of aminoacyl tRNA synthetases
1) amino acid and ATP enter active site of the enzyme
2) AMP is joined to the amino acid, accompanied by release and breakdown of pyrophosphate
3) AMP is displaced by tRNA creating an aminoacyl tRNA
4) aminoacyl tRNA is released from the enzyme
3 Sites of Ribosome
A = acceptor, P = peptidyl, E = exit
Ribozyme
a type of RNA that can act as an enzyme
in ribosome 23S rRNA act as peptidyltransferase enzyme
Translation Steps
formyl group help initiator tRNA enter the P site, which no other aminoacyl tRNA can do
1) aa-tRNA bind to EF-Tu and comes to A site
2) if there is codon-anticodon match, GTP is cleaved and EF-Tu released
3)23S rRNA form peptide bond
4) EF-ts is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor and recycles EF-Tu (GDP >GTP)
5)EF-G catalyzes translocation of the A site tRNA to P site making room on A site, EF-G uses GTP energy to move ribosome forward one codon
6)P site tRNA now moves to E site to exit
Initiation of Translation
Requires 3 initiation factors: IF1, IF2, IF3, and fMet-tRNA
IF3
Helps keep 30S dissociated
IF1
prevents fMet-tRNA from binding to A site
IF2
delivers fMEt-tRNA to P site and promotes the association of 50S subunit
Translation Termination
No tRNA correspond to stop codon so translation stops when they enter A site
termination codons are recognized by release factors
-RF1 & RF2 recognize stop codons and catalyze peptide release
-RF3 is GTPase that removes RF1/2 from ribosome to speed up termination
trans-Translation (tmRNA)
Mechanism to rescue ribosomes that reached the end of mRNA without a stop codon
release factors work only at a termination codon
requires transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA)
ribosome shifts from translating the mRNA to translating the tmRNA
EF-Tu deliver tmRNA to stalled ribosomes without any codon-anticodon matching
encode a tag sequence of 10 aa that is recognized by ClpXP protease to degrade de polypeptide
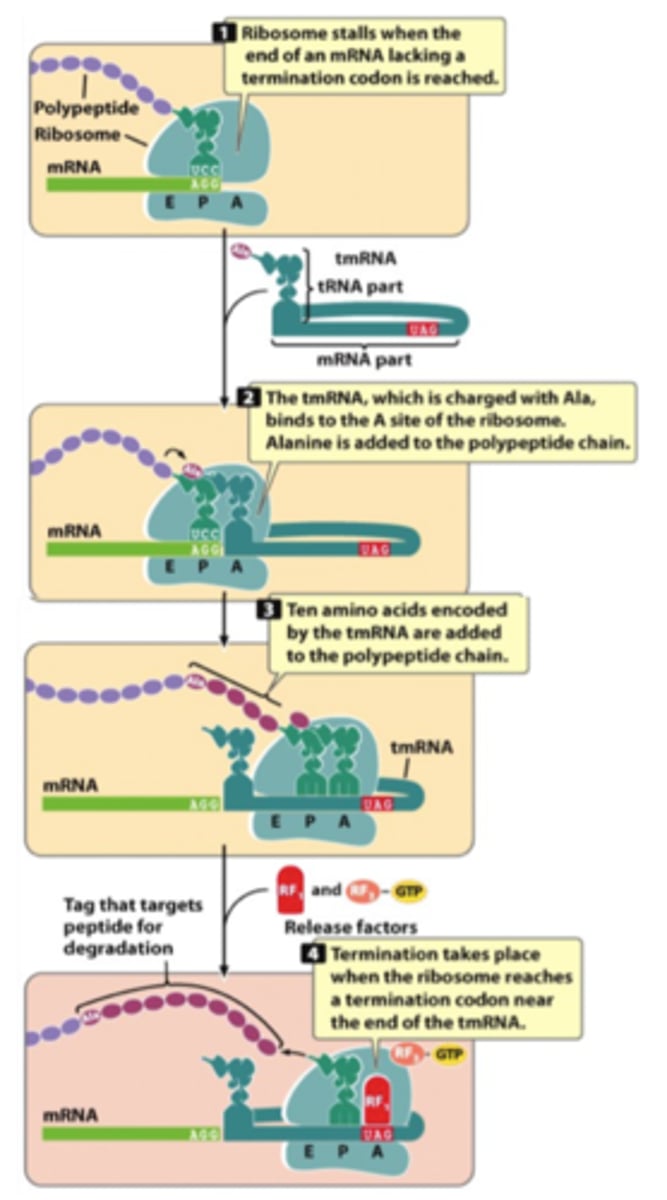
tmRNA
both tRNA and mRNA
aminoacylated with alanine
contains ORF that terminates in a stop codon
Difference between DNA damage and mutation
Mutation is what DNA damage becomes when repair fails
Spontaneous DNA Damage
removal of base/depurination
replication error - by polymerase with wrong pairing later fixed with mismatch repair
deamination - amino group removed causing mutation when DNA replicates
Induced
Alkylation - where methyl group inserted
UV light -cause dimers to forms resulting in distortion
Point Mutation
Mutation in a single base pairing during replication
Transitions
Purine for purine or pyrimidine for pyrimidine
Transversions
Purine for pyrimidine
Nonsense Mutation
Results in early stop codon
Missense Mutation
New amino acid
Ames test
Bacterial assay that measures the mutagenic potential of a compound and carcinogenic potential. Works by exposing bacteria that need histidine (an amino acid) to a test substance; if the substance causes a mutation that restores the bacteria's ability to produce its own histidine, the bacteria grow, signaling a positive (mutagenic) result
Mutation generates
Beneficial variants that improve fitness
Neutral variants that drift in populations
Deleterious variants that selection removes
Mutation serve as what
Molecular clocks as they accumulate over time, often use 16S rRNA gene to identify bacterial species as its highly conserved across all bacteria so we can design universal primers, and hypervariable as there are species-specific sequence signatures
Transcriptional Fusion
Promoter of a target gene is placed upstream of a reporter gene, allow to monitor promoter activity by measuring reporter protein without relying on the original gene's translation
Translational Fusion
Combining the coding sequences of two genes (gene of interest, and reporter gene like GFP) in frame to create a single larger fusion protein to track protein location and activity within a cell
Reporter Gene
Gene that makes a phenotype or protein of interest easily detectable to study
Fusion Protein
One protein composed by the fusion of two genes
Mutation
Change in DNA sequence
Mutant
Organism that carries a mutation
Strain
Genetic variant of an organism
Phenotype
Physical or biochemical characteristics of an organism
Genotype
The genetic constitution of an organism
Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP)
Jellyfish obtaining coelenterazine from its diet
Coelenterazine loads into the protein aequorin (calcium activate photoprotein)
Mechanical disturbance causes Ca2+ influx --> Aequorin flashes blue light
GFP absorbs the blue light and re-emits green light
Auxotrophs
Mutation on genes required to make essential metabolite
Luria-Delbruck Experiment (Fluctuation Test)
Random-mutation (Darwinism) vs directed change hypothesis (Lamarckism)
Found direct evidence that mutations occur spontaneously
How to isolate mutant
Screening: process of finding mutants - involves selective conditions to distinguish the mutant vs WT
Positive Selection
Condition which mutant but not WT can replicate - ex: mutant that acquired antibiotic resistance cassette
Negative Selection
Condition which mutant can't grow
Methodologies to create a mutant
Recombineering and allelic replacement
Gene Deletion by Allelic Exchange
Shuttle vector with Ab that replicates in E. coli but not in bacteria you want to delete the gene
Clone mutant gene into a plasmid and introduce vector into bacteria of interest
Need homologous region up and downstream of gene of interest depending on recombination machinery of cell for insertion
Select for Ab contained in vector
Cloning using restriction enzyme
Cut to get sticky ends and ligase back together
Or blunt ends but those are much harder to clone
Difference between DNA replication and PCR
PCR (in vitro) amplifies specific DNA segments using heat cycles, synthetic primers, and thermophilic polymerase, mimicking DNA replication (in vivo) which copies the entire genome within living cells using various enzymes, RNA primers, and consistent body temperature, with DNA replication producing Okazaki fragments while PCR synthesizes only leading strands