GCSE Year 10 – Atoms, Elements, Compounds & Periodic Table
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is an atom?
tiny building block that makes up everything around us
What are the three main subatomic particles, their charges, and relative masses?
Relative Mass - Proton: 1 Neutron: 1 Electron: 1/1840
Charge - Proton: +1 Nuetron: 0 Electron: -1
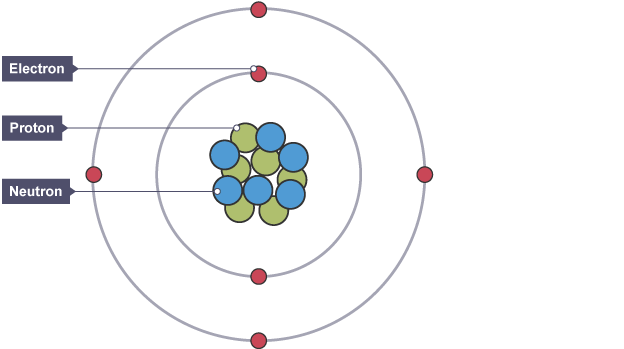
Where are protons, neutrons, and electrons located in an atom?
Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus; electrons orbit in shells.
Why does an atom have no overall charge?
Because the number of protons equals the number of electrons.
What is the atomic number (Z)?
The number of protons in an atom.
What is the mass number (A)?
The total number of protons and neutrons.
What is an element?
A substance made of atoms with the same number of protons.
What is a compound?
A substance made of two or more elements chemically joined in a fixed ratio.
How can compounds be separated?
Only by chemical reactions, not physical methods.
What is a mixture?
Two or more substances not chemically joined, each keeps its own properties.
Name some physical separation methods.
Filtration, evaporation, distillation, chromatography.
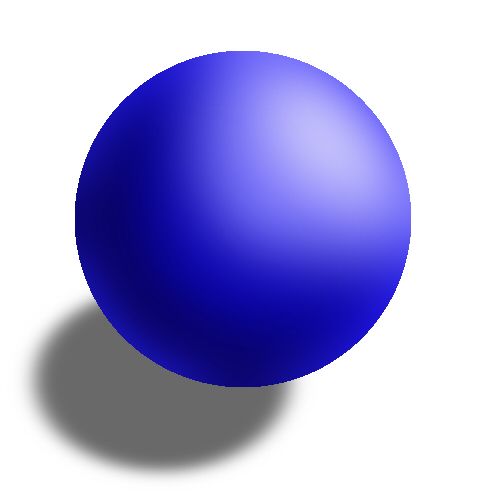
What did the Dalton model say?
Atoms are tiny solid balls with nothing inside.

What did the Plum Pudding model say?
Atoms are a positive ball with electrons inside.
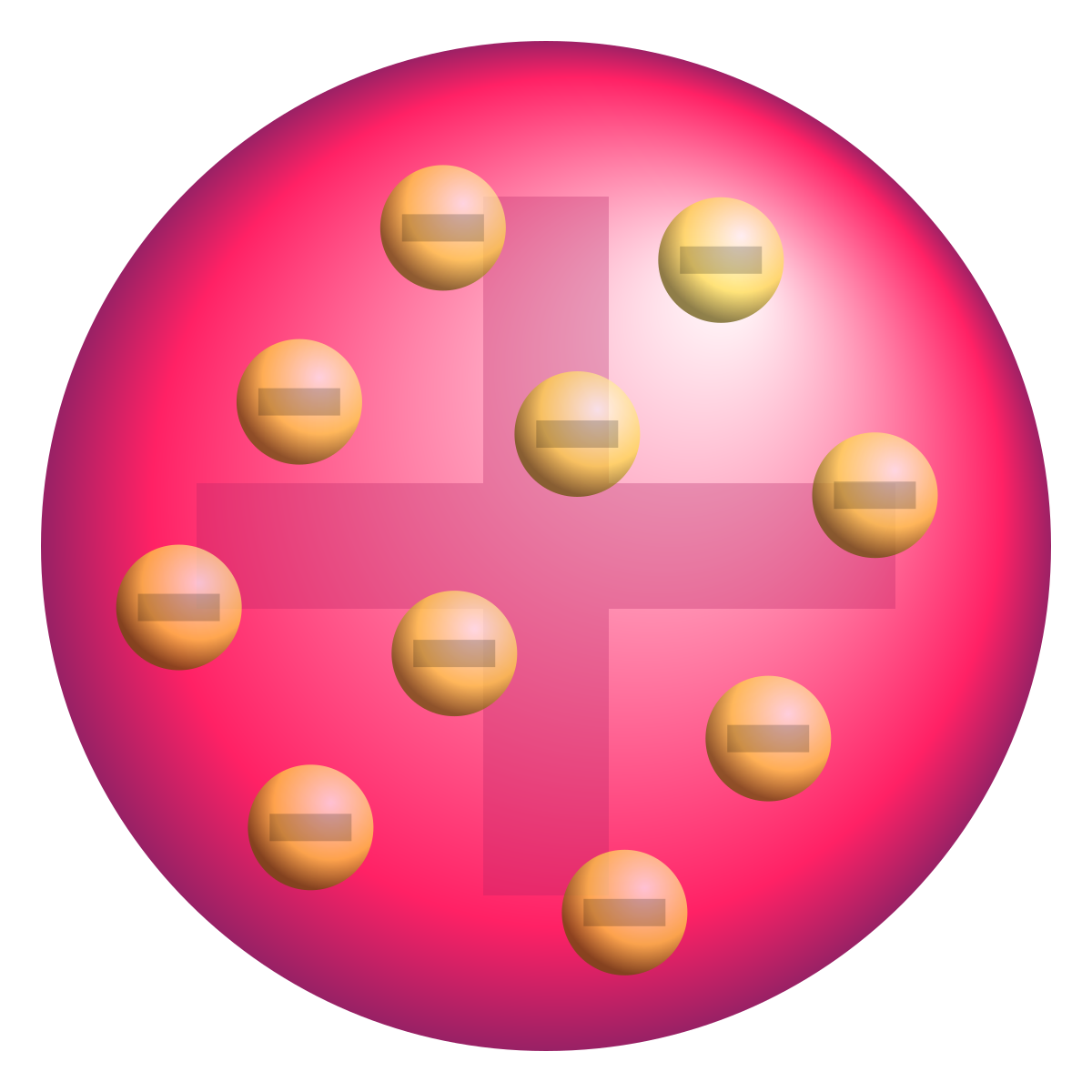
What did the Rutherford model show?
Nucleus is dense and positive; most of the atom is empty space.
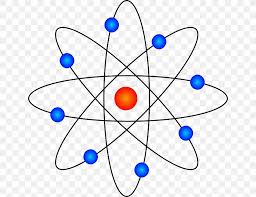
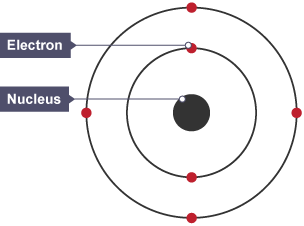
What did the Bohr model say?
Electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed shells.
What did Chadwick discover?
In 1932, James Chadwick discovered the nuetron
What are isotopes?
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
What is relative atomic mass (RAM)?
The weighted average mass of all isotopes.
How do electrons occupy shells?
Fill inner shells first, then outer shells.
Maximum electrons in the first shell?
2
Maximum electrons in the second shell?
8
Maximum electrons in the third shell?
8
Steps to balance chemical equations?
Write the unbalanced equation.
Count atoms of each element on both sides.
Balance one element at a time using coefficients (never change subscripts).
Balance H and O last.
Recount atoms → both sides must match.
Example:
H 2 + O 2 —> H_2O
Balanced:
2H_2 + O_2 —> 2H_2O
How are elements arranged in the periodic table?
By increasing atomic number.
What are groups?
Columns with the same number of outer electrons and similar properties.
What are periods?
Rows with the same number of electron shells.
Properties of metals?
Shiny, malleable, conduct heat and electricity, form oxides and ionic compounds.
Properties of non-metals?
Dull, brittle, poor conductors.
Properties of alkali metals?
Group 1, one outer electron, very reactive, reactivity increases down the group.
Properties of halogens?
Group 7, seven outer electrons, reactive, reactivity decreases down the group.
Properties of noble gases?
Group 0, full outer shell, very unreactive.