The Cell (A2.2)
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
what are the 3 main aspects of the cell theory?
all living things are composed of cells
cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things
cells come from pre-existing cells
what is deductive reasoning?
progression from a general idea to a specific conclusion
all organisms carry out what processes of life?
Mr. Sheng:
Metabolism
Reproduction
[response to]Stimuli
Homeostasis
Excretion
Nutrition
Growth
what is homeostasis
the maintenance of internal conditions within a narrow range
what is excretion
the removal of metabolic waste from an organism
What is response to stimuli
the ability of organisms to respond to internal/external stimuli
changing the position of the organism
what is metabolism
the sum of all the biochemical reactions that occur in living organisms
what is reproduction
the production of offspring, either sexually of asexually
what is nutrition
the processes that organisms use to obtain and use food (nutrients) for energy, growth, and repair
what is growth
the increase in mass, size, or number of cells of an organism
what are the features shared by all cells?
phospholipid (plasma membrane)
cytoplasm
DNA
Ribosomes
what are the 2 types of cells
prokaryotic
eukaryotic
what does a phospholipid do?
controls what enters and exits the cell
what does the cytoplasm do?
composed of mainly water
where most metabolism occurs
what does DNA do?
genetic material
what do ribosomes do?
used for protein synthesis
what is the difference between staphylococcus and bacillus in a prokaryotic cell
Staphylococcus: circular structure
Bacillus: rod structure
what is the structure of a prokaryotic cell? (5)
cell wall
plasma membrane
cytoplasm
naked DNA in a look (nucleoid)
70S ribosomes
what is the function of the cell wall in a prokaryotic cell?
provides the cell with strength and support
prevents the cell from bursting
composed of peptidoglycan
what is the function of the nucleoid in a prokaryotic cell?
naked DNA twisted in a loop
no nuclear membrane
contains a singular circular chromosome with DNA (no protein)
what is the function of the 70S ribosomes in a prokaryotic cell?
responsible for protein synthesis
what is the structure of a eukaryotic cell? (10)
plasma membrane
cytoplasm
nucleus
mitochondria
smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
80S ribosomes
Golgi apparatus
lysosomes
cytoskeleton
what is the function of the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell? (3)
double membrane with pores
contains DNA (chromosomes)
has histones bound to it
what is the function of the mitochondria in a eukaryotic cell?
site of aerobic respiration
produces ATP
has a double membrane
what is the function of the SER in a eukaryotic cell?
produces lipids
detoxifies blood
no ribosomes
what is the function of the RER in a eukaryotic cell?
site of protein synthesis
protein is designed to leave the cell
single membrane
send proteins to the Golgi apparatus
where are the 80S ribosomes in a eukaryotic cell?
on the rough ER
what is the function the Golgi apparatus in a eukaryotic cell?
packages proteins into vesicles for export
single phospholipid bilayer
what is the function of the lysosomes in a eukaryotic cell?
special vesicles w/ digestive enzymes
involved in the digestion of large molecules
what does the cytoskeleton do
made of microtubules + microfibers
gives cell structure
no ribosomes
what are the similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? (4)
both have:
phospholipid membrane
cytoplasm
DNA
ribosomes (70S in p, 80S in e)
what is the difference in membrane bound organelles between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
prok: not present
euk: present
what is the difference in mitochondria between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
prok: not present
euk: present
what is the difference in location of chromosomes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
prok: Nucleoid region in the cytoplasm
euk: Nucleus
what is the difference in number of chromosomes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
prok: one
euk: many
what is the difference in shape of chromosomes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
prok: Loop of DNA
euk: Linear
what is the difference in protein associated with chromosomes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
prok: NONE
euk: DNA wrapped around histone proteins
what is the difference in ribosomes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
prok: small 70S
euk: large 80S
what is the difference in cell wall between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
prok: composed of peptidoglycan
euk: plants (cellulose), fungi (chitin), animals (none)
what is the difference in cell size between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
prok: smaller
euk: larger
what are the differences between an animal cell, a fungi cell, and a plant cell?
Feature | Animal | Fungi | Plant |
Cell Wall | not present | chitin cell walls | cellulose cell walls |
Vacuoles | small; involved in storing materials and waste products | small or large; depends on the species of fungi | 1 large vacuole; involved in storing nutrients and waste |
Centrioles | present | not present | not present |
Plastids (what gives the plant color) | not present | not present | found in: - chloroplasts - chromoplasts - amyloplasts |
Cilia and flagella | present in some animal cells | not present | not present |
what are some atypical cells and nuclei (4)
aseptate fungal hyphae
skeletal muscle cells
red blood cells
phloem sieve tube elements
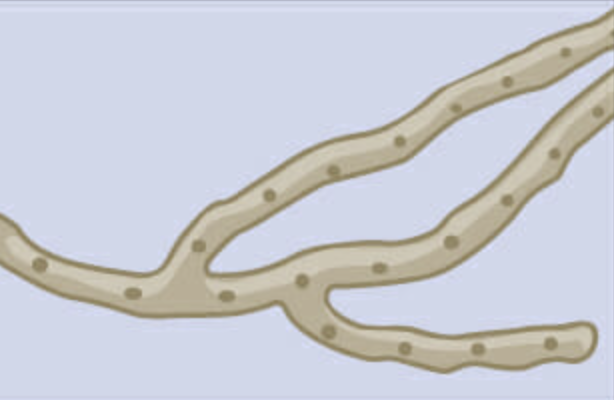
what type of atypical cell is this?
Septate hyphae: has a cell wall
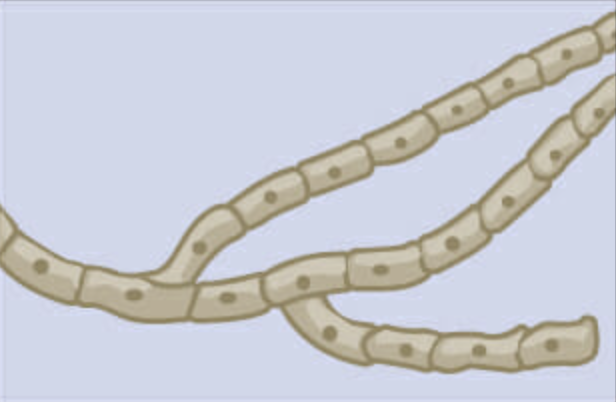
what type of atypical cell is this?
Aseptate hyphae: cell wall removed
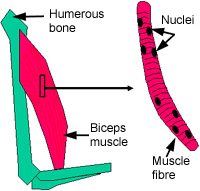
what type of atypical cell is this?
skeletal muscle cell
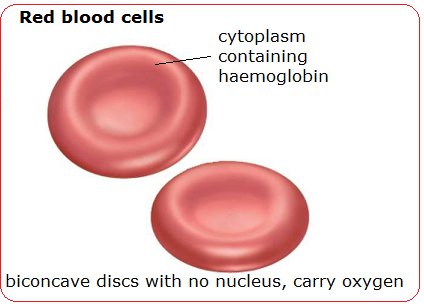
what type of atypical cell is this?
red blood cells
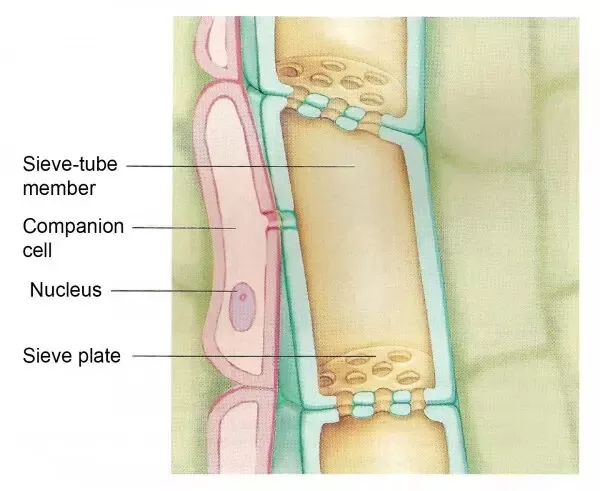
what type of atypical cell is this?
phloem sieve tube + elements
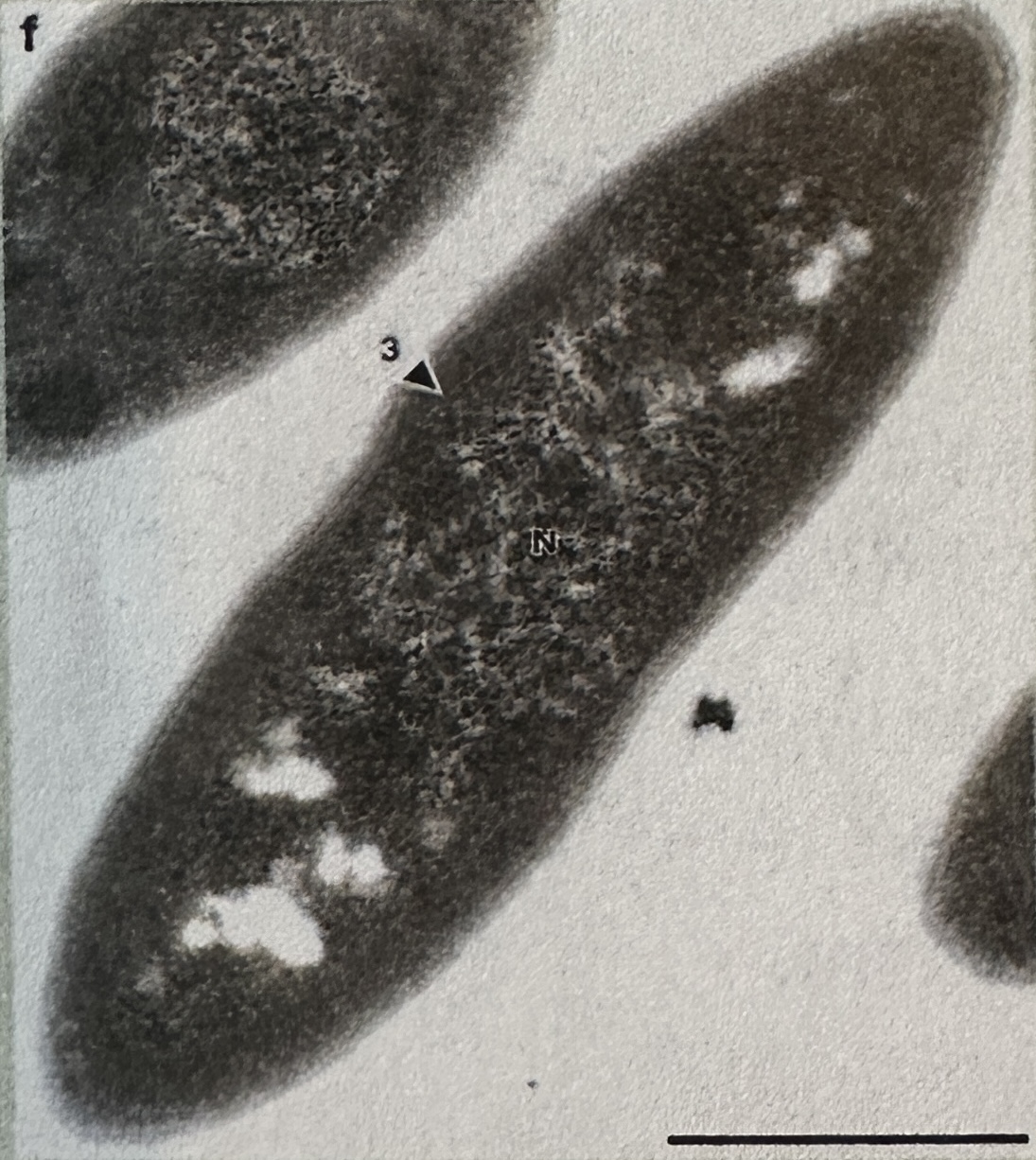
what type of cell is this
prokaryotic:
there is a clear nucleoid region
no nucleus present
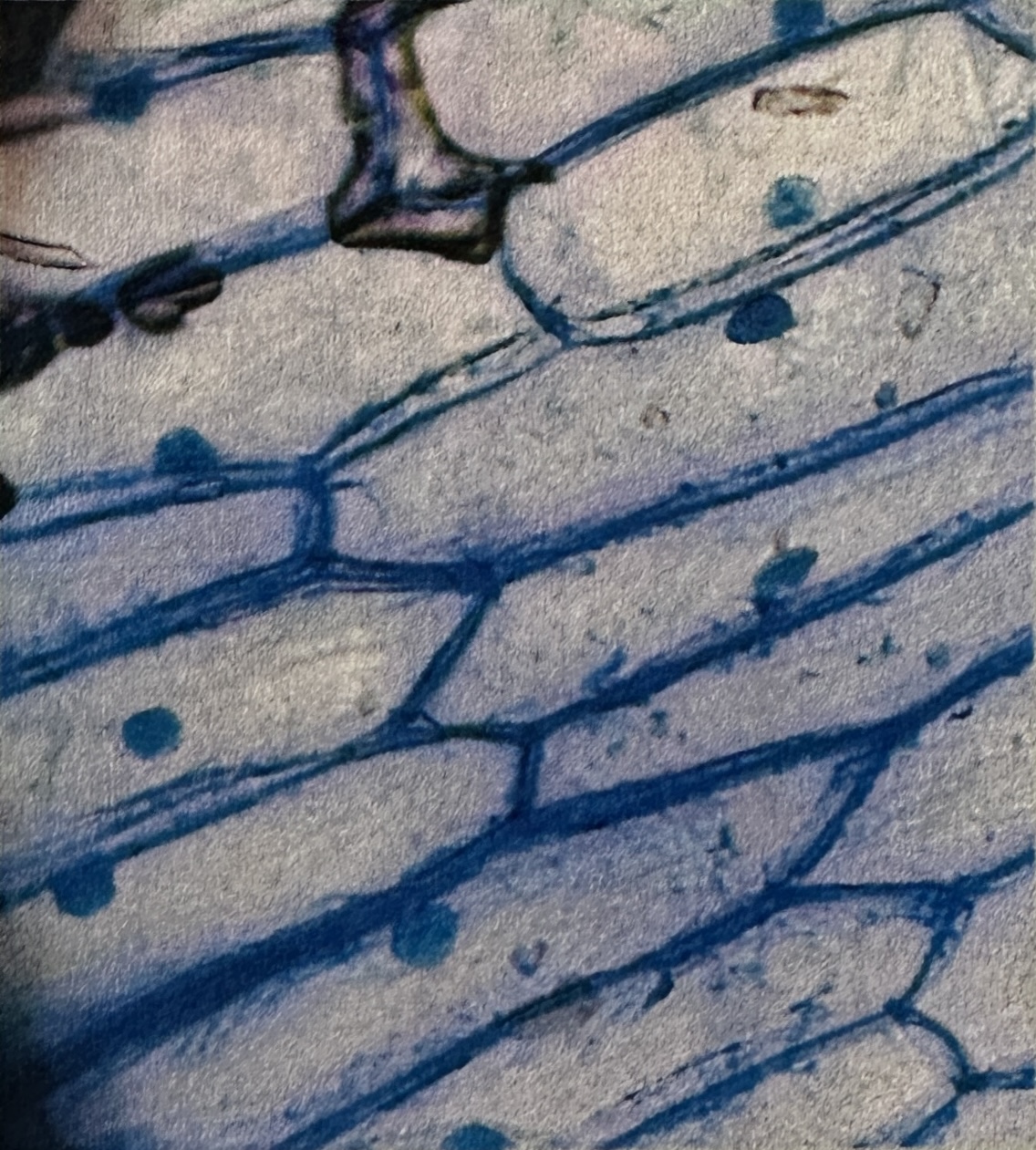
what type of cell is this
plant cell:
nuclei are visible
fixed regular shape
clear cell wall
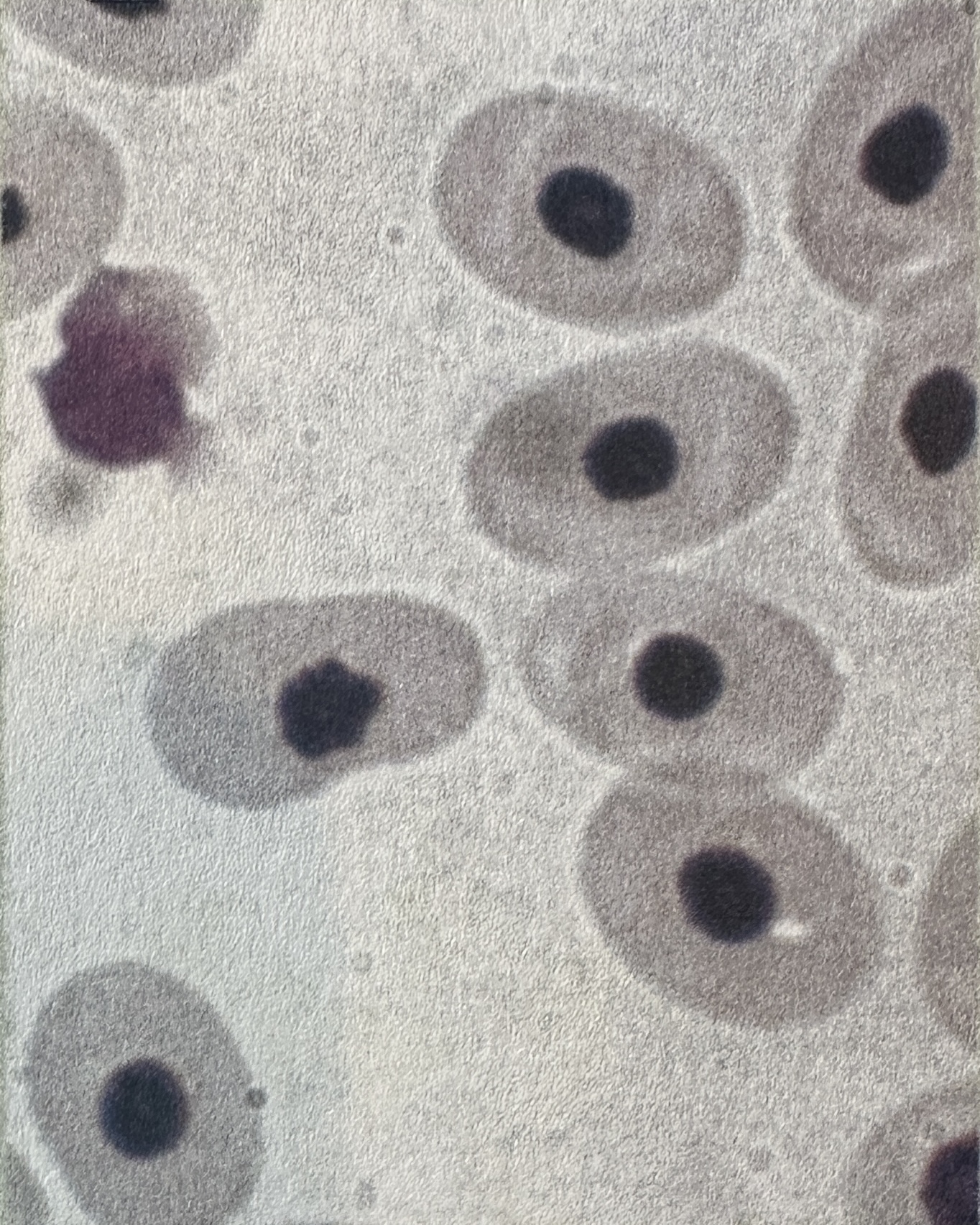
what type of cell is this
animal cell:
nuclei are visible
don’t have a cell wall around them
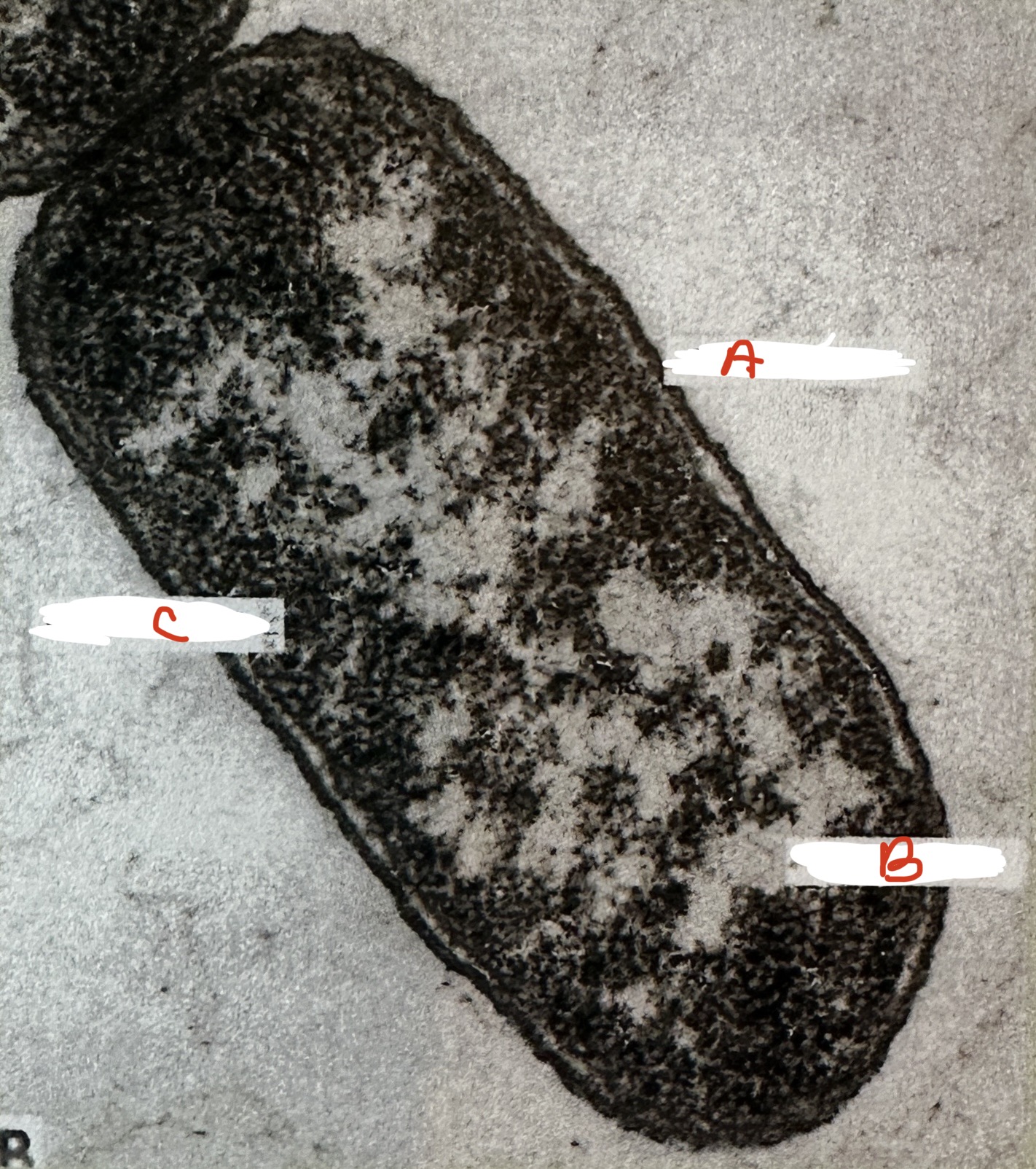
where is the nucleoid region?
B: nucleoid region is lighter, irregularly shaped region within the cytoplasm
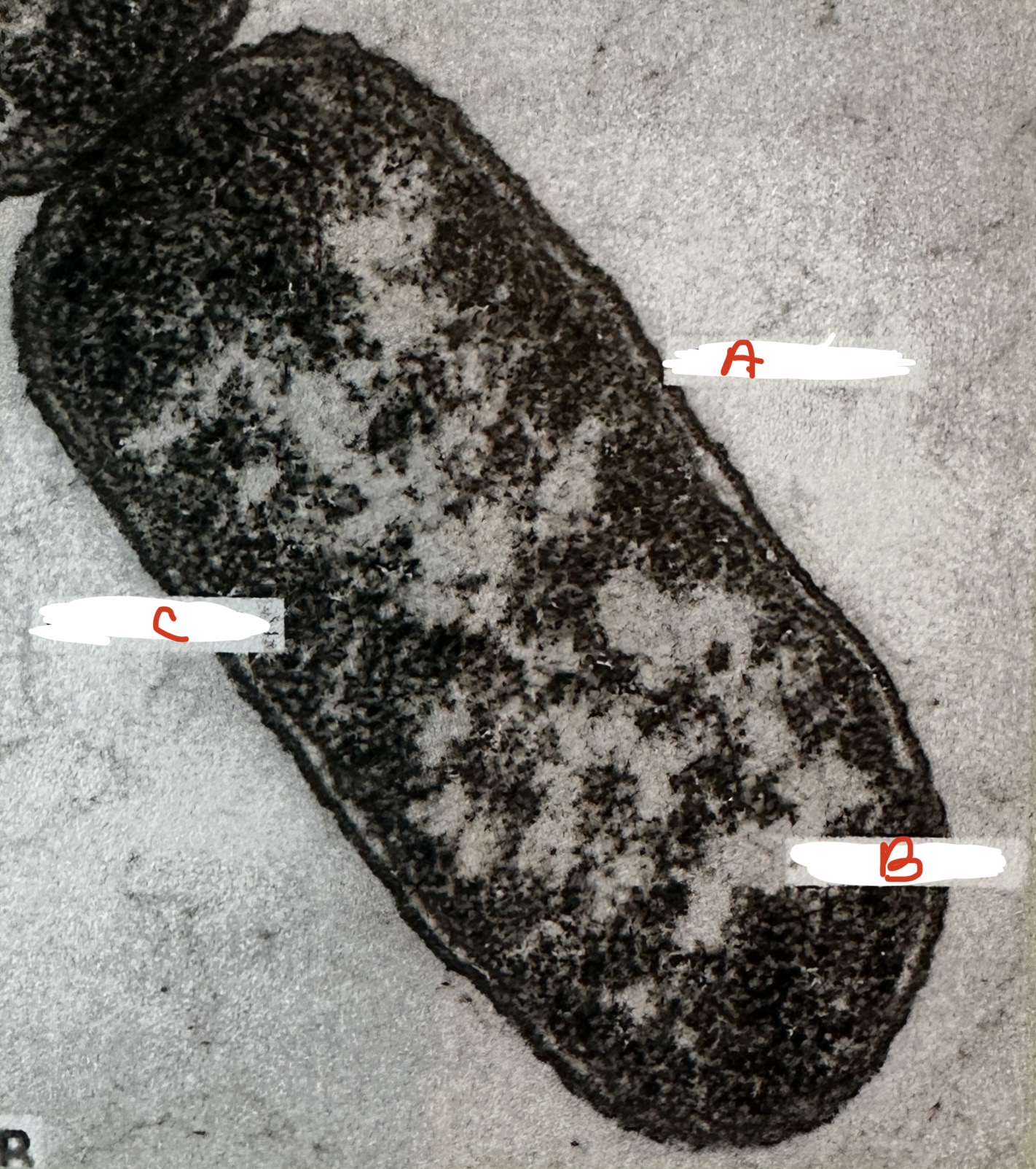
where is the cell wall
A: seen as a dark line around the outside of the cell
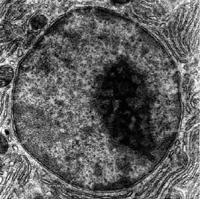
what does the nucleus look like?
the large dark circle with lighter spots what represent pores
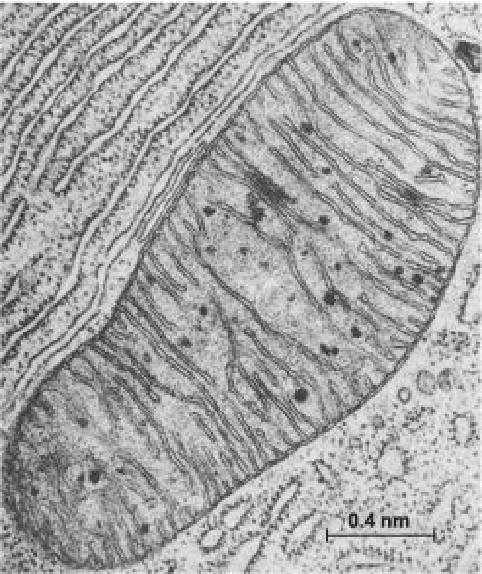
what does the mitochondria look like
has a double membrane
outer membrane is smooth
highly folded inner membrane (cristae)
represented through lines in a micrograph
what does the chloroplast look like
has a double outer membrane
has many membranes within the chloroplast
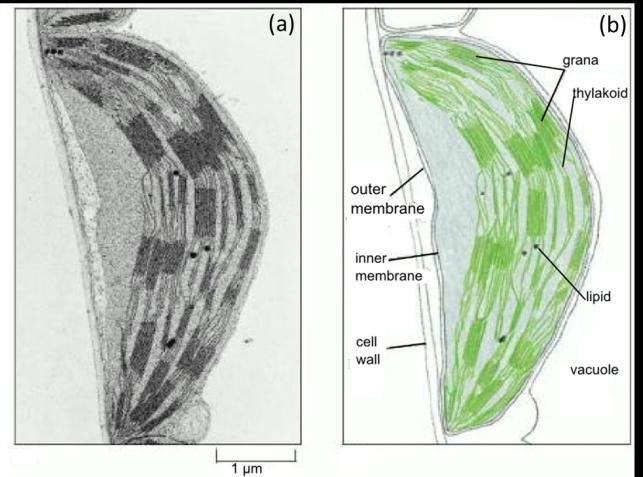
what does the sap vacuole look like
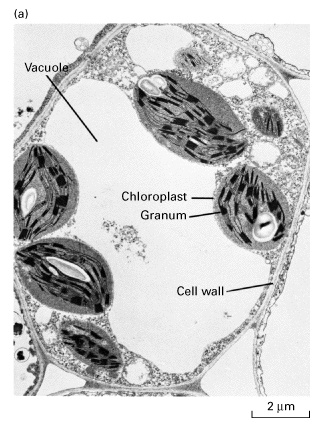
large vacuole with a single membrane
located in the centre of the cell
pushes all the other organelles against the cell wall
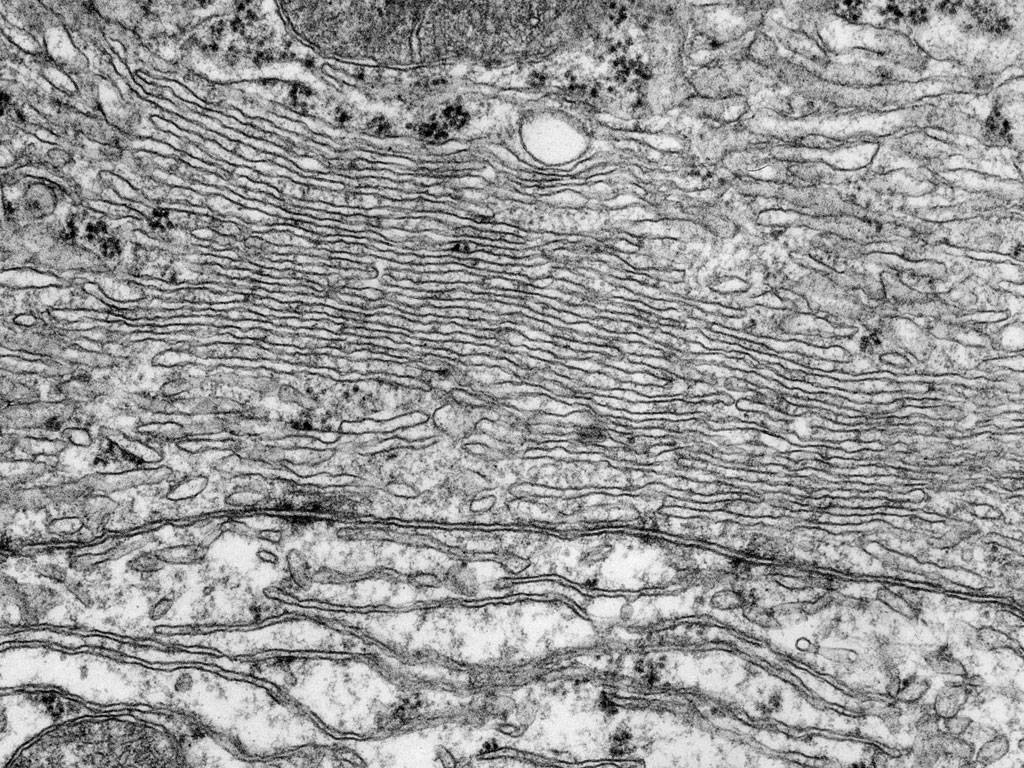
what does the rough endoplasmic reticulum look like
rough appearance
has ribosomes (black dots) all over it
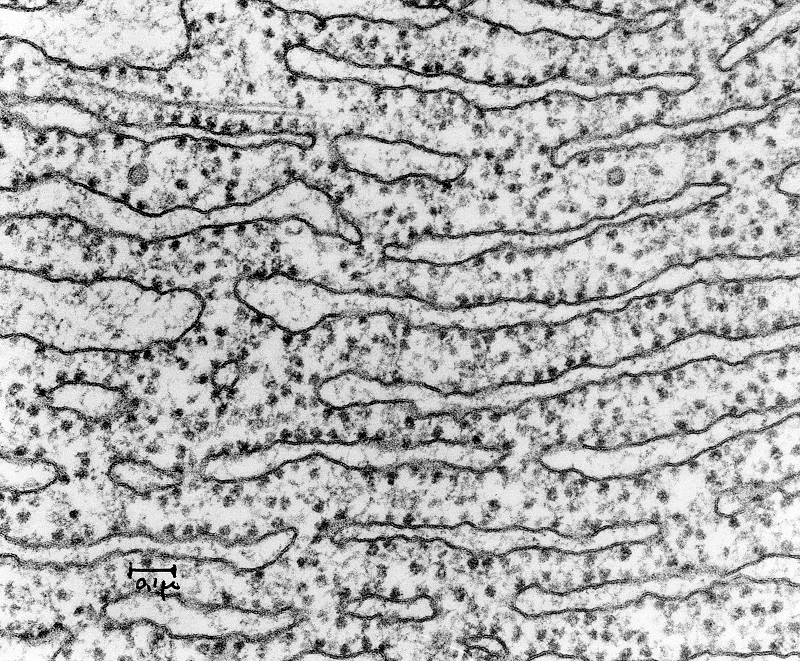
what does the smooth endoplasmic reticulum look like
no ribosomes present
smooth appearance
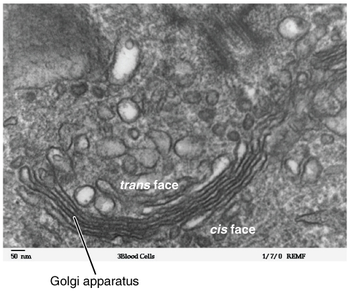
what does the Golgi apparatus look like
a series of stacked, flatten membranes
small vesicles around it
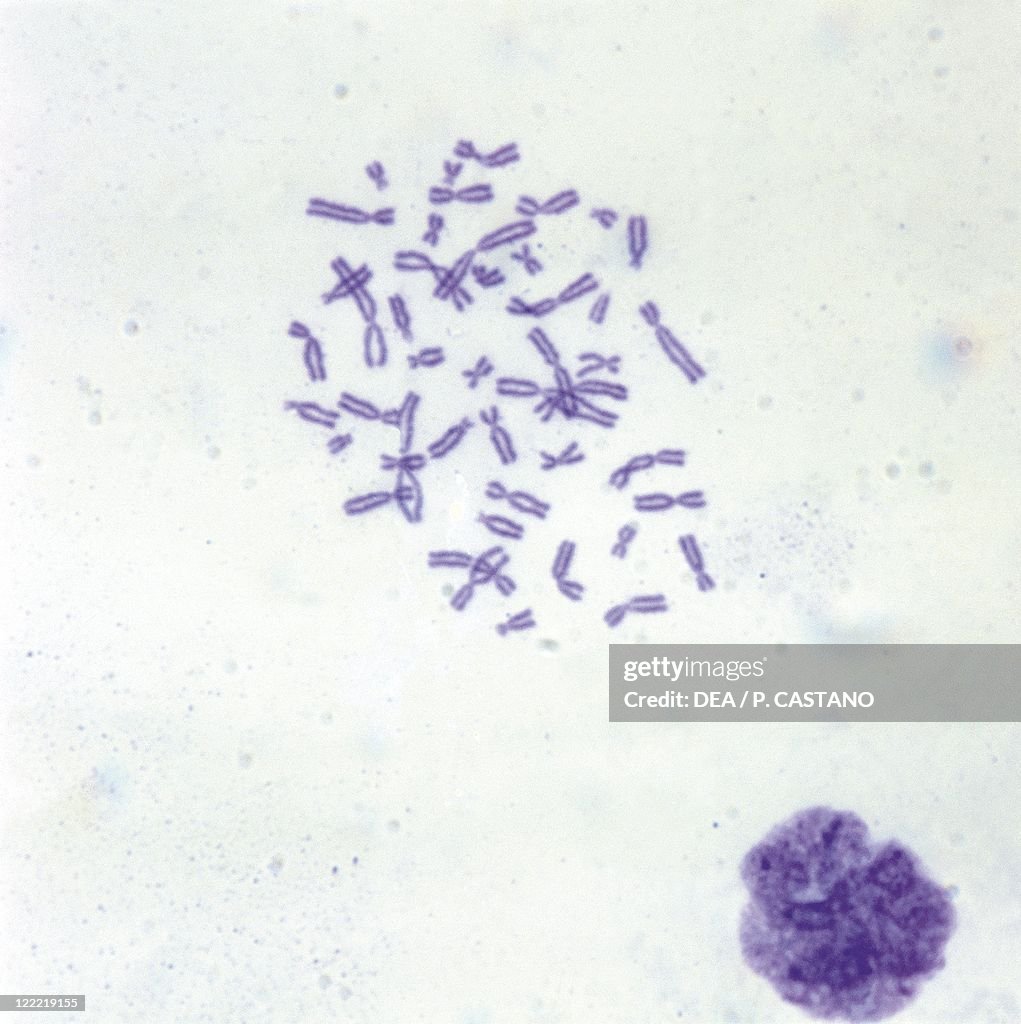
what does a chromosome look like
become visible during mitosis and meiosis
consist of 2 elongated DNA molecules
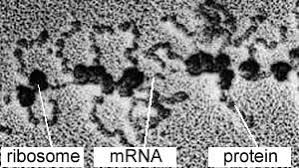
what do the ribosomes look like
spherical dots with a dark center
found floating in the cytoplasm
found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum
what does the cell wall look like
a line surrounding the plant cell
what does a plasma membrane look like
pushed against the inside of the cell (plant cells)
the outer boundary of the cell (animal cell)
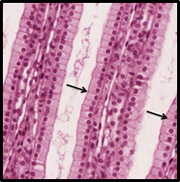
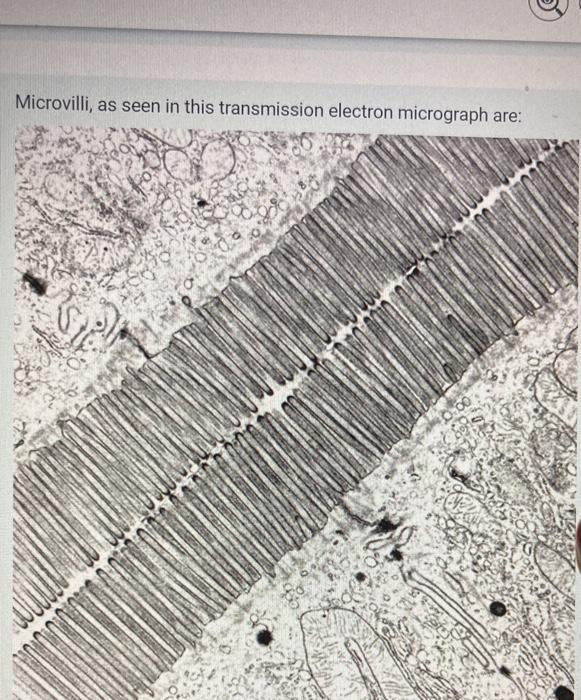
what do the microvilli look like
appear as long finger-like extensions of a cell
what are the factors that make a scientific theory
based on evidence
lots of science to back it up
what is an example of a scientific theory
endosymbiotic theory
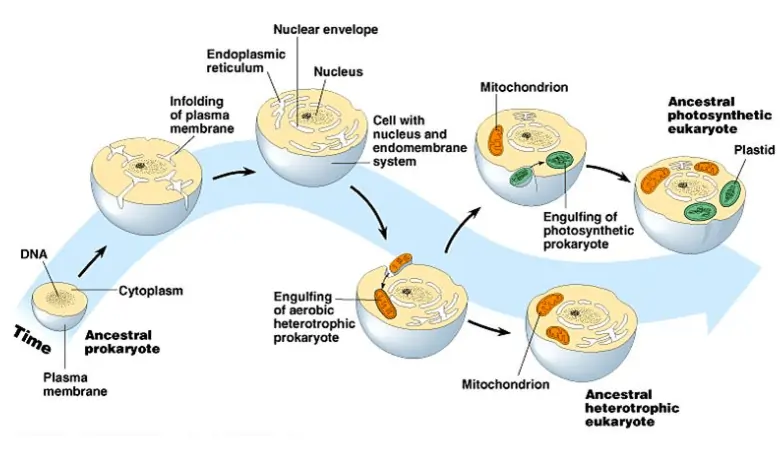
what is the endosymbiotic theory
explains that a sexually reproducing eukaryotic cell with a nucleus engulfed a small aerobic prokaryotic cell
the 2 cells worked together and developed a mutualistic (symbiotic) relationship with the host cell
the host cell provides food while the engulfed cell produces ATP energy
the smaller cell (aerobic cell) then evolves into mitochondria and leaves the host
what is the evidence for the endosymbiotic theory (5)
mitochondria + chloroplasts:
have a double membrane
have a single circular chromosome (w/ naked DNA)
have 70S ribosomes
reproduce through binary fision
similar size to modern prokaryotes
what is cell differentiation
some genes are turned on and some are turned off
what triggers different patterns of gene expression?
changes in the internal or external environment
what are the advantages of multicellularity
tend to be larger
have longer life spans
the death of one or a few cells doesn’t kill the organism
are more complex due to cell specialization
what are the advantages of immunofluorescence (4)
are specific
scientists can study the location, distribution, and quantity of specific biomolecules
can be used with living tissue
allows scientists to study cell division
can be used to detect molecules at low concentrations
can be used to label different molecules
what is immunofluorescence used for
to visualize specific protein or antigen in cells by binding a specific antibody to a fluorescent dye
easy way to remember how immunofluorescence works?
navigating around the cells is like navigating around a city (using lights)
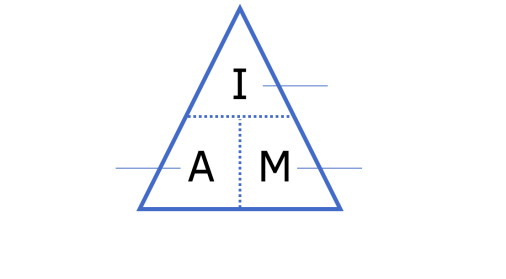
what is the formula to calculate the magnification of a cell
I (what you see the image as)/A (actual size)
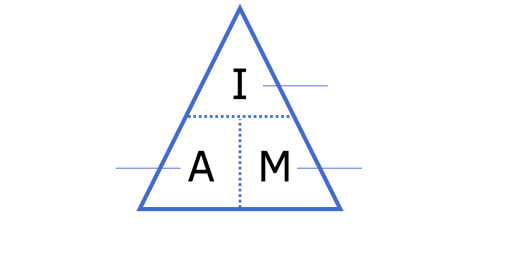
what is the formula to calculate the actual size of a cell
I (what you see)/M (magnification)
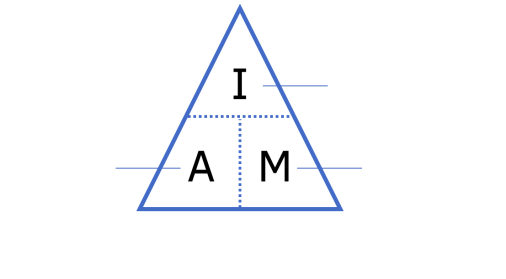
what is the formula to calculate the image of a cell
A (actual size) x M (magnification)
what is 1,000mm in µm
1,000,000µm
(add 3 0s)
what is the order starting from 1 centimeter
1cm, 10mm, 10,000µm, 10,000,000nm
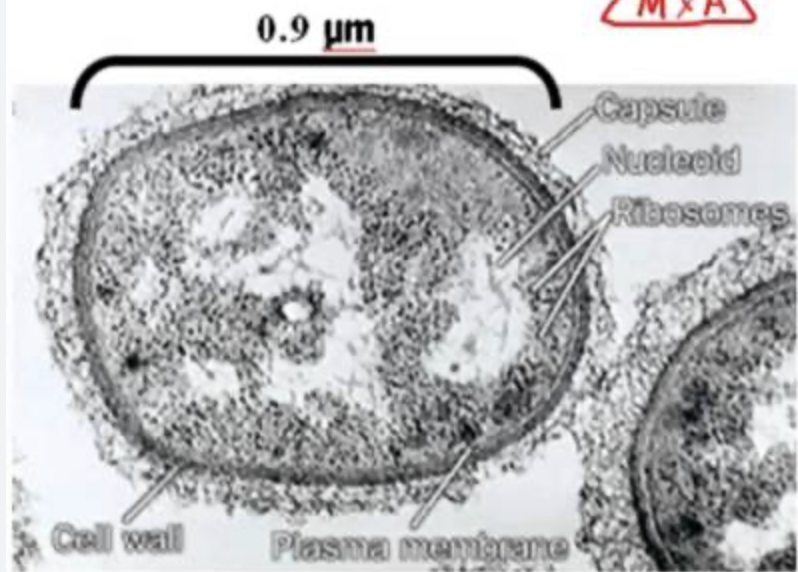
what number is the actual size
0.9μm
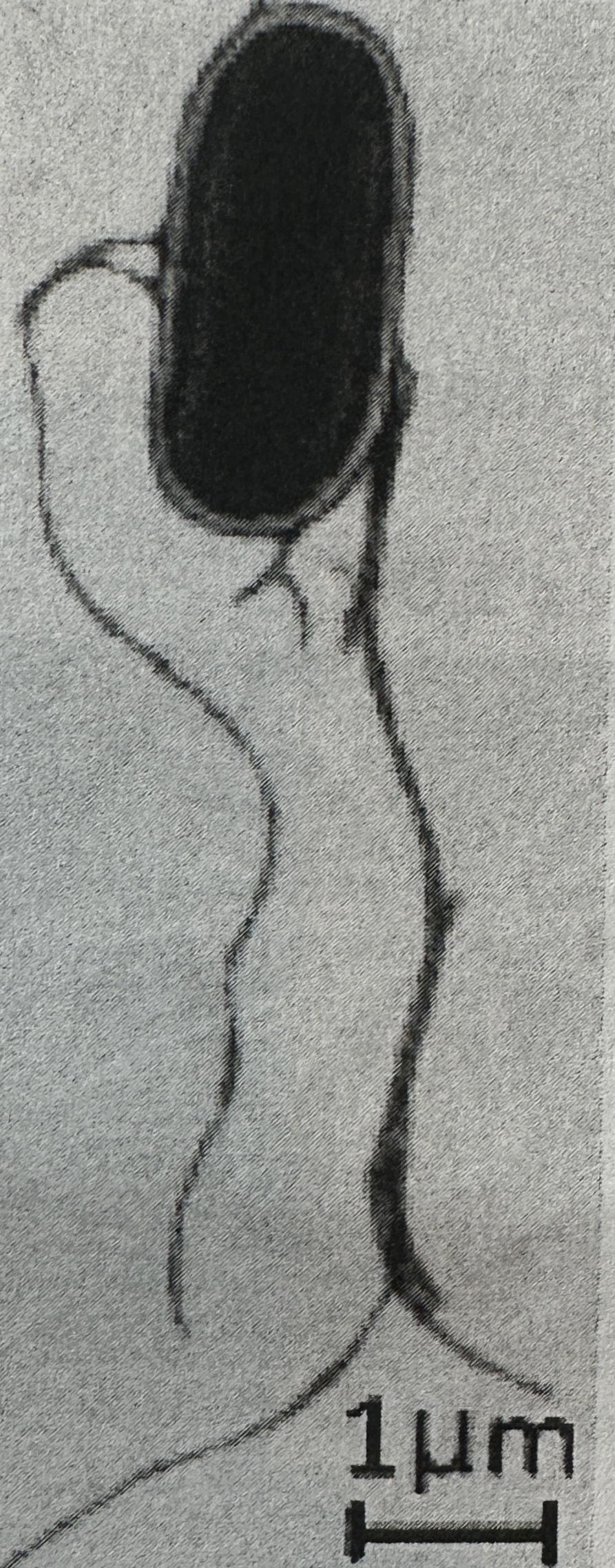
Calculate the magnification of the image
M = I/A
I = 1cm; A = 1µm
cm —> µm is 10,000µm
10,000µm/1 = 10,000X
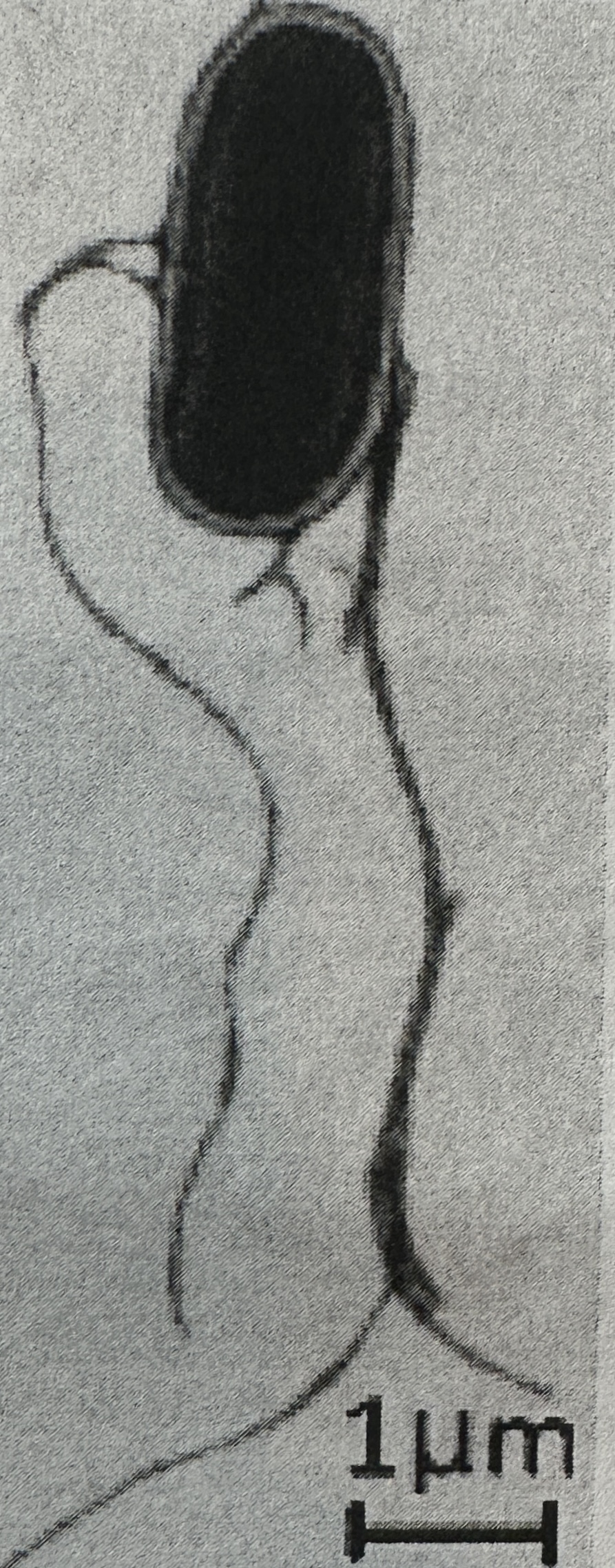
calculate the length of the cell body
A = I/M
I = 2.5cm; M = 10,000X (from prev. q)
2.5cm/10,000X = 25,
0000µm/10,000µm= 25µm
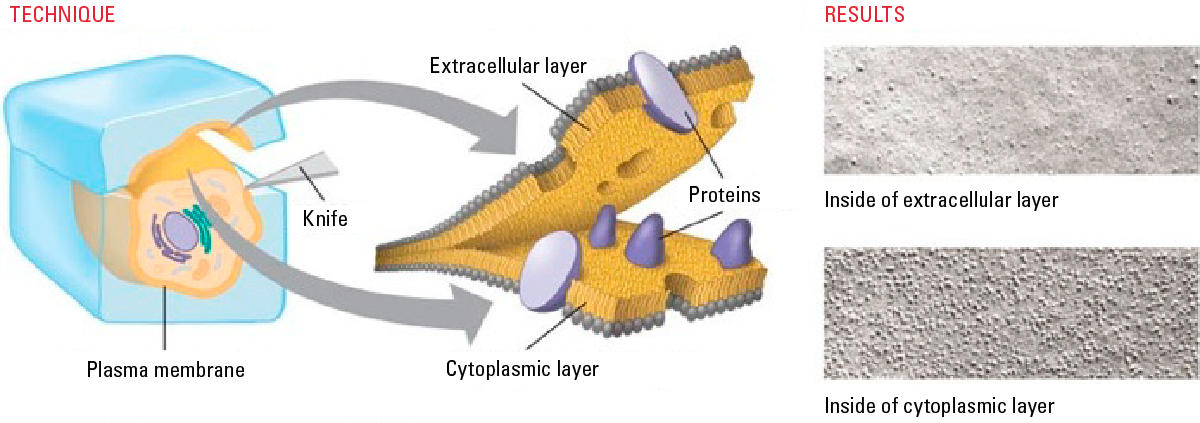
what is freeze fracture electron microscopy
membranes are rapidly frozen then fractured in area of weakness to allow scientists to analyze the structure of plasma membranes and to identify the integral proteins
what is the cryogenic electron microscope
photographs what happens to proteins in real life apart from just their crystalized structure
light vs. electron microscopes (5)
Advantages of a light microscope | Advantages of an electron microscope |
|
|