Health Systems Final
1/203
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
204 Terms
Electronic Medical Record (EMR)
Computerized documentation of a patient's healthcare at a single institution
Electronic Health Record (EHR)
Computerized documentation of a patient's healthcare over a period of time
Can include multiple institutions
Personal Health Record (PHR)
Computerized application for patient use
Contains information about patient visits and insurance coverage
What is in an Electronic Health Record (EHR)?
A comprehensive computer-based application
Helps store and manage healthcare records
Contains both clinical and administrative information
EHR Components
Clinical data repository
-- Database containing clinical information (allergies, medications, demographics, etc).
Interface
-- Digital device the provider uses to access patient centered information
EHR Capabilities
-- Enter orders, write notes, schedule appointments, etc. with support from CDS and CPOE.
Benefits of EHRs
Increased functionality as compared to paper-based medical records
24-hour accessibility for providers
Comprehensive format allows for multi-disciplinary approach.
Integrated applications (CDS, CPOE, etc.) help guide users
Contains computer based documentation systems to document clinical decisions in real time.
Limitations of EHR
Difficulties in data input
-- Most EHR systems have multiple ways of entering the same data
Lack of interoperability/sharing
-- Different systems (or even components of a single system) often encode similar information using different words, codes, etc.
-- EHR products from different vendors lack the ability to information share
The consequences of the limitations of EHR
Certain data not populating every relevant component of the patient chart
Can result in conflicting information within a single chart
Increases in difficulty in timely information sharing for a single patient seen by multiple health systems
Increases difficulty in collecting accurate data for research
Common US EHR vendors
EPIC
Oracle Cerner
MEDITECH
(Big three)
Others:
-- Nextgen
-- Valant
-- Praxis EMR
EHR systems are not
Interoperable across venders
Lacks the ability to exchange patient information and other data across different systems
When locating a patient in EHR
Find a patient by looking at an institution's patient list
Locate a patient by searching by Medical Record Number (MRN)
EHR Background patient information
The sidebar will contain information such as:
-- Patient name
-- Age
-- MRN
-- Allergies
-- Renal funciton
-- Height
-- Weight
Clinical documentation in EHR
There is a physician and pharmacist tab
Medications tab
Medication administration record Tab
Notes in EHR
Progress notes contain:
-- History of present illness
-- Past medical history
-- Medications prior to admission
-- Summary and plan for patient case
This tab also contains notes from other providers (nursing, care management, physical and occupational therapy, etc.)
Pharmacist notes in EHR
Example of pharmacist notes in an EHR:
-- Vancomycin dosing
-- Warfarin dosing
-- Bivalirudin infusion rate adjustments
-- Medication reconciliation notes
-- Anticoagulation and methotrexate counseling
Please note: dosage adjustments and pharmacist to dose medication initiatives are institution specific and require a set protocol to be in place.
EHR medication tab
Active medication list with drug, dose, route, and frequency, and start times
Medication Administration Records (MAR) in EHR
Displays all currently ordered or administered medications
Imaging in EHR
Allows easy access to results of computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), chest X-rays, and more.
Click on circle in charts for full results of the test
Laboratory results in EHR
Contains results from several encounters
Value in red if outside of normal limits
Trend labs over time
Trending labs over a period of time may alert the pharmacist of acute changes while admitted.
Labs can be trended over days, months, or even years.
What is Computerized Provider Order Entry (CPOE)?
The way in which providers electronically enter orders into an EHR
This includes any order (medications, labs, imaging, etc.)
May order one medication or multiple linked orders in the form of an order set.
CPOE and Error Reduction
Medication related errors most prevalent cause of medical errors
-- About 90% of medication errors occur at the ordering and transcribing stage
CPOE allows for:
-- Legible orders
-- Standard dosing regimens
-- Standardized administration instructions
-- Order sets for ease and efficiency of order entry
Benefits of CPOE
Medication error reduction
Timely
Care coordination
Research capabilities
CDS integration
Cost reduction
The CPOE Process
Provider sign in
-- Identity verification
-- Specific prescription authority and ordering privileges reviewed
Drug choice
-- Patient chart review
-- Choices of dose, route, and frequency are offered to provider
Dispense drug
-- Order transmitted to pharmacy for verification
-- Pharmacist reviews and verifies or rejects the order
Utilizing CPOE in Practice
Allows for selection of a single medication or multiple in the form of an order set
Provides suggestions for drug, dose, administration directions, duration, and frequency
Pharmacist use of CPOE
Pharmacist may order medication if:
1. There is a set protocol in place
2. A provider with prescription authority directly communicates the order to pharmacy
Clinical Decision Support (CDS)
Integrated within CPOE to alert providers of guideline or knowledge based information
Example of CDS alerts include:
-- Allergies
-- Duplicate therapies
-- Drug interactions
-- Dose too high/too low
-- Exceeding total daily dose
Benefits of CDS
Notifies provider of potentially serious adverse events
Requires documentation to bypass, requiring providers to slow down and think through alerts
Limitations of CDS
Potentially alerting providers of clinically insignificant problems
Alert fatigue
Disruption to workflow
Types of CDS alerts
Passive decision support
Active alerts
Passive decision support
Directs users to appropriate practices without workflow interruption
Examples: order sets, drop-down lists
Active alerts
Passive patient specific information and may be interruptive or non-interruptive
Examples: formulary substitutions, allergy warnings
Examples of CDS alerts
Duplicate therapy
-- Provides reasons to bypass alerts
Dose too high
-- Weight suggestions
What to consider when verifying
Is the medication indicated?
Correct dose?
Correct route?
Correct frequency?
Is the duration of the order appropriate?
What is the appropriate timing of this medication?
Are there any drug interactions?
Are there other possible or definite contraindications?
Patient specific considerations
Drug indication
Labs
Duplicate therapies
Allergies
Timing
You are the verifying pharmacist one evening, and an order for metoprolol comes into your queue. What parts of the EHR will you utilize to ensure the order is appropriate and safe for the patient?
Patient specific considerations
-- Labs
-- Side bar: Allergies
Medications tabs:
-- Check for duplicates, interactions, etc
Verification screen
-- Dose
-- Route
-- Drug
-- Timing
-- Administration instructions
Rejecting an order CPOE
Computer based documentation systems require the user to select a reason for discontinuation/order rejection
Appropriate documentation for clinical decision making
Approving and Order COPE
Once drug is deemed appropriate, the pharmacist can select verify to being the drug distribution process
CDS
May notify providers of important safety concerns, but never replaces the need for clinical judgement
Drug formulary
A continually updated list of approved medications and related information, representing the clinical judgment of pharmacist, physicians, and other experts in the diagnosis and/or treatment of disease and promotion of health
Aims to guide safe and effective medication use
Ongoing review process to ensure best practices
Formulary system
1. A structured method to assess medications for inclusion or exclusion
2. Establishes prescribing, dispensing, and administration guidelines
3. Balances clinical efficacy, safety, and cost
Formulary system pros
Promotes evidence based care
Reduce cost
Streamlines inventory control
Formulary system cons
Limits access to medications
Requires continuous evaluation
Contributes to dissatisfaction
Pharmacy and Therapeutics (P&T) Committee
Who
-- Multi-disciplinary: Pharmacist, nurses, physicians, administrators
What
-- Establish and maintain the formulary system
When
-- Ongoing process
-- Meetings multiple times a year at a regular cadence
Why
-- Provide patients access to safe, effective, and affordable medications/healthcare
How
-- Voting -> quorum requirements
-- Representation from all stakeholders
P&T Committee Responsibilities
1. Establish and maintain the formulary system
2. Select medications for formulary inclusion
3. Evaluate medication use and outcomes
4. Prevent and monitor adverse events and medication errors
5. Evaluate and develop drug therapy guidelines
6. Develop policies and procedures for handling medications
7. Educate on the optimal use of medications
P&T Subcommittee Examples
Antimicrobial Stewardship
Critical Care
Hematology/Oncology
Medication Safety
Preioperative Care
Ambulatory
Antithrombotic Stewardship
Hopsital Medicine
Open Formulary
Minimal restrictions
Broad medication availability
Closed Formulary
Limited access, with defined prescribing criteria
-- Expertise
-- Patient care location
-- Disease state
Formulary restrictions
Limits use of specific medication based on area of expertise, disease, location.
Examples:
-- Expertise: Only Cardiology/Pulmonology can order Tadalafil (Adcirca)
-- Disease: Tenectoplase for STEMI
-- Location: Vasopressin can only be administered in critical care units
Reason:
-- Safety
-- Monitoring
-- Cost
Therapeutic equivalents
Drug products with different chemical structure but of the same pharmacologic or therapeutic class and usually have similar therapeutic and adverse profiles
Therapeutic interchange
Authorized exchange of therapeutic alternatives in accordance with previously established and approved written guidelines/protocols.
Formulary changes
Formal process should be in place to continuously update the formulary
-- Involves a submission of request from medical staff
Request should include:
-- Agent to be considered if addition or deletion
-- Rationale for request
-- Expected annual use (number of patients)
-- Alternative agents currently on formulary
Drug Monograph
A written, unbiased evaluation of specific medications.
Includes:
-- Generic/Trade Name
-- Therapeutic/Pharmacologic Class
-- Pharmacology
-- Pharmacokinetics
-- Indications
-- Clinical studies
-- Adverse Effects/Interactions
-- Dosing Ranges
-- Dosage Form and Cost
-- Recommendation
Therapeutic Class Review
An evaluation of a group of medications with an established therapeutic class
Evaluates:
-- Indications
-- Pharmacokinetics/dynamics
-- Adverse effects
-- Drug interactions
-- Dosage regimens
-- Cost
Example: Evaluating the class of tetracyclines to determine which specific agents maintain, add, or remove from formulary
Drug-Use Evaluation (DUE)
Also known as: Medication Use Evaluation (MUE)
Systemic process used to assess the appropriateness of drug therapy by evaluating data on drug use in each healthcare environment against predetermined criteria and standards
Results and action plan can be presented to P&T committee to improve/implement systems.
Types of DUE's
Diagnosis related DUE
-- Patients with a specific disease or diagnosis
-- Example: Selected antibiotics fro community acquired pneumonia (CAP)
Prescriber related DUE
-- Patients managed by a service or provider
-- Example: Selected cardiovascular drugs may be limited to cardiology specialist
Drug specific DUE
-- Specific drug dose/frequency
-- Example: Dosage regimen of low molecular weight heparin
FOCUS-PDCA
Find a process to improve
Organize a team that knows the process
Clarify current knowledge of the process
Understand causes of process variation
Select process improvement
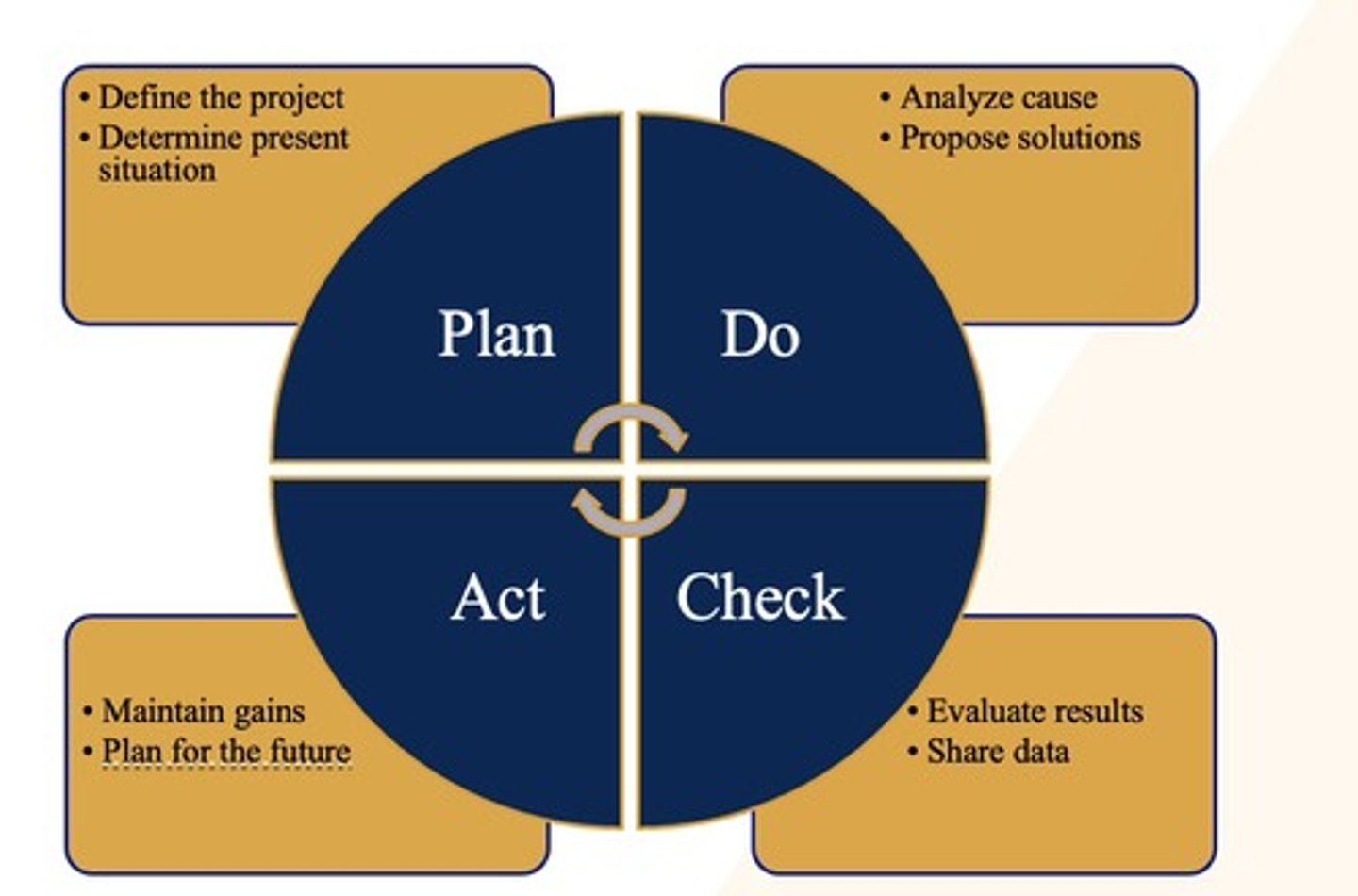
Medication Use Policies
Ensure safe and standardized medication use
Standardize medication prescribing, dispensing, and administrating process
DOES NOT REPLACE CLINICAL JUDGEMENT
Examples:
-- Verbal order acceptance polices
-- Controlled substance handling procedures
-- Adverse drug reaction reporting
-- Medication error documentation
Policies
Rules and guidelines to help direct the action of healthcare workers
Examples;
-- Verbal orders can only be accepted from a prescribing provider
-- If a patient experiences an ADR, then the supervising healthcare worker should fill out a safety report
Protocols
Written document that explicitly defines how to act based on specific inclusion and exclusion criteria
Examples:
-- Vancomycin pharmacist to dose
-- Warfarin pharmacist to dose
-- Renally dose-adjusted antibiotics
Purpose of Competencies
Ensure pharmacist maintain up to date clinical knowledge
-- Must be dedicated to life-long learning
Support standardization and quality of practice
-- Demonstrate proficiency in evolving therapeutic areas
Examples:
-- Licensure exams (NAPLEX, MPJE)
-- Specialty certifications (BCPS, BCCP)
-- Continuing eduction requirements
Pharmacist Competencies Once
Pharmacokinetics
Direct thrombin inhibitor therapy
REMS Drugs
CAR-T cell therapy
Pharmacist Competencies recurring
Media fill and gloved fingertip testing
Antimicrobial stewardship
CE credits for license renewal
Transition of Care simplified
Home --> Hospital --> Home
Defining transitions of care (TOC)
The coordination and continuity of care with the patient moves within or among healthcare settings, providers, or health states
Phases of care for TOC
Home --> ED --> ICU --> Floor --> Inpatient Rehab --> Home
NTOCC Seven Essential Interventions
Medication Management
Transition Planning
Patient and Caregiver Education
Information transfer
Follow up care
Healthcare provider engagement
Social Determinants of Health
Why does TOC matter?
20% of patients had adverse event within 3 weeks of discharge
30% patients had at least one medication discrepancy
20% medicare beneficiaries readmitted within 30 days
Consequences of Fragmented care
Medication error
Readmissions
Complications
Decreased functional status
Increased dependency
Activities during TOC
Comprehensive medication management (CMM)
Medication reconciliation
Medication and self-management education
Medication acquisition assistance
Follow up call or visit
Comprehensive medication management
1. Assessing the patient
2. Evaluating medication therapy
3. Developing and initiating plan of care
4. Provide ongoing follow up
Medication Reconciliation
Process of creating the best list possible of all prescription and non prescription medication, herbal, and vitamins the patient is taking
1. Medication history
2. Compare inpatients and outpatients medication lists
3. Address any discrepancies
Medication History
Pharmacy led
List should include:
-- Drug name
-- Dose
-- Frequency
-- Special instructions
-- Last refill
Allergy review
Discharge medication reconciliation
Medications started in the hospital
Medications ordered at discharge
Medication education
Ensure the patient understand
-- Indication of medication
-- Administration instructions
-- Changes to medication regimen
Develop self-care skills
-- Teach back process to optimize patient education
-- Assess health literacy
Medication Acquisition
Formulary and cost review
Co-pay cards
Prior Authorization
Meds to beds
Follow up
Provide a bridge from one care setting to the next
Assess adherence to care plan
Triage difficulties during transition
Clearly communicate with patient
Risk Stratification
LACE INDEX
8Ps Screening Tool
LACE INDEX
Length of stay
Acuity of admission
Comorbidities
ED Visits
8Ps Screening Tool
Polypharmacy
Psychological
Principle diagnosis
Physical Limitations
Poor health literacy
Patient support
Prior hospitalization
Palliative care
Barriers to effective transitions
Inadequate communication
-- Between providers
-- Between care settings
-- With the patient
Poor care coordination
-- Follow up
-- Labs and monitoring
Lack of role clarity
-- Who is responsible for care plans, medications or lab orders, follow up
What is clinical pharmacy? (Overarching definition of clinical pharmacy per ACCP)
Area of pharmacy concerned with the science and practice of rational medication use
What is clinical pharmacy? (Big picture)
Discipline of Clinical Pharmacy
-- Emphasis on caring values, specialized knowledge, experience, and judgement
Clinical Pharmacist
-- Manage therapy in direct patient care settings both independently and in collaboration with other health care professionals
Role of the clinical Pharmacist in Health Care
-- Medication resource for both traditional and non-traditional therapies
Attributes of clinical pharmacists
Desire to stay up to date with literature
Ability to critically evaluate literature
Maintain strong communication skills
Willingness to collaborate with other healthcare professionals
Desire to advocate for patients and for the profession
Development of strong leadership skills
History of Clinical Pharmacy
1960s = Initial pharmacist involvement in decision making and development of drug information centers occurred at University of Kentucky
1975 = John Mills and the Mills Commission release Pharmacist of the future, recommending pharmacy be considered a clinic profession
1979 = ACCP and the European Society of Clinical Pharmacy (ESCP) were formed to promote clinical pharmacy
1980 = New residency accreditation standards were released by the American Society of Health System Pharmacists (ASHP)
1980s = Hundreds of studies were published describing the value of clinical pharmacy services
1988 = Establishment of the first board certified pharmacy specialty: BPSC
1992 = The American Associations of Colleges of Pharmacy (AACP) House of Delegates Voted the PharmD as the only recognized professional degree in pharmacy
Advancements in clinical pharmacy led to acceptance of the following concept
A clinical pharmacist's primary responsibility is to identify, prevent, and resolve drug related problems in order to optimize drug therapy for each patient
Education of training of a clinical pharmacist
Tradition:
Pre-pharmacy --> pharmacy school --> PGY1--> PGY2 --> BCPE
Non Tradition:
Pre-pharmacy --> Pharmacy school --> Community, etc.
Board certification
Board of Pharmacy Specialities (BPS) is the post licensure certification agency that promotes recognition of Board Certified Pharmacists within the health care system
BPS certification = Voluntary process by which a pharmacist's education, experience, knowledge, and skills in a particular practice area are confirmed well beyond what is required for licensure.
Who is on the team in a clinical setting?
Attending physician
Nurse
Occupational Therapist
Dietician
Advanced Practice Provider
Clinical pharmacist
Speech-language pathologist
Social worker
Learners
Physical Therapist
Behavioral Therapist
Respiratory therapist
etc
A day in the life of an Ambulatory Clinical Pharmacist
Work up patients
Conduct Clinic + telemedicine visits
Discuss interventions with provider
Education and complete administrative task
A day in the life of an Inpatient Clinical Pharmacist
Work up patients (pre-round)
Care team rounds
Order verification, plan follow up (post round)
Education and complete administrative task
Pharmacist 's patient care process (PPCP)
Collect
Assess
Plan
Implement
Follow up: Monitor and Evaluate
Medication Reconciliation (PPCP)
Where does it land on the PPCP: Collect
Process of comparing the medications a patient is taking (and should be taking) with newly ordered medications
Obtain an accurate list of each patient's medications
-- Inpatient: Use to identify medications taken at home prior to hospitalization
-- Outpatient: Used to verify current medications at home and learn about any changes
Pre-rounds or Clinic Visit (PPCP)
Where does it land on the PPCP: Collect and Assess
Collect information from the patient and electronic health record (EHR)
-- Notes (past medical history, details from patient interview)
-- Results (labs, imaging, pathology, etc)
-- Medication dispense history
Use a problem oriented framework to determine treatment approach
Prioritize the patient's specific medication needs
Care team collaboration (PPCP)
Where does it land on the PPCP: Assess
Discuss overnight events or new information from last visit to determine clinical utility of each medication
Evaluate effectiveness, safety, accessibility, and affordability of each medication
Assess adherence and the patient's medication routine
Identify specific medication-related concerns requiring intervention
Where does it land on the PPCP: Plan and Implement
Collaborate with other care team members to optimize the medications necessary for the patient's active medical concerns
Review the care plan with the team toward the end of the visit or following rounds to ensure it is appropriately implemented
Inform the patient and/or caregivers about the plan
Implement Interventions (PPCP)
Where does it land on the PPCP: Implement
Review patient's chart to ensure labs and medication orders are placed correctly
Verify orders (inpatient only)
Document the care plan as indicated (i.e., note, acuity, etc.)
Drug Utilization Review (DUR)
Therapeutic duplication
Drug-disease contraindications
Drug-drug interaction
Drug-allergy interaction
Medication, dose, frequency, duration
Clinical misuse
After Visit or Post Rounds (PPCP)
Where does it land on the PPCP: Follow up: Monitor and Evaluate
Monitor necessary blood cultures, lab values, or imaging that may affect the medication plan
Collaborate and make changes to the plan as needed
Give appropriate hand off for any outstanding medication-specific concerns to covering pharmacist and other team members
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
Renal dose adjustment
Vancomycin + aminoglycosides
Warfarin dosing + continuous anticoagulation
Therapeutic interchange (non-formulary items)
Code Blue response
Pharmacist role in a medical emergency
-- Drug manipulation, dosing, and timing
Advanced Cardiovascular life support (ACLS)
Rapid Sequence Intubation (RSI)
Intensive care unit (ICU) and Floor codes