PT7651- Modalities & Physical Agents Midterm Exam
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Inflammation
Light green in image.
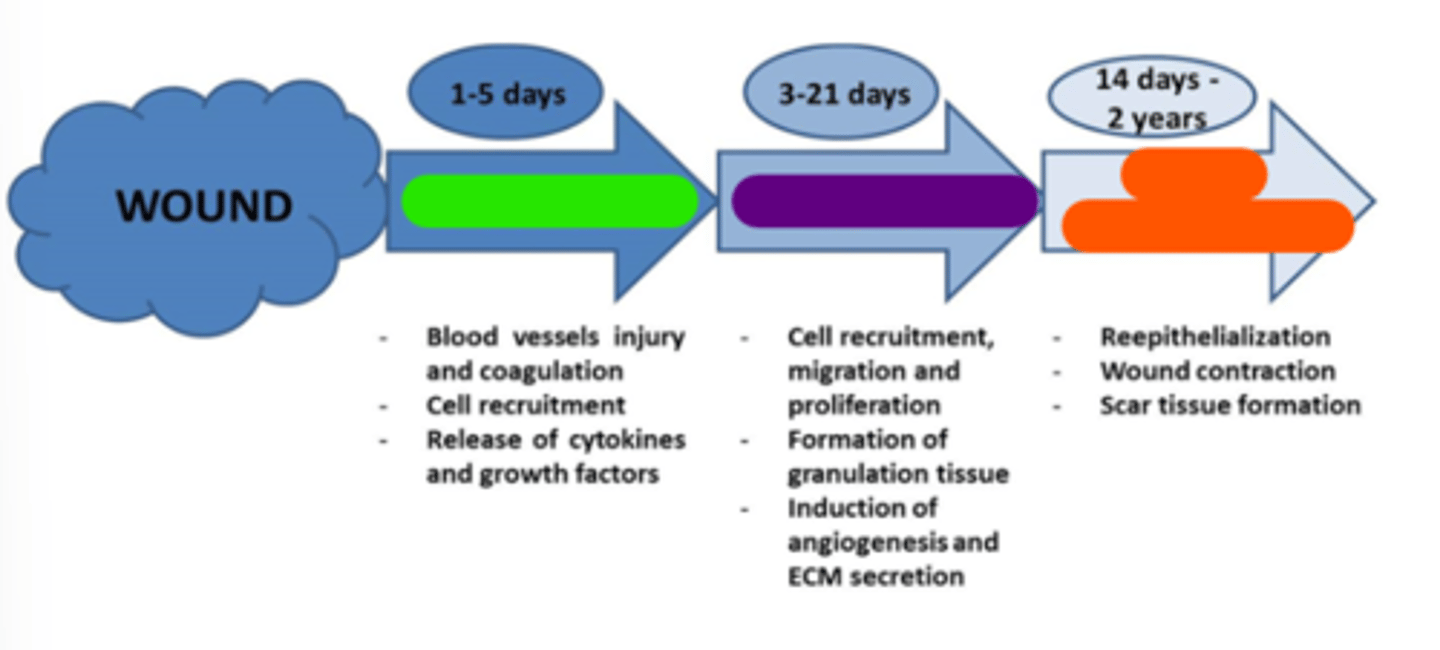
Proliferation
Purple in image.
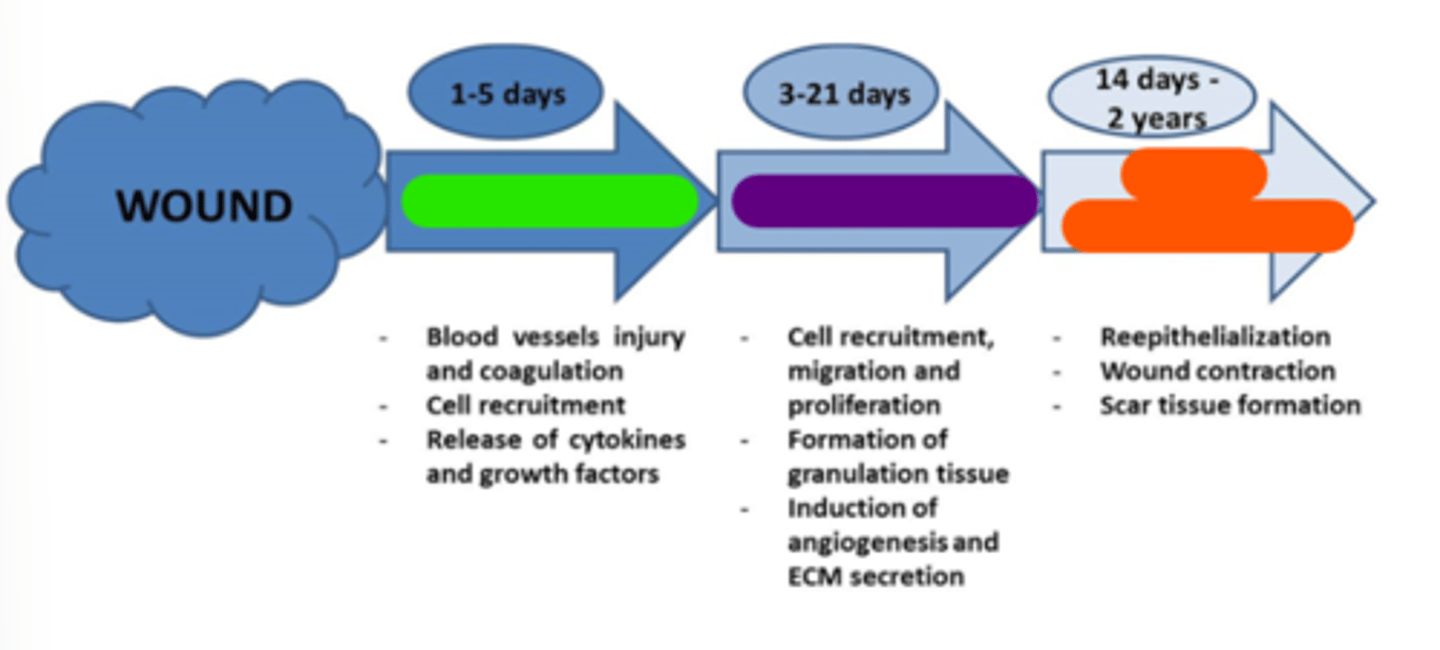
Tissue remodeling
Orange in image.
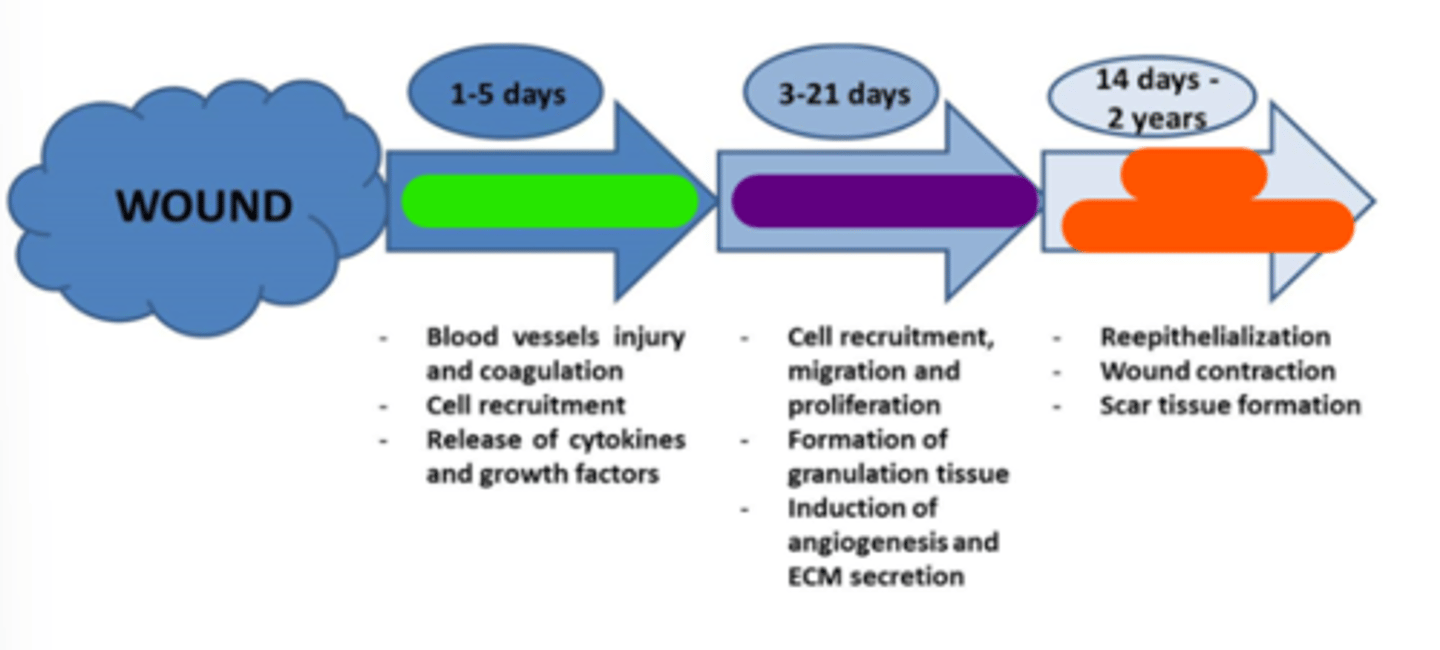
Early
Physical agents may be appropriate in all 3 phases of tissue healing; however, they are typically used ______________________ in the rehabilitation process. Some physical agents may not be appropriate (contraindicated) during certain phases of tissue healing (e.g. hot pack in the acute phase of an ankle sprain).
Inflammatory phase
Control inflammation, swelling (effusion), pain.
1-5
Inflammatory phase occurs at days ______________________ post-injury.
- Cryotherapy (cryokinetics)
- Iontophoresis
- Phonophoresis
- Sensory-level e-stim (high-rate TENS, interferential, premod)
- Light compression wrap or cryo cuff
- Galvanotaxis (HVPC) e-stim to drive out inflammation
What kind of modalities would be appropriate in inflammatory phase?
Heat/thermotherapy; muscle contraction
________________________ and _________________________ are contraindicated during inflammatory phase.
Proliferation (transitional) phase
Prevention of scar tissue, promote tissue healing.
3-21
Proliferation (transitional) phase occurs at days _______________________ post-injury.
- Pulsed ultrasound
- Pulsed diathermy
- Laser/light
- Low level motor e-stim
- Moderate compression
What kind of modalities would be appropriate in proliferation phase?
Tissue temperature rise (TTR)
_________________________ may or may not be appropriate during proliferation (transitional) phase depending on the presence of cardinal signs of inflammation.
Cryotherapy
During proliferation (transitional) phase, you may start treatment session with thermotherapy, but often end with _______________________.
Maturation (tissue remodeling) phase
Restoration of function, restore ROM, flexibility, promote scar tissue remodeling.
14 days-2 years
Maturation (tissue remodeling) phase occurs at ________________________ post-injury.
- Thermotherapy
- Continuous ultrasound
- Diathermy
- Motor level e-stim
What kind of modalities would be appropriate in maturation (tissue remodeling) phase?
Mechanical pain
Compression, tension, or pressure on tissue that triggers or activates nociceptors.
Movement-based; brace/splint; hydrostatic pressure
To treat mechanical pain, utilize ________________________ intervention.
- Unload tissue via NWB, ___________________, traction, movement)
- Reduce _____________________ (swelling)
- See grade I and grade II mobilizations
Chemical pain
Histamine, prostaglandins, kinins that trigger or activate nociceptors.
Chemical-based; tissue temperature; metabolic; NSAIDs
To treat chemical pain, utilize ________________________ intervention.
- Decrease __________________________ via ice
- Decrease __________________________ activity
- Medications that interfere with inflammatory process (iontophoresis, phonophoresis, oral _______________________)
Mechanical; more
Very few passive modalities are indicated for _______________________ pain.
Chemical pain → Passive modalities are likely ______________________ useful, but should still be limited.
Pain (palor), redness (rubor), swelling (tumor), heat (calor), loss of function (functio laesa)
What are the signs of inflammatory phase of healing?
Conduction
The transfer of thermal energy from one material to another through direct contact. Moves from higher temperature to lower temperature.
→; →; ←; ←; Game Ready; ThermEx
Examples of Conduction:
- Hot pack ____________________ patient
- Paraffin ____________________ patient
- Ice pack ___________________ patient
- Ice massage ______________________ patient
- Just putting your limb in a cool bath is technically conduction
- Cryo cuffs = _______________________ and _______________________ (does both hot and cold)
Convection
The transfer of thermal energy (heat) from one material to another via circulation of the heating medium (air, water, etc.)
The thermal agent is in motion.
Whirlpool, fluidotherapy
What is/are example(s) of convection?
Conversion
Energy from a non-thermal form is transformed/converted into heat as it passes through the body.
Ultrasound, diathermy
What is/are example(s) of conversion?
Radiation
The transfer of thermal energy from one material to another material without direct contact or an intervening medium.
It is typically transferred from a source of much greater temperature than the receiving material.
Infrared lamp (NOT commonly used in today's clinical practice), UV, lasers
What is/are example(s) of radiation?
Evaporation
The change of a liquid to a gas that results in the cooling of the skin.
Superficial but can produce deeper neuromuscular effects.
Vapocoolant spray (utilize before an injection or spray and stretch)
What is/are example(s) of evaporation?
- Desire/motivation
- Personality trait/genetics
- Memory of prior experiences
- Conscious expectations
- Unconscious classical conditioning
- Reward learning
- Observational social learning
- Modulation of anxiety
What psychological determinants impact placebo beliefs?
Clear; overt; learning; patient-centered; touch
What are treatment contextual factors that help to modulate therapeutic outcomes?
- _____________________ diagnosis
- ____________________-therapy
- Observational _______________________
- _________________________ approach
- Global process care
- Therapeutic ________________________
Professional; appearance; behavior
What are Physical Therapist contextual factors that help to modulate therapeutic outcomes?
- __________________________ reputation
- ___________________________
- Beliefs
- ___________________________
Expectations; previous; age
What are patient contextual factors that help to modulate therapeutic outcomes?
- ________________________
- Preferences
- ________________________ experiences
- MSK condition
- Gender
- ________________________
Verbal; non-verbal
What are patient-PT relationship contextual factors that help to modulate therapeutic outcomes?
Both ______________________ and _____________________ communication.
Environment; interior
What are healthcare setting contextual factors that help to modulate therapeutic outcomes?
- _____________________________
- Architecture
- ____________________________ design
Lab coat; explanation; expectation; verbal expression; paraphrase; forward
Be able to cite PT qualities that would help with placebo beliefs in patients.
- Improve professionalism, reputation, training, and expertise
- Use a _______________________ or tailored clothing
- Deliver clear diagnosis, prognosis, and _________________________ of the patient's problems
- Explore the patient's disease and illness; request and trust the patient's opinion
- Encourage questions, answer patient's questions and provide positive feedback
- Investigate _______________________, preferences, and previous experiences of the patient
- Consider the phase of the MSK condition, age and gender of the patient
- Be warm, confident, friendly, relaxed, and open during the clinical encounter
- Use _______________________ of empathy, support, sympathy, and language reciprocity
- Adopt psychosocial talk, partnership statements and ________________________
- Use positive messages associated with treatment for pain relief
- Use eye contact, smile, and caring expressions
- Use affirmitive head nodding, _____________________ leaning, and open body posture
- Interpret patient's non-verbal body language and expression
7°F
What is the therapeutic range of TTR?
>113°F
Leads to tissue injury.
<104°F
Little to no therapeutic or physiologic effect.
Up to 0.5 cm (superficial)
What is depth of treatment of thermotherapy?
1-2 cm
What is depth of treatment of cryotherapy?
Farther apart the electrodes are, the deeper the signal goes
What is depth of treamtent of e-stim?
Promotes tissue healing
Metabolic Physiologic Effect of TTR:
- Requires target tissue to undergo TTR
- ↑ cellular activity, chemical reactions, oxygen uptake by tissues → ________________________
RA; inflammatory cascade; myositis ossificans
Contraindications to Thermotherapy (Heat):
- Heat can accelerate conditions such as ________________________
- Heat increases the _________________________ associated with an acute injury
- If acute bleeding, heat can lead to more bleeding → ________________________
Vasodilation; ↑
Vascular Physiologic Effects of TTR:
- _______________________
- _________________ capillary permeability
- Blood supply to muscles is determined by metabolic demand (i.e., blood flow increases /c exercise).
↑; alpha motor neurons; golgi tendon organs; pain threshold; force and endurance
Neuromuscular Physiologic Effects of TTR:
- DOES NOT require TTR of target tissue because effects are through neurologic mechanisms
- __________________ nerve conduction velocity (2 m/s per 1°C increase in temperature)
- ↓ muscle spindle firing → Inhibition of _________________________
- Stimulation of _________________________ → Inhibition of alpha motor neurons
- Increases ______________________ → via gating mechnism of pain (DO NOT say that pain decreases)
- Heat ↓ muscle _______________________ so heat before therapy is NOT good!
Relaxing hydrogen bonds; creep; 104-110°F for 10 minutes
Connective Tissue Physiologic Effects of TTR:
- Requires target tissue to undergo TTR
- Improves plastic reformation of connective tissue by ___________________________ between collagen strands → helps promote tissue __________________________ when low loads are applied (low load, long duration is best /c heat).
- _________________________ is needed for optimal change.
Elevation
_______________________ of the tissue temperature prior to or during low-load stretch has been shown to create less tissue damage compared to a similar stretch at lower temperatures.
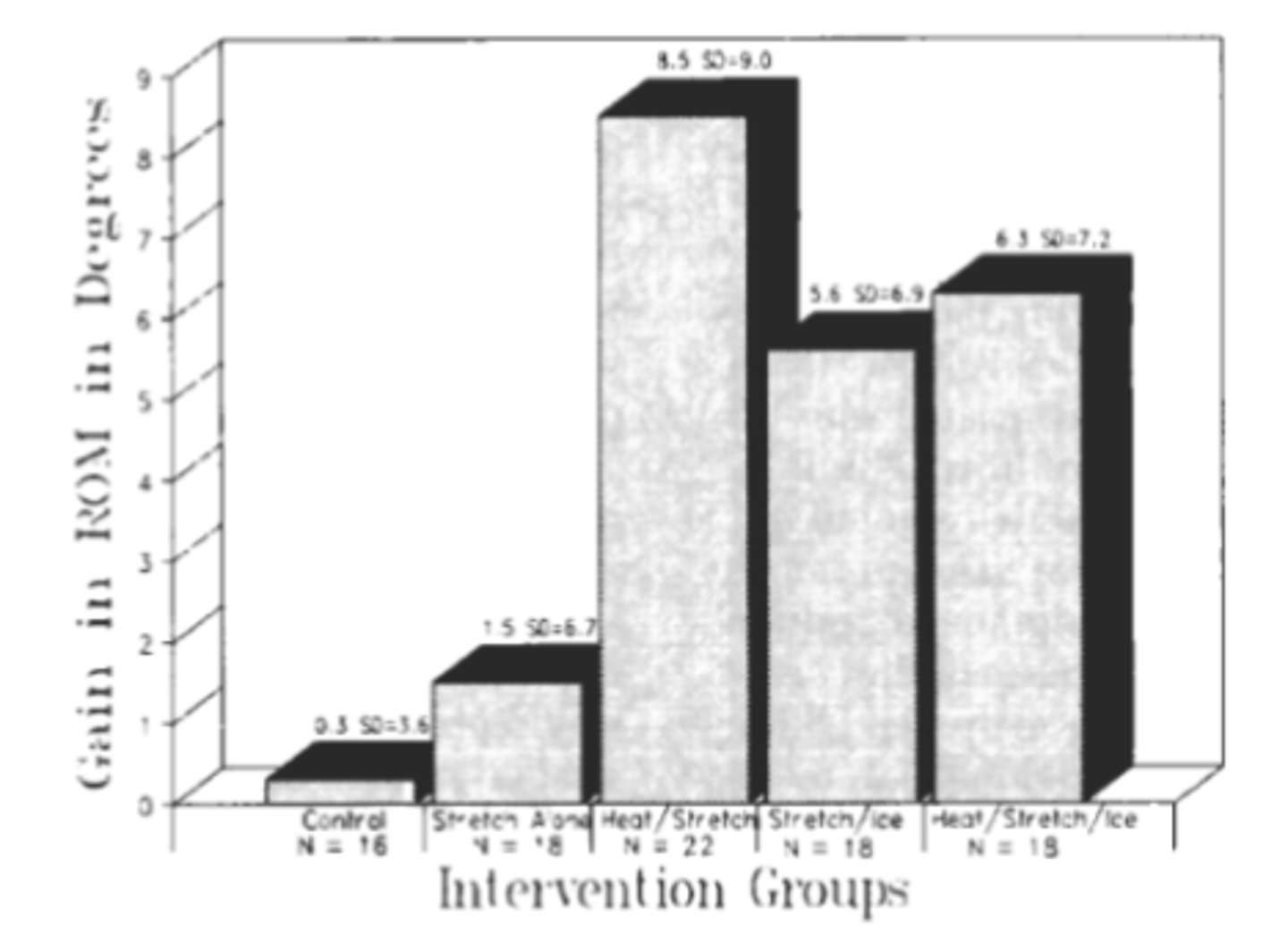
Blood flow; relax; extensibility; threshold
Indications for Thermotherapy:
- Increase _________________________
- ___________________________ muscles
- Increase tissue __________________________
- Reduce __________________________
- Increase pain _____________________________
Circulatory; bleeding; steroid; open wounds; pregnant; 4; radiation; anticoagulants
Contraindications to Thermotherapy:
- _________________________ impairments (DM, PVD, heart conditions)
- Hemophilia
- Acute trauma /c active _________________________
- Long-term _________________________ use (brittle capillary system)
- Malignancy
- __________________________ d/t lack of skin protection
- Over the abdomen if _______________________
- Presence of fever
- Very old and young (<______________ y.o.) d/t cognition and thickness of skin
- Tissues following _________________________
- Take caution if patient is on ___________________________
Inflammation; perception; effusion or swelling; spasticity; Uhthoff's sign
Indications for Cryotherapy:
- Control __________________________
- Reduce pain ___________________________
- Control ___________________________
- Decrease ____________________________
- Reduce ____________________________
Increases; force; decreases
Quick ice _________________________ muscle tone and _________________________ production, while long duration (prolonged) ice __________________________ muscle tone.
Raynaud's; over-regenerating; PVD; sensation
Contraindications to Cryotherapy:
- Any sensitivity or reaction to cold → Urticaria, _____________________, cryoglobulinemia
- __________________________ nerves
- Severe ___________________________
- Altered ___________________________
Denervation; edema; pain; strain
Indications for E-Stim:
- Weakness
- Muscle ___________________________
- ____________________________ not of organ origin
- Infections
- Inflammation
- Chronic or acute ___________________________
- Repeated joint ____________________________
Demand cardiac pacemaker; implanted defibrillator; unstable arrhythmia; carotid sinus; venous/arterio-thrombosis
Contraindications to E-Stim:
- ___________________________
- ___________________________
- ___________________________
- Over ___________________________
- Over ____________________________
- Pregnancy (over trunk)
Cardiac; sensation; open wound
Precautions for E-Stim:
- _________________________ disease
- Impaired ___________________________ or mentation
- Malignancy
- Skin irritation/______________________
Transdermal
Indications for Iontophoresis:
When patient needs help diffusing ___________________________ medicine through body
E-stim; organ
Contraindications to Iontophoresis:
- Same as ________________________
- Do not use for edema from ________________________ origin (CHF, CKD, etc.)
Layers; time; where; before and after; denied
Documentation for Thermotherapy:
- Document the number of _________________________
- _____________________ applied
- _____________________ modality was applied
- Skin was inspected _________________________
- That all contraindications were ________________________ by patient before treatment
Location; time; position; purpose; before and after; denied
Documentation for Cryotherapy:
- _____________________ where modality was applied
- ______________________ applied
- Patient __________________________
- ___________________________ of modality
- Skin was inspected _________________________
- That all contraindications were ________________________ by patient before treatment
Area; positioning; parameters; placement; duration; response
Documentation for E-Stim/Iontophoresis:
- ______________________ treated
- Patient ___________________________
- Stimulation ___________________________ (waveform, frequency, intensity, etc.)
- Electrode ___________________________
- Treatment _________________________
- _________________________ to intervention
20 minutes; mottling
Application TIme of Thermotherapy:
- ______________________ is max time
- More than this is at risk of ______________________ d/t body not being able to disperse heat from area
Mottling
Excessive or prolonged TTR will result in a rebound vasoconstriction (vasospasms) that is visually manifested by mottling → Pt can't disperse heat.
The release of massive amounts of chemical mediators such as histamine, prostaglandin, and bradykinin (potent vasodilator) will cause the transient paralysis of arteriole-sized vessels resulting in spasms and vasoconstriction.
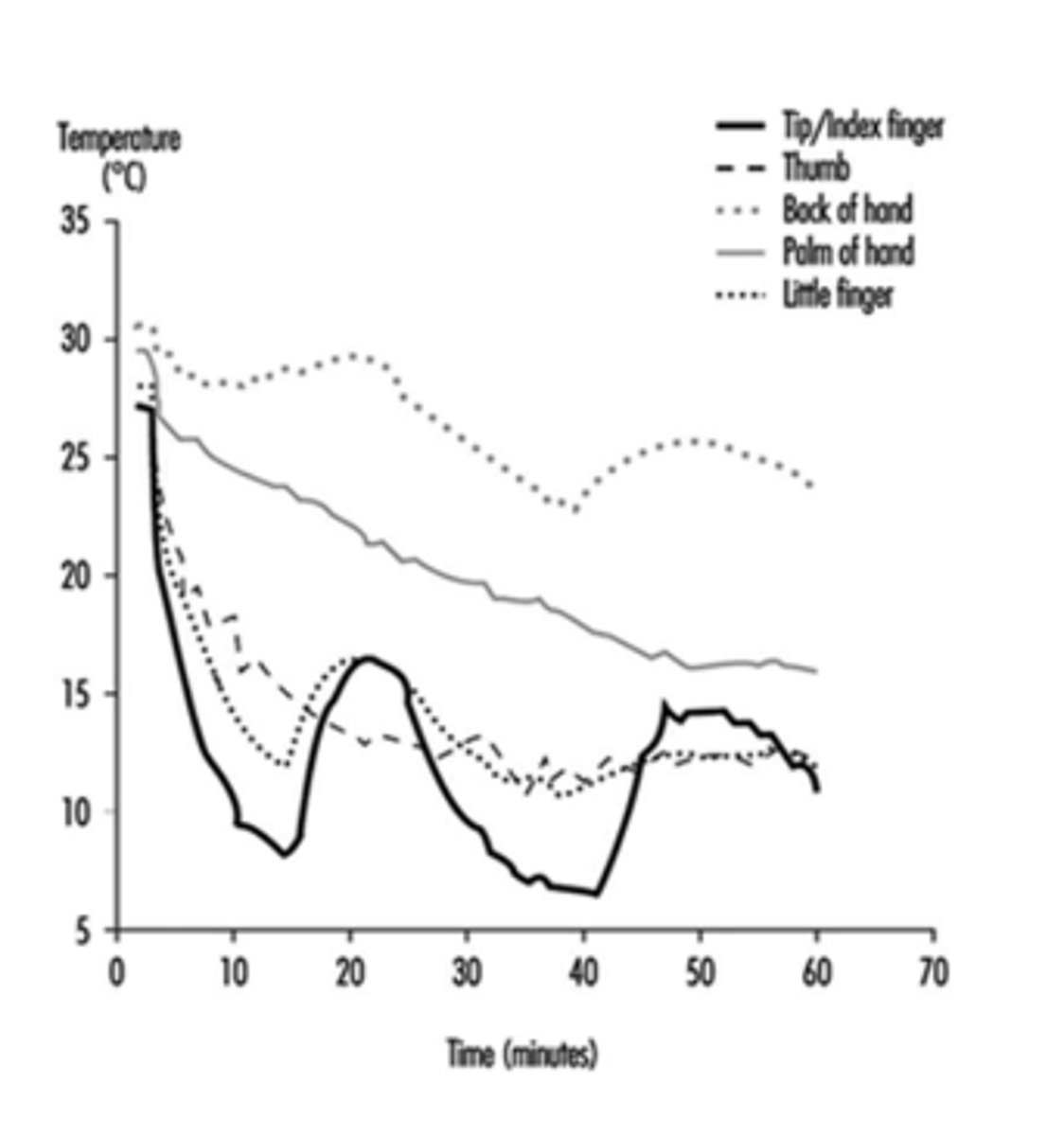
15 minutes; hunting response
Application Time of Cryotherapy:
- ________________________ is max time
- >20+ minutes, you get the __________________________
Hunting response
Alternating vasoconstriction followed by vasodilation.
As long as needed; 20-30 minutes
Application Time of E-Stim:
- High-rate TENS: Can be _________________________
- Low-rate TENS: __________________________ max
40 mA-mins
Application Time of Iontophoresis: ______________________
- 40 mA for 1 min
- 20 mA for 2 mins
- 10 mA for 4 mins
What are some examples of dose times for iontophoresis?
104-113°F
What temperature must you reach with thermotherapy to reach therapeutic effects?
No specific temperature, rule is to go to analgesia which is reported by patient.
What temperature must you reach with cryotherapy to reach therapeutic effects?
Intense cold → Burning → Aching → Analgesia (perception of numb) → Anasthesia
What are stages of cold?
mA-min
What are units of iontophoresis?
µs/µm
What are units for pulse duration?
Hz or pulses per second (pps)
What are units for frequency?
milliamps (mA)
What are units of current?
Transmission in spinal cord; endogenous opioid system; altered processing
What are the 3 mechanisms of pain centralization?
1. Facilitation of ________________________
2. Inhibition of ________________________
3. __________________________ of nociception in brain
Pain-gating
Pre-synaptic inhibition of the spinal cord via the A-beta fibers being stimulated. → Sensation of pain never reaches the brain for interpretation.
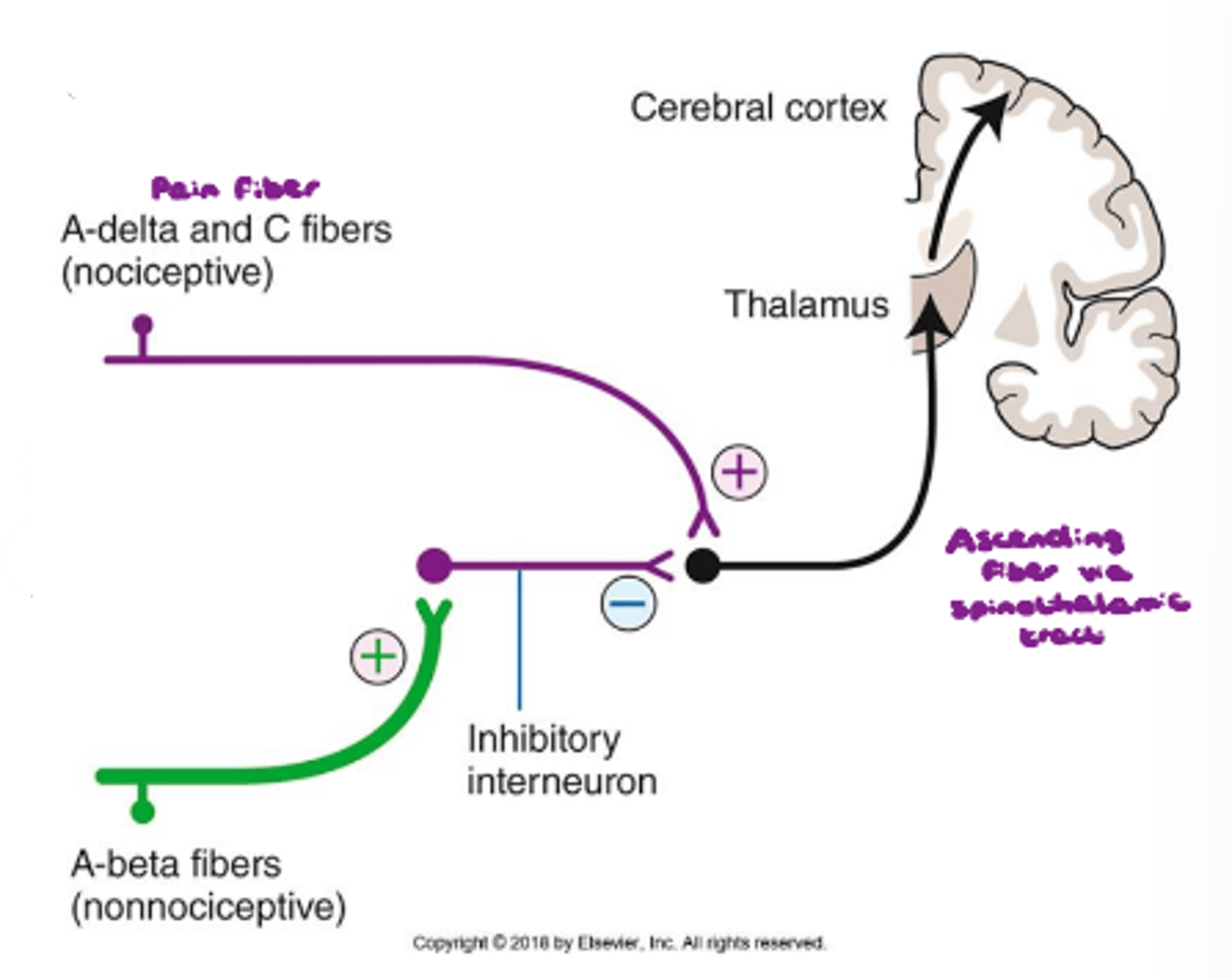
Inhibitory; spinothalamic tract; lowers; spinal cord; acute pain
Pain-Gating Mechanism:
- Interneuron has to have an _________________________ effect on ascending fiber
- Signal is transmitted via ________________________
- Never allows an action potential to occur → ________________________ resting membrane potential
- Interneuron blocks synapse at level of ___________________________
- More related to ____________________________
Endogenous opioid system
Our body naturally has opiopeptins (endorphins) that have analgesic effects. Mildly painful stimuli experienced for a long duration of time (like low-rate TENS) causes inhibition of GABA. → GABA normally inhibits release of endogenous opioids, but now they can be released and have an analgesic effect.
Inhibition of Ca²⁺ and promotion of outlfux of K⁺
Blue in image.

Inhibition of GABA release in PAGM and raphe nucleus
Teal in image.

Opioid release for several hours
Light green in image.

Pain gating mechanism; endogenous opioid system
High-rate TENS takes advantage of _________________________, while low-rate TENS utilizes _________________________.
Pulsed biphasic or Russian for 20-30 minutes
What kind of e-stim would be appropriate to utilize for edema d/t to lack of muscle contaction?
HVPC for 20-30 minutes
What kind of e-stim would be appropriate to utilize for edema d/t inflammation?
Chronic; 2-10; 100-300; small muscle contraction; 20-30 min; 4-5 hrs
Low-Rate TENS:
- For _______________________ pain
- Use low frequency: _______________________ Hz
- Use high pulse duration: ______________________ µs
- Want ___________________________ at level of stimulation
- Treatment is ____________________________ max (longer will cause DOMS)
- Effect lasts for _____________________________ after stimulation
Acute; 50-80; 100-150; sensory; no limit; disconnected
High-Rate TENS:
- For _________________________ pain or repetitive strain injuries
- Use high frequency: ___________________________ Hz
- Use low pulse duration: ___________________________ µs
- Want ________________________ level stimulation
- Treatment occurs only when the acute pain is felt
- _________________________ for how long it can be applied
- Effect wears off once e-stim is __________________________
80-100 Hz
What e-stim frequency is comfortable?
35-50 Hz
What e-stim frequency is needed to elicit tetanic contraction?
Russian, biphasic
What e-stim waveforms would be most appropriate for strengthening?
Interferential, biphasic, high-rate TENS
What e-stim waveforms would be most appropriate for acute pain?
Interferential, biphasic, low-rate TENS
What e-stim waveforms would be most approrpiate for subacute pain?
- Pulse duration: 125-350 µs
- Frequency 35-80 pps
- Can turn up pulse duration if patient is not able to tolerate increased intensity
- Can place moist hot pack over skin prior to e-stim or utilize dry needling to decrease resistance
If your goal is a muscle contraction, what parameters and changes to your set up would help with ensuring a muscle contraction?
- Pulse duration: 40-100 µs (below 200 µs)
- Frequency: 100 pps
- May need to just ask patient when they stop feeling muscles contract when you're turning down current/frequency/pulse duration
Similarly, if your goal is to stimulate at the sensory level, what can be adjusted to prevent a muscle contraction?
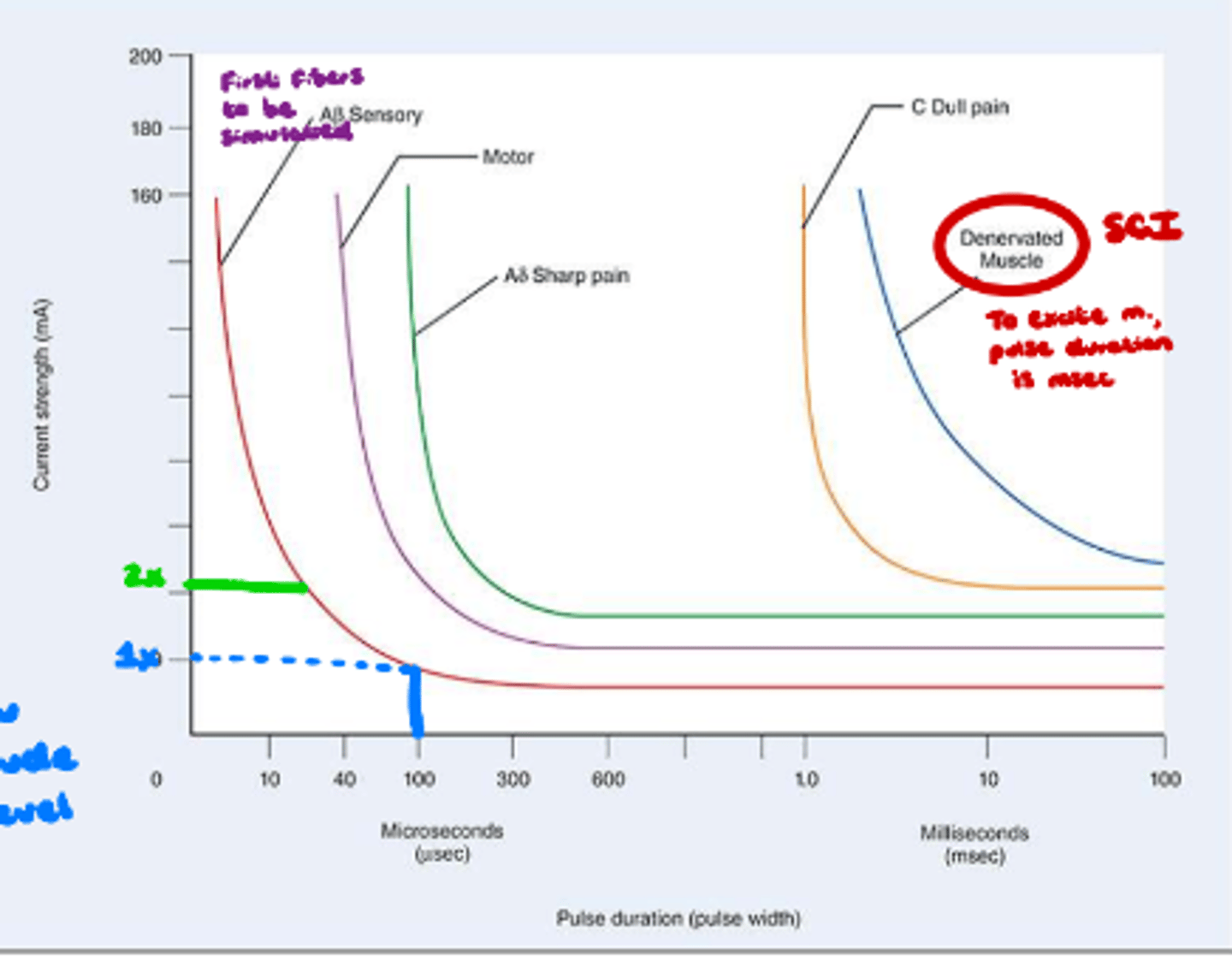
Strength-duration curve
What does image show?
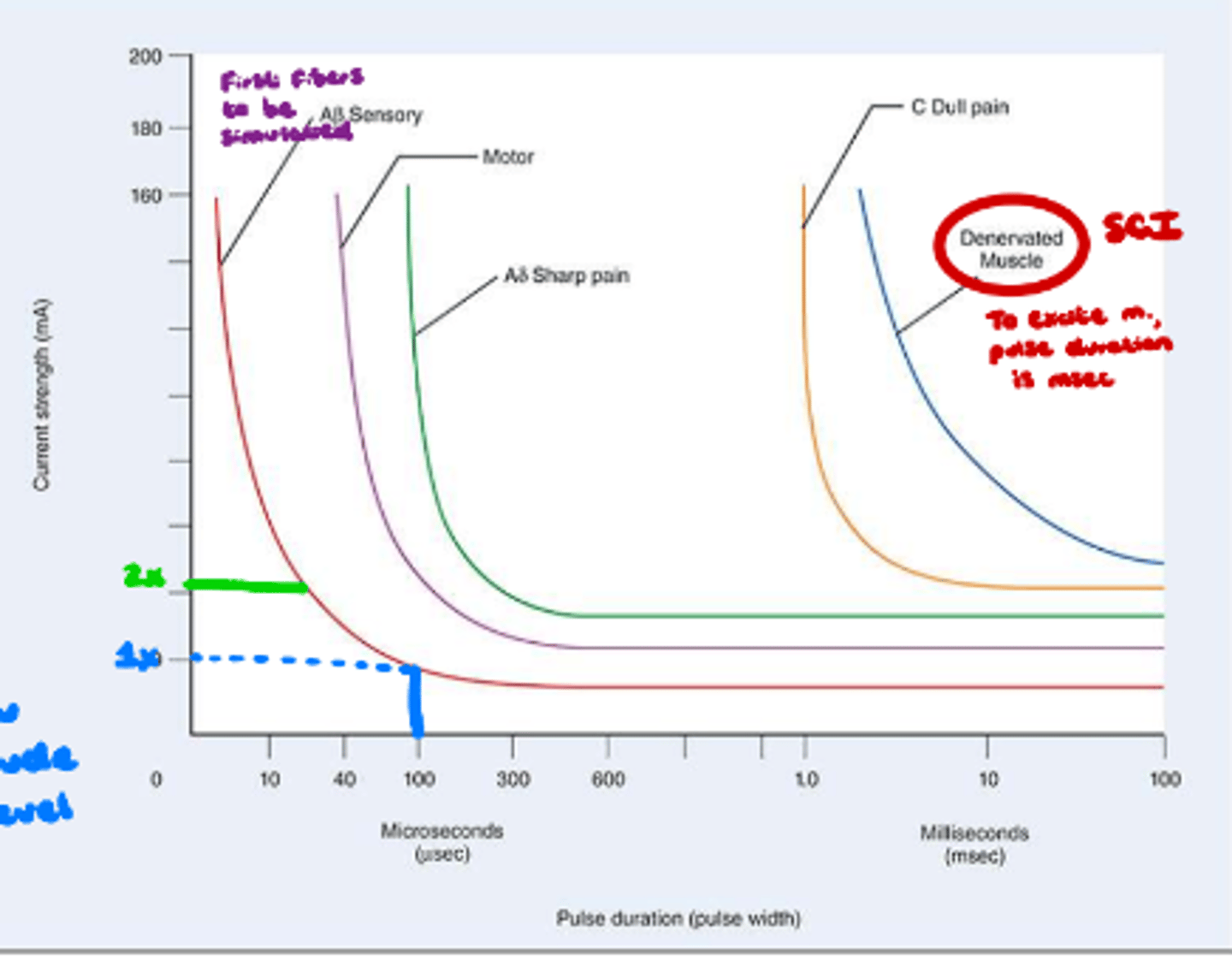
Rheobase
Least amount of pulse duration needed to stimulate nerve.
Setting pulse duration at this will allow you to set current/amplitude at a tolerable level.
What is clinical application of rheobase?