higher business - operations
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
factors to consider when choosing a supplier
price, quality, location, lead time, reputation, discounts
inventory management system
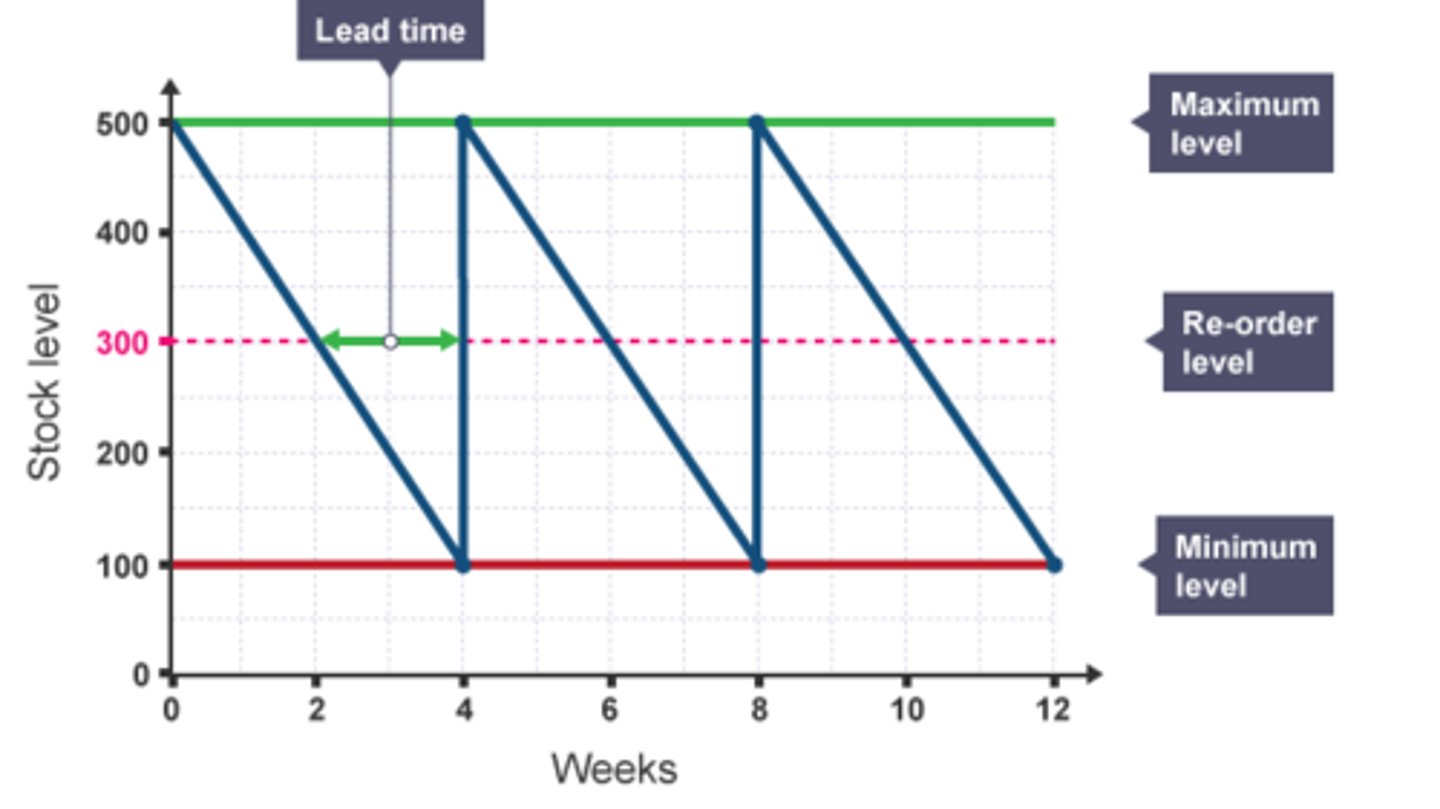
maximum inventory level
the largest amount of items to be stored on site
minimum inventory level
the lowest amount of items to be stored on site
re-order level
the level at which stock is re-ordered, epos links to system and automatically reorders
purpose of controlling stock
supplies could go out of date, supplies could go out of fashion, risk of theft, money tied up in stock
consequences of understocking
business may run out and hold up production, no bulk buying discounts, increased delivery costs, increased admin costs
factors affecting inventory levels
storage available, demand, lead time, skill of staff, finance
computerised inventory control disadvantages
costs a lot to set up, train staff to operate, breakdowns can halt production
computerised inventory control advantages
new stock automatically re-ordered, accurate monitoring or stock, allows for decisions on slow moving stock, highlights regional variations, theft deterrent
JIT production
producing what is needed when needed and nothing more
advantages of JIT
less storage space needed, respond to changes in demand, close relationship with suppliers built
disadvantages of JIT
depends on reliability of supplier, production halted if delays in supplies, sales lost if demand not met
features of effective warehousing
large buildings, central locations, ground level only, large loading bays
centralised storage
large buildings in a central location that store inventory and distribute raw materials to factories or finished goods to retail outlets
advantages of centralised storage
cheaper for one large warehouse than many small, easy for suppliers to deliver, economies of scale consistent procedures
disadvantages of centralised storage
inventory has to be dispersed eventually causing delays, wastage of theft, expensive for specialist stock and equipment
decentralised storage
storing stock in many locations in smaller warehouses or storerooms
decentralised storage advantages
inventory always close at hand, more responsive to local needs, no consequences of understocking
decentralised storage disadvantages
inventory has to be delivered to multiple locations, expensive for multiple locations, inconsistency in procedures
logistics management
ensure the right materials are delivered to the right location on time for a low of a cost as possible
role of the logistics manager
ensure delivery, order correct resources adhere to production budgets, give out instructions to warehouse staff, motivate staff
capital intensive production
producing products that mostly utilise machinery
automation
fully automatic, use of robotics controlled by CAM
mechanisation
involves humans and machinery working together to produce products
automation advantages
robots are consistent and accurate, robots can do dangerous jobs, robots can work 24/7, low wage costs
automation disadvantages
huge investments, breakdowns bad, no human touch, demotivated workforce
mechanisation advantages
improves accuracy and speed over hand made, some human touch
mechanisation disadvantages
human error still possible, cant work 24/7
labour intensive advantages
no high capital set up costs, human touch, motivated workforce
labour intensive disadvantages
human error, workers need breaks and holidays, costs for training
factors affecting the method of production
quantity of goods, skills of workforce, cost of labour, finance available, technology available
methods of controlling quality
quality control, quality assurance, quality circles, quality standards, mystery shoppers, bench-marking
quality control
a method of inspection, checking the product only at then end of the manufacturing process
quality assurance
method of prevention, checking the product throughout the manufacturing process
quality control advantages
ensures faulty products aren't sold, avoids bad PR
quality control disadvantages
not lean, wasteful, reworking takes time
quality assurance advantages
leaner than quality control, can spot where faults occur
quality assurance disadvantages
can still lead to waste, many check points can slow down production
quality circles
groups of workers who meet to discuss ways of improving products or processes
quality circles advantages
increases motivation, lowers staff turnover, good suggestions
quality circles disadvantages
lost working time, strong personalities can sway a discussion
quality standards
established specifications used to measure the degree of excellence of a good or service
quality standards advantages
proves the product has met a good standard, can be used as a marketing tool, higher prices can be charged, less complaints
quality standards disadvantages
lengthy process, agreed standards need to be maintained, requires thorough checks and audits
mystery shoppers
researchers posing as customers who gather observational data about a store
mystery shoppers advantages
keeps staff on their toes, no bias is shown, can improve service without complaints being made
mystery shoppers disadvantages
staff may resent the shoppers and take feedback personally, not a full evaluation could be an off day, businesses need to pay mystery shoppers
benchmarking
method of ensuring quality by coping the best in the business, the market leader
benchmarking advantages
can create a good target for staff, aiming to be the best is motivating
benchmarking disadvantages
may be hard to find trade secrets, only ever as good as the benchmark
continuous improvement
ongoing small, incremental improvements in all parts of an organization
quality management
a total commitment by everyone in an organization to improve the quality of procedures and products by reducing waste, errors, and defects
requirements for quality management to be effective
high quality inputs, rigorous selection, high quality training