Biological Bases of Behavior - Unit 2
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
Heredity
Passing on of traits from one generation to another
Nature vs nurture
Genes vs environment
What psychological perspectives lean on the nature side of the debate?
biological, cognitive, evolutionary
What psychological perspectives lean on the nurture side of the debate?
psychodynamic, behavioral, sociocultural
Epigenetics
How a person’s environment and behavior changes the way your genes work
Brain plasticity
Changes in the brain at a cellular level
Nervous system
Fast, short lasting messages
Endocrine system
Slow, target large areas of the body
Homeostasis
Ability to maintain internal stability
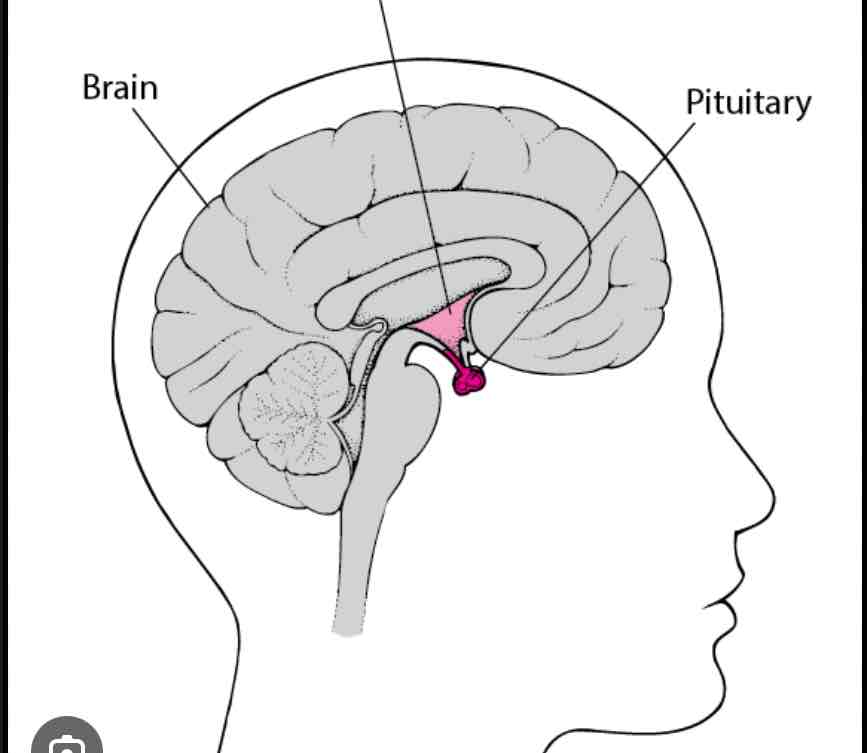
Pituitary gland
Base of the brain, connects nervous and endocrine systems, master gland
Growth hormones, oxytocin, vasopressin
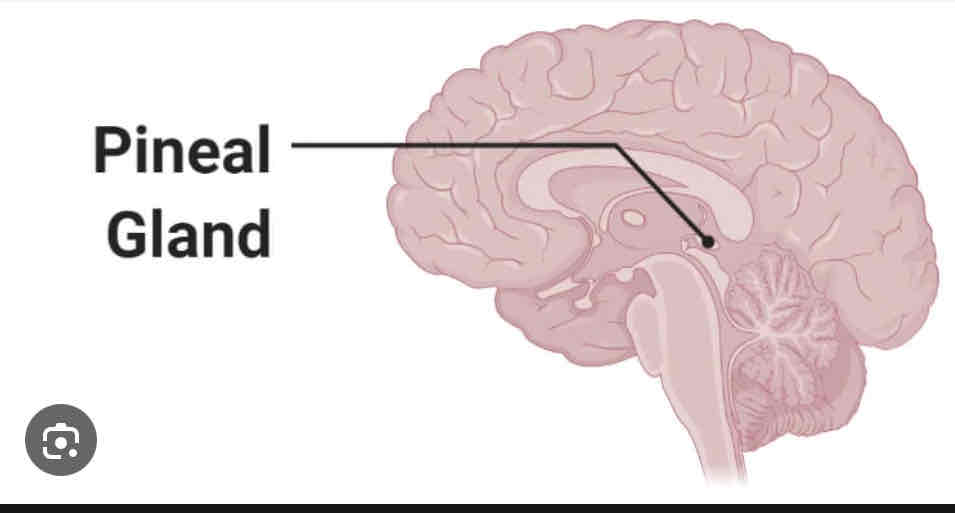
Pineal Gland
Above brainstem in midbrain, regulates sleep cycles
Melatonin
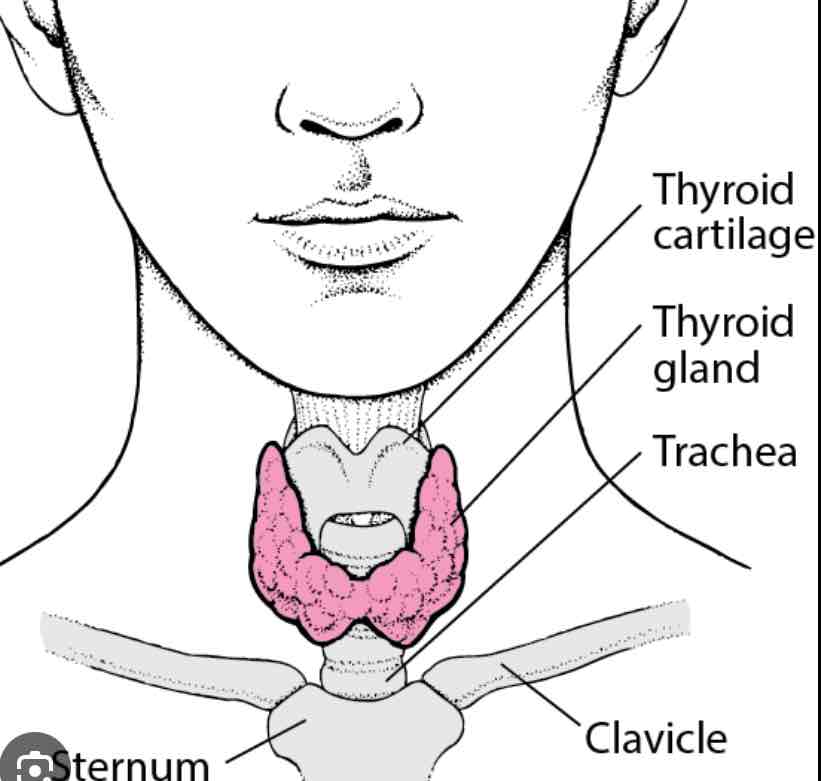
Thyroid and parathyroid gland
In the throat, regulates metabolism
Thyroid and parathyroid hormones, calcitonin
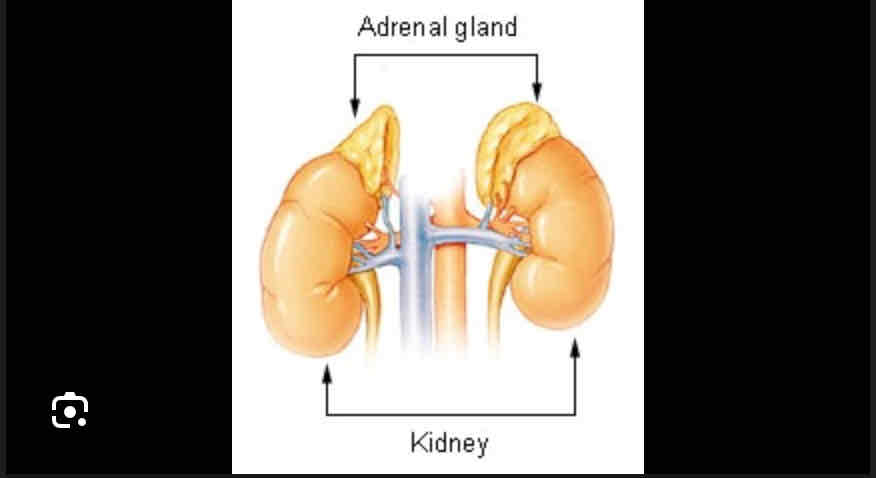
Adrenal glands
Above kidneys, regulates blood pressure
Norepinephrine, epinephrine, aldosterone
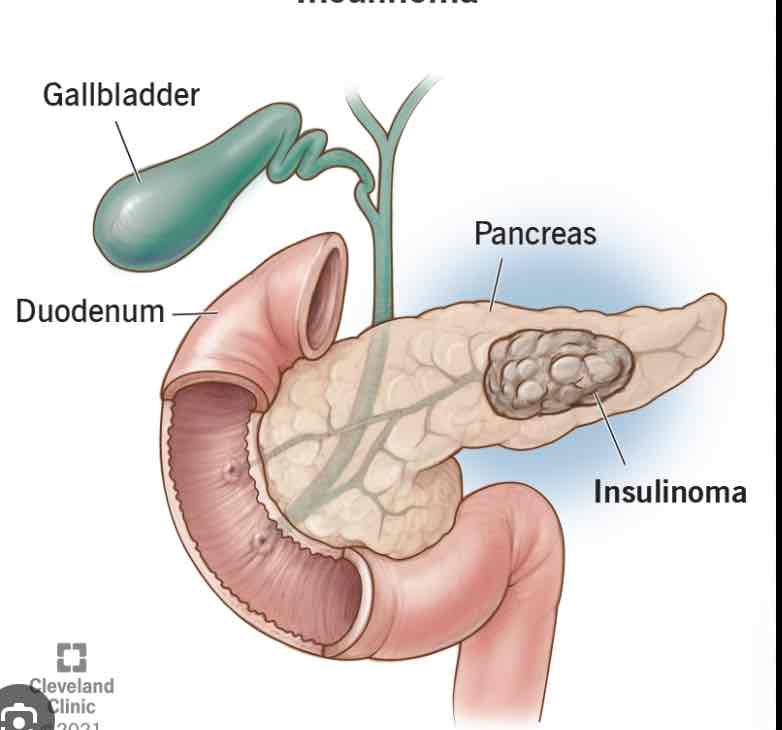
Pancreas
By the stomach, regulates sugar levels
Insulin, glucagon
Gonads
Ovaries and testes, reproduction
Testosterone, estrogen, progesterone
Central nervous system (CNS)
Brain and spinal chord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Nerves that branch off the CNS
sensory branch
Picks up info from outside stimuli
Motor branch
Impulses from the brain to neurons
Afferent
Approaching the brain
Afferent
Exiting the brain
Efferent
Exiting the brain
Somatic nervous system
Involuntary processes, smooth and cardiac muscle
Two divisions of autonomic nervous systems
Sympathetic and parasympathetic
Branches of PNS
Sensory and motor
Sympathetic
Arouses
Parasympathetic
Calms
Glial cell
Provides neurons with nutrients, most abundant cell in nervous system
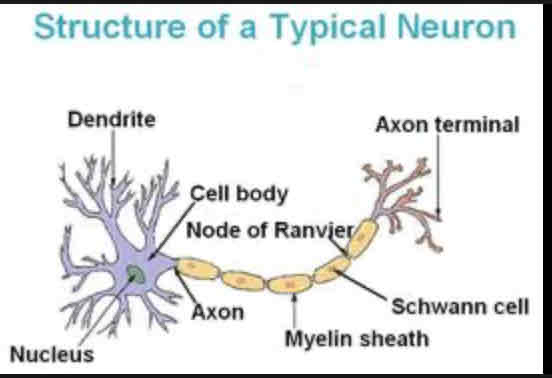
Dendrites
Extension of cell body, receive chemical messages through receptors
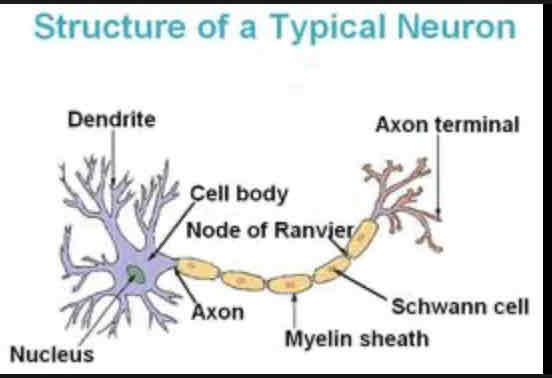
Nucleus
Houses genetic material
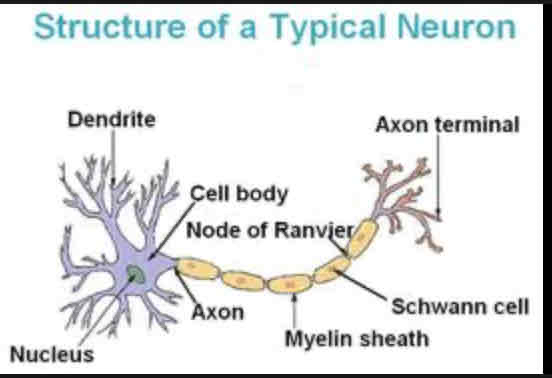
Soma
Cell body that contains the most organelles
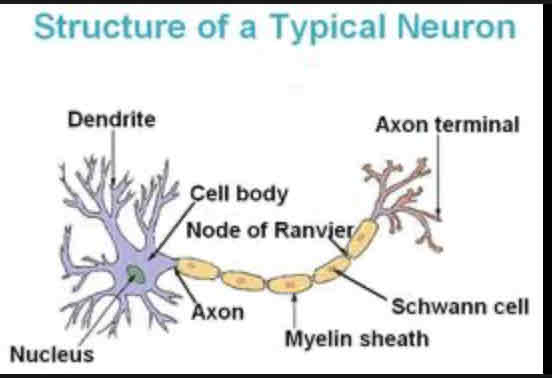
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps where the axon is exposed, increases speed of action potential
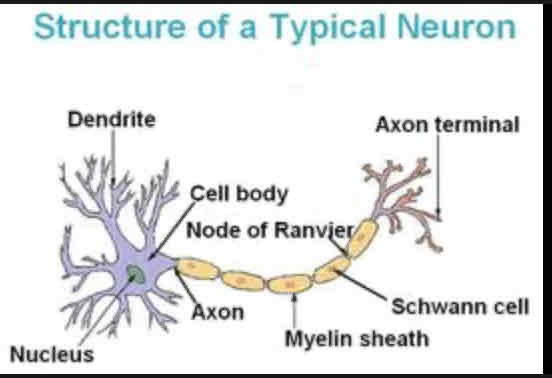
Axon
Longest part of the neuron, connects soma to axon terminal
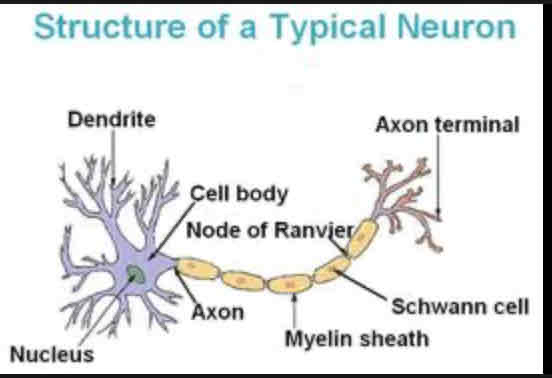
Myelin Sheath
Protects axon and increases speed of action potential
Axon terminal
neurotransmitter release into the synapse
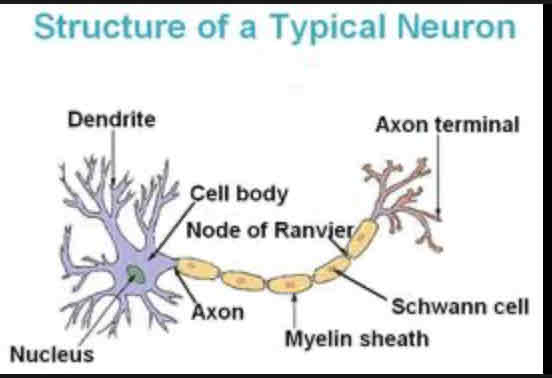
Schwann cells
Produces myelin sheath
Action potential
Neuron fires an electrical impulse down the axon
Can a neuron fire a partial action potential?
All or nothing
Resting Neuron
More positive ions outside the neuron, will not fire
Depolarization
Positive ions move inside the cell and trigger an action potential
Repolarization
Neuron returns to resting potential
Refractory period
Time when neuron cannot fire, waiting for repolarization
Synapse
Space between the axon terminal of one neuron, and dendrites of another
Electrical synapse
Connected neurons, fast
Chemical synapse
Synaptic gap in between, slow
Neurotransmitter
Chemical messenger sent by a neuron
Presynaptic terminal
Releases neurotransmitter
Releases neurotransmitter
Postsynaptic terminal
Receives neurotransmitter
Reputake
Sending neuron reabsorbs the neurotransmitters
Excitatory neurotransmitter
Increases likelihood of neuron firing
Inhibitory neurotransmitter
Decrease likelihood of neuron firing
Hyperpolarization
Inside of neuron becomes extremely negative, moves further away from action potential
Acetylcholine
Excitatory, contracts muscles, learning, memory
Dopamine
Excitatory, contracts muscles, learning, memory
Dopamine
Happy hormone, satisfaction and motivation, addictive
Serotonin
Inhibitory, mood, sleep, hunger, arousal
Endorphins
Inhibitory, pain control, lower stress
Glutamate
Excitatory messages, long term memory, learning
GABA
Inhibitory, sleep and movement
Agonist
Increase effects of a neurotransmitter
Antagonist
Decrease or stop the effects of a neurotransmitter
How do agonists work?
Mimic neurotransmitter, block reuptake (neurotransmitter stays in the synapse)
How do antagonists work?
Block receptors on the postsynaptic terminal, block release at presynaptic terminal
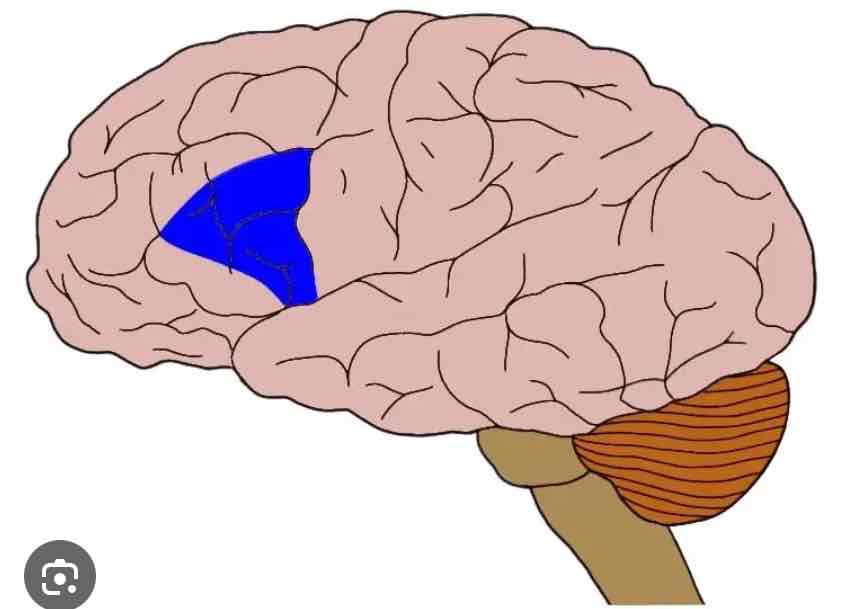
Broca’s Area
Frontal lobe, controls speech muscles
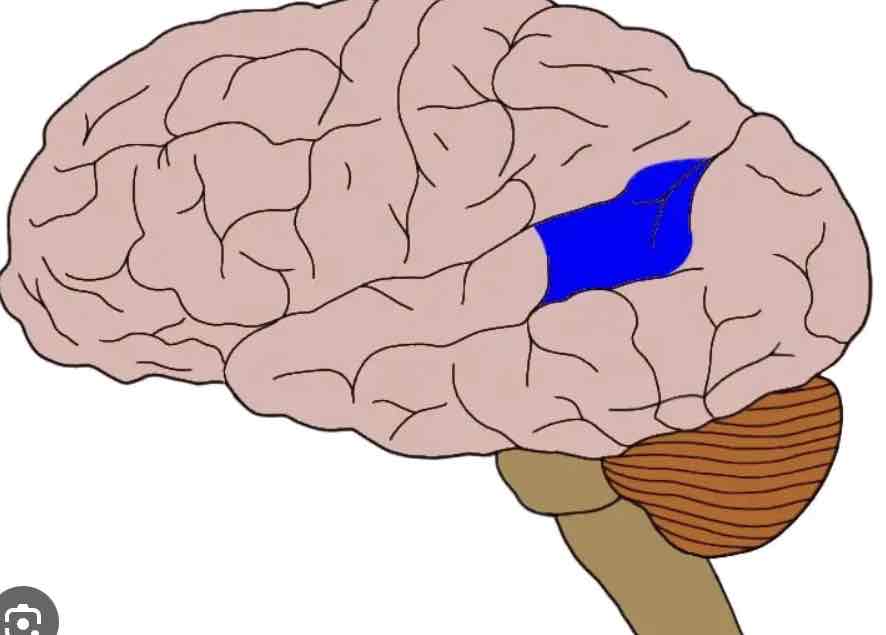
Wernicke’s aArea
Temporal lobe, ability to comprehend and create speech
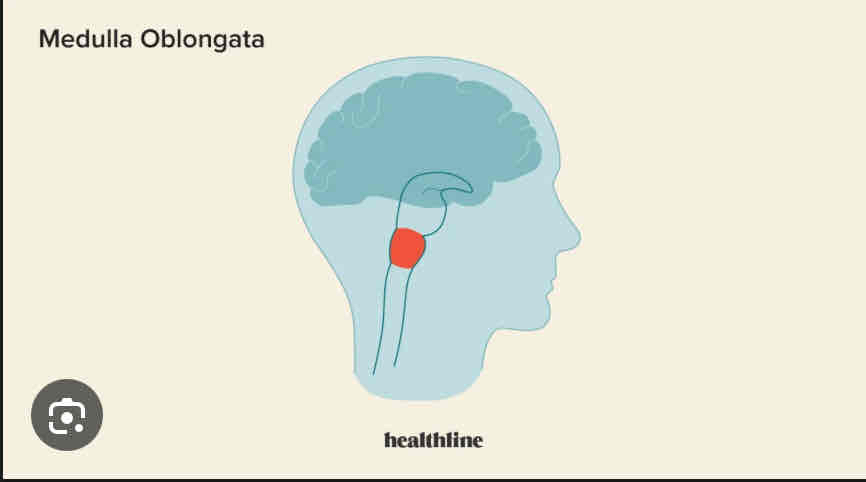
Medulla Oblongata
controls breathing, heart rate, blood pressure
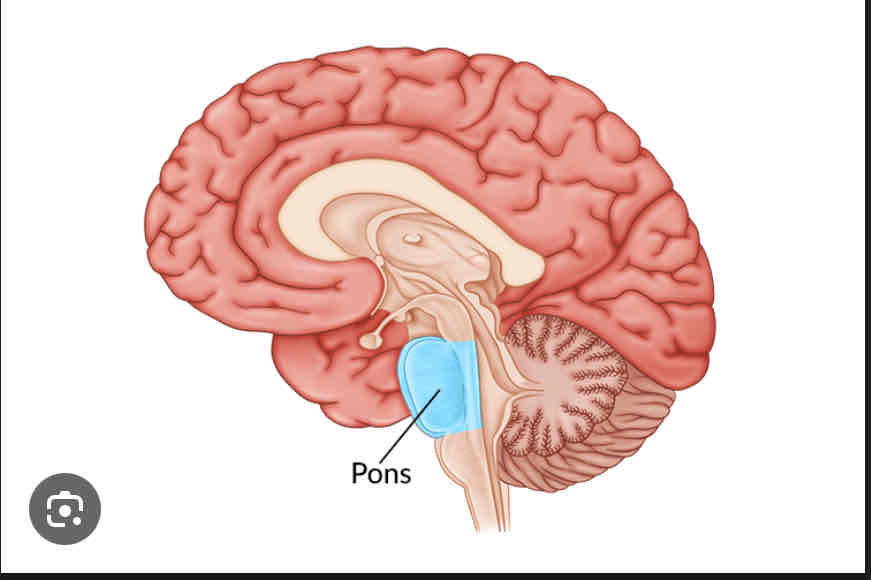
Pons
Coordinates movement and sleep
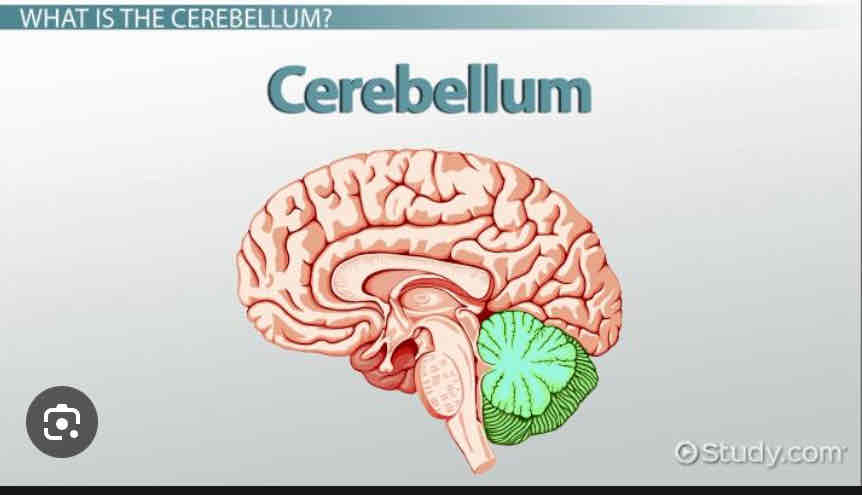
Cerebellum
Smooth muscle movements, maintains equilibrium
Brain Stem
Contains midbrain, pons, and medulla (autonomic functions)
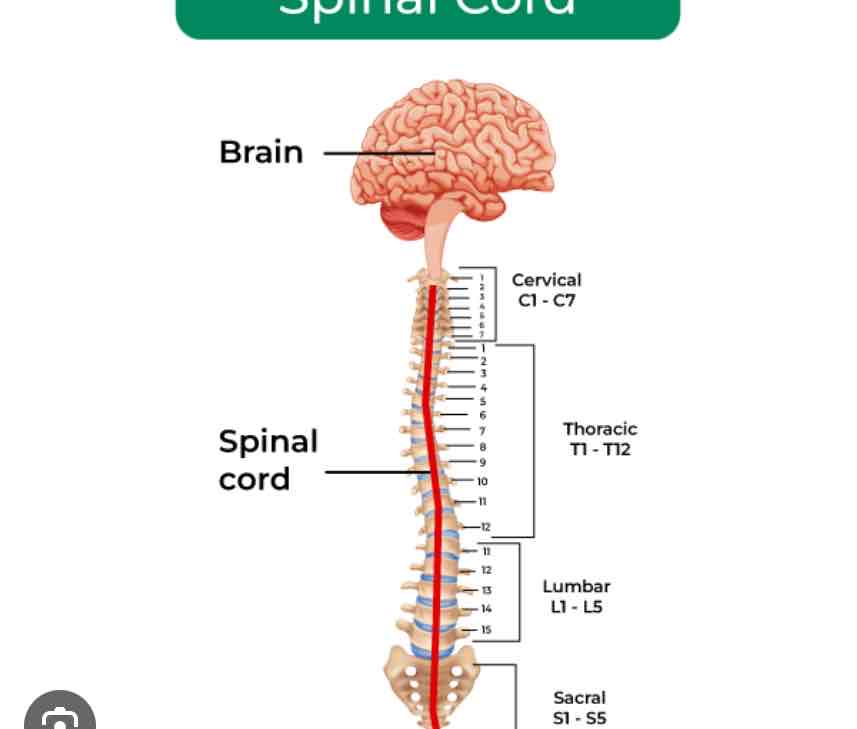
Spinal Cord
Connects brain to the rest of the body
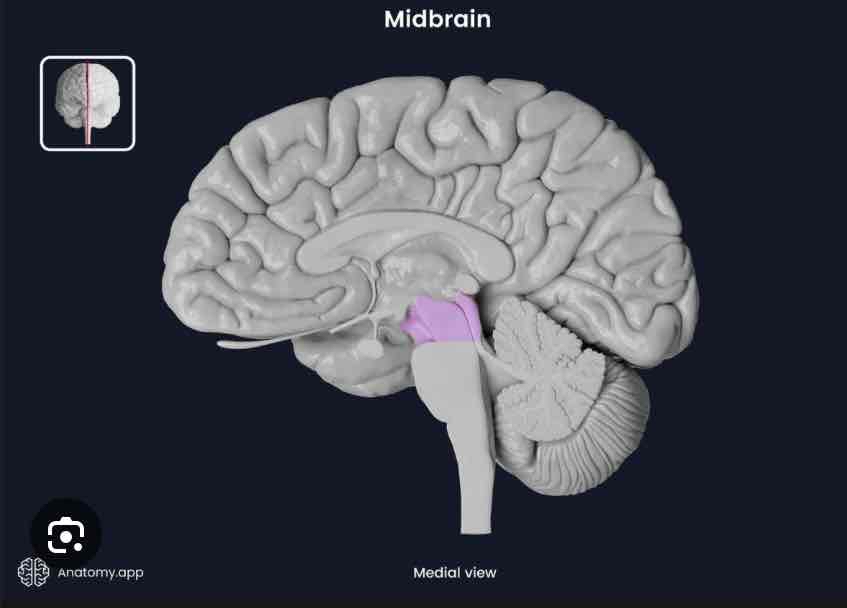
Midbrain
Part of the brainstem, relays info from visual and auditory systems
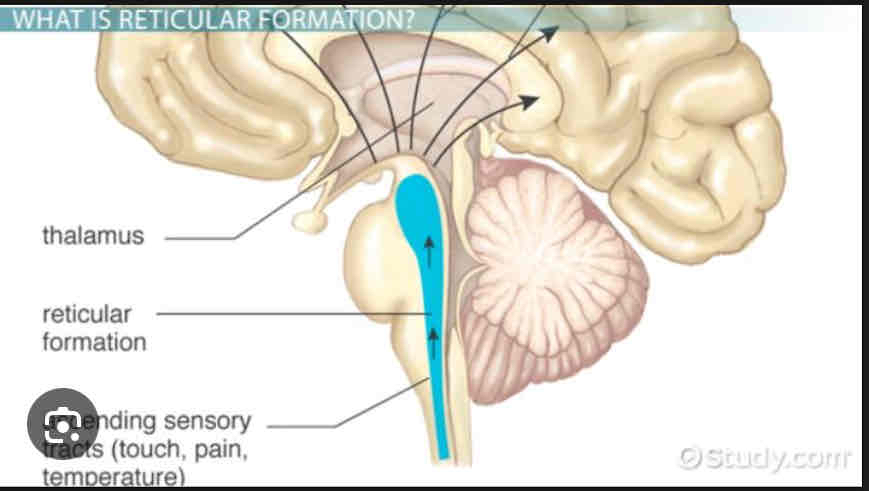
Reticular Formation
Nerves and fibers through the brainstem, alertness and arousal
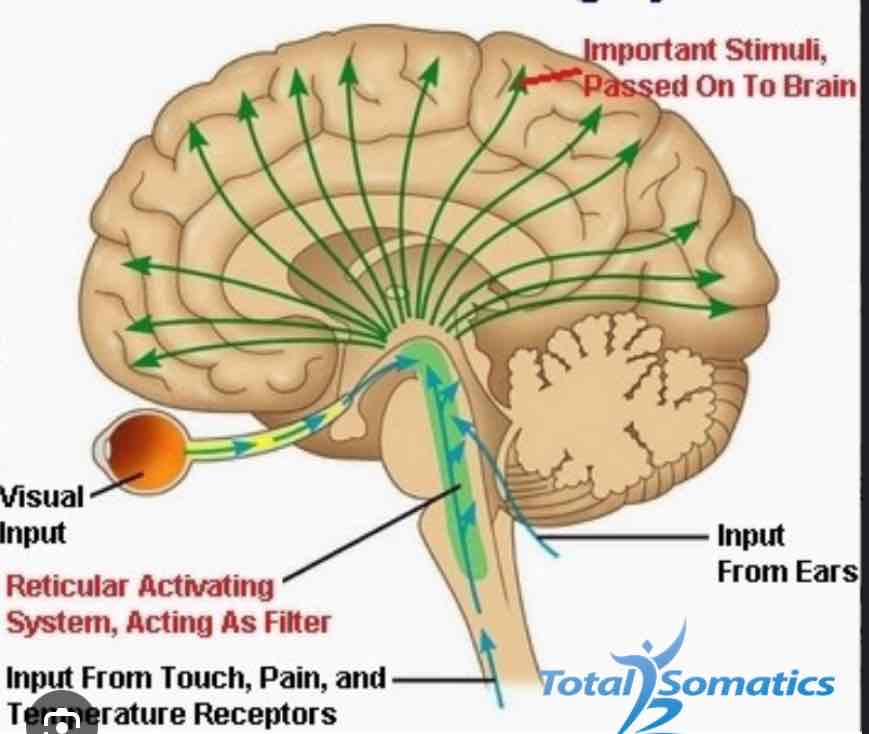
Reticular Activating System
Part of reticular formation, sleep-wake cycles
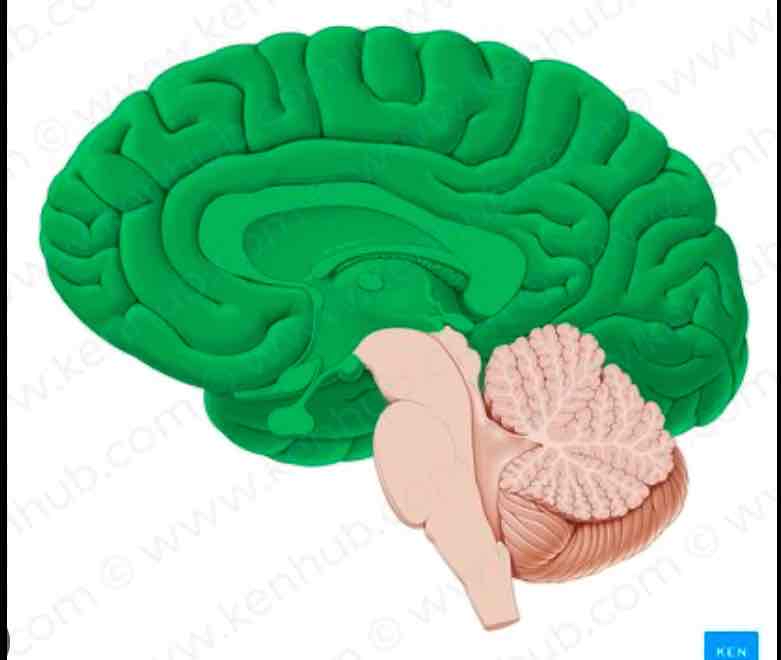
Cerebrum
Everything except the cerebellum and brainstem
Cerebral Cortex
Thin layer of gray matter over the brain
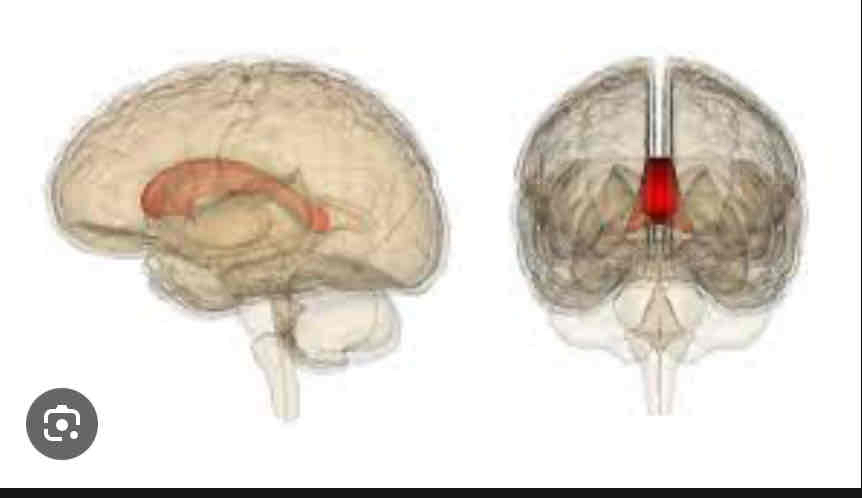
Corpus Callosum
Connects both hemispheres of the brain
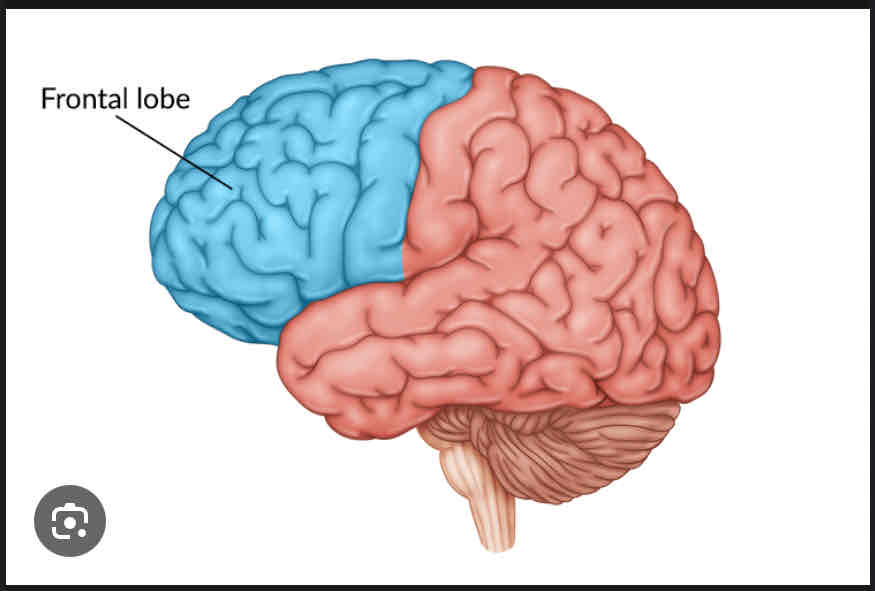
Frontal Lobe
Higher level thinking and motor functions
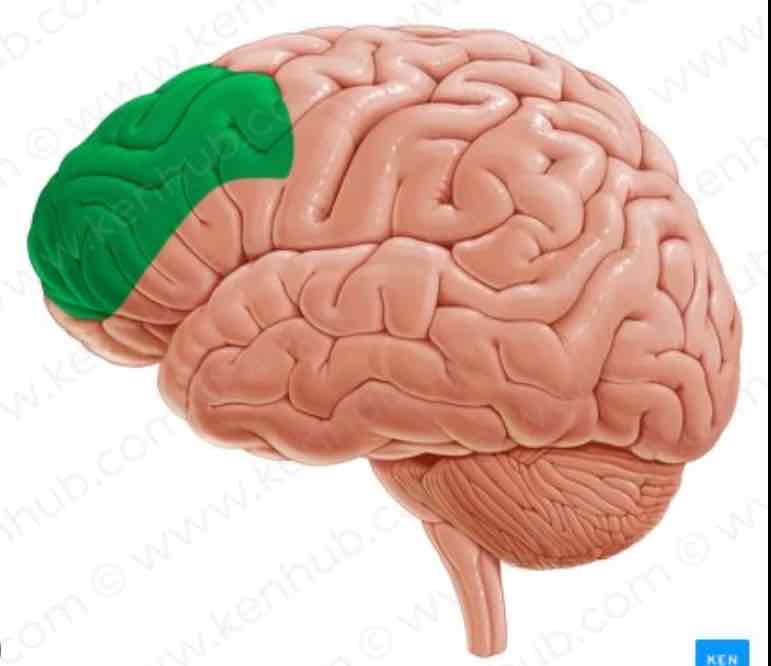
Prefrontal Cortex
Frontal Lobe, planning, emotions, complex thought
Motor Cortex
Motor Homunculus
Parietal Lobe
Somatosensory Cortex
Occipital Lobe
Visual Corte
Temporal Lobe
Angular Gyrus
Auditory Cortex
Thalamus
Limbic System
Hippocampus
Amygdala
Hypothalamus
Nucleus Accumbens
Basal Ganglia
Brain lateralization
Left and right hemispheres are different
Left brain
Logic and language
Right brain
Spatial concepts, creativity
Phineas gage
Pole went through his head, he was fine
Corpus Callosum Cut
No loss of intelligence but the two hemispheres can no longer communicate