bio 108 topic 26: intro to chordates
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What’re chordates
bilaterian animals that belong to clade deuterostomia
Bilaterally symmetrical coelomates with segmented bodies
Most have vertebral backbone
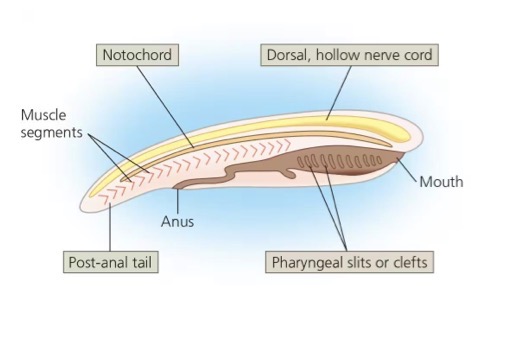
Shared derived traits of chordates
Notochord
Dorsal, hollow nerve cord
Pharyngeal slits or clefts
Muscular post anal tail
Expand on notochord
longitudinal flexible rod bw digestive tube and nerve cord Pharyngeal slits
Skeletal support
Forms during embryogenesis
What is the shared derived traits of dorsal, hollow cord
Nerve cord of chordate embryo developed from a plate of ectoderm that rolls inward to form a neural tube, which is dorsal to notochord
What’re pharyngeal slits or clefts and 3 functions
grooves in pharynx in chordates
Allows water entering mouth to exit through slits
Suspension feeding
Gas exchange
What is the trait of muscular post-anal tail
common in most adult chordates
Tail contains skeletal elements and muscle
Tail is greatly reduced during embryonic development
Lancelets
marine suspension feeders that retain traits of the chordate body plan as adults
Wriggle backwards into sand
Water exits body thro atropore
Subphylum Cephalchordata
Tunicates
subphylum Urochordata
closely related to other chordates than are to lance let’s
Most resemble chordate body plan during larval stage
As adults tunicate draws in water thro siphon
Sessil
Sea squirts (shoot water) when attacked
Can reproduce asexually by budding