CHEM 420- Chap 5 (Reactivity Ratios)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What types of structures can form during copolymerization?
Statistical, alternating, block, or graft
What does the terminal model show?
The rate that a monomer adds depends on the identity of the monomer that added previously
What happens when k12 >> k11 and k21 >> k22?
Alternating copolymer exists
What happens when k11 >> k12 and k22 >> k21?
A homopolymer or block copolymer (and perhaps a graft copolymer) results
What happens when k12 = k11 and k21 = k22?
A statistical copolymer exists
How does the steady state assumption apply to copolymerization?
For copolymerization at steady state, the number of active chain ends of each type ([M1*] and [M2*]) doesn’t change because the rate of their initiation = rate of their termination; meaning [M1*] and [M2*] are constant
Define reactivity ratios (r1 and r2):
r1 = k11/k12 ; r2 = k22/k21
Steady state of copolymerization equation:
k12 [M1*] [M2*] = k21 [M2*] [M1*]
Rate equation for the consumption of monomer 1:
- d[M1]/dt = k11 [M1*] [M1] + k21 [M2*] [M1]
Rate equation for the consumption of monomer 2:
- d[M2]/ dt = k22 [M2*] [M2] + k12 [M1*] [M2]
Define F1 and write its equation:
mole fraction of monomer 1 in the polymer being formed
= d [M1] / d [M1] + d [M2]
analogue of “y”
Define f1 and write its equation:
mole fraction of monomer 1 in the feed
= [M1] / [M1] + [M2]
analogue of “x”
What forms during special case I when r1 = r2 = 0?
An alternating copolymer
What forms during special case III when r1 = r2 = 1?
A statistical copolymer
What forms during special case II when r1 = r2 = ∞ ?
Two homopolymers
What is special case IV when r1r2 = 1?
“Ideal” copolymerization
The copolymer grows randomly and the polymer composition matches the monomer feed throughout the reaction. No drift, no blockiness
Fineman- Ross plot:
x axis = (x²/y)
y axis = x (1 - (1/y))
x = f1/f2 (feed ratio)
y = F1/F2 (copolymer composition ratio)
What factors affect monomer reactivity?
Sterics
Resonance (that stabilizes propagating radical)
Polarity (nucleophile + electrophile)
Copolymers with 2 monomers have:
2^n kinds of n-ads
Copolymers with 3 monomers have:
3^n kinds of n-ads
What happens during first-order Markovian statistics?
The polymerization depends only on one previous event: the addition of the last monomer in that chain; aka terminal model
What happens during zeroth-order Markovian statistics?
The probability of adding monomer A or B does not depend on any previous event
What happens during second-order Markovian statistics?
The probability of adding monomer depends on the last two monomers in a chain; aka penultimate model
What is the number fraction of sequence of A (or B) units:
Within a sample, how common is a sequence of -(A)n- units
Ex: Number fraction of -B-A-A-A-B- sequences, NA (3)
NA (3) = P5 {BAAAB} / P2 {AB}
What is the number average length of A (or B) runs:
Within a sample, what is the average length of unbroken runs of -(A)n-
Ex: for number average length of A runs, l A
l A = P {A} / P2 {AB}
What is the run fraction or number:
Within a sample, what is the fraction of runs that occur (out of the total possible)
R = 2P2 {AB}
What is the measure of the departure from randomness:
Within a sample, do monomers add alternately, randomly, or as blocks
χ = P2 {AB} / P1 {A} P1 {B}
Write the number average length of A (or B) and how to find them:
l A = 1 + (rA)(x)
l B = 1 + (rB)/x
x = [A] / [B]
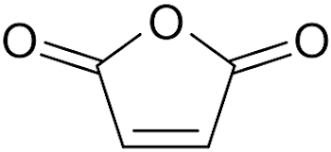
What kind of copolymerization occurs between styrene and maleic anhydride?
Nearly alternating
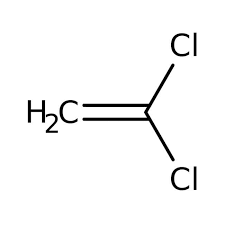
What kind of copolymerization occurs between vinylidene chloride and methyl acrylate?
Nearly random
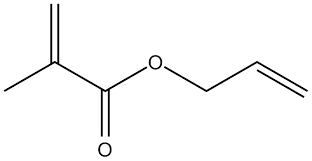
What kind of copolymerization occurs between acrylonitrile and allyl methacrylate?
Somewhat blocky
Describe composition drift:
Occurs when monomers have different reactivities. The more reactive monomer is consumed faster at the beginning. As [A] decreases, the less reactive monomer B is consumed more, leading to a gradual change in copolymer composition. This happens b/c:
Actual consumption of monomers over time does not maintain original 1:1 ratio, even though that was the starting concentration—- if rA doesn’t equal rB
The greater difference b/w rA and rB, the more dramatic the compositional drift