APES ch.5 - Earth Systems
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
rocks, tectonic plates, earths layers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what does the structure of the Earth look like?
Core, Mantle, Crust
how can divergent plate boundaries shape Earths landscape?
can form ridges and new rocks
how can convergent plate boundaries shape Earths landscape?
trenches form and old rock is recycled
how can transform fault boundaries shape Earths landscape?
highest earthquake activity and breaks form
how can processes shape Earth’s landscape?
tectonics, weathering, erosion, and deposition work together to reshape Earth’s features - such as volcanoes and coastlines
how can tectonic plate shifts cause earthquakes?
they build up stored energy, then from the sudden release of energy they slip
how can tectonic plates shift cause volcanoes?
when they collide the oceanic plate subducts under the continental plate and sinks into the mantle then it releases water which then turns into magma and rises into the newly formed volcano
what is the rock cycle? what are the different forms of rocks? what process can lead to the formation of each type?
igneous rocks form when magma cools and hardens, sedimentary rocks form when sediments from weathering and erosion get compacted, metamorphic rocks form when existing rocks are changed by heat and pressure
how does weathering and glaciation cause sedimentation?
weathering breaks down rocks and minerals so they are able to move easier and then glaciers use erosion to remove rock fragments and then deposition uses the collection of new material such as sediment, rock fragments, or soil to form new rock
how are minerals extracted? (have an awareness of how these extraction processes can have environmental consequences)
mining
- mining can cause habitat loss and dust pollution
what is soil? what is it composed of?
it is a mixture of weathered rocks (minerals), organic matter, water, air, and living organisms
how is soil formed?
parent material is weathered and fragments move upward and then organic material builds up as plants and other organisms die and then greater amounts of organic material are present in a mature soil
what is an intrusive igneous rock?
an igneous rock that forms within earth as magma cools
what is an extrusive igneous rock?
an igneous rock that forms when magma cools above the earth
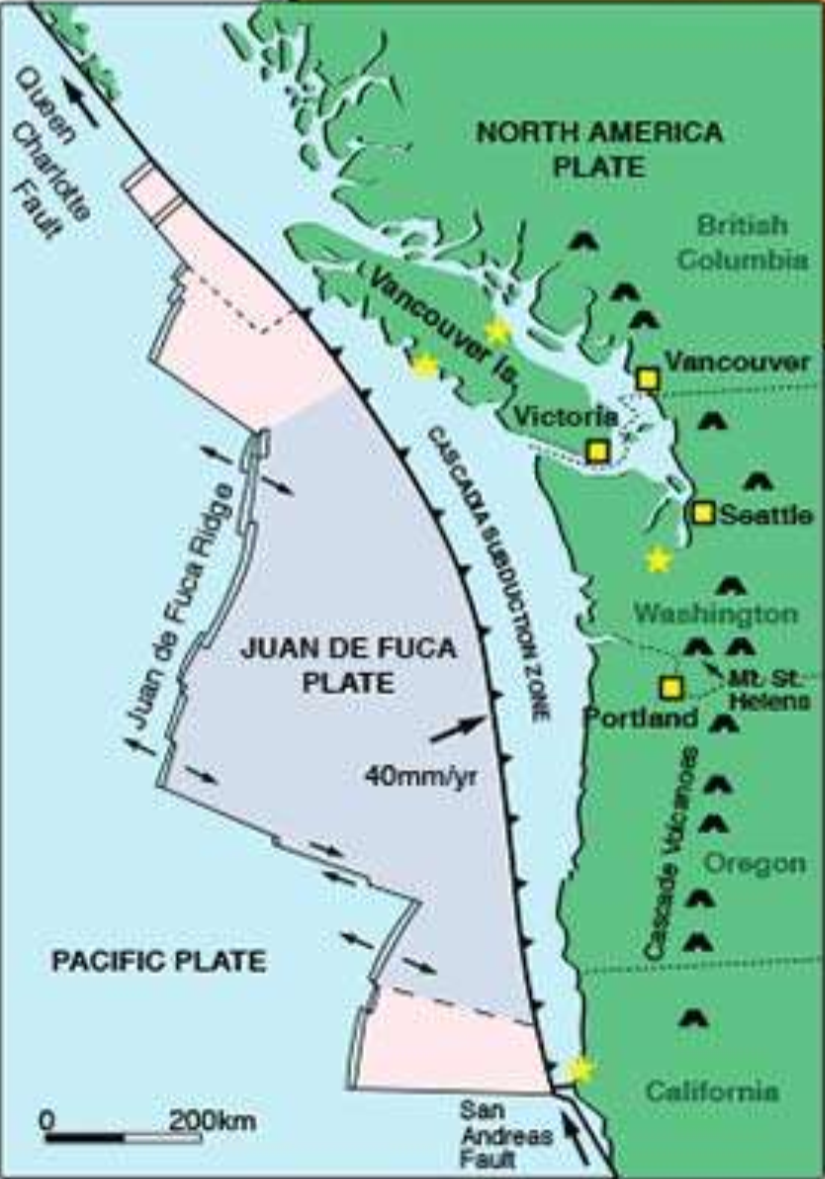
where is the convergent plate boundary?
on the Cascadian subduction zone
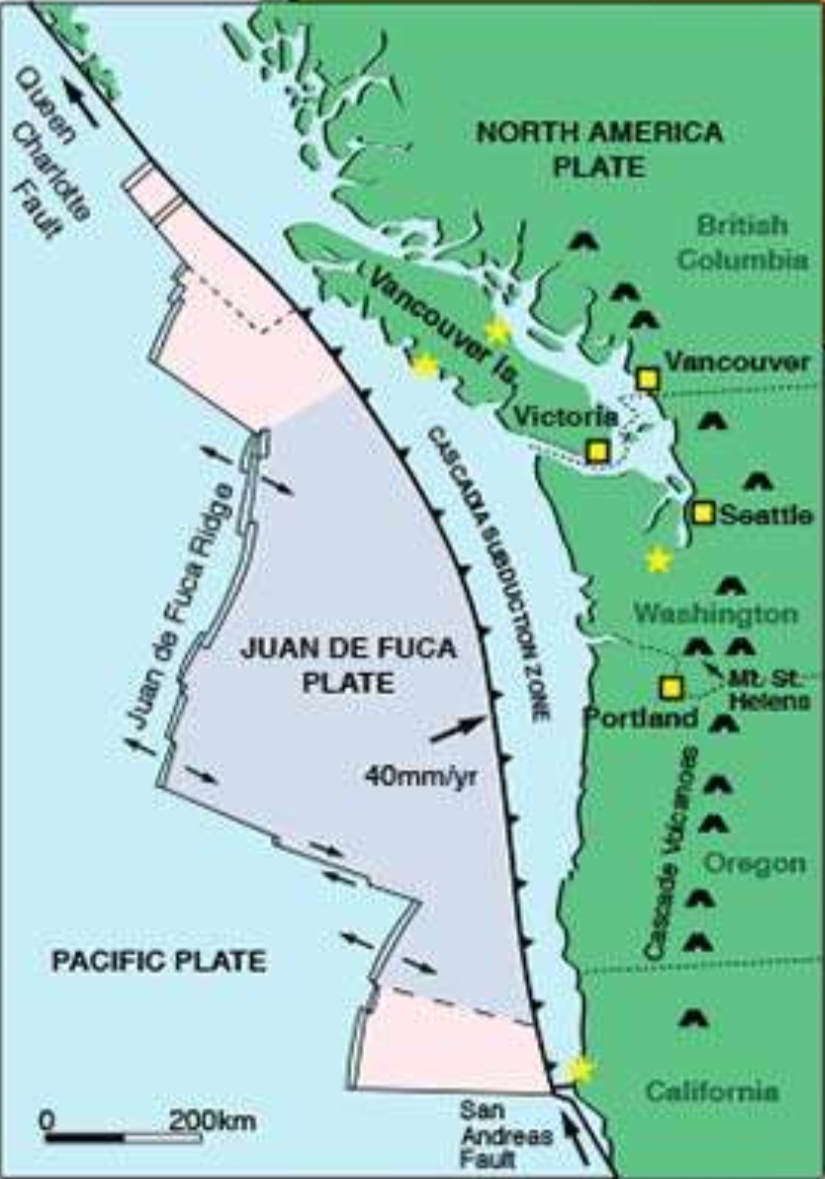
where is the divergent plate boundary?
at the Juan de Fuca ridge
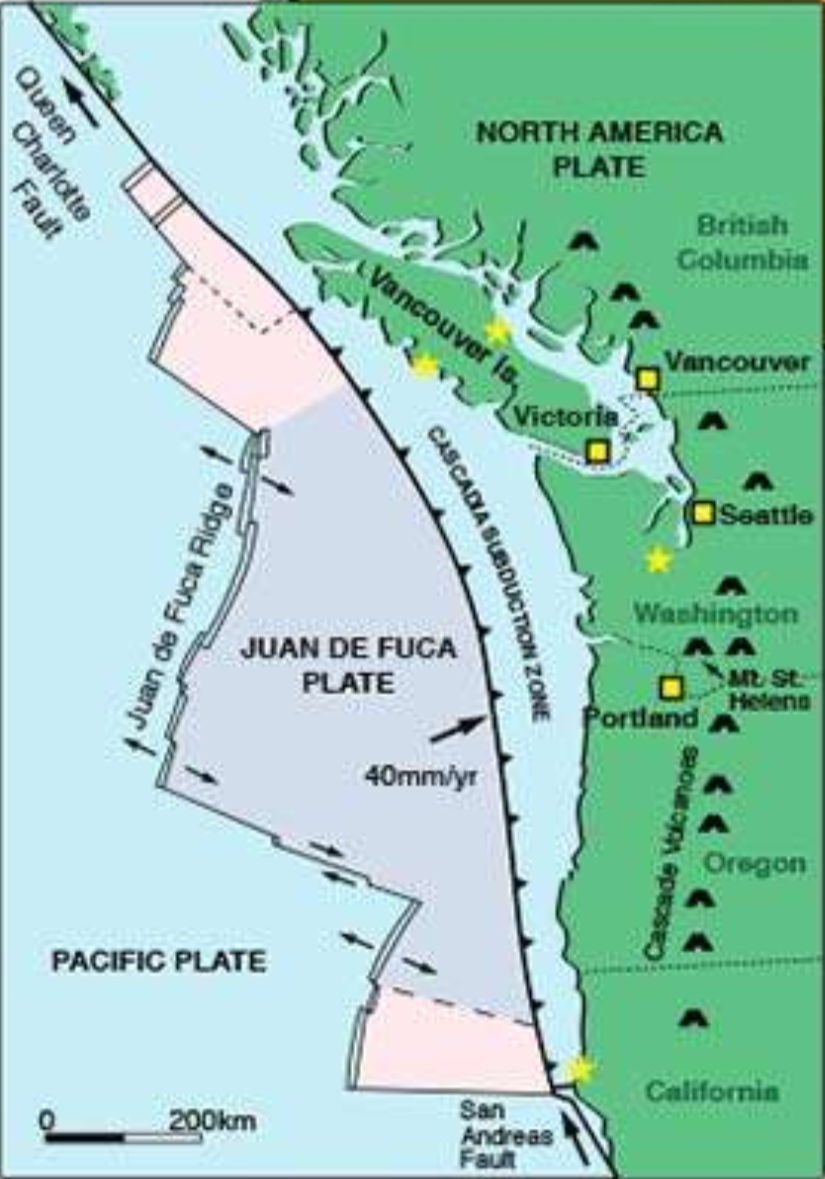
where is the transform fault boundary?
the Queen Charlotte fault and the San Andres fault
what is weathering? what is erosion?
weathering is the breaking down of the rocks and minerals and erosion is the movement of the broken down pieces from one location to the other