CH 6 & CH 7 Microbial Growth & Control of Microbial Growth
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What are the Physical Requirements for Growth?
Temperature
pH
Osmotic Pressure
Minimum meaning?
It means the lowest temperature which a species will grow.
Optimum meaning?
Temperature at which the species grow best.
Maximum meaning?
Highest temperature at which growth is possible
What does it mean when there are cold loving microbes, mostly found in the oceans depths or polar regions.
It is a psychrophile.
Which microbe love the moderate temperature?
Mesophile
Which microbe is a heat lover?
Thermophile
Where do bacteria grow best in terms of pH?
They grow best in a narrow pH range near neutrality.
Very few grow at an acidic pH below 4.
What are acidophiles?
Bacteria that are tolerant of very low acidity.
What can inhibit microbial growth?
Alkalinity can inhibit microbial growth.
Microorganisms require what for growth?
They need water for growth
What are the two solutions in osmotic pressure?
Hypotonic Solutions → water enters the cell
Hypertonic Solutions → water leaves the cell
What can osmotic pressure cause?
It can cause plasmolysis → shrinkage of the cells cytoplasm.
What are the chemical requirements?
Carbon & Oxygen are needed for chemical requirements.
What is needed for ALL organic compounds in a living cell?
Carbon
What are the differences between chemoheterotrophs vs chemoautotrophs & photoautotrophs?
Chemoheterotrophs receives carbon from their source energy.
Chemoautotrophs and Photoautotrophs derive their carbon from Co2
What effect does Obligate Aerobes & Facultative Anaerobes have?
Obligate Aerobes effect is → It’s only aerobic growth, oxygen is required.
Facultative Anaerobes effect is → Both aerobic and anaerobic growth; greater growth in presence of oxygen.
What does Obligate Anaerobes and Aerotolerant Anaerobes effect?
Obligate Anaerobes → Only anaerobic growth; growth ceases in presence of oxygen.
Aerotolerant Anaerobes → Only anaerobic growth; but growth continues in the presence of oxygen.
What is the effect on Microaerophiles?
Only aerobic growth; oxygen required in low concentration.
What are the Toxic Forms of Oxygen?
Obligate Aerobes
Facultative Anaerobes
Aerotolerant Anaerobes
What enzymes MUST the toxic forms of oxygen have?
Superoxide Dismutase → To neutralize toxic forms of superoxide radicals
Catalase → To neutralize peroxide produced during normal aerobic respiration.
What is a culture media?
Culture media is a nutrient material prepared for growth of microorganisms in a laboratory.
What do the culture media require?
Moisture
Balanaced pH
Suitable level of Oxygen
Temperature
NEEDS to be STERILE
What is Chemically Defined Media vs Complex Media?
Chemical defined media is a medium whose exact chemical composition is known.
Complex media is a culture medium in which the exact chemical composition is not known.
What is the difference between selective media vs differential media?
Selective Media
Designed to suppress the growth of unwanted bacteria and encourage growth of desired microbe.
Differential Media
Makes it easier to distinguish colonies of desired microorganism
Ex. → blood agar is a medium used to identify bacterial species that destroy red blood cells.
How does a colony arise?
They arise from a single spore.
What is the streak plate method? How do we do it?
It’s a isolation method to get pure cultures..
Inoculating look is dipped into a mixed culture and streaked in a pattern to dilute
How does the growth of bacterial cultures work?
They divide by binary fission.
Doublings
Generation time.
What is generation time?
Time required for a cell to divide.
Most have a generation time of 3 hours.
What is the growth phase curve?
It’s a curve that shows the growth of cells over time.
There are 4 basic phases → Lag → Log → Stationary → Death
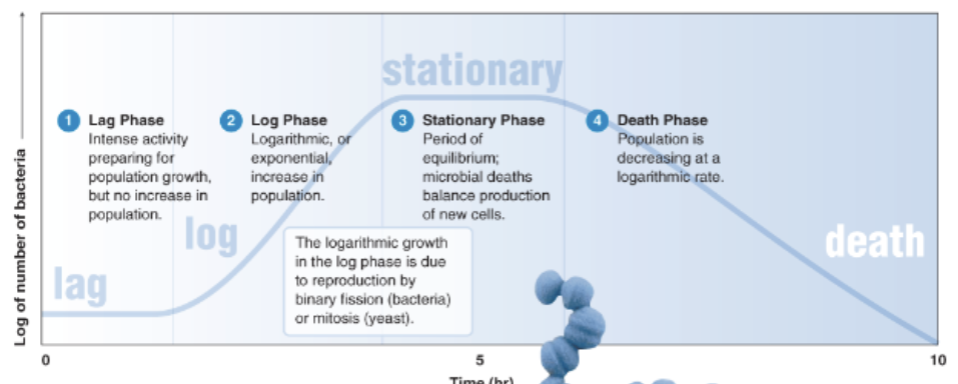
Explain the 4 phases of bacterial growth?
Lag → Intense activity preparing for population growth, there is no increase in population
Log → Logarithmic or exponential, increase in population occurring
Stationary → Period of equilibrium; microbial deaths balance production of new cells.
Death Phase → Population is decreasing at a logarithmic rate.
What is the meaning of sterilization?
Removal of all living microorganisms
What is commercial sterilization?
Used in heat treating canned food
What is disinfection?
It’s directed at destroying harming microorganisms
What is Antisepsis?
Treatment directing at living tissue
What is degerming?
Mechanical removal of the microbes
What is sanitization
Lower microbial counts to safe public health levels.
What do the microbial control agents do?
-Alteration of Membrane Permeabillity.
PM is targeted by many microbial control agents
-Damage to lipids or proteins causing cell lysis
Proteins can be denatured
Nucleic Acids can be damaged
What are the physical methods of microbial control?
Moist Heat Sterilization
Pasteurization
High - Efficiency particulate air
Desiccation
Dry Heat Sterilization
Direct Flaming & Hot-Air Sterilization
Explain Moist Heat Sterilization?
It kills microorganisms by denaturing proteins
Boiling kills vegetative forms of bacterial pathogens in 10 minutes.
It’s not always a reliable sterilization procedure.
Autoclaving
High temps generated by steam under pressure in a autoclave
Preferred sterilization in health care environment
Explain Pasteurization
Mild heating to kill microorganisms that causes food spoilage but doesn’t alter the taste of food
Lowers microbial numbers
Ice cream, yogurt and beer all have their OWN pasteurization times and temps
What is HEPA?
(High-Effieciency Particulate Air)
Has filters removing almost all microorganisms
What is Desiccation?
M-O can’t grow but can be viable for many years
Cells resume growth and division when water is available
Resistance of vegetative cells to desiccation varies.
Viruses are generally resistant to this method
Bacterial endospores are also very resistant
In the hospital setting, we must be careful about endospores in dust, clothing, bedding, dried mucus, urine and pus.
What is Dry Heat Sterilization? What are the two types?
Direct Flaming
Sterilizing the inoculating loop by holding it to an open flame
Heat the inoculating loop until it glows red
Hot-Air Sterilization
Sterilization in an oven at 160 C for about 2 hours
What is Chemical Methods of Microbial Control?
It’s to control the growth of microbes on both living tissue and inanimate objects.
Can a disinfectant be suitable?
No single disinfectant can be suitable for all circumstances.
What is Biocide, Fungicide, & Virucide?
Biocide → kills microorganisms
Fungicide → Kills Fungi
Virucide → inactivates viruses
What is zone of inhibition?
It’s a area around the spot of the antibiotic where the bacteria does not grow.
What is disk-diffusion method?
It is disks containing antibiotics and used to determine microbial susceptibility to chemotherapeutic agents
What are the types of Disinfectants?
We have..
Surface Active Agents → Soaps & Detergents and Quaternary Ammonium Compounds
Phenols & Phenolics → Bisphenols → Hexachlorophene & Triclosan
What is a hexachlorophene used for?
Used in prescription lotion; used for surgical control procedures; used in nurseries
What is Triclosan used for?
It’s an ingredient in antibacterial soaps, toothpaste, cutting boards, knives.
What are Phenols and Phenolics?
They help control surgical infections in the operating room.
What is Quaternary Ammonium Compound?
It disrupts plasma membranes, so cell components leak out of the cell
Most effective at treating against Gram + bacteria.
What are soaps and detergents?
Limited germicidal action but does not remove microorganisms.
Biocides are more effective against Gram+ or Gram-?
Gram+, they tend to be more effective against it.
What does Gram - have?
Has an external LPS
Porins are structural openings in the wall of Gram -
Highly Selective
What are Mycobacteria?
These are
Non-endospore forming bacteria
Has greater normal resistance to chemical biocides
Has a waxy, lipid-rich component
Who are more resistant to disinfectants and antiseptics? Non-enveloped viruses or Enveloped Viruses?
Non-Enveloped viruses are more resistant than enveloped viruses