Biol 224 Lecture 29: Adrenal Glands, Pineal Glands, Pancreas, and other Endocrine Tissues
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
In class notes from 10/23 but transcribed from notebook to ipad
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Adrenal (Suprarenal) gland
Adrenal medulla
Adrenal Cortex

Adrenal Medulla
Neuro-endocrine cells
Secretes epinephrine (~75-80%) and norepinephrine (~20-25%)
Produce increased availability of energy resources
Produce increased rate and force of cardiac contractions and other sympathetic effects
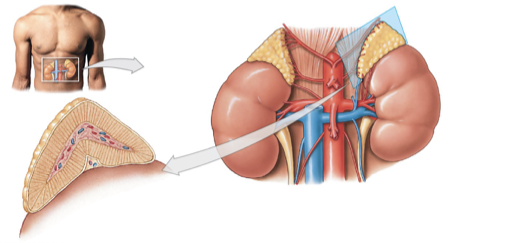
Adrenal Cortex
Gland cells
Secretes steroid hormones (corticosteroids)

How does the adrenal cortex produce increased availability of energy?
cause breakdown of glycogen in liver to release glucose for use by brain
cause breakdown of fat to release fatty acids for use by other cells of body
What is adrenal medulla controlled by?
Autonomic NS activity
Types of corticosteroids secreted by the adrenal cortex
Mineralocorticoids
Glucocorticoids
Androgens
Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)
Secreted if sodium is low, potassium is high, or bp is low
cause retention of sodium and water and loss of potassium
Why would aldosterone cause higher bp?
Causes the reabsorption of sodium, water follows where sodium is high, if in blood, larger volume of blood which equates to higher blood pressure
Glucocorticoids (cortisol)
Secreted in response to ACTH release from anterior pituitary and stress
Causes decrease use of glucose and increase rate of glycogen synthesis (mobilizies lipids and fatty acids for energy, conserves glucose for brain) → breaking down adipose tissue for energy saves glucose for brain
have anti-inflammatory effects
Androgens
Encourages bone and muscle growth, blood formation
primary role is in children and women; testes of adult males produces larger amounts
Pineal gland
Secretes melatonin

Increased sunlight exposure causes
Decreased melatonin secretion
Possible functions of pineal gland
Setting circadian rhythms
Anti-oxidant
Inhibiting reproductive functions (mostly in other animals, because they’d rather give birth in summer with longer days than winter)
Seasonal Affective Disorder
Depression correlated with decreased sunlight exposure and increase melatonin
Treatment: light therapy
Pancreas
99% of pancreas is exocrine cells (Breaks down everything)
secretes enzymes into digestive tract
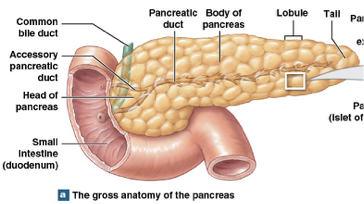
Endocrine cells occur in small clusters
Islets of Langerhans or pancreatic islets
Secrete hormones involved in regulation of glucose levels
Alpha Cells
Secrete glucagon in response to blood glucose levels
Beta cells
Secrete insulin in response to high blood glucose levels
Glucose storage
Don’t store much glucose
Tiny amounts in liver stored as glycogen (chain of glucose)
Liver makes glucose from fatty acids
gluconeogenesis is triggered by glycogen → causes us to use fatty acids
Why is insulin called an absorptive hormone?
Insulin lowers blood glucose levels
when we eat we absorb many things, insulin controls where these nutrients/macromolecules go
What is insulin secreted by?
Beta cells
Function of Insulin
Lowers blood glucose levels
increases rate of glucose uptake and utilization in insulin dependent cells
glucose used for energy production and/or synthesis of glycogen and other energy storage macromolecules
increased uptake of fatty acids and synthesis of triglycerides in adipose cells
Increased uptake of amino acids and synthesis of proteins
Glucagon is secreted by what
Alpha cells
Glucagon Function
Raises blood glucose levels
Increase rate of glycogen breakdown
Increase glucose manufactured by liver (gluconeogenesis from amino acids)
Increased release of fatty acids into blood from adipose tissue
glucose sparing: most cells start using FA as energy source instead of glucose
Glycogen breakdown in liver
Glucose released into blood
Glycogen breakdown in muscle
Glucose remains in muscle cells
Diabetes
Excess urination
Diabetes insipidus
Polyuria and inadequate ADH secretion
Polyuria
Excess urine production
Diabetes mellitus
Glucose
Polyuria
Glycosuria
Hyperglycemia
Breakdown of lipids and proteins as energy source for cell metabolism (ketone bodies, ketoacidosis)
Glycosuria
Glucose in urine
Hyperglycermia
Abnormally high glucose levels (normal while fasting is 100 mg, here it’s in couple hundreds)
No insulin receptors or they don’t bind to insulin
Ketone bodies and Ketoacidosis
a life-threatening complication of diabetes that occurs when the body does not have enough insulin to use glucose for energy. As a result, the body breaks down fat for fuel, producing ketones that accumulate in the blood and make it acidic.
Why does diabetes make you pee more?
Urine is made from plasma, lots of water drawn to glucose, ton of water in kidneys makes you pee more
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
1 and 2
Type 1
Insulin dependent (autoimmune)
inadequate insulin production
body destroys beta receptors on pancreas which means it cannot make insulin
Type 2
Non - insulin dependent
inadequate insulin receptor response
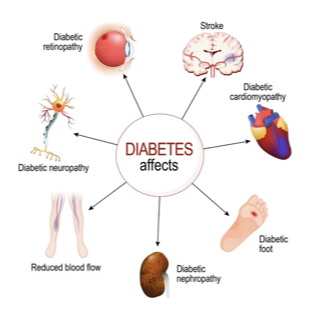
Effects of high glucose and or low insulin
Diabetic microvascular disorders and diabetic cardiovascular changes
Endocrine tissue of other systems
Adipose tissue
Intestine
Gonads
Kidneys
Adipose Tissue
Leptin feedback control for appetite (tells us that we have energy and don’t need to eat, but doesn’t work well on humans)
Resistin - reduces insulin sensitivity (Main reason why overweight people have higher risk of diabetes)
Fat secretes hormones
Adipose: energy storage
Intestine
Coordination of digestive activities
Gonads
Ovaries and testes secrete hormones involved in reproductive functions
Kidneys
Hormones regulating blood volume, blood pressure, blood pressure levels
Draw what happens in diabetes
