5. Shoulder - Lopez
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Bone Framework of the Shoulder (3)
Proximal Humerus
Pectoral girdle
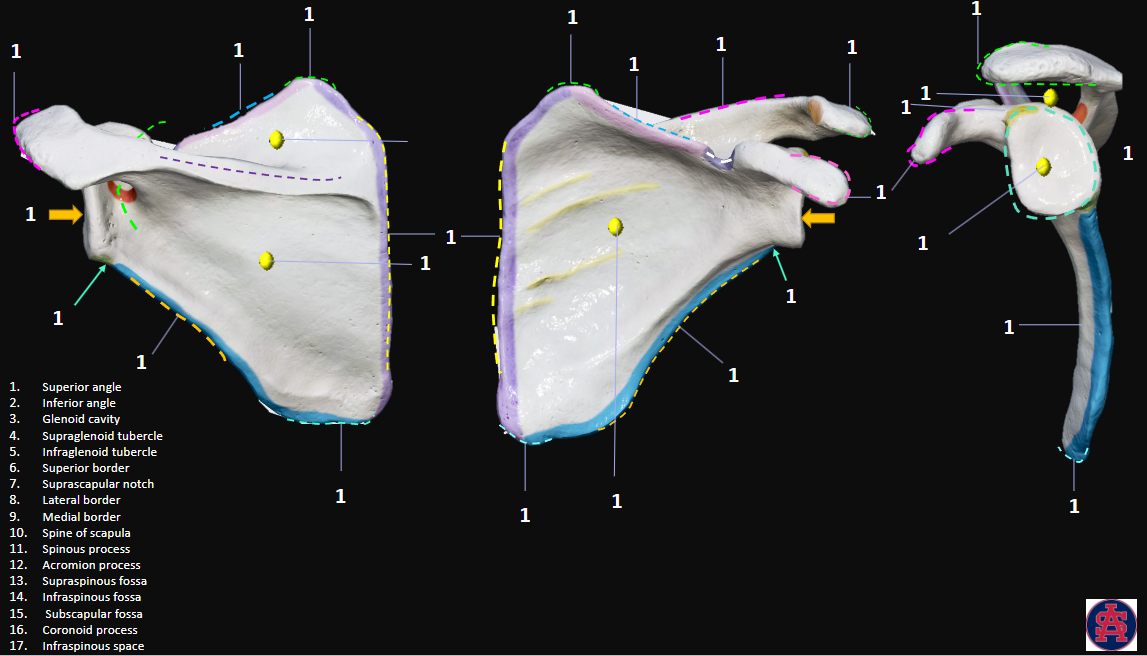
Scapula
Clavicle
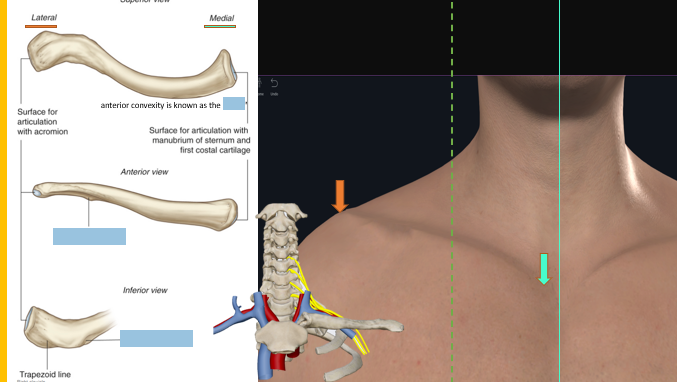
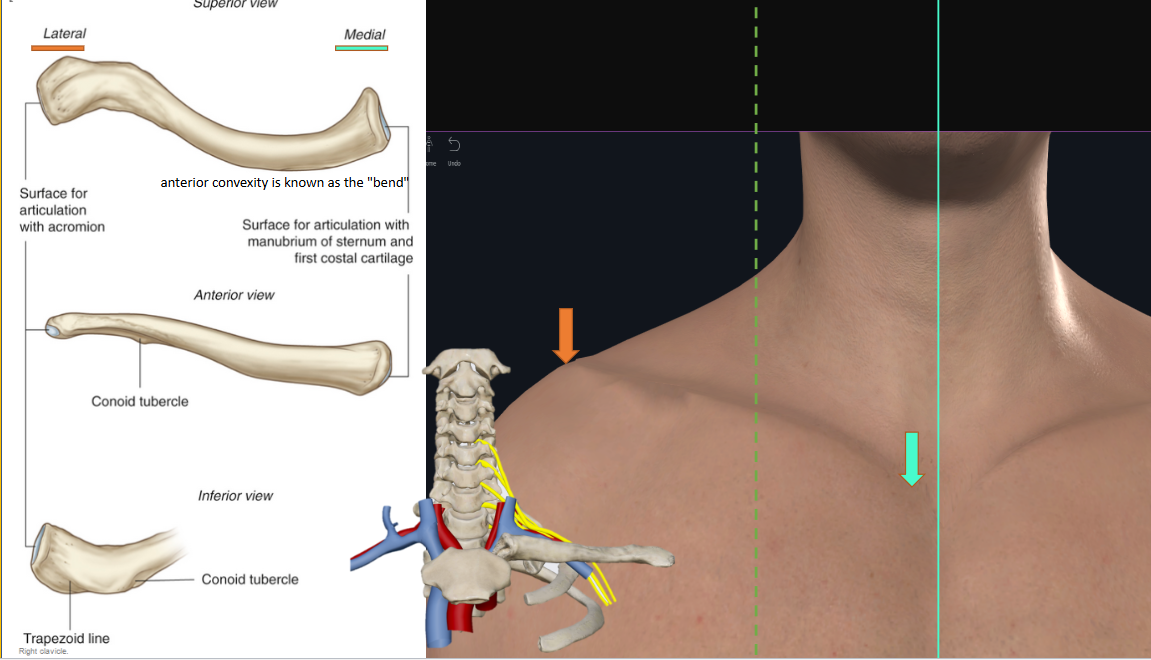
Scapula
Where is it positioned?
Where is the medial border?
ROM results in what?
scapula is usually positioned between the 2nd and 7th ribs
medial border is located about 6cm lateral to the spine
ROM results w/ cooperation between the SC and AC joints
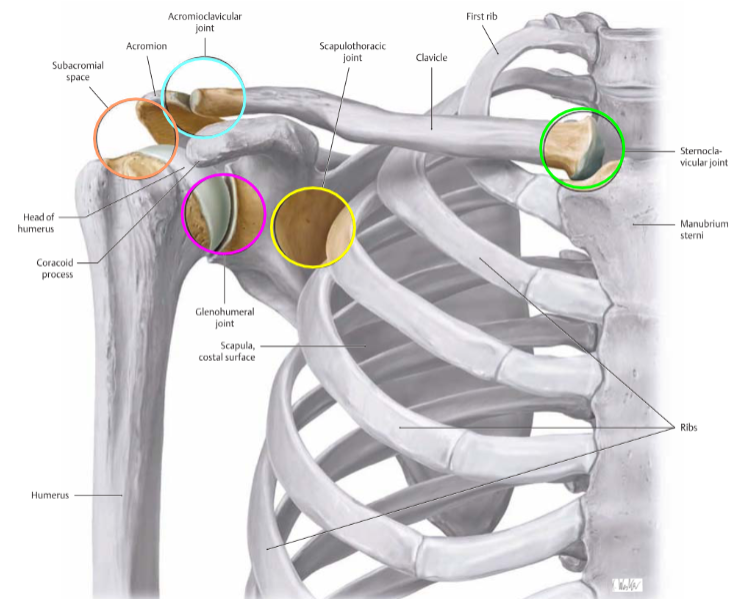
5 Shoulder Joints and Spaces (4, 1)
which one is not a true joint
Scapulothoracic
not a true joint
Sternoclavicular
Acromioclavicular
Glenohumeral
Subacromial Space
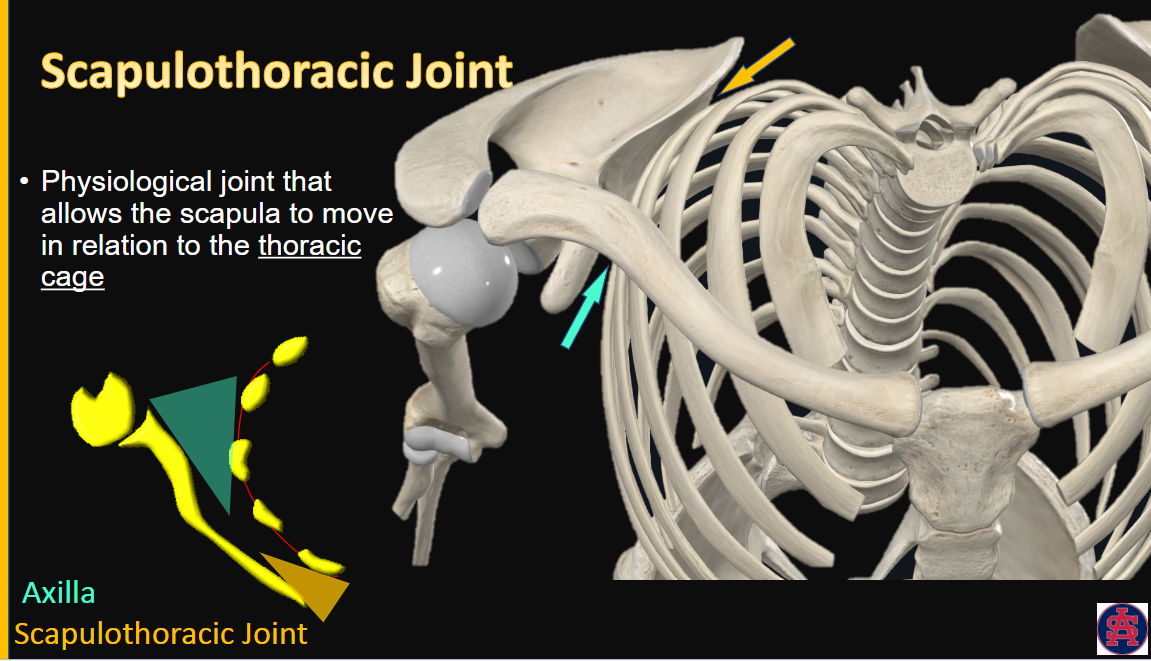
Scapulothoracic Joint
function
located where?
physiological joint that allows the scapula to move in relation to the thoracic cage
between rib cage and scapula
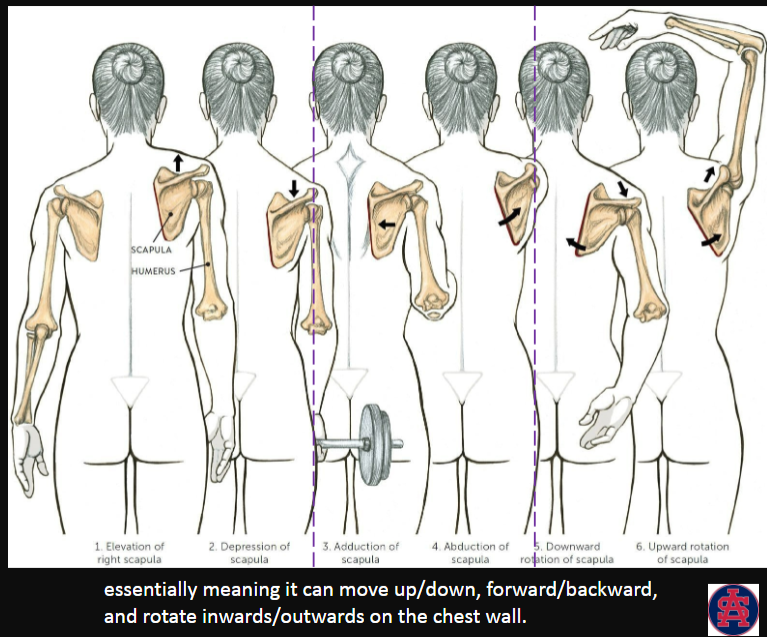
What are the 3 degrees of freedom of the scapula?
elevation/depression
protraction/retraction
downward rotation/upward rotation
aka
up/down
forward/backward
rotate inwards/outwards on the chest wall
Acromioclavicular Joint
joint between what?
what type of joint?
functions? (3)
between Scapula and Clavicle
AC joint is a multiaxial joint
3 Degrees of Freedom:
protraction/retraction
elevation/depression
total range of motion 15o
lateral rotation/medial rotation
total range of motion 30o
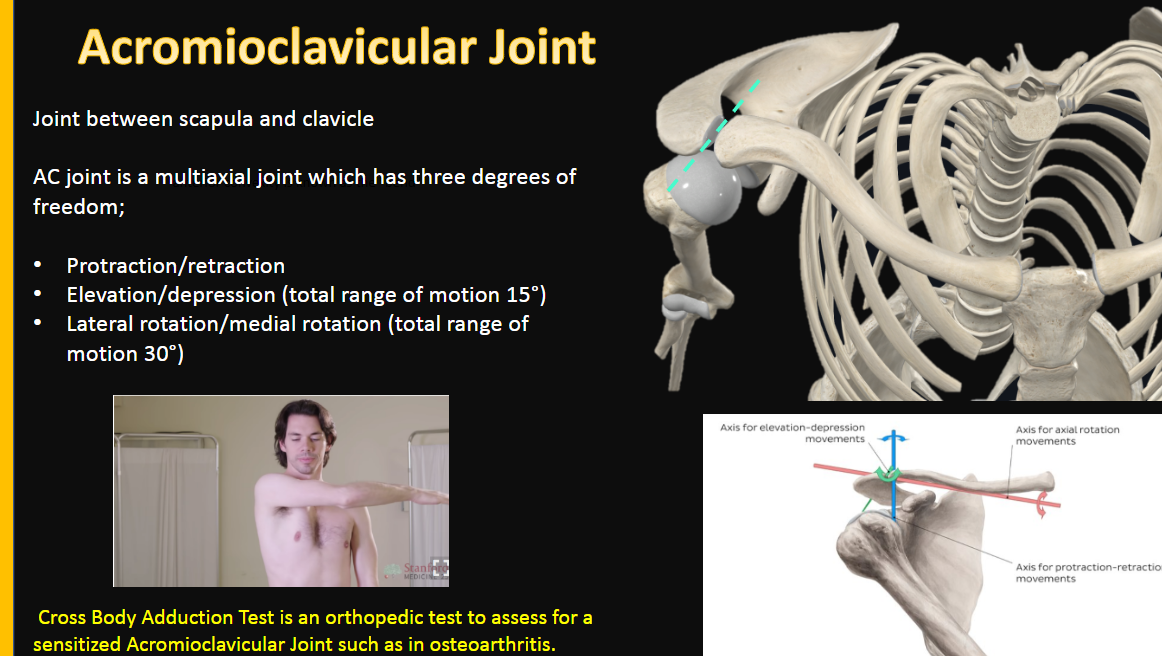
Acromioclavicular Joint
what test can assess this joint for osteoarthritis?
Cross Body Adduction Test
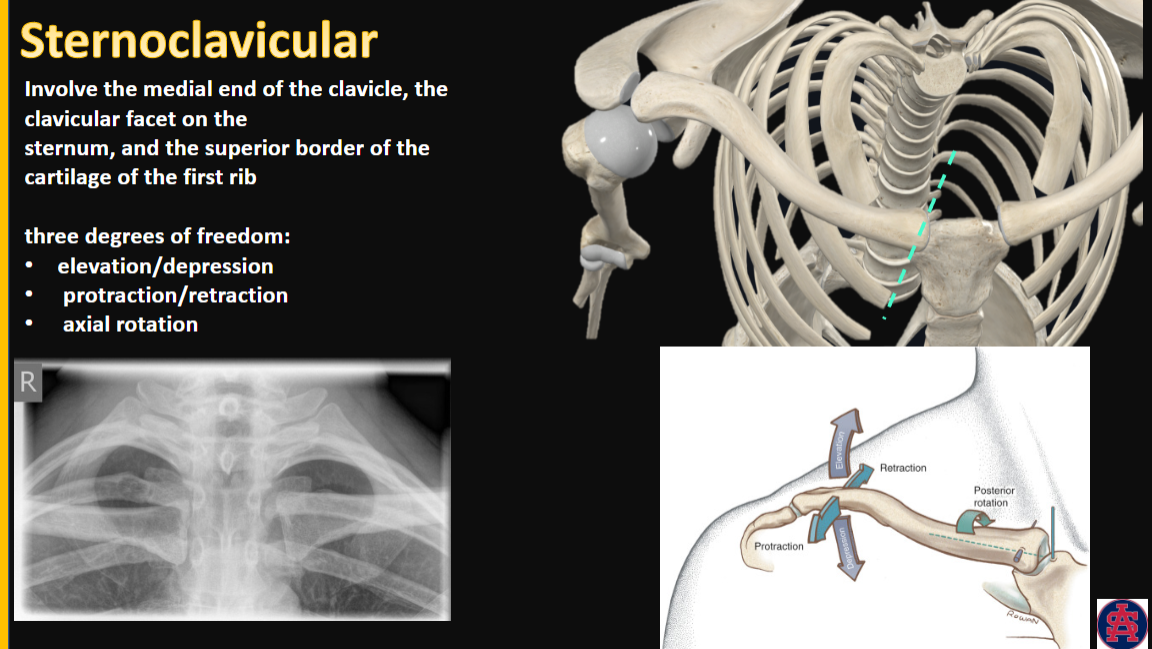
Sternoclavicular Joint
involves what? (3)
functions (3)
involves:
medial end of the clavicle
clavicular facet on the sternum
superior border of the cartilage of the first rib
3 degrees of freedom:
elevation/depression
protraction/retraction
axial rotation
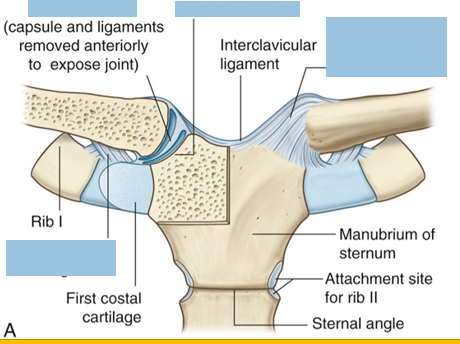
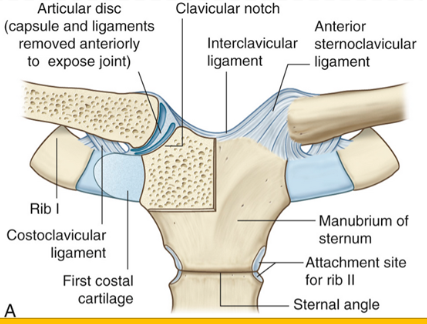
The following joints provide Ligament Stability to what ligaments?
Sternoclavicular Joint (3)
Acromioclavicular Joint (2)
Coracoclavicular Joint (2)
Sternoclavicular Joint
Costoclavicular ligament
Sternoclavicular ligament
Articular disc
Acromioclavicular Joint
Acromioclavicular ligament
Coracoacromial ligament
Coracoclavicular
Trapezoid
Coronoid
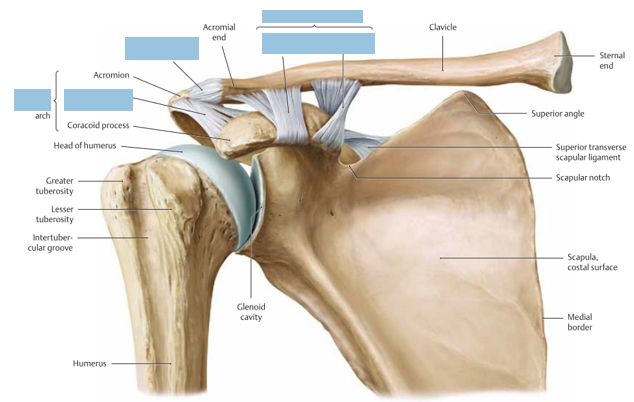
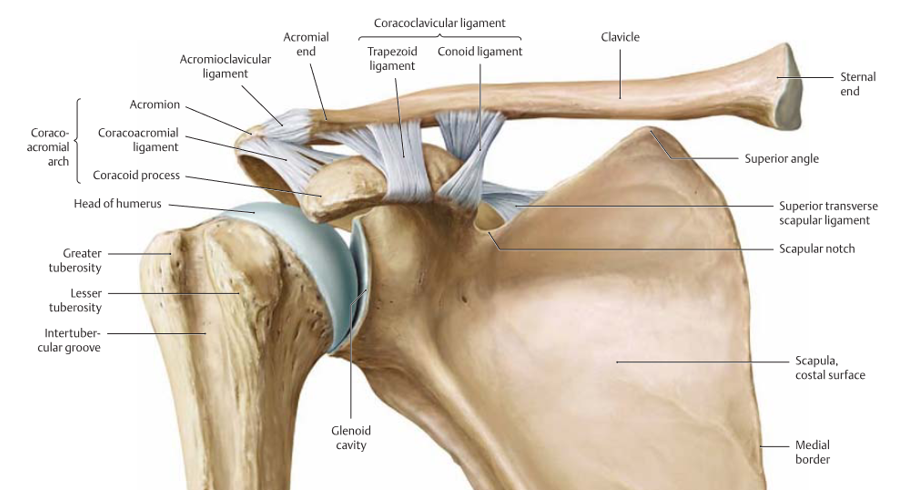
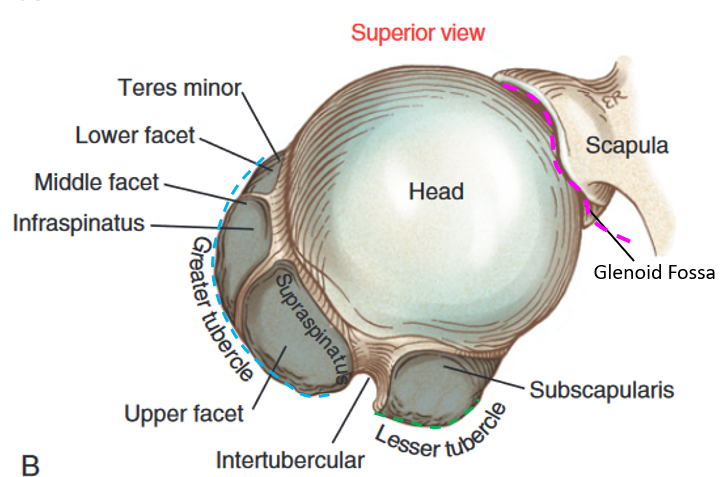
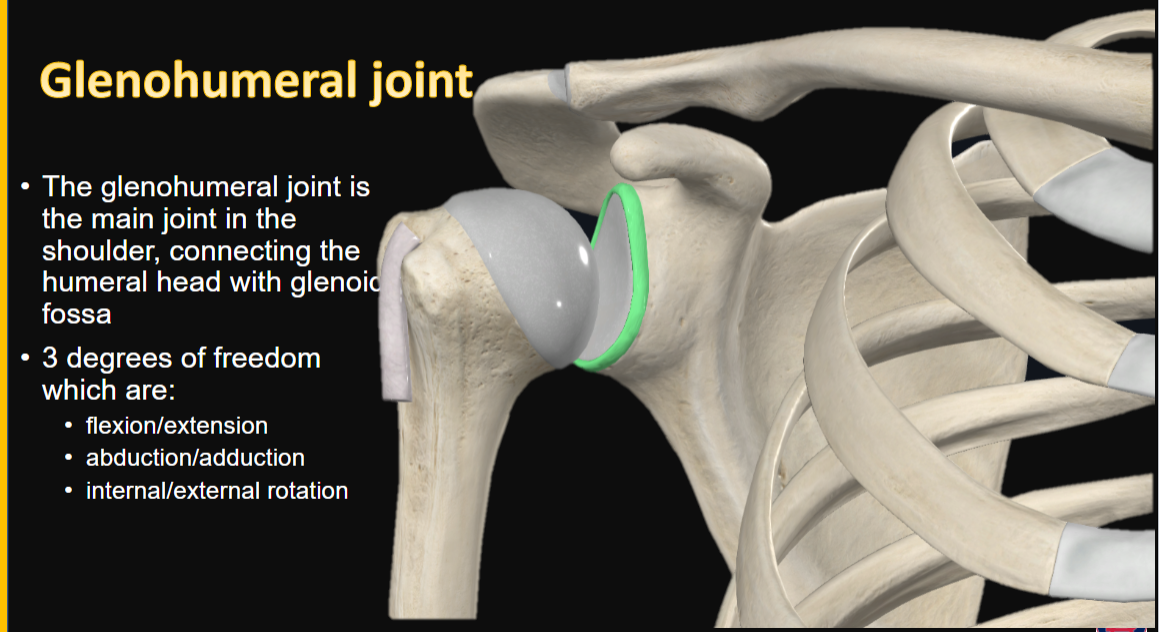
Glenohumeral Joint
connects what? (2)
characteristic
function (3)
main joint in the shoulder
connects the humeral head with glenoid fossa
3 degrees of freedom
flexion/extension
abduction/adduction
internal/external rotation
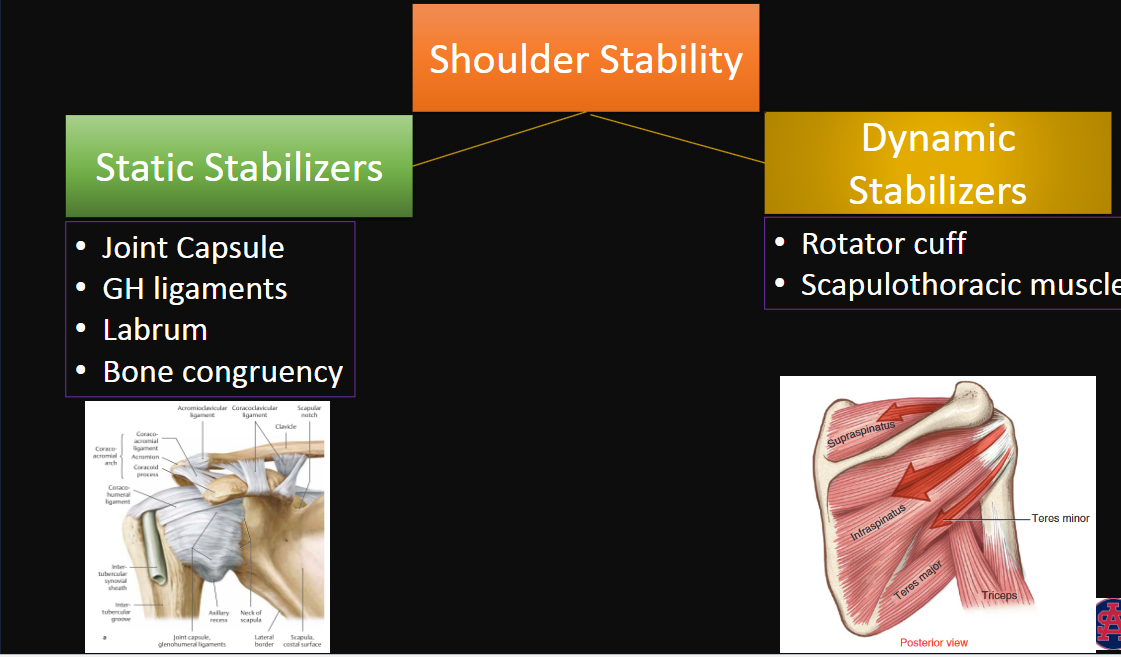
Shoulder Stability
Further divided into what types? (2)
Examples of each (4, 2)
Static Stabilizers and Dynamic Stabilizers
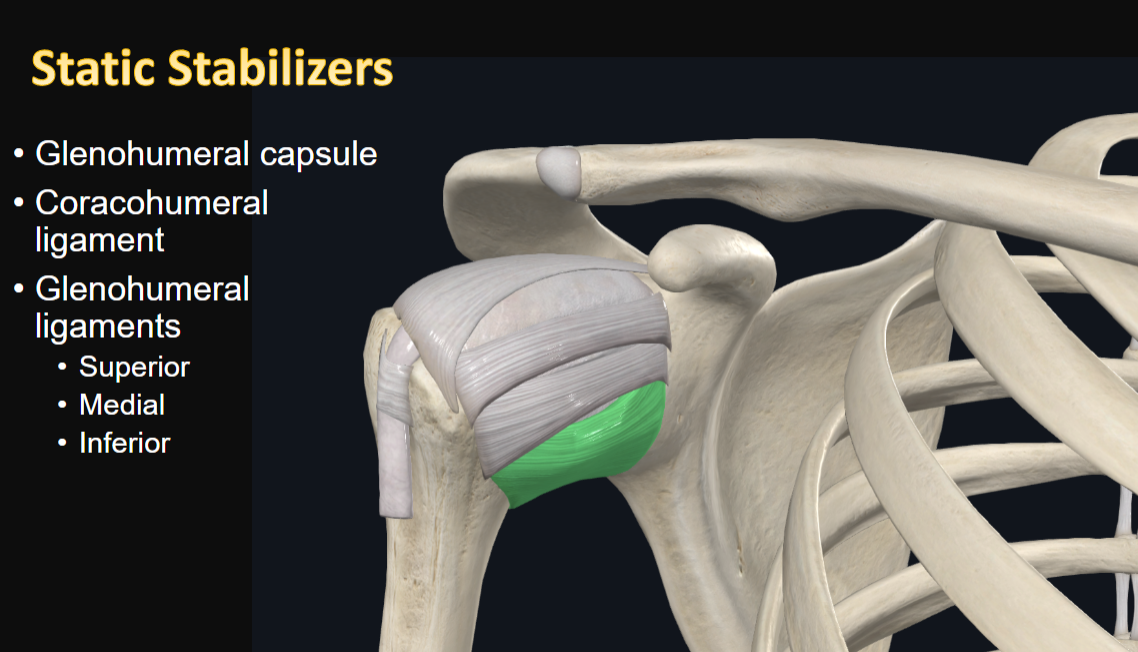
Static Stabilizers
examples (3)
Static Stabilizers
Glenohumeral capsule
Coracohumeral ligament
Glenohumeral ligaments
Superior
Medial
Inferior
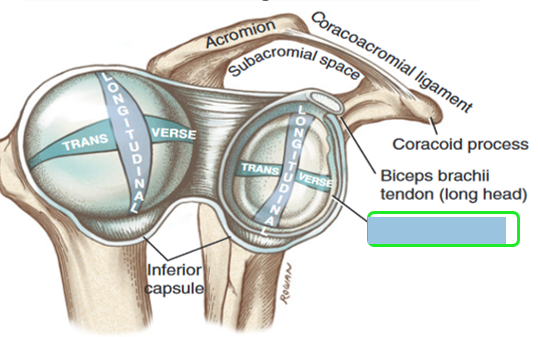
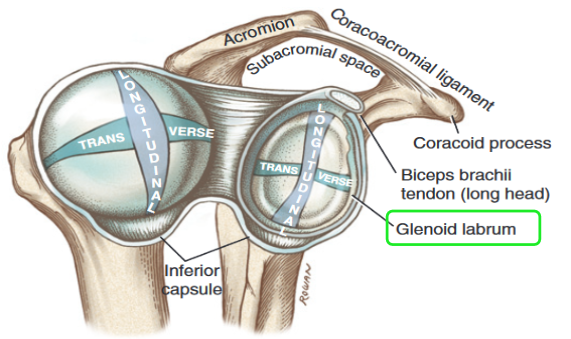
What muscle groups move the shoulder? (2)
Axio-appendicular Muscles
Scapulohumeral Muscles
Axio-appendicular Muscles
connect what?
primary functions (2)
connect the axial skeleton (spine/ribs) to the appendicular skeleton (shoulder girdle, upper limb)
functions:
stabilize and move the shoulder girdle
Axio-appendicular Muscles
further divided into what 2 groups?
muscles of each group (4, 3)
Anterior Axio-appendicular Muscles
Pectoralis Major
Pectoralis Minor
Subclavius
Serratus Anterior
Posterior Axio-appendicular Muscles
Trapezius
Rhomboids
Latissimus Dorsi
Scapulohumeral Muscles
connect what? (2)
function
connect the Scapula to the Humerus
primarily moves the shoulder joint
Scapulohumeral Muscles
muscles within this group (3 - 1,1,4)
Muscles:
Deltoid
Teres Major
Rotator cuff muscles
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres Minor
Subscapularis
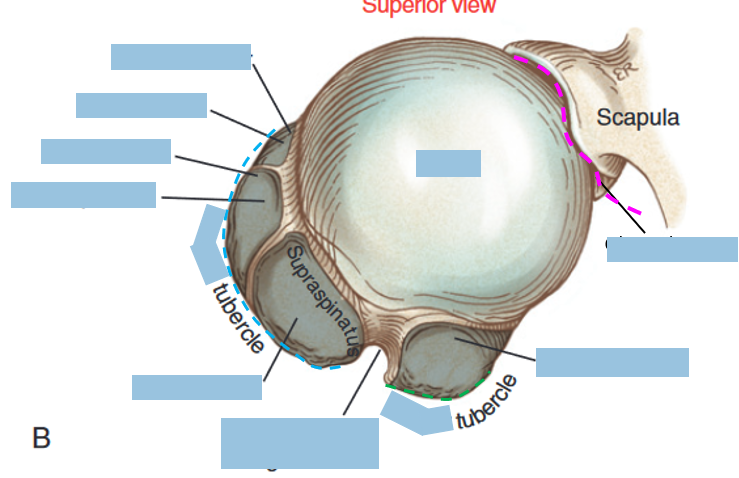
Rotator Cuff Muscles
part of what muscle group?
muscles within this group? (4)
Rotator cuff muscles
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres Minor
Subscapularis
Scapulohumeral Muslces
Trapezius
action (4)
innervation (2)
location
Trapezius
action:
elevates, retracts and rotates the scapula
lower fibers depress the scapula
innervation
spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
cervical plexus (C3, C4)
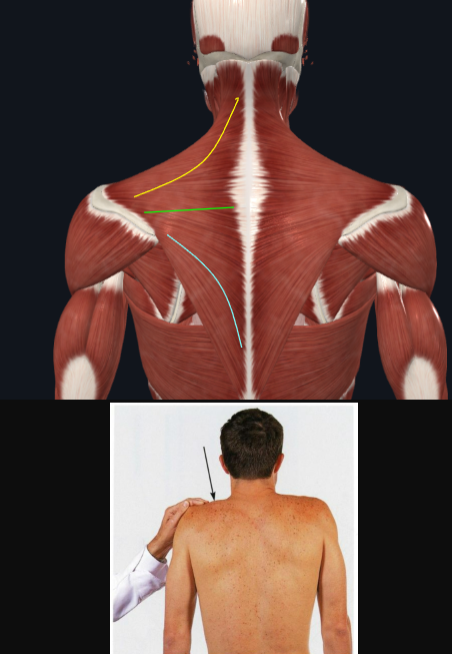
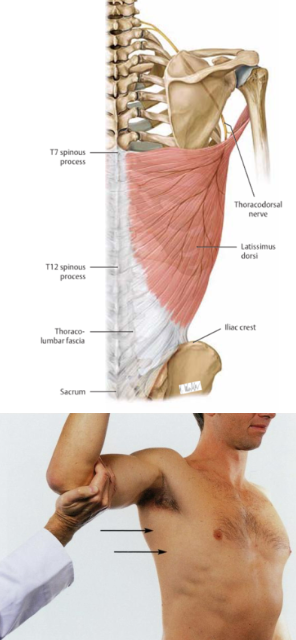
Latissimus Dorsi
action (3)
innervation (1)
location
Latissimus Dorsi
action:
extends, adducts, and medially rotates the humerus
innervation:
thoracodorsal nerve (C6-C8)
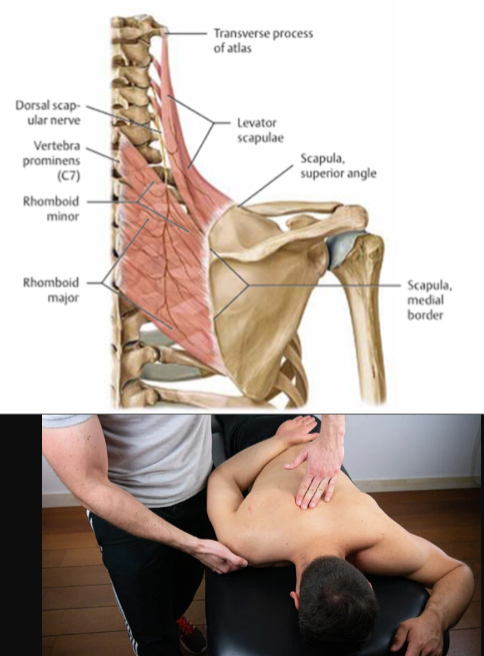
Levator Scapulae
action (3)
innervation (2)
location
Levator Scapulae
action:
elevates the scapula
tilts its glenoid cavity inferiorly by rotating the scapula
innervaation:
dorsal scapular nerve (C5)
cervical nerves (C3, C4)
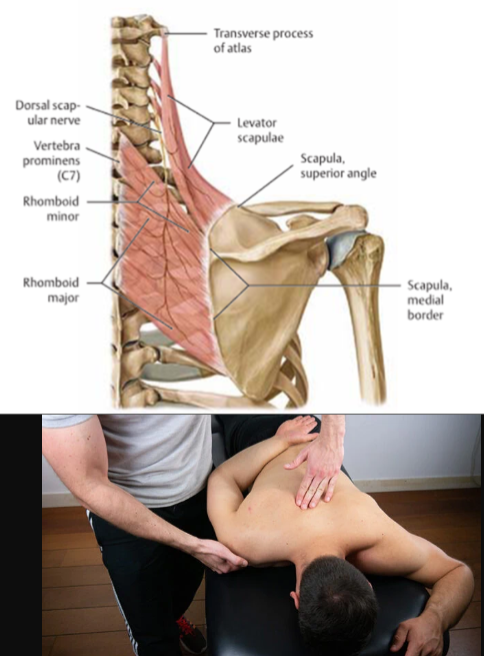
Rhomboid Major/Minor
action (4)
innervation (1)
location
Rhomboid Major/Minor
action:
retracts the scapula
rotates the scapula to depress glenoid cavity
stabilizes the scapula
innervation:
dorsal scapular nerve (C4, C5)
Pectoralis Major
action (3)
innervation (2)
location
Pectoralis Major
action:
adducts and medially rotates the humerus
clavicular head assists in flexion
innervation:
medial + lateral pectoral nerves (C5-T1)
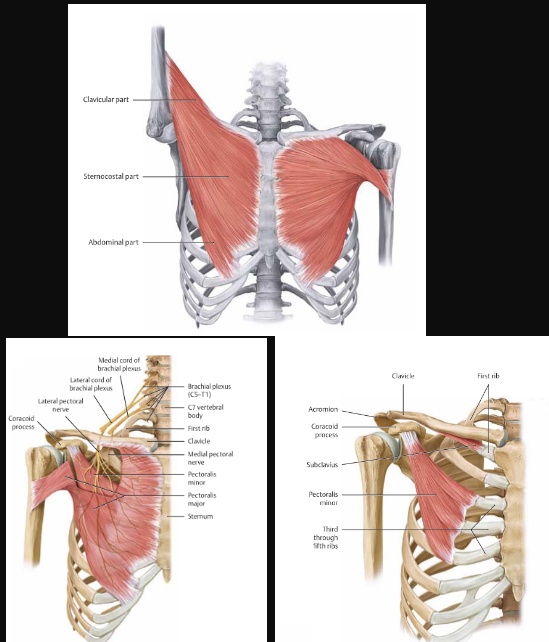
Pectoralis Minor
action (3)
innervation (1)
location
Pectoralis Minor
action:
stabilizes the scapula by drawing it inferiorly and anteriorly against the thoracic wall
innervation:
medial pectoral nerve (C8, T1)
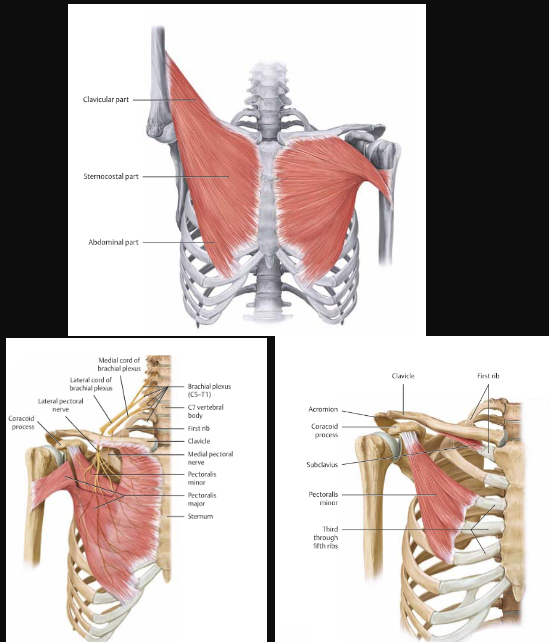
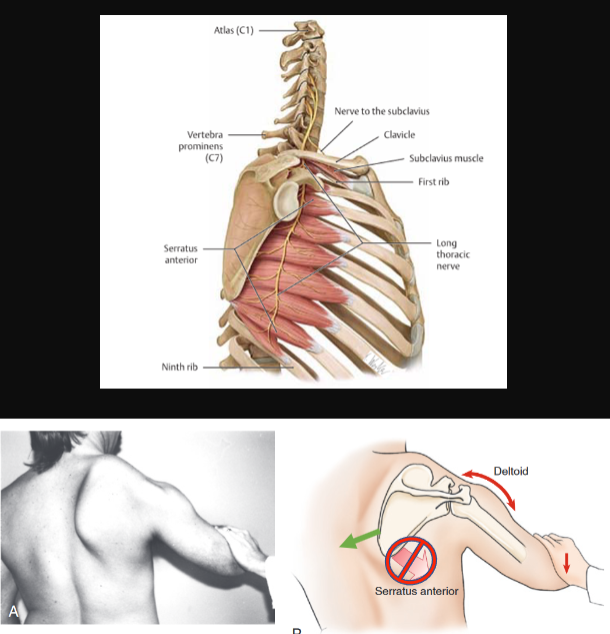
Serratus Anterior
action (3)
innervation (1)
location
injury causes what
Serratus Anterior
action:
protracts and rotates the scapula
holds it against the thoracic wall
innervation:
long thoracic nerve (C5-C7)
injury causes Winged Scapula
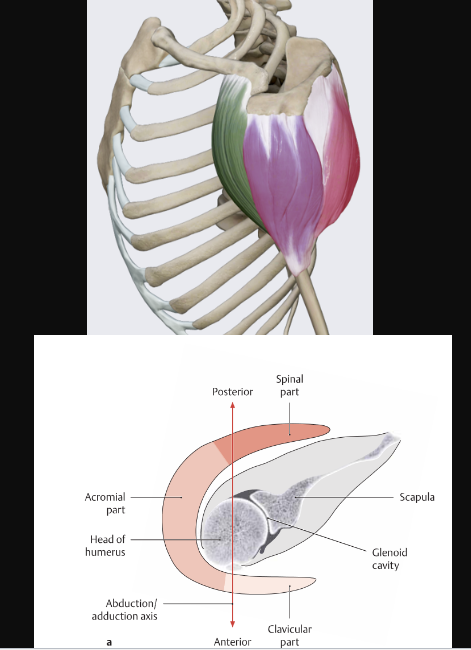
Deltoid
action (3-2,1,2)
innervation (1)
location
Deltoid
action:
anterior fibers - flex and medially rotate the arm
middle fibers - abduct the arm
posterior fibers - extend and laterally rotate the arm
innervation:
axillary nerve
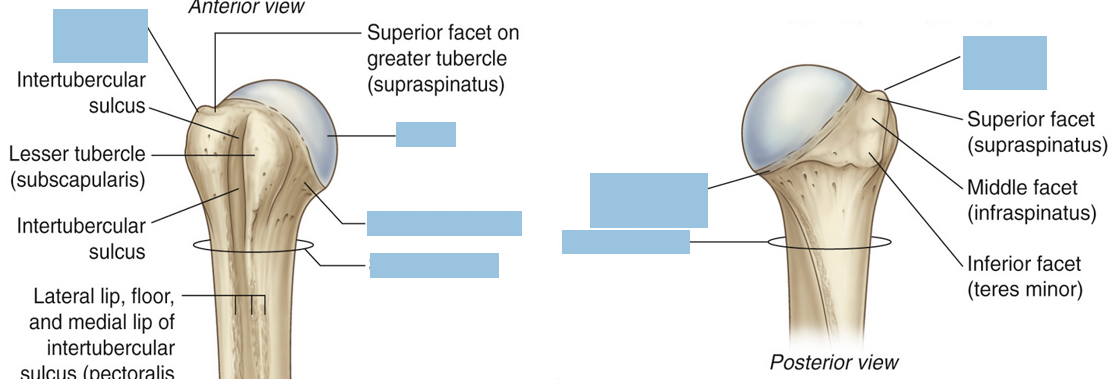
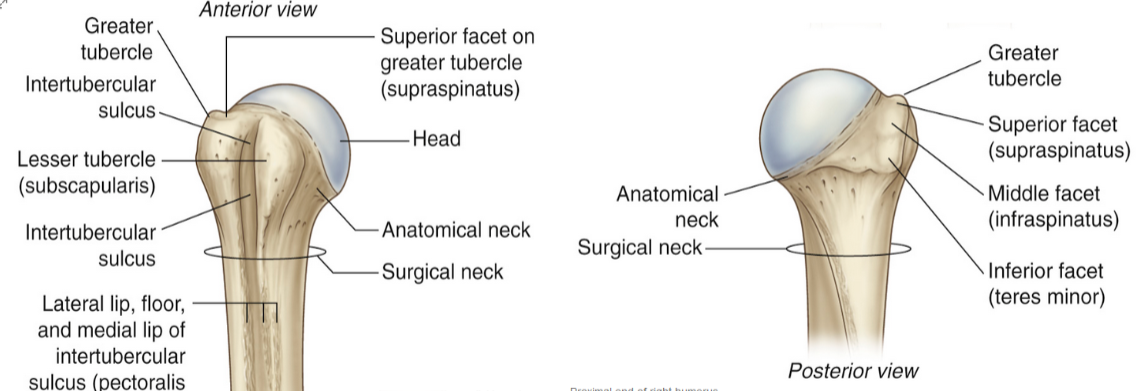
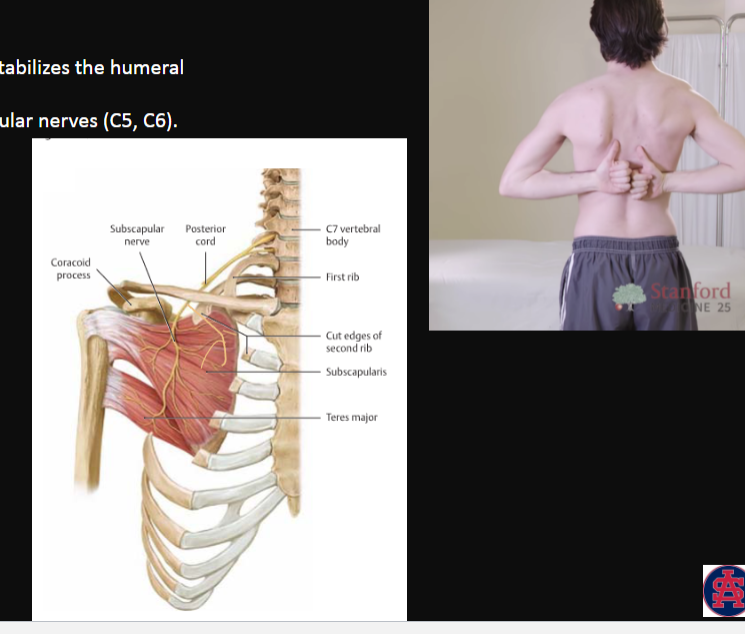
Subscapularis
action (2)
attaches where?
innervation (2)
location
Subscapularis
attaches to the lesser tubercle of the humerus!
action:
medially rotates the arm
stabilizes the humeral head
innervation:
upper/lower subscapular nerves (C5, C6)
Supraspinatus
action (2)
innervation (1)
location
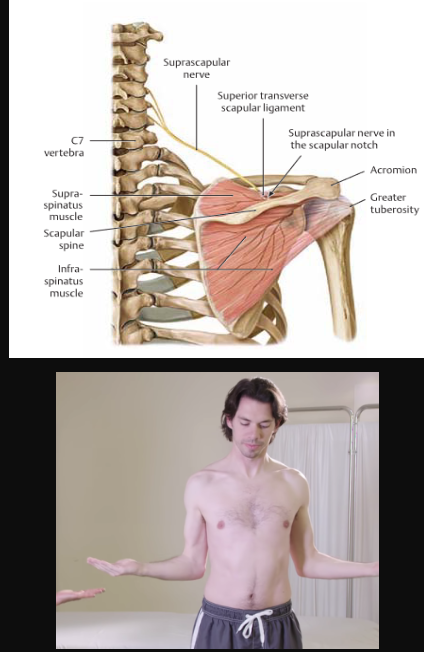
Supraspinatus
action:
initiates abduction of the arm (first 15o)
stabilizes the humeral head
innervation:
suprascapular nerve (C5, C6)
Infraspinatus
action (2)
innervation (1)
location
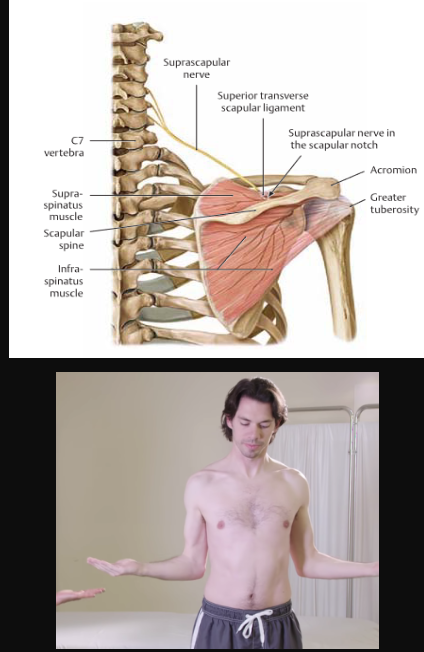
Infraspinatus
action:
laterally rotates the arm
stabilizes the humeral head
innervation:
suprascapular nerve (C5, C6)
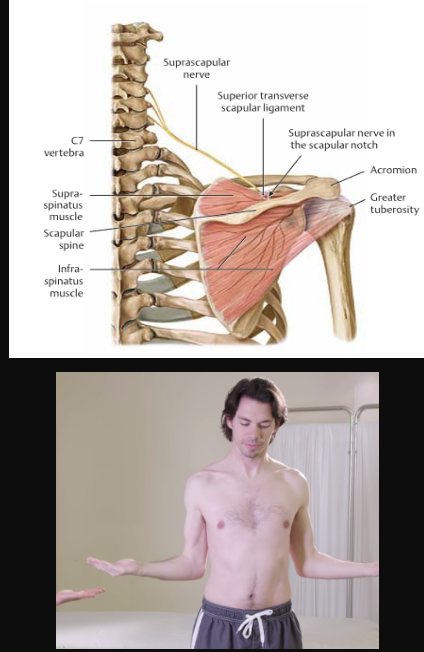
Teres Minor
action (2)
innervation (1)
location
Teres Minor
action:
laterally rotates the arm
stabilizes the humeral head
innervation:
axillary nerve
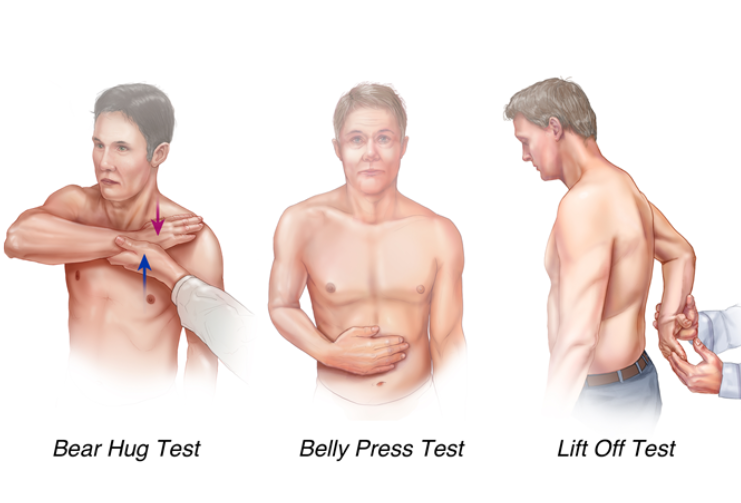
Testing for Subscapularis (3)
Bear Hug Test
Belly Press Test
Lift Off Test
What joint is the most mobile joints in the body? allowing a wide range of motion (ROM)
The Shoulder Joint
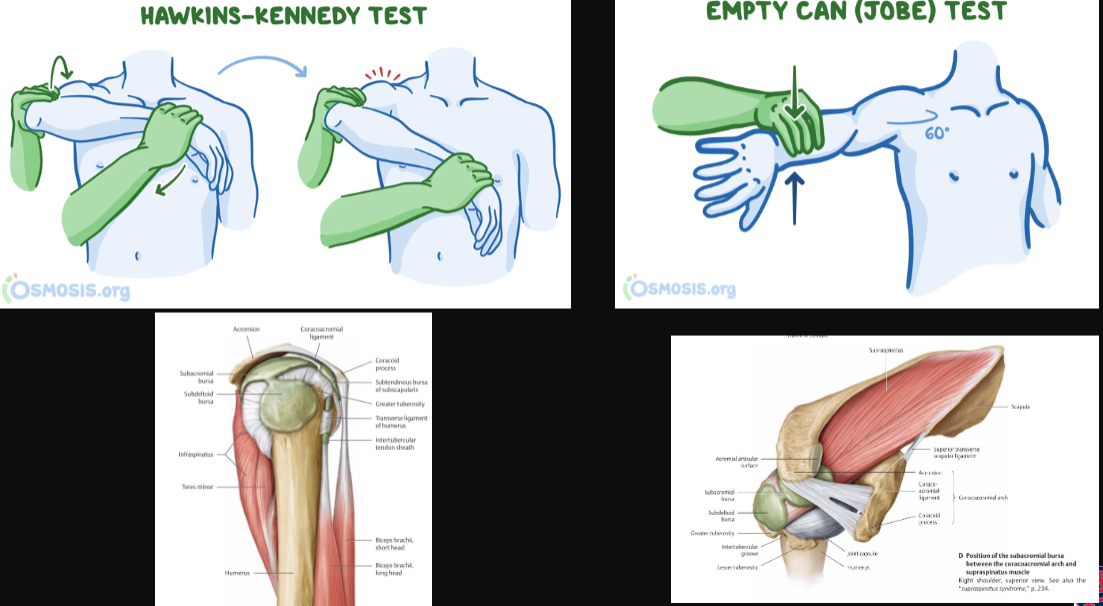
Supraspinatus Tests? (2)
Hawkins-Kennedy Test
Empty Can (Jobe) Test
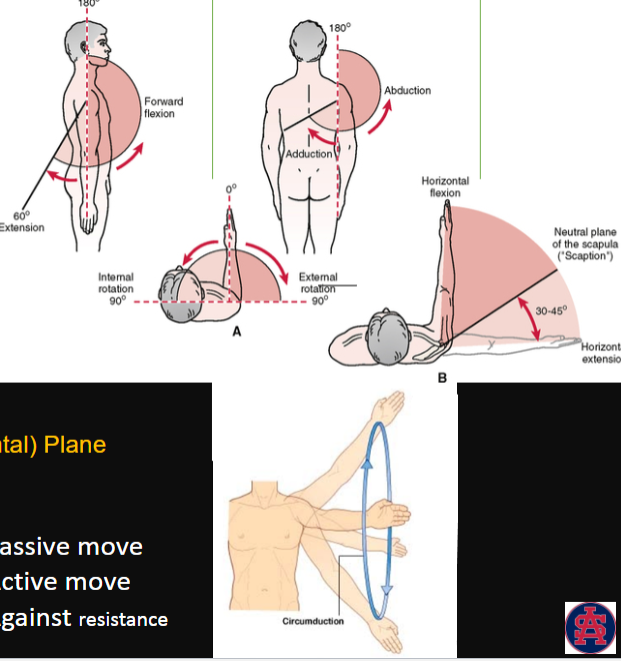
Shoulder Joint
movements in the Sagittal Plane? (2)
movements in the Coronal (Frontal) Plane (2)
multiplanar movement? (1)
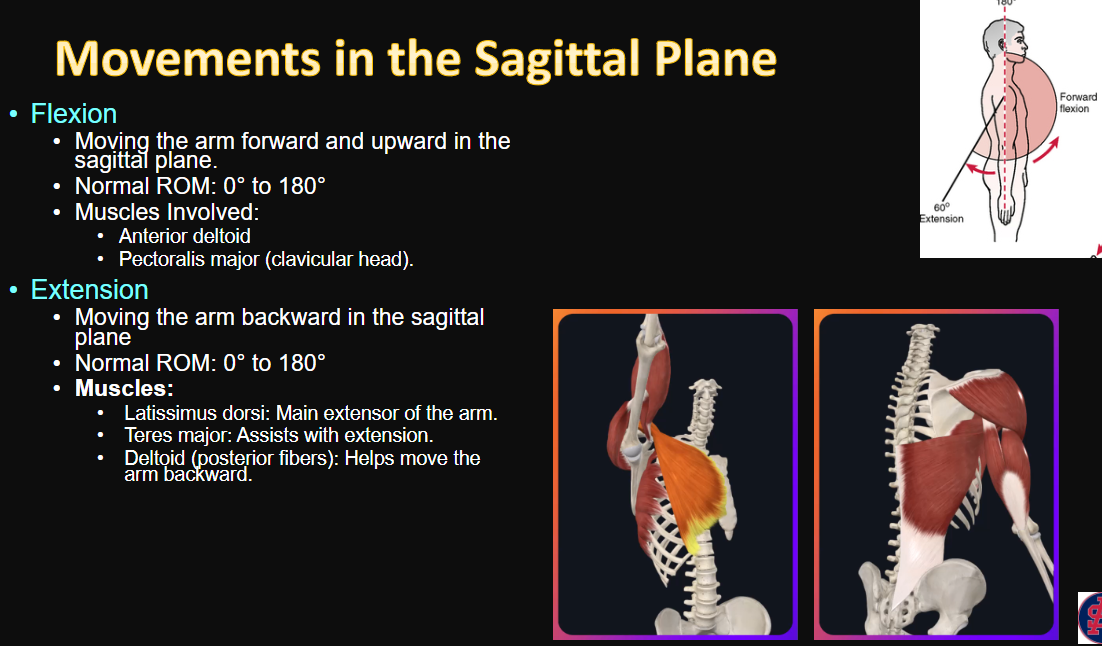
Movements in the Sagittal Plane
flexion
extension
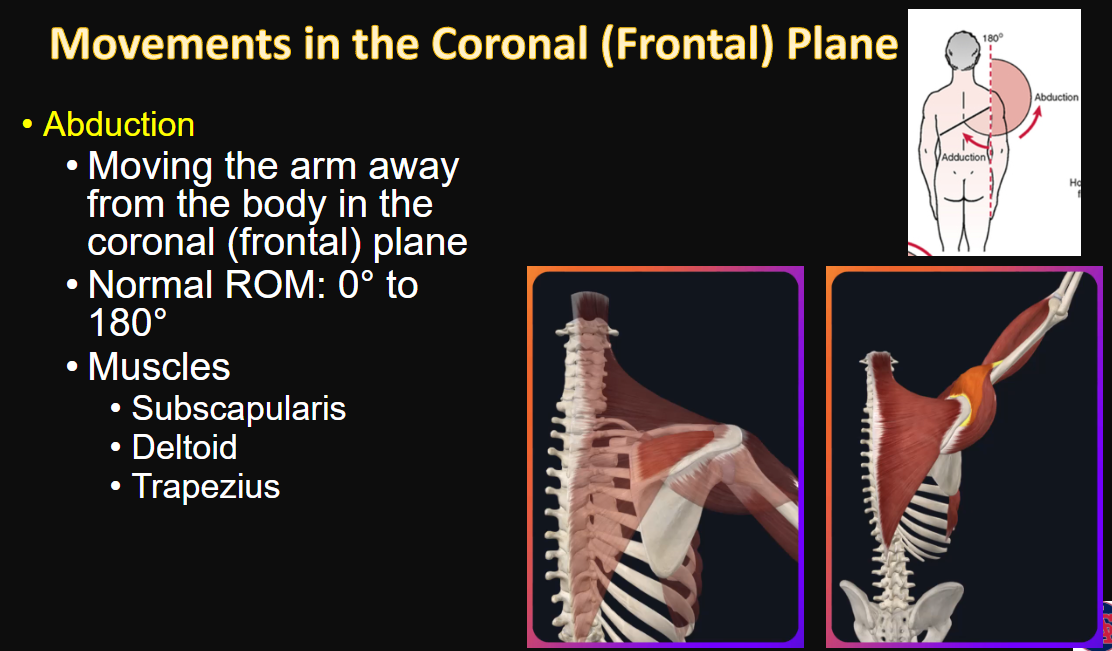
Movements in the Coronal (Frontal) Plane
adduction
abduction
Multiplanar movement
circumduction
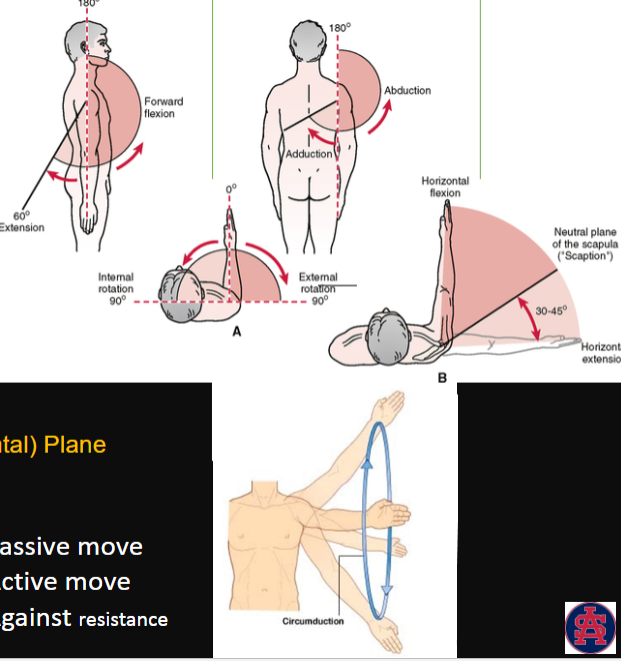
Shoulder Joint
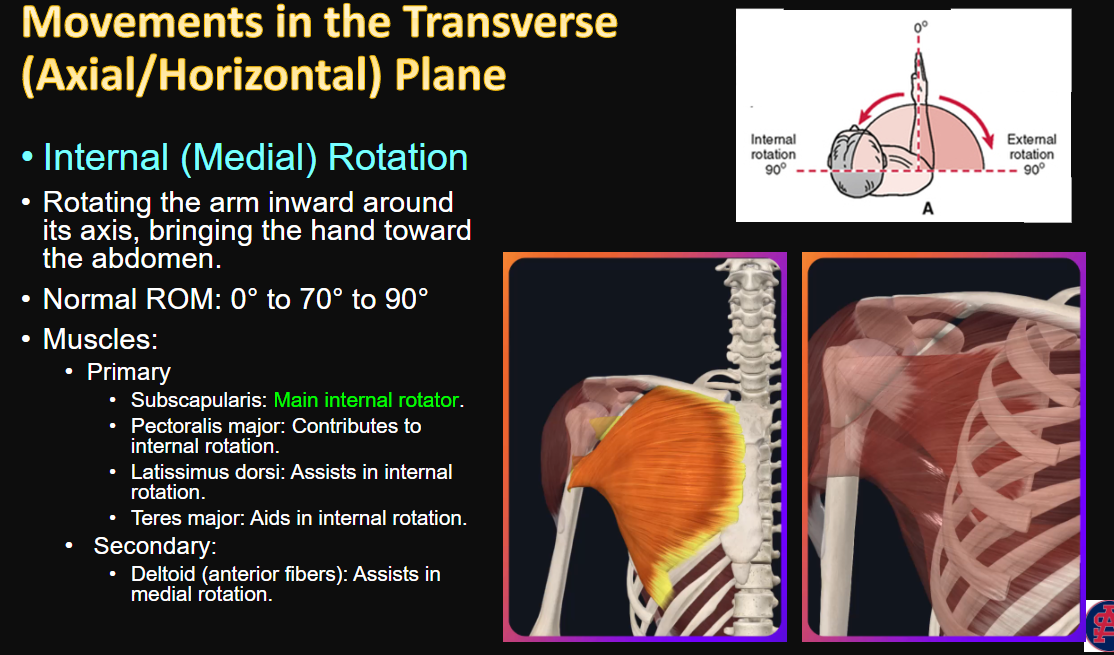
movements in the Transverse (Axial/Horizontal) Plane? (4)
Internal (medial) rotation
External (lateral) rotation
Horizontal Abduction/flexion
Horizontal Adduction/extension
Movements in the Sagittal Plane
2 groups?
movement, ROM, and muscles of each
2, 1, 2
1, 1, 3
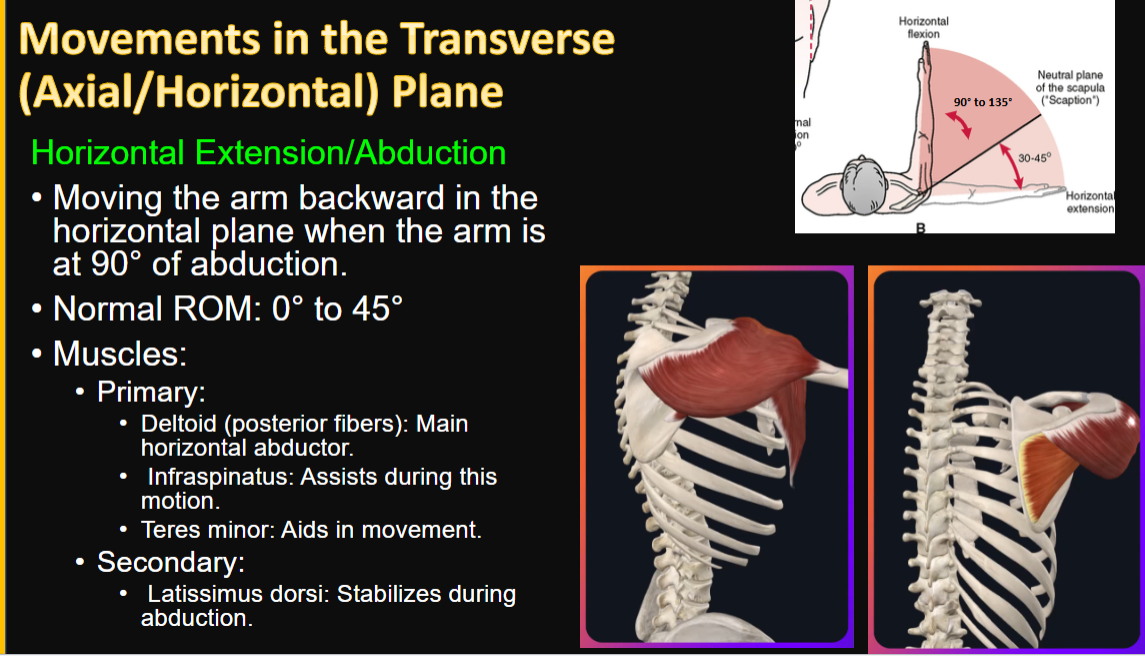
Movements in the Transverse Plane
Horizontal Extension/Abduction
movement, ROM, and muscles
1, 1, 4
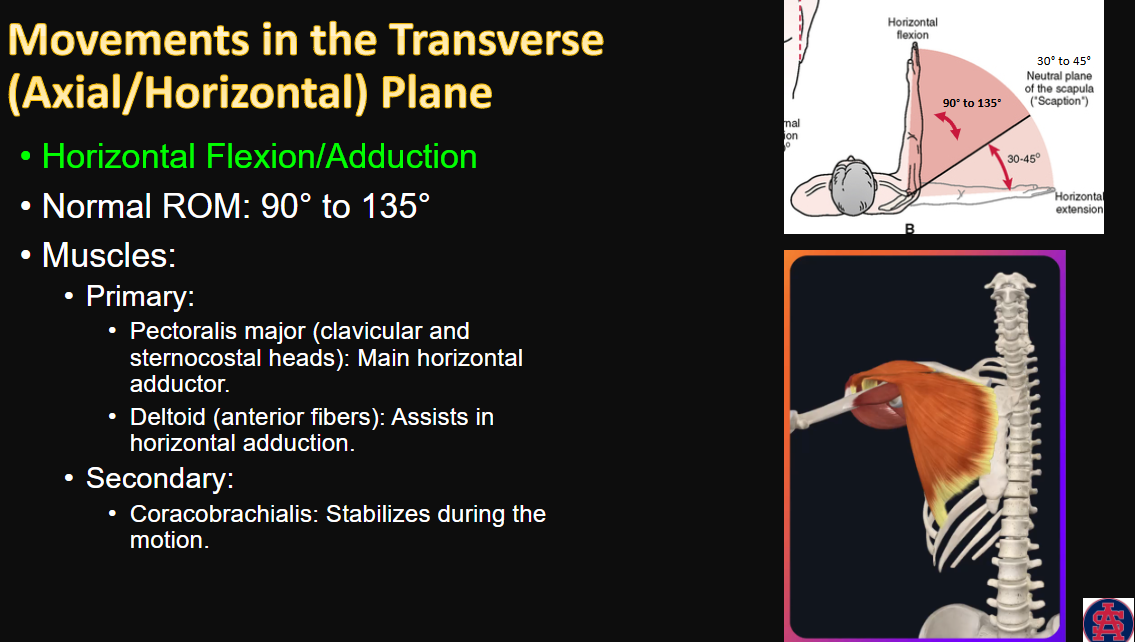
Movements in the Transverse Plane
Horizontal Flexion/Adduction
movement, ROM, and muscles
1, 1, 3
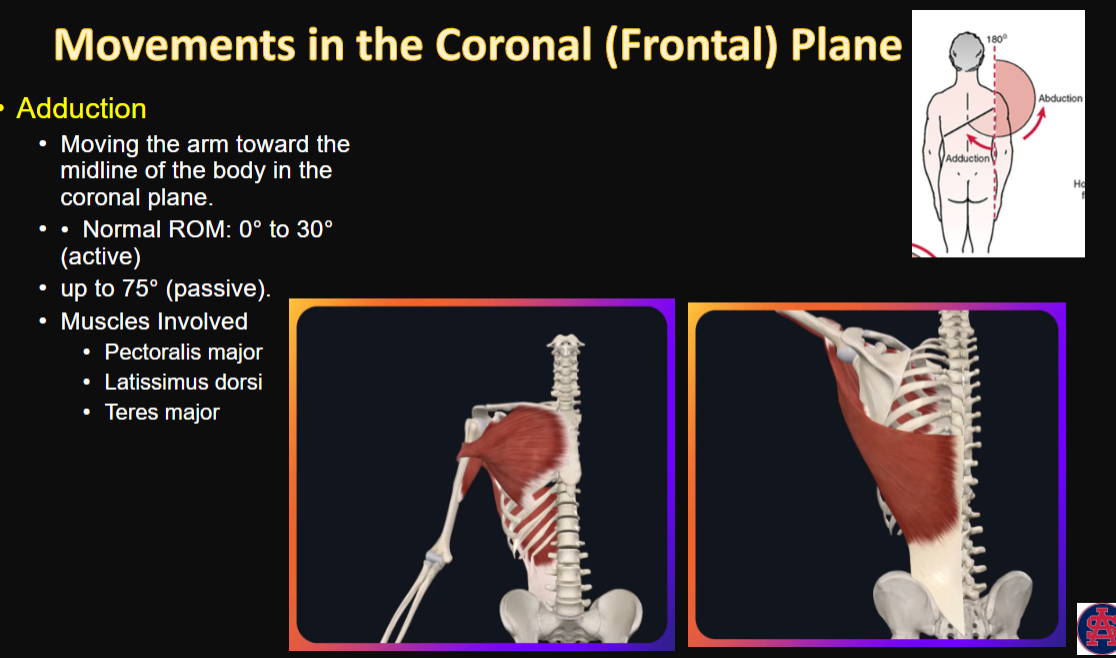
Movements in the Coronal (Frontal) Plane
Adduction
movement, ROM, and muscles
1, 2, 3
Movements in the Coronal (Frontal) Plane
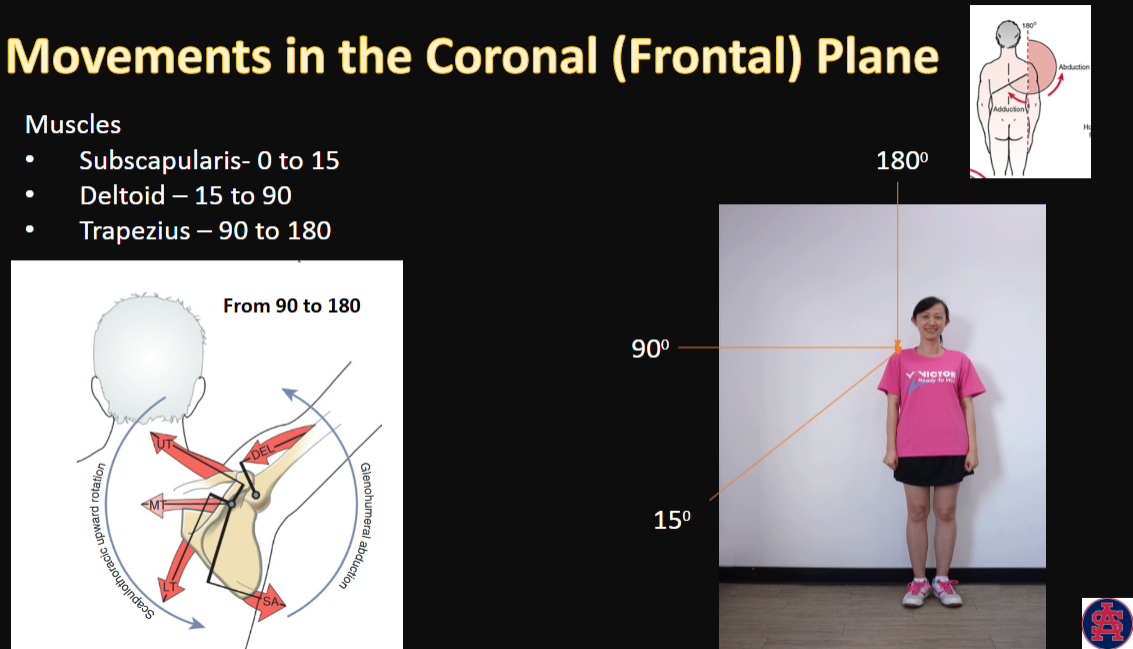
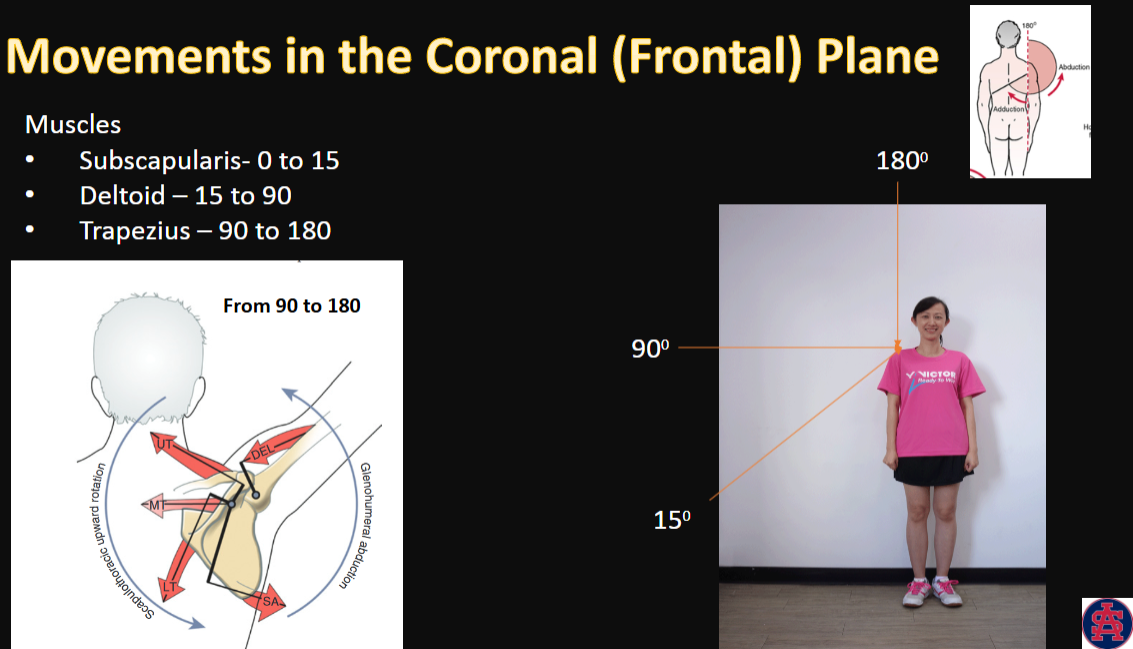
Abduction
movement, ROM, and muscles
1, 1, 3
SUPRASPINATUS (not subscapularis)
Movements in the Coronal (Frontal) Plane
muscles + angles (3)
SUPRASPINATUS (not subscapularis)
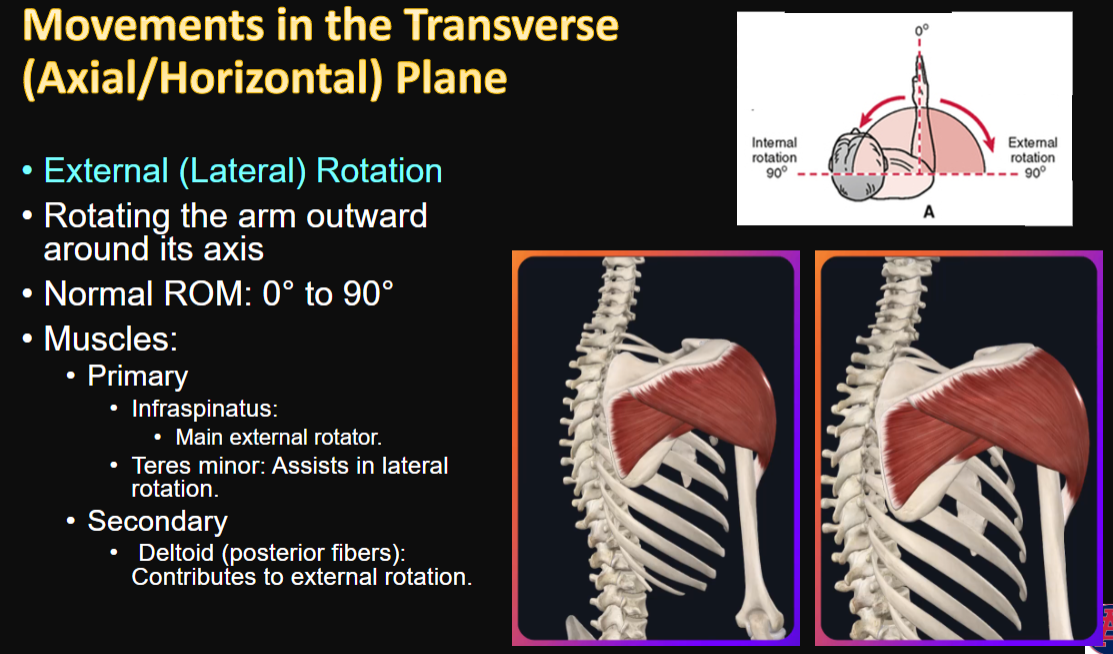
Movements in the Transverse Plane
External (Lateral) Rotation
movement, ROM, and muscles
1, 1, 3
Movements in the Transverse Plane
Internal (Medial) Rotation
movement, ROM, and muscles
2, 2, 5
Which muscle is the main internal rotator?
Subscapularis is the main internal rotator!
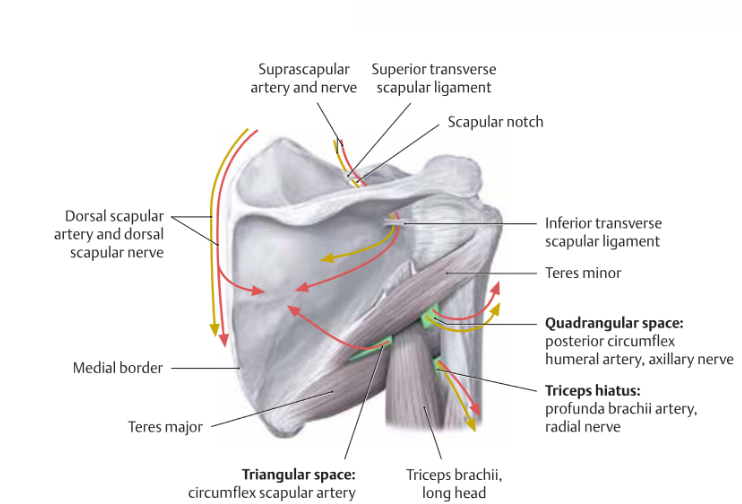
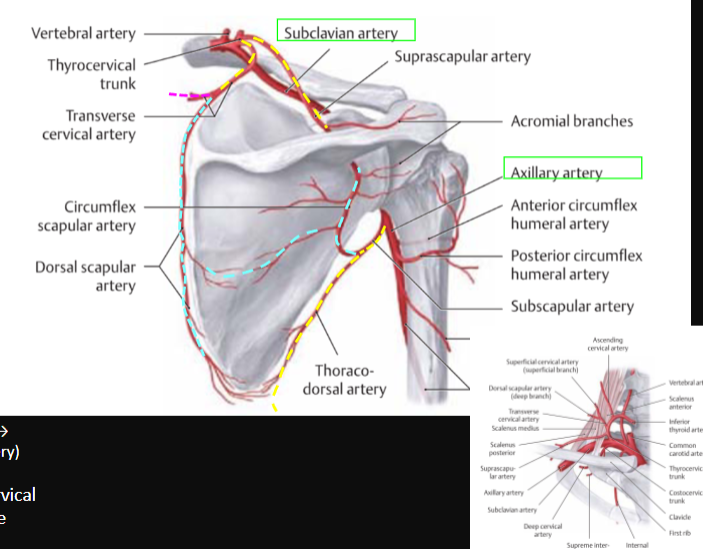
Arterial Supply of Scapular Region
2 main ones?
Subclavian Artery
Axillary Artery
Subclavian Artery
what comes off of it? (6)
Thyrocervical Trunk
Suprascapular Artery
Transverse Cervical Artery
Superficial branches
Deep branches
Dorsal Scapular artery
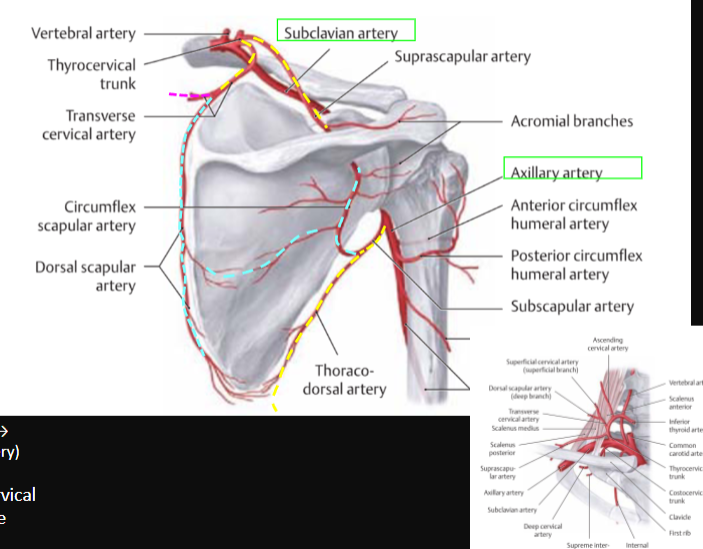
Axillary Artery
what comes off it? (5)
Subscapular Artery
Circumflex Scapular Artery
Thoracodorsal Artery
Anterior Circumflex Humeral Artery
Posterior Circumflex Humeral Artery
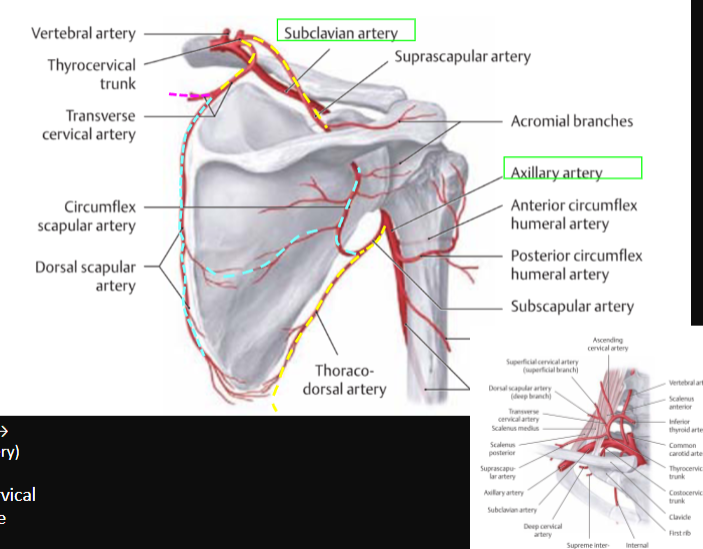
Scapular Anastomosis
between what? (2,2)
Suprascapular Artery (from thyrocervical trunk) ←→ Circumflex Scapular Artery (from suprascapular artery)
Dorsal Scapular Artery (from transverse cervical artery) ←→ Circumflex Scapular Artery (from Subscapular)
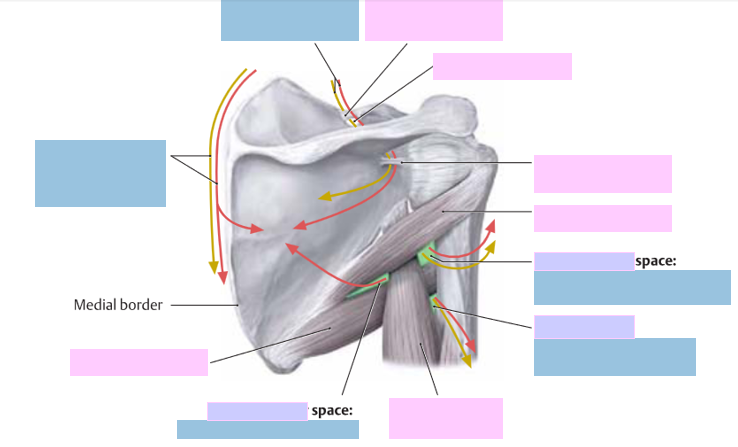
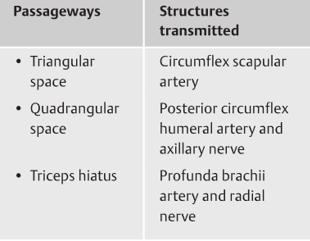
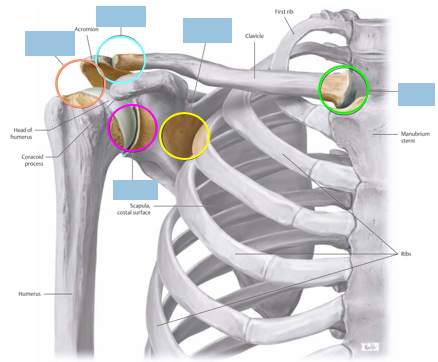
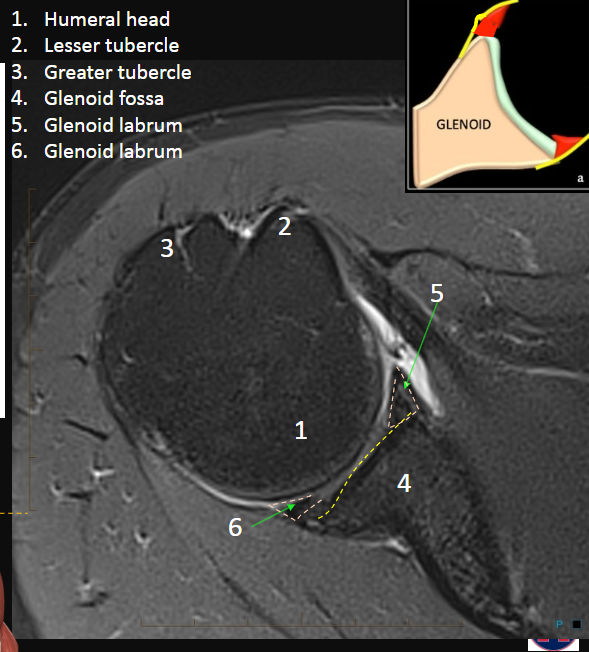
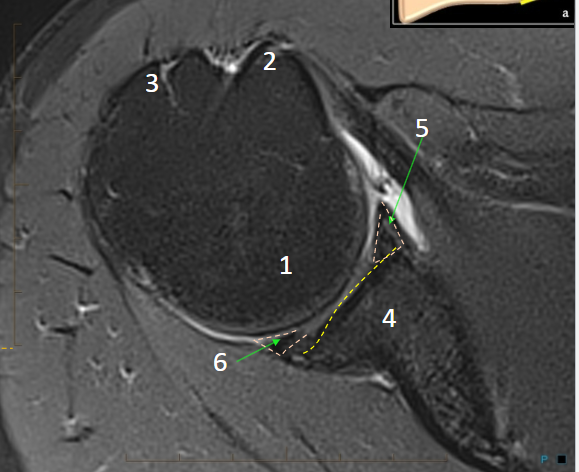
Label nerves, arteries, muscles, structures