iCEV Slides - The Skeletal System
Skeletal system
The body’s framework of bones, providing structural support to the body and protecting vital organs
Types of skeletal tissue
Bone, cartilage, and ligaments
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards reviewing iCEV's slides on the skeletal system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Skeletal system
The body’s framework of bones, providing structural support to the body and protecting vital organs
Types of skeletal tissue
Bone, cartilage, and ligaments
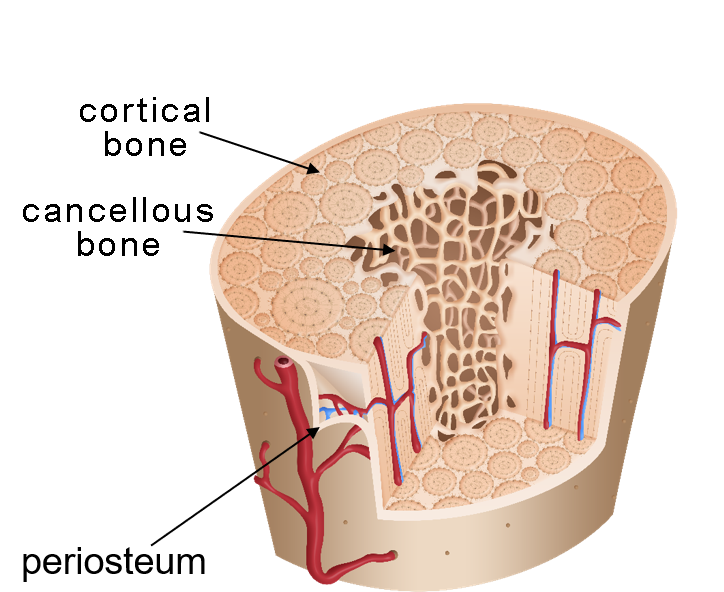
Types of bone
Cortical (compact) and cancellous (spongy)
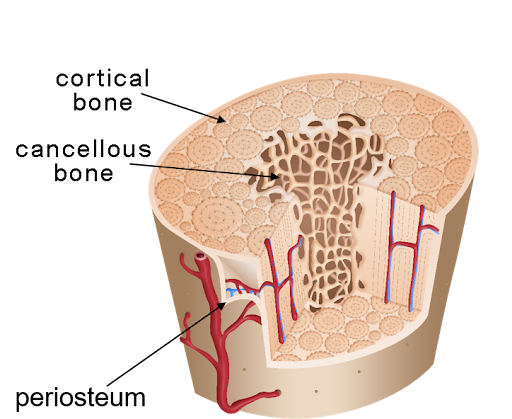
Cortical bone (compact bone)
The hard, dense outer layer of a bone
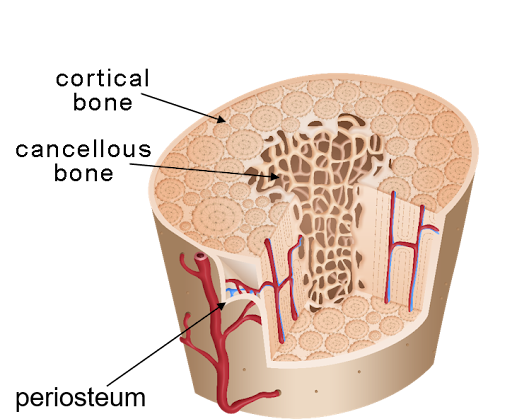
Cancellous bone (spongy bone)
The lighter, porous inner layer of a bone
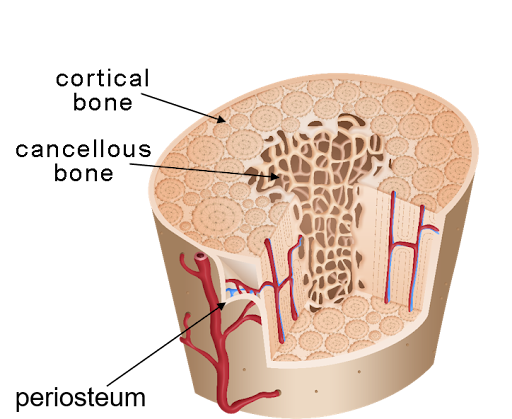
Periosteum
The thin outer layer of a bone
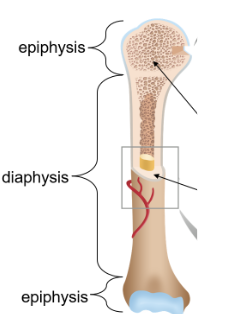
Diaphysis
The shaft extending throughout the middle of the bone containing the medullary cavity lined with endosteum
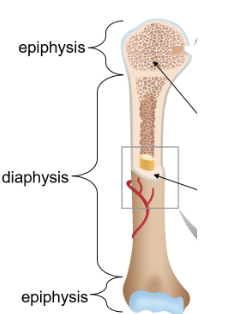
Epiphyses
Ends containing cancellous bone covered with hyaline cartilage for growth
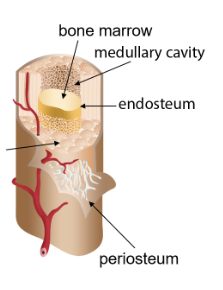
Bone marrow
Cells in the medullary cavity which can become platelets or red or white blood cells
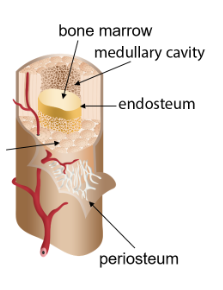
Medullary cavity
Cavity in the diaphysis (middle) of a bone that holds the bone marrow
Types of bone cells
Osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts
Osteoblasts
Cells that develop bone matrix through ossification
Osteocytes
Mature, inactive osteoblasts incorporated into mature bone
Osteoclasts
Cells that break down old or damaged bone
Types of bone shapes
Long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid (classified by shape and function)
Long bones
Hard, dense bones which provide strength, structure, and mobility—have a diaphysis and two epiphyses; types invlude the humuerus, radius and ulna, femur, and tibia and fibula
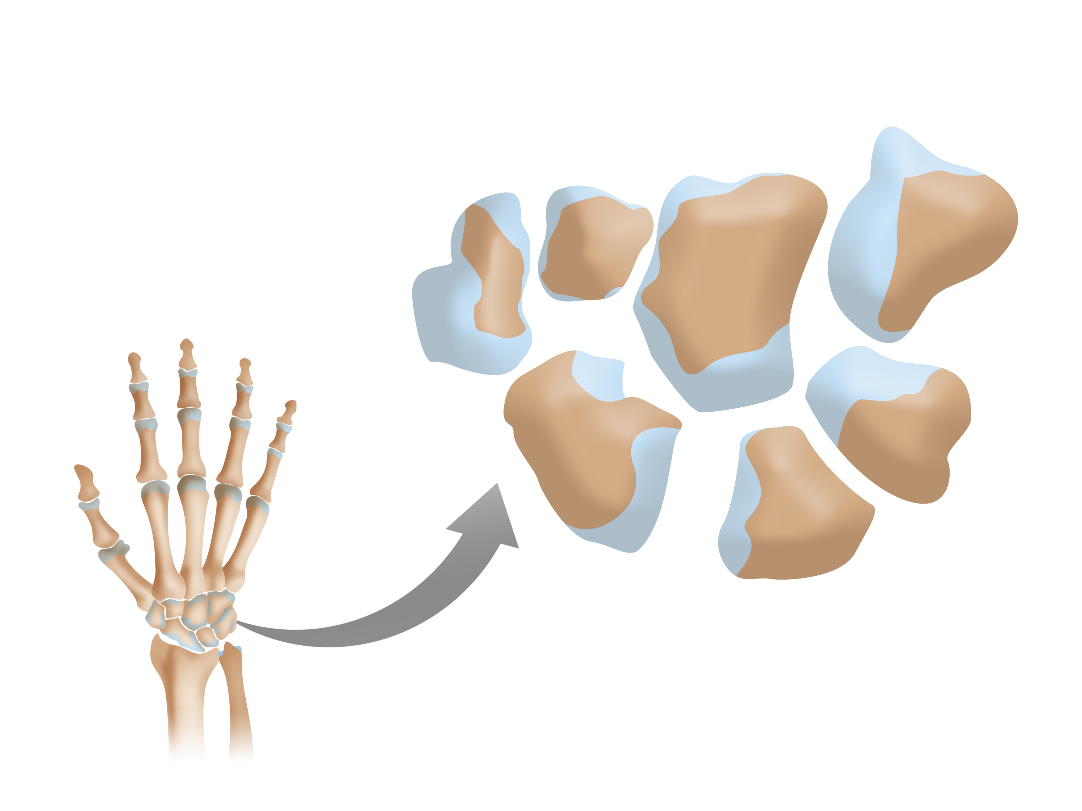
Short bones
Cube-like bones that do not contain a diaphysis and contain almost entirely cancellous (spongy) tissue; includes carpals and tarsals
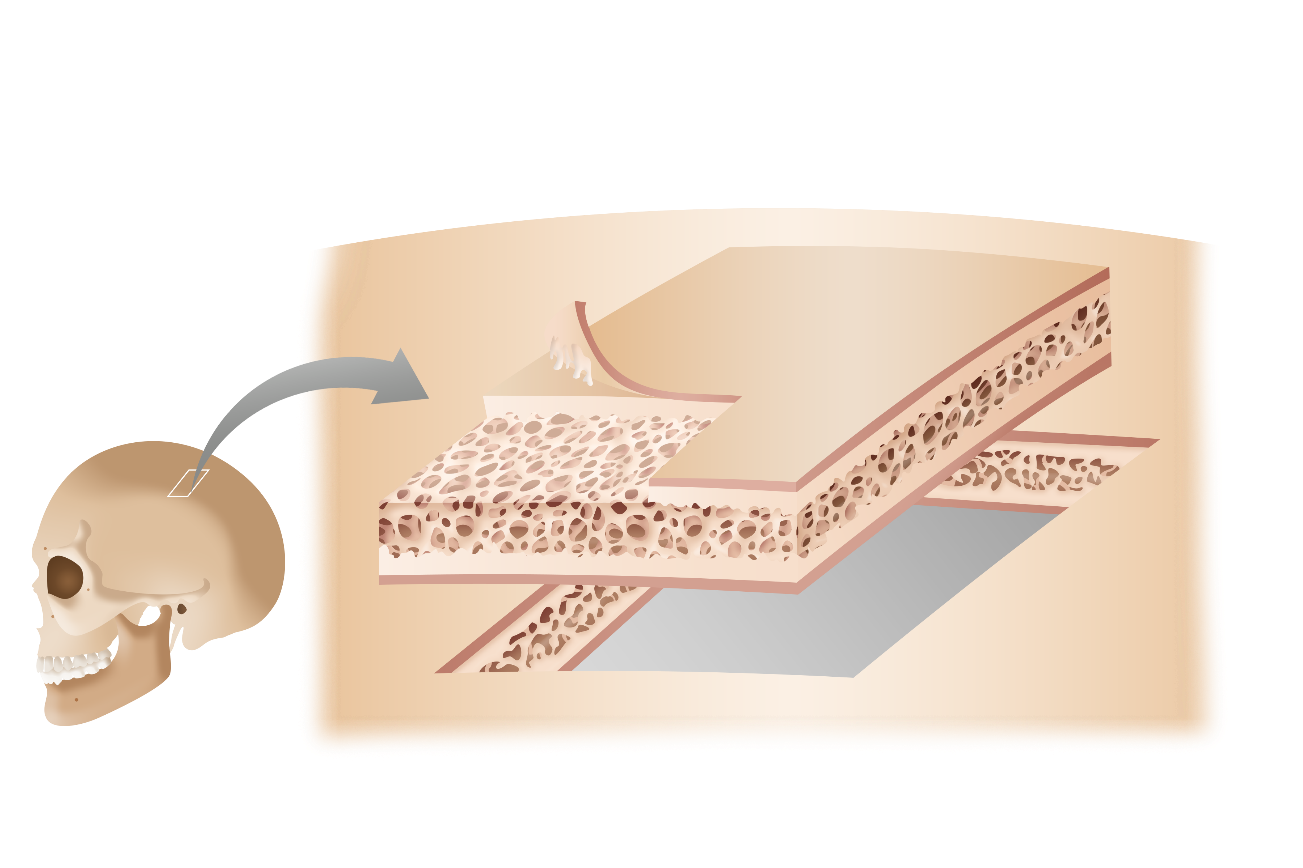
Flat bones
Thin, broad, and often curved bones with a cancellous bone layer sandwiched between two layers of cortical bone; protects internal organs and allows for attachment
Types include the skull, sternum, and ilium
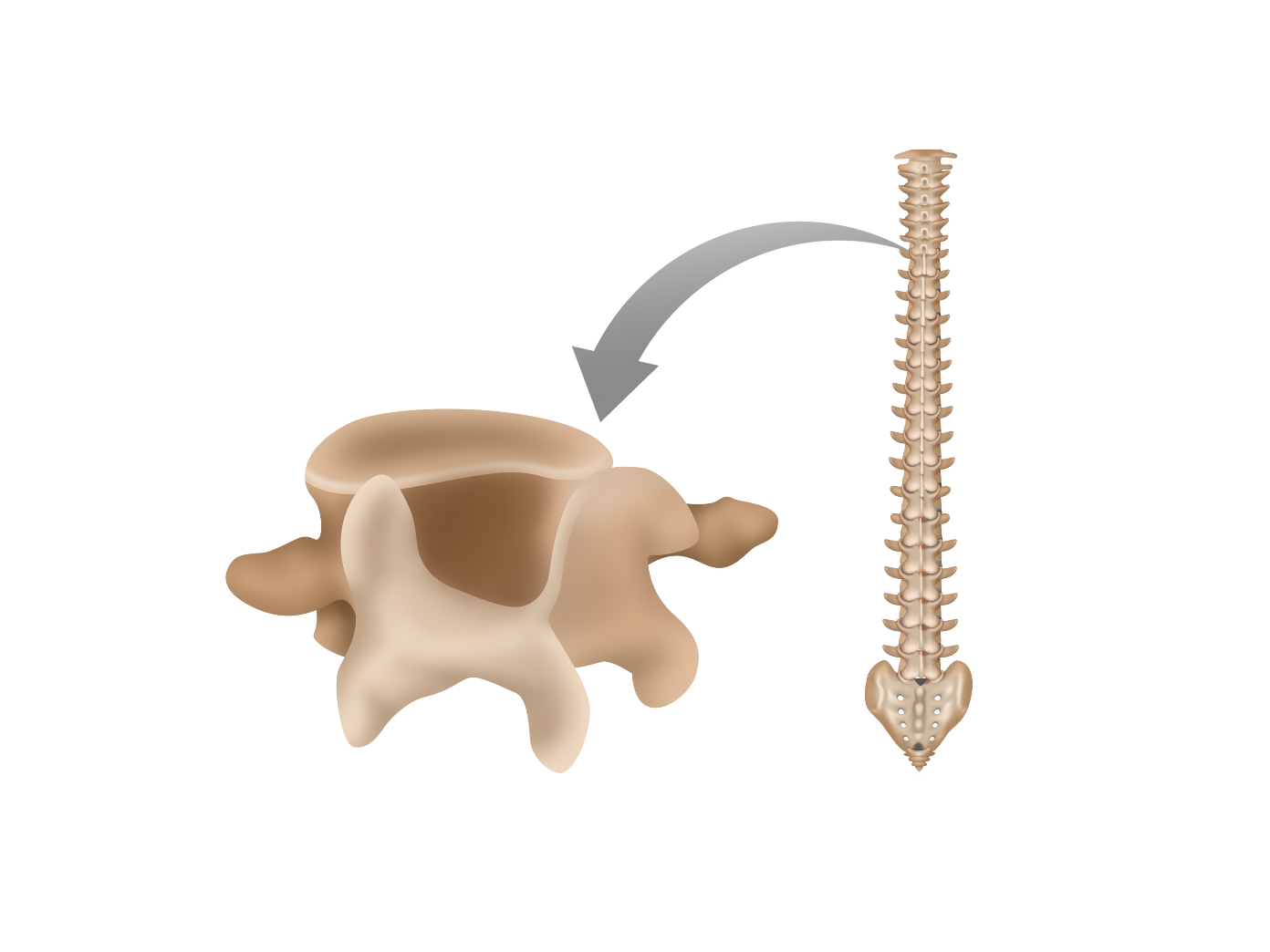
Irregular bones
Bones that are not uniform in shape with different types of surfaces; includes the vertebrae, sacrum, and coccyx
Sesamoid bones
Bones developed and embedded inside tendons that vary in shape and serve to protect the tendons
Tendons
Tough, flexible connective tissue connecting bones to muscles
Articulation
Where two bones meet
Head
The rounded surface of an articulation
Crest
A ridge on a bone
Condyle
A rounded surface on a bone
Projection
A raised marking on a bone
Process
A prominent feature on a bone
Fossa
A shallow depression on a bone
Foramen
A hole in a bone
Cartilage
A flexible connective tissue found in elbows, knees, and ankles, enhancing bone strength and providing support for the joints
Hyaline cartilage
Glassy cartilage which reduces friction and absorbs shock on most joint surfaces
Fibrocartilage
The strongest type of cartilage which provides ridigity and absorbs shock; lines bony grooves
Elastic cartilage
The most flexible type of cartilage; it provides shape and support and is found in the ears, nose, and parts of the respiratory system
Ligaments
Tough, dense, and fibrous connective tissue that form connections among bone and cartilage to stabilize joints
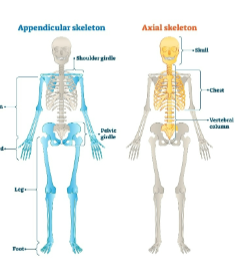
Human skeleton
Contains 206 bones with the axial and appendicular skeleton
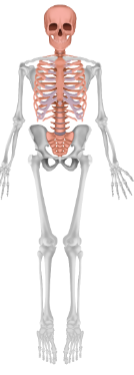
Axial skeleton
Forms the central axis of the body; supports the brain, spinal cord, and organs
Includes the skull, vertebral column, sternum, and ribs
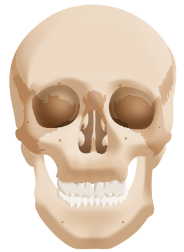
Skull
Consists of 22 bones forming the head; 8 form the cranial cavity and 14 form the facial bones
Cranial cavity
Cavity made of 8 bones that protects the brain
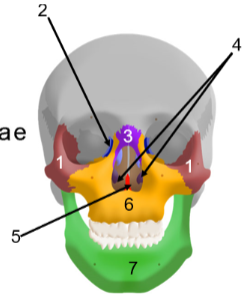
Facial bones
14 bones that form the face to provide sensory organ cavities for the eyes, nose, and mouth
Consists of:
two zygomatic (cheek) bones
two lacrimal (tear duct) bones
two nasal (nose bridge) bones
two inferior nasal (below nose) bones
vomer (nose)
two maxillary (upper jaw) bones
mandible (lower jaw)
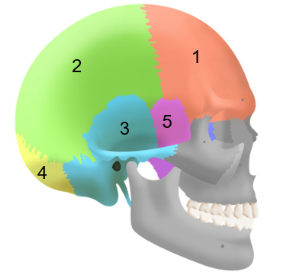
Cranial bones
Consists of:
the frontal bone
two parietal bones
two temporal bones
the occipital bone
the sphenoid bone
the ethmoid bone (inside)
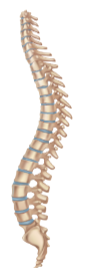
Vertebral column
Also called the spinal column or spine, it is a curved structure of 26 irregular bones including the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae, as well as the sacrum and coccyx

Cervical vertebrae
The top seven vertebrae of the neck for flexibility, notated as C1 to C7
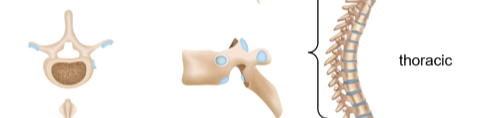
Thoracic vertebrae
The twelve vertebrae below the cervical neck vertebrae, has overlapping spinous processes for stability and attaches to ribs
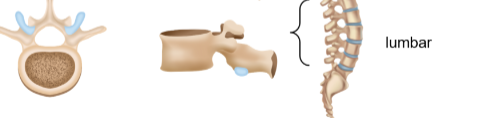
Lumbar vertebrae
The largest and strongest vertebrae to support the weight of the upper body
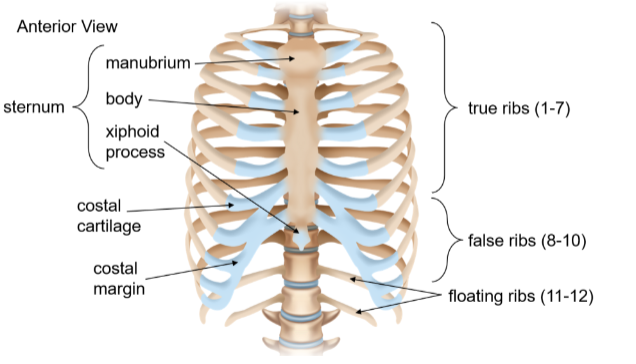
Thoracic cage
Also known as the rib cage, it forms the thoracic cavity to enclose and protect organs of the chest with 12 pairs of ribs and the sternum
Sternum
A narrow, flat bone at the body’s midline about six inches long formed by the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process bones; it attahces to the ribs

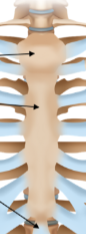
Manubrium
The widest and most superior portion of the sternum
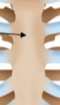
Body (corpus)
The elongated middle portion of the sternum

Xiphoid process
The smallest and most inferior portion of the sternum; it is initially cartilaginous and ossifies gradually
Appendicular skeleton
Consists of symmetrical pairs of bones on either side of the axial skeleton; includes the clavicles, upper and lower limbs, and pelvis

Clavicle
A long bone with a slight S-curve in the anterior shoulder to transfer force and allow motion from the arm to the trunk
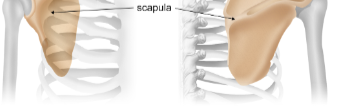
Scapula
A flat, triangular-shaped bone forming the posterior shoulder surrounded by muscle to anchor the arms
Upper limbs
Limbs attached to the pectoral girdle at the scapula, made of 30 bones with:
the arm (humerus)
the forearm (ulna and radius)
the hand (8 carpals, 5 metacarpals, and 14 phalanges)
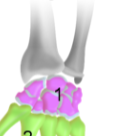
Carpal bones
Short bones in the wrist and base of the hand
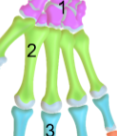
Metacarpal bones
Long bones forming the palm of the hand
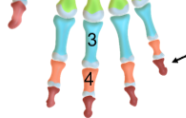
Phalanges (fingers)
Long bones forming the digits divided into proximal, middle, and distal sections
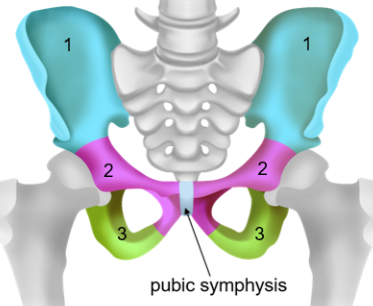
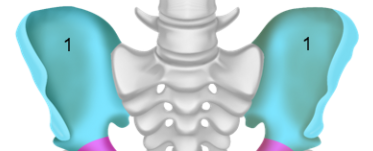
Pelvic girdle
Sometimes referred to as the hip; is a large, curved bone formed by the fusion of three bones (ilium, pubis, and ischium)
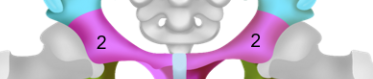
Ilium
The flat, superior, and largest portion of the pelvis attached to the sacrum and the sacroiliac joint
Pubis
The anterior portion of the pelvis; is a V-shaped bone

Ischium
The roughly arc-shaped bone in the pelvis; the posteroinferior (lower back) portion
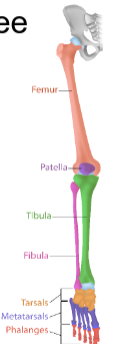
Lower limbs
Consists of 30 bones in the three regions with the:
thigh (femur)
leg (patella, tibia, and fibula)
foot (tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges)

Tarsal bones
The short bones in the ankle organized in three rows
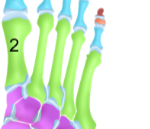
Metatarsal bones
Long bones along the foot; the distal tarsal bones to the proximal phalanges

Phalanges (toes)
Long bones forming the toes
Calcaneus
The longest bone in the foot; it is also called the heel bone and transmits force to the ground

Joints
Also known as articulations, these are where two bones come together to support body movement
Joint functional classifications
Synarthrosis, amphiarthrosis, and diarthrosis
Synarthrosis
Joints that are nearly immobile, such as the sutures of the skull
Amphiarthrosis
Joints that provide limited mobility, such as the pubic symphysis of the pelvis
Diarthrosis
Joints that provide the greatest range of motion and are the most common, such as the elbow, shoulder, or ankle
Joint structural classifications
Fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints
Fibrous joints
Joints joining bones by fibrous connective tissue, most commonly synarthroses (immovable)
Cartilaginous joints
Joints joining bones by hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage; are mainly amphiarthroses (somewhat movable)
Synovial joints
Joints joining bones through a joint cavity with synovial fluid; are most common diarthroses (very movable)
Flexion
The decrease of the angle between two bones of a joint
Extension
The increaes of the angle between two bones of a joint
Adduction
Movement towards the body’s midline
Abduction
Movement away from the body’s midline
Circumduction
Movement of a limb in a circle (circumference)
Rotation
The movement of a limb around an axis (turn arm)
Inversion
The tilting of the foot towards the midline
Eversion
The tilting of the foot away from the midline
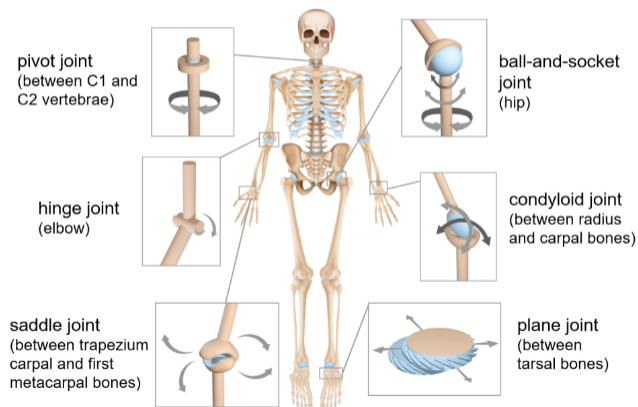
Synovial joint classifications
Can be further divded based on movement, such as:
ball and socket joint
pivot joint
hinge joint
saddle joint
plane joint
condyloid (ellipsoid) joint
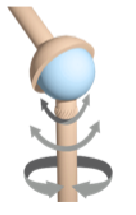
Ball-and-socket joints
Rounded surface of a bone within a depression in another bone, allowing for the most movement in all axes; includes the shoulder and hip
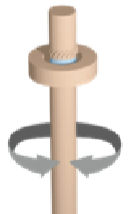
Pivot joints
Rounded portion of a bone enclosed in a ring shape of another bone held in place by a ligament; allows rotational movement in the neck and radius and ulna
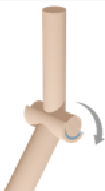
Hinge joints
Formed by a convex edge of one bone fitting into a concave edge; allows for flexion and extension in the elbow, knee, and ankle
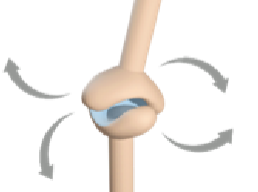
Saddle joints
Formed by two joints with concave and convex regions allowing flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction in the thumbs and inner ears
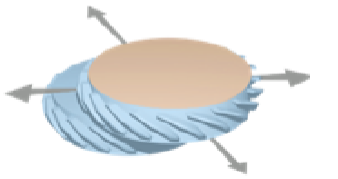
Plane joints
Formed by two sliding flat bones allowing for inversion, eversion, flexion, and extension in the vertebrae, metacarpals, and metatarsals

Condyloid joints
Also called ellipsoid joints, they are formed by egg-shaped bones in a similarly shaped socket allowing for flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction in the wrist, fingers, and jaw