College Psychology Test 1
1/173
Earn XP
Description and Tags
My knowt that I made and Noelle's
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
What is psychology?
The scientific study of behavior and natural processes. It’s goal is to describe, predict, and explain behaviors.
Empiricism
Our knowledge originates in experience
Structuralism
What exists
Introspection
To sit down and think
Functionalism
How we function
Neuroplasticity
How the brain changes/adjusts to experiences
Neurons
Building blocks of neural information center
Cell body
Each has one
Dendrite
Receive and integrate information
Axon
Passes message to other axons
Glial cells
Spidery “glue cells”
Threshold
Signals by a minimum intensity
Refractory period
Resting pause
All-or-none response
The level of stimulation will not affect it. It will either respond or it won’t.
Myelin sheath
Fatty tissue that insulates and speeds up the impules of axons
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Communication to muscles and brain regions is slow, with diminished muscle control and impaired cognition.
Synapse
Meeting point between neurons
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers
Reuptake
Excess neurotransmitters finally drift away and are broken down by enzymes or reabsorbed by the sending neuron.
Acetylcholine
Enables muscle function, learning and memory
Dopamine
Influences mood/emotion
Seratonin
Affects mood
Norepinephrine
Helps control alertness and arousal
GABA
Major inhibitory transmitter
Glutamate
Exitory and memorial
Endorphins
Inhibity
Endorphin
Natural chemicals produced by the body that act as painkillers and mood enhancers. They help reduce pain, improve mood, and promote a sense of well-being.
Agonist
Increases a neurotransmitter’s action
Antagonist
Decreases a neurotransmitter’s action
Sensory neurons
Transmit sensory information from the body's sensory organs to the central nervous system (CNS)
Motor neurons
Transmit signals from the central nervous system to muscles and glands, allowing for voluntary and involuntary movements
Sympathetic mode
Fight or flight response
Parasympathetic mode
Rest and digest
Endocrine system
Sends molecules as messages through bloodstream (hormones) that go to various glands
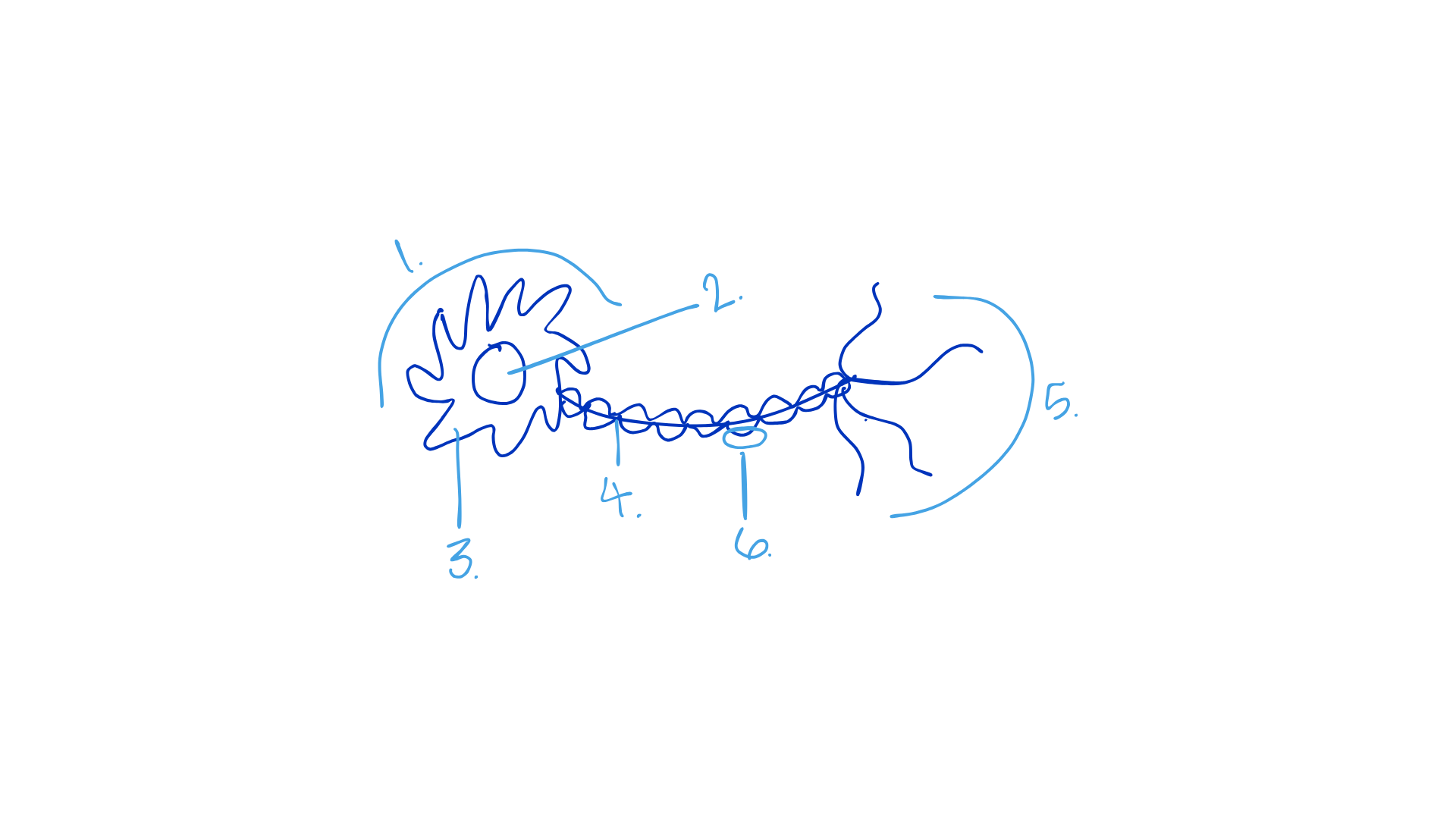
Label these!
Cell body
Nucleus
Dendrites
Axon
Terminal of the axon
Myelin sheath
Cerebellum
“Little brain” helps coordinate voluntary movement, also enables nonverbal learning, judgement of time, memory
Medulla
Controls the most basic functions such as breathing and heartbeat
Pons
Coordinate automatic and unconscious movements
Reticular Formation
Nerve network in the brainstem that enables alertness, arousal from coma to wide awake
Thalamus
“inner chamber” all sensory messages go through this
Hypothalamus
Governs bodily maitnence
Amygdala
Neuron clusters that enable aggression and fear
Hippocampus
Holds conscious, explicit memories
Corpus collosum
Axon fibers connecting the two cerebral hemispheres
Motor cortex
Stimulating this region in the right or left will cause movement on the opposite
Somatosensory
Recieves information from skin senses
Visual cortex
Recieve. segement, and integrate visual info.
Auditory cortex
Processing auditory information

Lobes of the brain
Frontal
Parietal
Temporal
Occipital
Functions of frontal lobe
Speaking, problem solving, muscle movements, making plans and judgement
Functions of parietal lobe
Includes the sensory cortex, controls touch, sensory and perception
Functions of the temporal lobe
The auditory processing areas
Functions of the occipital lobe
Visual areas, recieve visual information from the opposite visual field
What the Phineas Gage incident helps us understand:
Frontal lobe damage changes personality completely
What happens if the motor cortex is damaged?
Paralysis of some kind
What parts of the brain, if injured would cause death?
Medulla - we would be incapable of basic human functions
Consciousness
Our subjective awareness of ourselves and our environment
What 2 things make up consciousness
Awareness of self
Awareness of environment
Hypnosis
Altered state of consciousness
Cognitive neuroscience
Brain activity linked with mental processes
Etymology
The study of the origin and history of words, including their meanings and changes over time.
Selective attention
Where our awareness focuses
Inattentional blindness
Focusing on only one thing
Change blindness
Phenomenon where individuals fail to notice significant changes in their visual environment
Parallel processing
Your mind taking care of routine business
Sequential processing
A cognitive process that involves completing tasks in a step-by-step manner, following a specific order.
Flashcard: Brain Plasticity
The brain's ability to change and adapt by forming new neural connections throughout life, allowing for learning, memory, and recovery from injury.
Psychology
scientific study of behavior and mental processes
Goal of psychology
describe, predict, and explain behavior
Socrates & Plato
dualism: mind (soul) is separate from the body, ideas thought
and traits are inborn (character/intelligence), knowledge is innate (nature>nurture)
Aristotle
monism: mind (soul) and body are connected / cannot exist separately, knowledge grows from observations and memories (nurture>nature)
Rene Descartes
Dissected animals, observations = key tool, mind is the same as the soul but mind and body are separate entities, mind = non-physical substance
Francis Bacon
father of scientific method, incorporated experiments and research into psychological findings especially how we notice / remember things, compared objects
John Locke
mind at birth is a blank slate, all ideas from experience (nurture), father of empiricism
Empiricism
knowledge originates in experience
Wilhelm Wundt
father of psychology, first to use experimental psychology, opened psych only lab, mental map: physical - chemistry - biology - psychology - philosophy, sensations / apperceptions
Edward Titchener
first US psychologist, structuralism, introspection
Structuralism
what exists
Introspection
sit down and think about it
William James
sought to identify how the mind and consciousness worked, what is the purpose / practical applications to life, interested in how humans function adapt flourish and survive, functionalism
Functionalism
how we function
Sigmund Freud
developed the 1st comprehensive theory of personality, gained his understanding of human behavior simply through non-scientific consultations with patients. Sexual in nature - dreams. Stress and early childhood (unconscious forces) highly influence behavior
Ivan Pavlov
classic conditioning-simple behaviorism, use of dogs in research, Russian psychologist
Jean Piaget
swiss scientist, observed children and attempted to explain how children reason through various stages of life
John Watson & B.F. Skinner
behaviorists, observed and measured people's behavior as they respond to different surroundings. Definition changes: psychology is the scientific study of observable behavior very strict definition, introspection to the trash
Carl Rogers & Abraham Maslow
1960's humanists, stresses self-fulfillment and worth, focused on ways that current environments nurture or limit growth potential and the importance of love / acceptance satisfied, high level of free will, people are basically good and capable of perfection (self actualization)
Psychology's 3 main levels of analysis
biological, psychological, social-cultural --> biopsychosocial
Biological*
focuses on the brain and nervous system - anatomy. neuroscience structure, function, development, genetics, biochemistry of the nervous system
BUZZ WORDS: chemicals, medication, physical causes, genetics, hormones, brain chemistry
Evolutionary
evolutionary theory to all behavior and mental processes --> chances to ancestral environments. Ex: global warming causes people to have darker eye color which helps see at night.
BUZZ WORDS: evolved, higher being, higher order, adaptation, survive (nature)
Charles Darwin
Psychodynamic
unconscious thoughts and conflicts between internal drives and society. Early family experiences influence behavior, thought, and emotion
BUZZ WORDS: unconscious, guilt, conflict, repression, denial, anal retentive
Sigmund Freud, Erik Erikson, Alfred Adler
Behavioral*
humans are the products of learning and associations (nurture). Role of heredity is greatly deemphasized as is mental processes
BUZZ WORDS: rewards, punishments, learned habits, training-conditions
John Watson, B.F. Skinner, Albert Bandura
cognitive*
mental process involved in how we direct our attention, perceive, remember, think, and solve problems. input vs output --> we take info from the environment
BUZZ WORDS: cognitive therapy, thinking, irrational thinking
Piaget
humanistic
positive human qualities, capacity for self-actualization, free will. people are inherently good in nature, we can reach perfection
BUZZ WORDS: inner world, self, personal growth, free choice, free will, understanding life events
Carl Rodgers, Abraham Masslow
sociocultural*
social and cultural environments influence behavior and mental processes --> societal influeces,, pressures, ethnicity, race, religion. Studies differences in ethnic and cultural groups in a country.
BUZZ WORDS: setting, society, situations, groups, race, culture, gender, religion, peer pressure
Behavior Genetics
study of the effects of heredity on behavior. To what extent are abilities, personalities, sexual orientations, sociability, psychological disorder determined by genes from our parents?
Neuroplastiity
the brains ability to repair itself
Neurons
Individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information.
Cell body
the cells life-support center
Dendrite
receive messages from other cells
Axon
passes messages away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands