chapter 10
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
genetic material
information necessary for life stored in DNA or RNA for viruses
heredity
transmission of information from an organism to its progeny or cell to cell for single celled organisms
central dogma
DNA —> RNA —> Protein
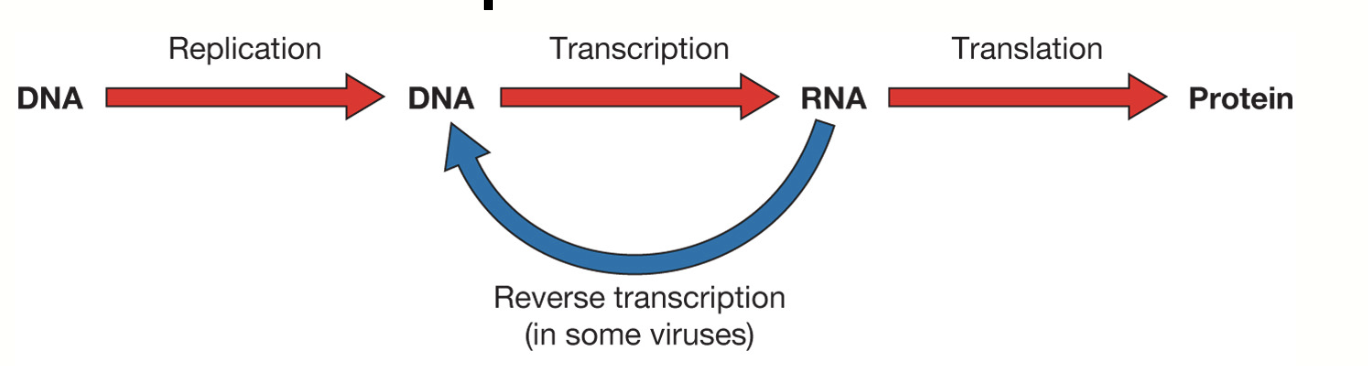
Replication
using DNA as a template to make new DNA
transcription
using DNA as a template to make RNA
Translation
using RNA to link amino acids to make proteins
Reverse transcription
what retroviruses use to synthesize DNA from an RNA template
characteristics of DNA
has a double helix chain of nucleotides
backbone is made of sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate
the nucleotide bases are A, T, G, and C
specific sequence of nucleotides is used to make more DNA or RNA and transfer info to next generation
RNA
ribose as sugar
no T but has U
single stranded
information for protein encoding
chromosome
organized strand of DNA
it is linear in eukaryotes and circular usually in prokaryotes
plasmid is organized but not necessary for organisms survival
gene
basic unit of heredity
part of a chromosome
sequence of nucleotides that is functional
the structure and function of an organism is encoded in its genes
gene language analogy
language = nucleic acid
alphabet = ATGC
sentence = gene
endless combos that can used to make sentences of differing lengths
DNA replication in prokaryotes
DNA strand separates at the replication fork
Replication begins and each strand is a template for the replication of its partner
each daughter cell gets one chromosome from the parent cell —> semi-conservative
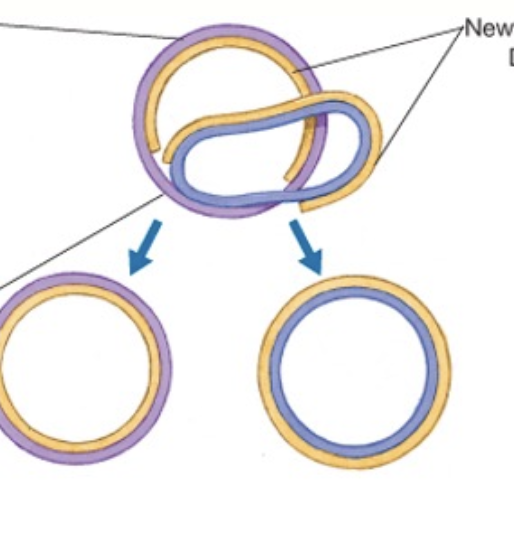
eukaryotic vs prokaryotic (transcription and translation)
eukaryotes
translation happens in the nucleus and mRNA has to leave it to to go to the cytoplasm
individuals ribosomes in the cytoplasm carry out translation to form proteins
prokaryotes
translation and transcription both happen in the cytoplasm
they use polyribosomes which means you can have multiple proteins being made immediately and you dont have to move from one location to another
uses 80-90% of bacteria cells energy
how does DNA control ALL of the cells functions
it makes more DNA and is responsible for protein synthesis directly
indirectly, the proteins it makes can be enzymes which synthesis lipids and carbohydrates which are the other things necessary for the cell
mutation
a permanent change in a cells DNA sequence in various ways
usually happens in the nucleotides of DNA and it is transmitted from parent to daughter cell
always affects genotype, not always expressed in phenotype
what are mutations responsible for
evolutionary changes, can be good or bad
different strains of microorganism species
what could cause mutations?
physical agents
ex: induced by x-rays or UV light
chemical agents
induced by arsenic, tobacco, benzene
biological agents
induced by viruses and bacteria
chance
spontaneous, errors in DNA replication
genotype
Genetic information contained in the DNA of the
organism
phenotype
specific characteristics displayed by the organism
point mutation
a mutation that changes a single base
silent
doesn't change the amino acid that gets transcripted
nonsense
encodes a stop codon so no more amino acids are produced
missense
conservative
results in another amino acid with similar biochemical properties —> less damage
non-conservative
results in amino acid with different properties —> more damage
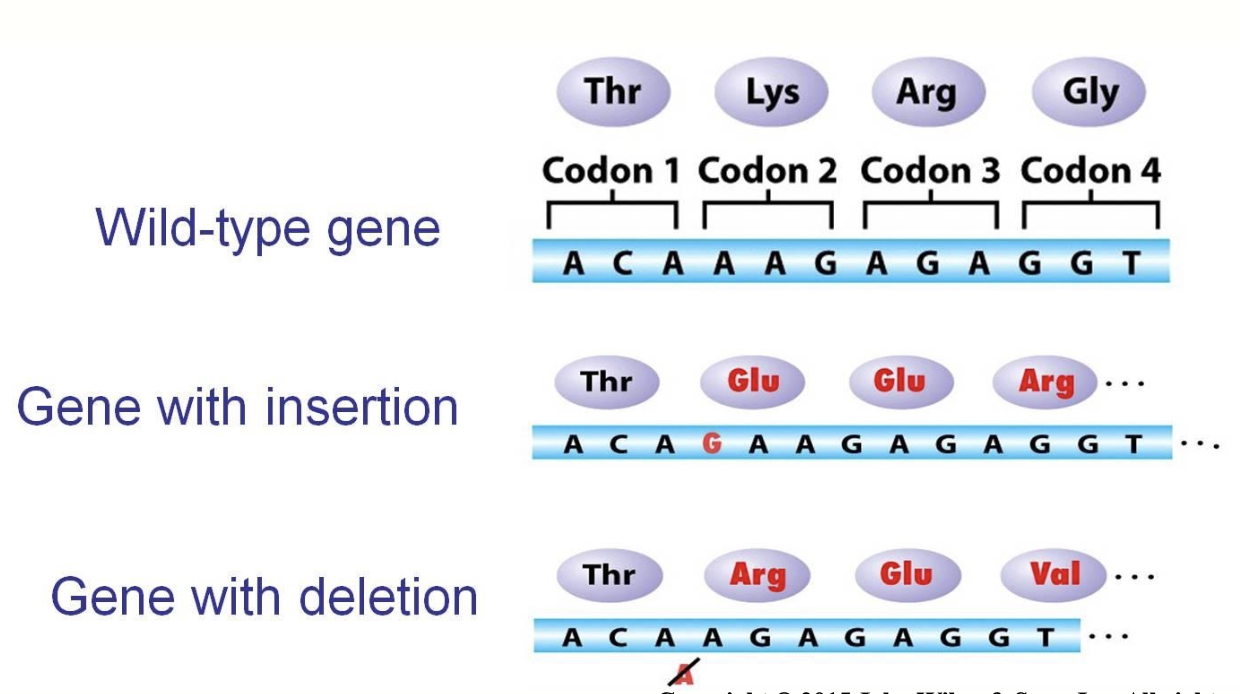
frameshift mutation
an insertion or deletion of one or more bases that shifts all of the bases by one or more which changes the amino acid
transposon
some bases of the DNA move from one part of the chromosome to another part but keep the same 5’-3’ orientation
inversion
some bases of the DNA move from one part of the chromosome to another part but have flipped orientation 3’-5’