MGMT 471 Study Guide (Midterm)
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
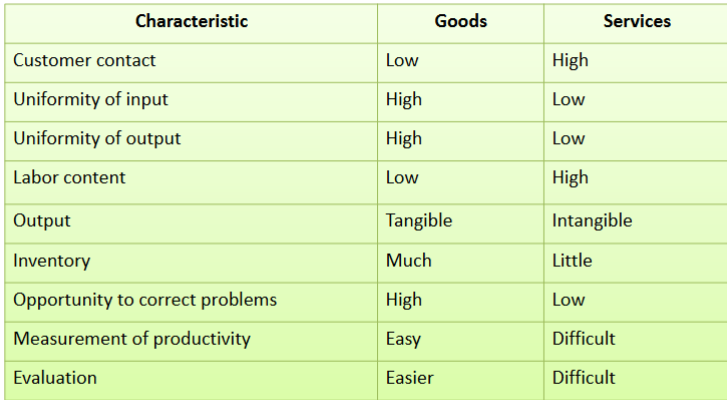
Definition of Goods
Physical items that include raw materials, parts, subassemblies, and final products.
Definition of Services
Activities that provide some combination of time, location, form, or psychological value.
Manufacturing vs. Service Employment Level
DECREASE in Manufacturing Employment:
Technological Advancements
Globalization
INCREASE in Service Employment
Consumer Behavior
Four Characteristics of Service
Intangibility, inseparability, variability, perishability.
Definition for Intangibility
Services cannot be seen, tasted, felt, heard, or smelled before being purchased
Definition of Inseparability
Customers and employees co-produce the service
Services are produced and consumed at the same time
Definition of Variability
Quality depends on who provides them and when, and where they are provided
Definition of Perishability
Services can’t be saved, stored, returned, or resold
Characteristics of Service vs. Goods
Planning (Definition)
The process of determining how the organization can get where it wants to go and what it will do to accomplish its objectives (with a clear mission, vision, and goals)
Innovation (Definition)
Sustaining long-term innovation strategies
Creating competitive advantage and value for customers and the organization
Three Types of Innovation
Transformational, Substantial, Incremental.
Transformational Innovation Definition
Products that are radically new
Substantial Innovation Definition
Products that are significantly new
Incremental Innovation Definition
New products that provide improved performance or greater perceived value (or lower cost)
Product-Market Expansion/Growth Strategy
In order to be successful, Companies must identify, evaluate, and select opportunities then develop strategies to capture them
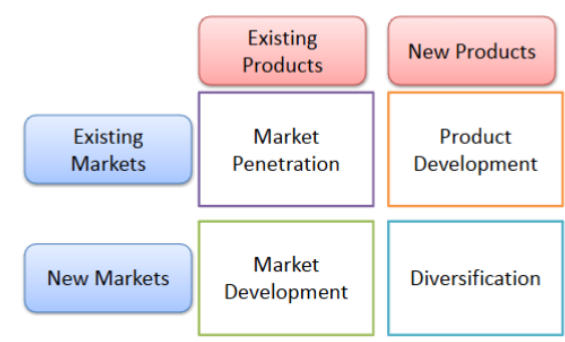
Four Types of Corporate Strategies
Concentration, Vertical Integration, Concentric Diversification, Conglomerate Diversification
Concentration Strategy Definition
A strategy employed for an organization that operates a single business and competes in a single industry.
Vertical Integration Strategy Definition
Expanding the domain of the organization into supply channels or to distributors within the same industry.
Concentric Diversifcation Strategy Definition
Moving into new businesses that are related to the company’s original core business.
Conglomerate Diversification Strategy Definition
A strategy that involves expansion into unrelated businesses by producing unrelated products.
SWOT Analysis Definition
A strategic development tool that matches internal organizational strengths and weaknesses with external opportunities and threats.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths (Internal)
Skilled management, positive cash flow, positive brand image, etc.
Weaknesses (Internal)
Lack of production capacity, no reliable suppliers
Opportunities (External)
New technology, increasing global demand
Threats (External)
New Competitors Entering the market
Customer Needs Definition
Provide critical information for determining value opportunities.
Customer Value Definition
Customer Value = Benefits - Cost
= Benefits Provided by a Product/Service - All of the Costs Incurred by the Buyer
Customer Satisfaction Definition
A measure of how products and services meet or exceed customer expectations.
Market Segment Analysis
Research of existing and potential customers (i.e. - Aging Baby Boomers)
Challenges associated with Innovation
Transformational Innovations
Customers may not be good guides to new product ideas
Potential customers may not understand how the new product will replace existing products
Management’s vision may be faulty
Challenges of New Product Development
All New Products
Potential of disrupting existing/sustaining products
Potential negative impacts on leading products
Cannibalization
Franchising Basic Concept
Primary growth strategy of hotels/motels during 1960s, 70s, and 80s
One of the driving forces of the hotel business
Management Contracts Basic Concept
Developers/owners = Usually no desire/ability to operate
Real estate and physical plant can be owned by different entities
One of the driving forces of the hotel business
Franchising - History in the U.S.
Began in 1907 when the Ritz Development Company franchised the Ritz-Carlton name in NYC
Holiday Inn grew through the strategy of franchising
Management Contracts - History in the U.S.
The Hotel Industry’s rapid boom since the 1970s
Hotel management companies = Little or no up-front financing
Franchising (Benefits)
Plans and Specifications
National and International Advertising
Central Reservation System (CRS)
Volume discounts (furnishings, fixtures, equipment, etc.)
Low fee % charged by credit card companies
Less risky than starting your own business
Franchsing (Drawbacks)
High fees (typicaly 3-4% of room revenue)
Franchisor’s agreement
Lack of freedom (standards set by the franchisor)
Failure to follow the standards: Termination of contract
Franchisor - Direct influence on business
Two Types of Management Companies
1st Tier & 2nd Tier
1st Tier Management Companies Definition
Management companies that operate hotels for owners using the management company’s trade name as the hotel brand
2nd Tier Management Companies Definition
Management companies that operate hotels for owners and do not use the management company name as part of the hotel name
Hotel Classifaction/Types
Diamond Rating (AAA) & Star Rating (Forbes Travel Guide)
Room Rates - The Four Types of Plans
American Plan (AP), MAP (Modfiied American Plan), European Plan (EP), and Continental Plan (CP)
Definitions of the Four Types of Plans
American Plan (AP) - Room and three meals a day
MAP (Modified American Plan) - Room plus two meals
Breakfast + Lunch or Dinner
European Plan (EP) - Room only, meals extra
Continental Plan (CP) - Room plus (continental) breakfast
Rack Rate Definition
Full price at which rooms are sold to customers before discounts
Can be the highest rate quoted for a guest room
Revenue Management Definition
A demand forecasting technique used to maximize revenue per available room. Based on principles of supply and demand.
Law of Supply Definition + Concept
The concept of economics that recognizes:
When demand is held constant, an increase in supply leads to a decreased selling price
With demand held constant, a decrease in supply leads to an increased selling price
Law of Demand Definition + Concept
The concept of economics that recognizes:
When supply is held constant, an increase in demand results in a rise in the selling price.
With supply held constant, a decrease in demand results in a lower selling price.
ADR (Average Daily Rate) Calculation
Total Revenue from Room Sales / Total # of Room Sales
Occupany Rate Calculation
Total Rooms Sold / Total Rooms Available
RevPAR Calculation
Total Revenue from Room Sales / Total Rooms Available
GOPPAR Calculation
Total Gross Operating Profit / Total Rooms Available
Room Achievement Factor Calculation
ADR / Rack Rate
Yield % Calculation
OCC% * Rate Achievement Factor
PMS Definition
Computer-based lodging information system that relates to both the front and back office activities (Reservation, Room Control and Management, Cashiering, Reporting)
CRS Definition
Allows operators to access the inventory of room availability of each hotel in the chain. Interfaces with hotel’s inventory and simultaneously deducts from the inventory of rooms once a reservation is made.
CRO Definition
Hotels provide rates and available information to the CRO by data communication lines. Automatically updates the CRS so that guests can get the best available rates when they book through the central reservation office.
Housekeeping Facts
Largest department (# of employees)
Up to 50% of employees work in Housekeeping
Hard work + low pay
Highest turnover rate
Outsourcing Staff
Functions most likely to be outsourced:
Pool maintenance
Equipment maintenance
Security
Floral arrangements
Landscape management
Valet parking
Functions least likely to be outsourced:
Front desk
Bell staff
Housekeeping
Concierge
Hotel F&B Facts
F&B Divison is generally the 2nd largest operating division (behind Rooms Division).
Hotel F&B Changing Trend
Traditionally: 20% of the hotel’s profit
Operated strictly as an amenity - not a profit generator
Focused more on in-house guests
Now: 25-30% of the hotel’s profit
Attracting more local guests + catering (events)
Hotel restaurants now generate substantial profit
Hotel restaurants vs. Other restaurants
Labor costs = 40%
Labor costs = 30%
Hotel restaurants have a 10% loss of profit compared to other restaurants
Hotel F&B Challenges
Hotel (in-house) guests are not always predictable
Difficult to predict # of expected covers
Too Many -> Delays & poor service
Too few -> Employees underutilized (labor costs)
Capture rate: # of in-house guests who dine in the hotel restaurants
F&B RevPAR vs. Rooms RevPAR
F&B RevPAR is more stable than Rooms RevPAR
Ability of hotels to attract local patrons to their restaurants, lounges, and catering facilities
Especially evident during recessionary years (i.e. 2009): Declines in F&B revenue were less than the decreases observed in rooms revenue
F&B Division - Catering
Banquet related revenue is greatest source of F&B revenue:
Catering Revenue: 55.5% (includes room rental, audio visual fees, service changes, etc.)
Restaurants: 30.2%
Lounges: 5.6%
Room Service: 4.4%
Linear trend of banquet and catering RevPAR increasing as the total amount of meeting space increases
F&B Divison - Room Service
Doesn’t generate enough profit
Needs to operate 16-24 hours/day
Other challenges:
Delivering orders on time
Avoiding complaints of excessive charges
Food Cost Calculation(s)
Food Cost / Menu
Or
Foost Costs / Food Sales
Labor Cost % Calculation
Labor Cost / Food Sales
Prime Costs Calculation
Food Costs + Labor Costs
Prime Costs %
Food Costs % + Labor Costs %
Beverage/Bar Management
Profit margin from beverage is higher than the food profit margin
Beverages - Approximately 20-30% of total sales in a restaurant
Beverage/Bar Challenges
Inventory control challenges:
Installing and ensuring responsible alcoholic beverage service
Pilferage
Employees stealing liquor
Overcharging or mischarging
Overpouring or giving away drinks to receive larger tips
Restaurant Forecasting
Most business (including restaurants) operate by formulating a budget
Forecasting Restaurants sales: Restaurant forecasting is used not only to calculate sales projections but also to predict staffing levels
Two Components:
Guest Counts (# of covers): # of guests patronizing the restaurant over a given time period
Average guest check: Total sales / # of guests
Pricing Strategy
Cost-based Pricing (Lower Limit)
Food Cost %
Labor Cost %
Profit (BEP)
Contribution Margin
Demand-based Pricing (Upper Limit)
Quality & Positioning
Competition Prices
Technology Accept (Conflicting View)
High level of security
Reduced cost
Increased acceptance
Technology Reject (Conflicting view)
Privacy issues
Interpersonal service
Technology anxiety
Biometrics Definition
To describe measurable physiological and/or behavioral characteristics that are unique to the individual and can be used to verify the identity.
Biometrics - Physiological Measures
Fingerprinting
Iris Scans
Retina Analysis (Blood Vessels)
Face Recognition
Hand-Line Patterns
Biometrics - Behavioral Measures
Hand-Written Signature Verification
Voice Recognition
Gait Analysis (walking)
Biometrics - Pros (Fingerprint, Iris-Scan, Voice Scan)
Fingerprint
Ease of use
Multiple Finger Enrollment
Iris-Scan
High Level of Accuracy
Voice Scan
No Negative Perception
Biometrics - Cons (Fingerprint, Iris-Scan, Voice Scan)
Fingerprint
Some failure to enroll
Iris-Scan
Requests User Training
High False Rejection
Voice-Scan
Low Quality Capture
Problem with Noise
Self-Service Technology (SST) Definition + Example
Any facility that enables consumers to produce services for themselves without assistance from employees
Ex: Self-Serve Restaurant with Cubby System
Self-Service Technology (SST) Positive Aspects (Management + Customer Perspectives)
Management Perspective
Reduced labor cost
Increased productivity (e.g. - service delivery speed)
Increased customer satisfaction
Customer Perspective
Greater Control
Convenience + Speed
Enjoyment from using the technology
Self-Service Technology (SST) Negative Aspects (Management + Customer Perspectives)
Management Perspective
Initial installation cost
Potential loss of interpersonal contact
Difficulties in service recovery
Loss of up-selling opportunities
Reliability (technology failure)
Maintenance
Customer Perspective
Technology anxiety
Loss of personal interaction
Self-Service Technology (SST) - Conflicting Views
Is it just a shift of service deliver with the same level of service quality?
Or is it taking away the memorable experience (human interaction)?
Corporate Citizenship Concepts
Corporate social RESPONSIBILITY, Corporate social RESPONSIVENESS, Corporate social PERFORMANCE
Corporate social RESPONSIBILITY Definition
Emphasizes obligation and accountability to society.
Corporate social RESPONSIVENESS Definition
Emphasizes actions and activities.
Corporate social PERFORMANCE Definition
Emphasizes otucomes and results.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Definition
Managerial obligation to take actions to protect and improve both the welfare of society as a whole and the interests of organizations. A company’s obligation to exert its positive impact and minimize its negative impact on society.
Three Types of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Ethical, Altruistic, Strategic.
Ethical CSR Definition
Represents a minimal level of social responsibility.
Altruistic CSR Definition
Being a good corporate citizen by giving back to society.
Strategic CSR Definition
To accomplish strategic business goals.
Cause-related marketing (CRM) Definition + Example
Definition: A particular marketing strategy that links product sales to the support of a charity to create and maintain favorable brand images
Ex: Both Starbucks (Ethos) and Happy Meal donations
Green Hotels Information (Going Green)
Commercial buildings in general
Produce 38% of all carbon dioxide emissions
Consume 40% of total energy consumption
Use 68% of all electricity
Hotel Industry: 4th most intensive energy user in the US Business Sector
Why - Operators 24/7 non stop -> Water, energy use, waste, etc.
Ex: DO not change my towels movement
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) Definition
An internationally recognized green building certification system.
Managerial Approach to Tipping
Motivate servers to deliver good service
Measure server performance
Identify dissatisfied customers
What Affects Tip Size?
Selling (Based on total check amount)
Personalized Apperances
Entertaining Customers
Personal Interactions
Adding Personal Touches to the Check
Definition of a Tipped Employee
Under the FLSA, a tipped employee is one who customarily and regularly receives more than $30 a month in tips.
Tip Credits Definition
A provision under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) that allows employers to pay tipped employees less than the federal minimum wage, as long as the employees’ tips make up the difference.
Tip Credits (Federal Minimum Wage, Minimum Cash wage for Tipped Employees, Tip Credit & Earning Minimum Wage)
Federal Minimum Wage: $7.25 per hour
Minimum Cash Wage for Tipped Employees: $2.13 per hour
Tip Credit: The Difference between the federal minimum wage and the minimum cash wage for tipped employees is $5.12 per hour. This $5.12 is considered the “tip credit.”
Earning Minimum Wage: If an employee’s tips combined with the $2.13 cash wage don’t equal at least the federal minimum wage of $7.25 per hour, employer must make up the difference.
Tipflation Definition
Refers to the increasing expectation and size of tips over time, often without a corresponding increase in service quality.
Causes of Tipflation
Cultural Shifts
Technology Influence
Economic Factors
COVID-19 Impact