FAR: F1-F6
1/402
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
403 Terms
Classified balance sheet
Current assets/liab vs non current assets/liab
You have an asset that’s worth $100K. Has 10 year useful life.
End of year 6, it depreciated by 30K. What is the depreciation amount for year 7 if the useful life stays the the same and there’s no salvage value?
End of Year | Asset Value | Depreciation |
1 | 90 | 10 |
2 | 80 | 10 |
3 | 70 | 10 |
4 | 60 | 10 |
5 | 50 | 10 |
6 | Impaired: -$30K | |
7 | Depreciation? | |
8 | ||
9 | ||
10 |
End of Year | Asset Value | Depreciation |
1 | 90 | 10 |
2 | 80 | 10 |
3 | 70 | 10 |
4 | 60 | 10 |
5 | 50 | 10 |
6 | 10 = 50 - 30 (impar) -10 (depreciation during yr) | 10 |
7 | 2.5 =10/4 | |
8 | ||
9 | ||
10 |
In year 6, subtract the impaired amount and the depreciation to get to the ending asset value.
Example of expired and unexpired cost
Expired: COGS (IS)
Unexpired: inventory (BS)
What is salvage value and when is it relevant?
When depreciating PP&E, salvage value tells you how much you can get for your PP&E at the end of its useful life.
Relevant for all depreciation methods accept declining balance.
Note: If the PP&E is on leased land, (you won’t have access to it at the end of your lease), then you consider that there is no salvage value to you.
what are incremental costs?
extra costs you incur only if you generate the asset.
Ex: Sales commission.
It’s related to asset generation, like getting a contract. It’s incremental because you wouldn’t have incurred the cost unless you had gotten the asset.
Ex of a non-incremental cost:
Advertising cost → Not directly related to getting a new sales contract or asset.
Sales people salaries → You would have incurred this cost anyway.
What does the acronym BASE stand for in inventory accounting, and how is it used?
mnemonic to remember the inventory equation:
Beginning Inventory + Purchases − COGS = Ending Inventory
Beginning Inventory
Add Purchases (or Additions)
Subtract Cost of Goods Sold (or Subtractions)
Ending Inventory
You can rearrange it to solve for any missing amount, such as purchases.
Multiple step vs. single step income statement
Multiple step: operating versus non-operating.
Single step: all revenues together, all expenses together
What counts as discontinued operations
Operations that have been disposed or are held for sale
Do you calculate EPS including discontinued operations?
EPS for income from continuing operations must be reported on the face of the income statement.
Also, a separate EPS and diluted EPS must be shown including income from discontinued operations as well.
What is an estimated liability on purchase commitments?
What would the journal entry look like?
When a company promises to buy goods at a fixed price in the future.
Ex:
May Y1: Contract signed → I promise to buy your corn next year for $5M.
NO JOURNAL ENTRY.
You haven’t incurred the expense yet, you just know you will have to pay 5M in future.
Dec 31 Y1: The price of corn drops to $3M.
Dr. Loss on purchase commitments $2M
Cr. Liability on purchase commitments $2M
Sep Y2: Receive Corn
Dr. Corn Inventory $3M
Dr. Liability on purchase commitments $2M
Cr. AP $5M
3 causes of gains and losses from discontinued operations
operations
sale
Impairment
Where does discontinued operations show up on the income statement?
After continuing operations and before net income. Discontinued operations is shown net of tax.
When are foreign currency gains and losses reported?
anytime there is a remeasurement of transactions that occurred in foreign currency.
Ex: quarterly financials, year-end reporting, Any unrealized remeasurement of an actual transaction
Comprehensive income formula
Net income ± OCI changes
Purpose of comprehensive income statement
Captures real economic gains/losses (translation, pensions, AFS securities, hedges) that cause volatility but don’t reflect core operations → recorded in equity, not net income.
What is OCI? + PUFI pneumonic
Other comprehensive income
P: Pension adjustments
U: unrealized gains and losses from available for sale debt securities (bonds)
F: Foreign currency adjustments from translating financials of overseas subsidiaries or from consolidations. (Not from transactions)
I: Instrument specific credit risk
What are the two statements that OCI go to?
Statement of comprehensive income and statement of stockholders equity through (AOCI) accumulated other comprehensive income line
How is basic earnings-per-share calculated?
Income available to common stockholders / weighted average common shares outstanding (WACSO)
How is WACSO calculated?
For each new issuance:
(Existing outstanding stock value + Value of issuance) * (# of months in year that issuance is outstanding / 12)
For each buy back:
(Existing outstanding stock value - value or buyback) * (# of months in year that issuance is outstanding / 12)
for stock split:
Treat stock split as if occurred in beginning of year
What is diluted EPS?
If all of the convertible bonds or preferred stock, etc. Were converted to additional shares of common stock, then the denominator of earnings per share would be higher, causing EPS to be diluted or lowered.
What is the if converted method and the treasury stock method?
If converted method assesses if convertible bonds or preferred stock are dilutive, including additional shares in the WACSO for diluted EPS if they are dilutive.
Treasury stock method for options/warrants assumes proceeds from their conversion are used to repurchase shares, and the net effect impacts diluted EPS.
What is a contingent share?
Stock that will only be issued if certain conditions are met
How do contingent shares affect EPS?
Contingent shares will only be included in EPS if all the conditions are met
What are the 3 main types of filings to the SEC?
10 – K
10 – Q
8 – K
4 Components of 10 – K
Financial disclosures
Summary of financial data
Management discussion and analysis (MD&A)
Audited GAAP financial statements
3 deadlines for filing 10 – K for 3 different kinds of filers
60 days - large accelerated: >$250M public float
75 days- accelerated: $75M - $250M public float
90 days - all other: <$75M public float
Public float = # of common shares outstanding x market price
3 Components of 10 – Q
Unaudited GAAP financial statements
Interim Management Discussion & Analysis
Certain disclosures
2 deadlines for filing 10 – Q for 3 types of filers
40 days - large accelerated + accelerated
45 days - all other
Purpose of 8 – K
Disclose changes for material events
5 components of stockholders equity (CARAT)
CARAT
Common Stock
Additional paid in capital
Retained earnings
Accumulated other comprehensive income
Treasury stock
What are the three categories of capital stock?
Authorized- allowed to sell
Issued- can sell soon
Outstanding - currently sold
Common shareholders equity
Total stockholders equity minus preferred stock
Book value per share
Common shareholders equity Divided by number of common shares
4 Types of preferred stock
Cumulative
Participating
Convertible
Mandatory redeemable
cumulative preferred stock?
Set dividend amount every period, what’s not paid gets added to dividends in arrears
Dividend in arrears
Unpaid dividends to preferred shareholders. These must be paid before any dividends can be paid to common shareholders.
Dividends in arrears are not liabilities until they are declared as payable
Participating preferred stock
Preferred stock holders, receive their fixed dividend, common stock holders get equal amount. If $ still remains from declared dividend, remainder is split amongst common and preferred prorata.
Opposite of participating preferred stock is non-participating preferred stock where they only receive their fixed dividend
Additional paid in capital
Amount paid for stock by stockholders above par
What kind of account is treasury stock?
Contra-equity
Debit = Inc
Credit = Decrease
Treasury stock is always subtracted from total stockholders equity
What 5 events can increase or decrease retained earnings
Income
Losses
All dividends
Error adjustments
Accounting principle changes Cumulative effects
Quasi reorganization
Quasi reorganization?
Instead of legally, declaring bankruptcy, a company can essentially decide an accounting reset button That clears all their books to 0
What are the 2 methods to record treasury stock?
Cost method
Legal/ Par value method
When are “gains/losses” recognized w Cost method vs par method
Cost method: when reissue stock
Par method: When repurchase stock
What are each of the following SEC Regulations?
S-X
S-B
S-K
S-T
S-X → Financial statements look SEXY (form & content, e.g., 10-K, 10-Q).
S-B → Small Business disclosures.
S-K → Non-financial info is KOOL 😎 (MD&A, descriptions).
S-T → Tech rules for electronic filing (EDGAR).
How do stock splits and stock dividends affect:
Shares outstanding
Retained earnings
Total stockholders equity
What are the steps to valuate inventory at LIFO using the lower of cost or market method?
A. Find the following:
Historical cost
Replacement cost
NRV = Selling price - costs to dispose
Floor = NRV - Profit
B. Find the “Market” value.
Market = Middle number between 2-4.
C. Inventory value = Whatever is smaller between Historical Cost and Market.
How are gains/losses from treasury stock shown under both cost and par method?
Never show treasury stock “gains/losses” on the income statement.
Gains go to APIC–TS, not Retained Earnings.
Losses reduce APIC–TS first, then hit Retained Earnings if APIC–TS is exhausted.
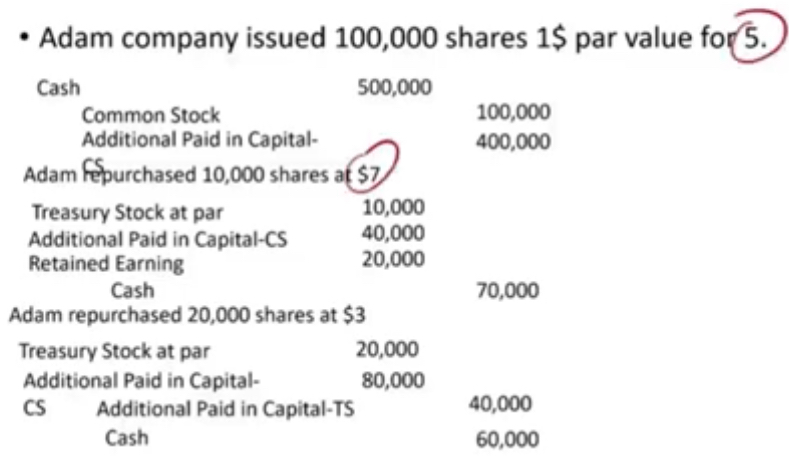
Journal entry for stock repurchase, and re-issue using cost method
Repurchase:
Dr. Treasury stock (Amount paid to buy back)
Cr. Cash
Reissue above buyback cost:
Dr. Cash
Cr. APIC -TS
Cr. Treasury stock
Reissue below buyback cost:
Dr. Cash
Dr. APIC -TS
Cr. Treasury stock
Journal entry for stock buyback, and re-issue using legal method
Credit cash for amount paid
Debit treasury stock at par
Debit APIC-CS at amount above par when originally issued
If loss, and there is balance in APIC-TS, debit APIC-TS. If no balance in APIC-TS, debit RE
If gain, credit APIC-TS
What are stock rights and how are they accounted for?
Stock rights = give existing shareholders the option to buy new shares (usually at a discount) to maintain their ownership % when new stock is issued.
Usually short-term and nontransferable.
Accounting:
Memo only when issued (no journal entry).
If exercised → record cash received + adjust Common Stock/APIC.
If allowed to expire → no entry needed.
When do dividends reduce retained earnings?
Date declared
How are property dividends recorded?
At fair value on declaration date, (same with gains and losses)
Difference between common stock and APIC
Common stock is the value at par
APIC is the value above par
What is a stock dividend?
Give more shares to stockholders (Not cash)
Ex: 10% stock dividend on 1,000 shares → receive 100 extra shares.
How do stock dividends affect total equity?
Stock dividends don’t affect total equity because their value is being shifted from a reduction of retained earnings to an increase in common stock and APIC
2 types of stock dividends and how they recorded
Small = <20-25% : recorded at FV
Large = >25% : recorded at par
What is the stock split and how is it recorded?
Ex: 2-for-1 stock split on 1,000 shares → now you own 2,000 shares, but each has half the par value.
No JE, just a memo
No change in equity.
Increase in # of stock outstanding retroactively
More # stock = lower EPS
If a stock split or stock dividend is issued after the balance sheet date (let’s say in Year 2), should it be considered in the Year 1 EPS calculation?
Yes.
Stock splits and dividends increase the WACSO, so they need to be recognized retroactively because this is relevant information for the viewer of the financial statements.
5 steps to recognize revenue
I am a STAR
Identify the contract with the customer
Separate performance obligations
Transaction price determination
Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations
Recognize revenue when the entity satisfies a performance obligation.
what kind of contract modification would count as a new contract?
Scope increases (more work)
Price increases
2 methods of recognizing revenue:
the completed contract method
the percentage of completion method
2 methods of calculating percentage of completion:
Input - efforts expended. Ex: costs incurred or labor hours expended.
Output - results achieved. Ex: units produced, milestones achieved.
What is construction in progress (CIP)?
CIP:
Asset - B/S account
Represents the costs of a project that are not completed yet.
GP is also added to CIP
CIP is recognized in the balance sheet JEs for both point in time and % of completion method
B/S JEs to recognize:
CIP
billings on CIP
*used in both % of completion and point in time projects*
Dr. CIP (Costs incurred so far)
Cr. Cash
Dr. AR: Billing in progress ($ you’ve asked the customer to pay already — can be <>CIP)
Cr. Billings on CIP (Contra-Asset — is the reverse of CIP)
I/S JEs for % of completion method?
Dr. CIP — GP
Dr. Construction Expense
Cr. Revenue— Long-term contracts
Point in time contract will not have this revenue/expense entry until the project is complete.
Process to calculate % rev recognized on long-term construction projects?
What are the total expected costs for the project? → Costs actually incurred to date + Estimated costs
What % of total costs have been incurred? → Costs actually incurred / Total Expected Costs
Revenue to recognize is based on the #2 → % from #2 x total contract revenue
What happens if CIP > Billings?
What happens if CIP<Billings?
If CIP>Billings → Asset
If CIP<Billings → Liability
How to record loss in long-term construction project?
Recognized immediately in period incurred or probable to be incurred.
Same for both % of completion and point in time contracts.
JE:
Dr. Loss on construction project
Cr. CIP
What kind of costs to obtain a contract are treated as assets vs expenses?
Asset: expected to be recovered and directly related to the contract
Expenses: would be incurred regardless of if the contract was obtained
Principal vs Agent
Principal - the entity in control of the good/service. Records gross amount of revenue for providing.
Agent - helps principal sell to customer. Records commission as revenue.
Forward Option
Entity has an obligation to repurchase the asset.
Call Option
Entity has a right (option) to repurchase the asset.
Put Option
Customer has the right to require the entity to repurchase the asset.
Bill and Hold arrangement
special conditions where entity can recognize revenue even though customer doesn’t have control over product.
this is because:
it is a specialized product/service
is set aside and ready to be provided to the customer
Consignment Relationship
principal provides a dealer/agent with product.
principal recognizes revenue when agent sells to customer.
Principal recognizes revenue when expiration of time in contract.
Warranties are accounted for as a …
separate performance obligation.
Accounting Estimate change
prospective treatment.
ex: depreciation, change in useful life of asset.
no prior period adjustment needed.
Accounting Principal change
switching from one acceptable accounting method to another.
Ex: FIFO to LIFO, cost to equity method for investments, % of completion to point in time.
Wrong Ex: Cash to accrual is NOT acceptable method bc GAAP requires accrual→ this would be error correction.
when multiple years are presented on financial statements for comparison, change in principal requires restatement of prior years shown.
Cumulative effect of change adjusts beginning RE, net of tax.
Exception: When changing from FIFO to LIFO
Investment income vs return of capital
Under equity method:
Investment income = Company earnings * % ownership
Return of capital = proportion of dividends received
Accounting Entity change
when there’s a consolidation or merger. in this case, the entity must restate any prior period financials that are being presented on the statements for comparison.
Accounting Error
4 examples?
anytime there is:
mathematical mistake (ex: adding/subtracting incorrectly)
misapplication of GAAP (ex: expenses an asset instead of capitalizing)
misuse or oversight of facts available at the time (ex: forgetting to record depreciation)
fraud/intentional misstatement
corrections affect the retained earnings and are shown net of tax. If prior statements are shown to compare, these need to be restated
Summary of significant accounting policies
description of all significant policies included in financial statements
1st footnote: general description
2nd footnote: significant accounting policies
What’s included:
measurement based used in prepping the F/S
specific accounting principals and methods
Remaining notes to the financial statements
4 examples?
subsequent events
fair value estimates
contingency losses
contractual obligations
tells about various assumptions used in preparation that might not be clear in current statements.
Disclosures of risks and uncertainties
Nature of operations
Use of estimates in preparation of financials
Vulnerability due to certain concentrations
relying too heavily on a certain customer or industry that is vulnerable.
tells about the business environment of the entity to provide additional clarity for investors.
Subsequent Event
an event or transaction that occurs after the balance sheet date but before financial statements are issued or are available to be issued.
2 types of Subsequent Events
Type 1 - Recognized → condition that existed at B/S date → should be recognized in F/S
Type 2 - Nonrecognized → condition that did not exist at balance sheet date → should not be recognized in financial statements.
F/S = Available vs Issued
available → board approves the financials. could take weeks or months after year-end, depending on the company.
issued → same dates for 10-K or 10-Q, once widely distributed
Time period to continue evaluating subsequent events
Public companies → evaluate events until F/S are issued
Private companies → evaluate until statements are available
why reissue financial statements?
if there is a material accounting error, something has been omitted, auditors require it, or there is a change in accounting entity.
subsequent events after reissue?
should not recognize events that occurred after the original issue date unless required by GAAP.
most advantageous market
best price with lowest transaction costs
principal market
highest volume sold
3 types of FV valuation techniques:
MIC
Market
Income
Cost
Market Approach
Think: “What are others paying for something similar?”
Uses prices and info from actual market transactions (comparable companies, sales of similar assets).
Example: Using the P/E multiple of similar public companies to value your private company.
Cost Approach
Think: “What would it cost to replace or reproduce this?”
Based on the amount currently required to replace the service capacity of an asset, adjusted for depreciation/obsolescence.
Example: Valuing a machine by what it would cost to buy a new one today, minus wear and tear.
Income Approach
Think: “What future cash flows will this bring me, discounted back to today?”
Converts expected future amounts (like cash flows, earnings, or cost savings) into a single present value.
Example: DCF (discounted cash flow model).
FV hierarchy of inputs
Ranked by reliability. 1 = most reliable.
Level 1: Observable, active, identical. Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (most reliable).
Ex: Closing price of Apple stock on NASDAQ.
Level 2: Observable, quoted. Other observable inputs (directly or indirectly).
Ex: Prices for similar assets, interest rate curves, yield spreads.
Level 3: Unobservable and assumption based (least reliable, based on company assumptions/models).
Ex: Discounted cash flow for a private company’s shares.
FV disclosures
Fair value disclosures:
Valuation technique (MIC)
Which level of inputs were used (Level 1 to 3)
Changes in methods/assumptions from prior periods
Needed because it helps users judge quality and reliability of reports.
Exceptions for FV disclosures
if it is not practical to measure
can’t be reasonably determined
not super reliable
Special Purpose Frameworks
OCBOA
alternate set of accounting rules from GAAP/IFRS.
OCBOA → other comprehensive bases of accounting
exist because it might be cheaper or simpler than GAAP and are used when GAAP isn’t required.
Main condition: financial statements have to be clear on which framework is being used.