Module 1 Notes
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Endocrine System,
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
endocrine system
a communication system of the body
slow; long
the endocrine system is ___ but ____ lasting
secretes hormones into circulation
what does the endocrine system do?
No
Are all glands part of the endocrine system?
Yes
Are all endocrine organ systems glands?
exocrine glands
secretes substances into ducts that empty onto skin or into a cavity
exocrine glands
sebaceous glands and lacrimal glands are examples of what type of gland?
endocrine glands
ductless; secrete chemical (hormone) directly into circulation
it travels in the blood until it reaches a target organ
where do hormones go once released by an endocrine gland?
the target organ has receptors on cells that bind the hormone. This will trigger a reaction within the cell
once the hormone reaches a target organ what happens?
growth, homeostasis, electrolyte balance, etc.
What do hormones regulate?
hypersecretion
too much hormone
hyposecretion
too little hormone
steroid and thyroid hormones
which hormones are lipid soluble?
False
Lipid soluble hormones cannot pass directly through the membrane.
Mechanism of Action for Steroid and Thyroid hormones
passes directly through the membrane with the help of a transport protein
transport proteins
the use of _____ decreases the filtering of the hormone into the urine
Mechanism of Action for Protein Hormones
cannot pass through the membrane, so it binds with a receptor cell to utilize a second messenger to do the job.
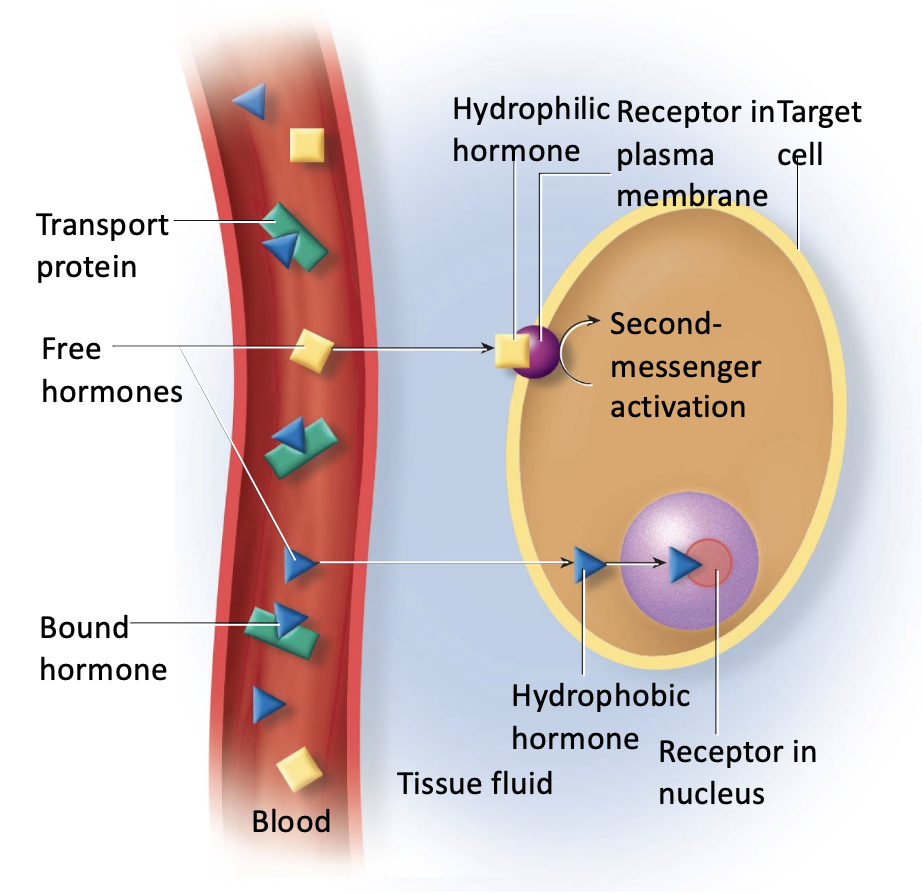
insulin, growth hormone
examples of nonlipid soluble (protein) hormones
estrogen, testosterone, cortisol, T3/T4
examples of lipid soluble (steroid and thyroid) hormones
nonpolar
are steroid and thyroid hormones polar or nonpolar?
polar
are protein hormones polar or nonpolar?
pituitary gland
attached to the hypothalamus by the infundibulum
master endocrine gland
what is the nickname for the pituitary gland?
releasing; inhibiting hormones
The hypothalamus produces ______ or ___________ that act on the anterior pituitary
capillary network (the primary plexus)
Nerve cells within the hypothalamus secrete substances into a _________ that then drains through the infundibulum and into the anterior pituitary.
secondary plexus
these releasing and inhibiting hormones from the hypothalamus enter the ________ and signal the anterior pituitary to either inhibit or increase the release of hormones.
tropic hormones
In response to releasing hormones, released from the hypothalamus, the anterior pituitary may release _________ that stimulate other endocrine glands to release their hormones.
thyroid stimulating hormone
If the hypothalamus secretes Thyroid releasing hormone, the pituitary secretes ___________
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
If the hypothalamus secretes corticotropin releasing hormone, the pituitary secretes ___________
follicle stimulating hormone; luteinizing hormone (LH)
If the hypothalamus secretes gonadotropin releasing hormone, the pituitary secretes ___________
prolactin
If the hypothalamus secretes prolactin releasing hormone, the pituitary secretes ___________
growth hormone
If the hypothalamus secretes growth hormone releasing hormone, the pituitary secretes ___________
T3/T4 released from the thyroid
What does thyroid stimulating hormone do to which organ?
cortisol secreted from the adrenal cortex
What does Adrenocorticotropic hormone do to which organ?
stimulates development of follicles in the ovary, which then produces estrogen and sperm
What does follicle stimulating hormone do to which organ?
causes ovulation; stimulates testicles to secrete T
What does Luteinizing hormone do to which organ?
promotes development of the mammary glands
What does prolactin do to which organ?
promotes growth to the target organ
What does growth hormone do to which organ?
tissue (bone, skeletal muscle, cartilage) and liver
what has receptors for growth hormone?
insulin-like growth factors
the binding of growth hormone causes the cell to synthesize and secrete what?
promotes uptake of amino acids
promotes lipolysis
promotes glycogenolysis
“Glucose Sparing Effect”
The effects of IGFs:
hyposecretion
this problem during childhood can lead to dwarfism
hypersecretion
this problem during childhood can lead to gigantism
hypersecretion
this problem during adulthood can lead to acromegaly
the anterior pituitary creates its own hormones while the posterior pituitary releases hormones created by the hypothalamus
Explain how the functioning of the anterior pituitary is different from that of the posterior pituitary.
promote uptake of amino acids
promotes lipolysis
promotes glycogenolysis
What are the effects of IGF’s
The hypothalamus produces GHRH, causing the anterior pituitary to release GH, causing the liver to create IGF, leading to glycogenolysis
If a patient is hypoglycemic, how does the body respond? (Hypoth., Ant. Pit., Liver, ___)
The hypothalamus will produce GHIH, keeping anything else from happening.
If a patient is hyperglycemic, how does the body respond? (Hypoth., Ant. Pit., Liver, ___)
gigantism is where the person becomes taller (and therefore larger) and acromegaly is the thickening of bone tissue
How is acromegaly different from gigantism?
posterior pituitary
which endocrine gland has hormones that are produced and released by neurons with cell bodies in the hypothalamus and axon terminals in the organ?
ADH
which hormone does the hypothalamus secrete when you are dehydrated?
kidneys reduce urine output, vasoconstriction, increase in blood pressure
what are the 3 major effects of Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
frequent urination, excessive thirst, electrolyte loss
what are the symptoms of hyposecretion (in relation to ADH), or diabetes insipidous?
give ADH
treatment for diabetes insipidous
triggers uterine contractions, “milk letdown”, ejaculation
3 major effects of oxytocin (2 female 1 male)
follicular/parafollicular cells
what type of cells are in the thyroid gland?
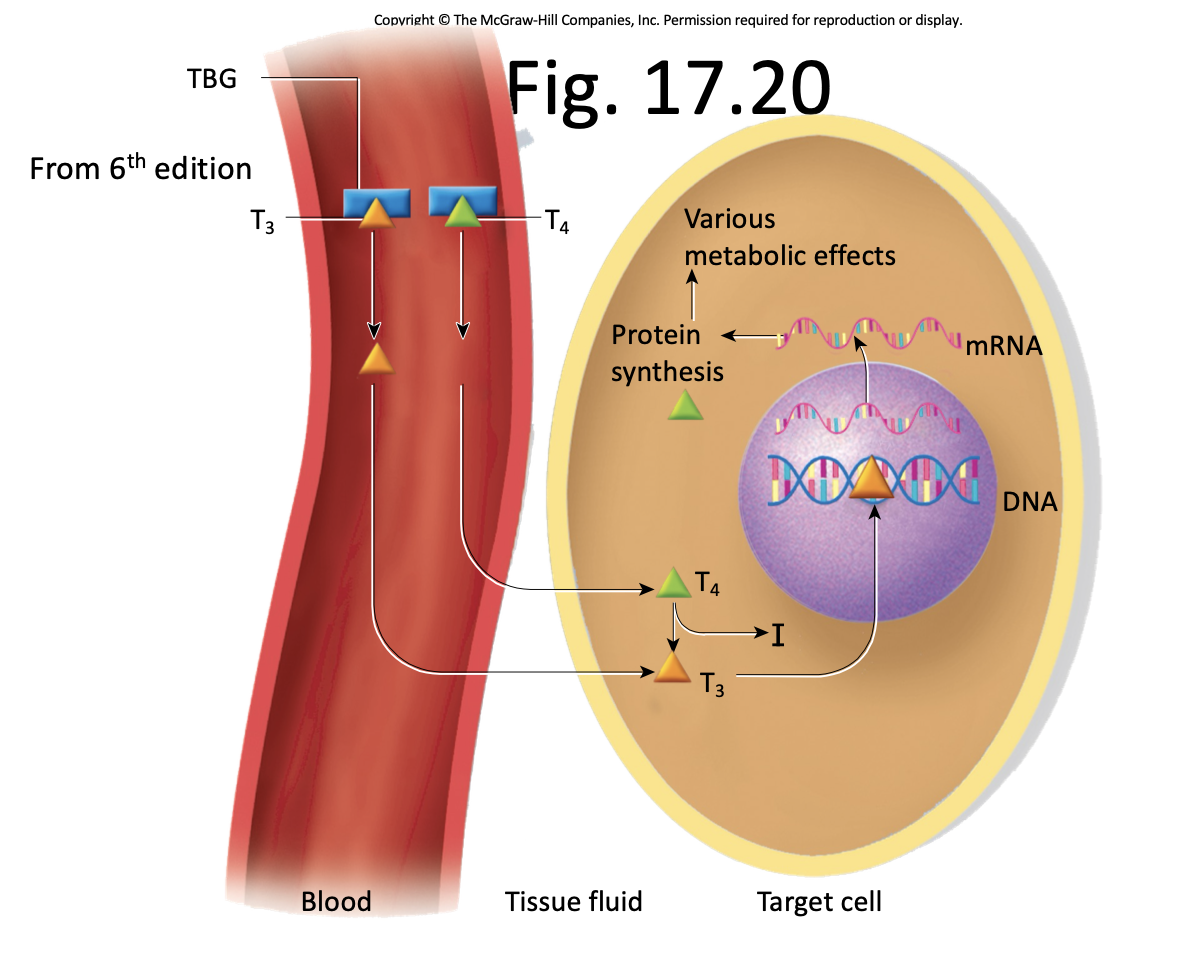
T3/T4
what do follicular cells in the thyroid secrete?
calcitonin
what do parafollicular cells in the thyroid secrete?
increases basal metabolic rate (BMR), promotes protein synthesis, promotes catabolism of glucose and fatty acids.
3 main effects of T3/T4
increases the number of Na/K pumps and upregulates the number of beta receptors that bind NE/E
how does T3/T4 promote protein synthesis?
TSH remove I from bloodstream, TGB, TGB + I + I + I into lysosome into bloodstream
Explain how T3/T4 is made (explain out loud, type key words)
goiter forms
what would happen if iodine was not available?
no negative feedback
what causes a goiter to form when there is no iodine for the thyroid?
hypothyroidism
not enough thyroid hormone is produced
hyperthyroidism
too much thyroid gland is produced
congenital hypothyroidism
condition that causes dwarfism and mental retardation in children
Give specific examples of how T3 and T4 would increase basal metabolic rate
dry skin
weight gain
slowed reflexes
hair loss
decreased body temperature
tired
“brain fog”
constipation
symptoms of hypothyroidism
myxedema
subcutaneous swelling, especially facial skin
grave’s disease
autoimmune disorder where an antibody mimics TSH
flushed, moist skin
hot
weight loss
increased heart rate
anxious
diarrhea
symptoms of hyperthyroidism
exophthalmos
protrusion of eyes
calcitonin
released when blood calcium levels increase
calcitonin
acts to decrease blood calcium levels
calcitonin
what is hyposecreted when there is increased demineralization of bone?
calcitonin
what is hypersecreted when there is increased activity of skeletal muscle and neurons?
parathyroid gland
what gland is on the posterior surface of the thyroid?
parathyroid hormone
what hormone is released when blood calcium levels decrease?
kidneys detect low BP, secrete Renin; Renin converts angiotesinogen to angiotensin I; lungs use ACE to convert angiotensin I to II, which causes the adrenal gland to produce aldosterone
Explain how the detection of low blood pressure by the kidneys leads to the secretion of aldosterone by the adrenal glands
stimulates cells to break down proteins
stimulates lipolysis
the amino acids and fats travel to the liver where they undergo gluconeogenesis to make glucose
How does cortisol maintain blood glucose levels?
estrogen
what do granulosa cells produce?
testosterone
what do interstitial cells (leydig cells) produce?
progesterone
what do corpus luteum produce?
sperm and egg
what are the gametes?