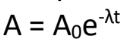RT203 - RADIOACTIVITY (BASICS)
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
No solving, just the basics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Radioactivity
Process of losing energy to reach a stable state.
This excited state can last for a few moments to billion of years and is measured in terms of half-lives.
This lose of energy can be in form of pure energy, particles, or both.
The nuclei of some nuclides are not stable
They disintegrate or undergo nuclear transformation spontaneously and in random process
Radioactivity
is the emission of particles and energy in order to become stable.
Radioactivity Decay
results in emission of Alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays.
Half-Life
the time required for a quantity of radioactivity to be reduced to one-half its original value.
1 Bq
1 per second
the number of decaying nuclei per second
1 Cu
3.7 x 10^10 Bq
(1852-1908)
Henri Becquerel
Henri Becquerel
Discover the radioactivity in 1896
1896
Henri Becquerel Disocovered Radioactivity in?
Henri Becquerel
He noted that a piece of mineral containing uranium when placed over an exposed photographic plate just as if it has been exposed to light.
The blackening of the photographic plate was due not to light but to a radiation being emitted by the uranium mineral.
photographic plate, radiation being emitted by the uranium mineral.
The blackening of the __________________ was due not to light but to a _____________________________.
(1867-1924)
Marie Curie
Pierre & Marie Curie
Discovered that polonium and radium also emit radiation.
Polonium & Radium
Pierre & Marie Curie discovered?
Artificial Radioactivity
Radioactivity produced by man
Irene Curie-Joliot produced the first radioactive product when they bombarded aluminum with alpha particles from polonium source to study the emitted neutrons and positrons.
Irene Curie-Joliot
Produced the first radioactive product when they bombarded aluminum with alpha particles from polonium source to study the emitted neutrons and positrons.
Alpha Particles
Beta Particles
Gamma Rays
Radioactive elements emitted into 3 types of radiation
Alpha Particles
Fast moving helium nuclei; positive electrical charge
Beta Particles
Negative electrical charged electrons.
Gamma Rays
o Electromagnetic waves of very short wavelength and travelling within the speed of light.
o No charge at all.
Half-Life
the time in which a radioactive substance will lose half of its activity through disintegration.
Half-Life
The amount of time that is required to reduce the radioactivity to 1⁄2 of its present value.
Physical Half-Life
Biological Half-Life
Effective Half-Life
3 Types of Half-Life:
3.83 Days
Half Life of:
Radon Gas
2.7 days
Half Life of:
Gold-198
Physical Half-Life
the average time required for the decay of half the atoms in a given amount of a radioactive substance.
Biologic Half-Life
the time in which a living tissue, organ, or individual eliminates, through biologic processes, half of a given amount of a substance that has been introduced into it.
Effective Half-Life
the half-life of a radioactive isotope in a biologic organism, resulting from the combination of radioactive decay and biologic elimination.
Alpha Decay
Beta Negative Decay
Beta Positive Decay
Gamma Ray Emission
Electron Capture
Types of Decay:
Alpha Decay
Americium 241 – smoke detectors
Alpha Decay
If substances emitting alpha particles are ingested, inhaled, injected or introduced through the skin, then it could result in a measurable dose.
Alpha Decay
accompanied by gamma photon emission.
Alexander Litvinenko's 2006 murder
Polonium-210
Russian dissident ___________________________ by radiation poisoning is thought to have been carried out with _______________, an alpha emitter.
Alpha Decay
Russian dissident Alexander Litvinenko's 2006 murder by radiation poisoning is thought to have been carried out
with polonium-210, an alpha emitter.
Beta Minus
Beta Plus
2 types of Beta Decay:
Beta Minus
Interacts with neutron
Beta plus
Interacts with protons
Electron Capture
is a process in which a proton-rich nuclide absorbs an inner atomic electron (changing a nuclear proton to a neutron) and simultaneously emits a neutrino.
Radioactive Decay Law
• Julius Elster and Hans Geitel observed that the strength of a pure radioactive substance decrease exponentially.
• Radioactivity was found to be a property of the individual atoms, not of a substance as a whole.
• Statistical nature of disintegration was established.
• Random process
• Universal law that describes the statistical behavior of a large number of nuclides
Julius Elster & Hans Geitel
observed that the strength of a pure radioactive substance decrease exponentially.
• Curie (Ci)
• Becquerel (Bq)
• 1 Bq = 1 disintegration per second
• 1 Ci = 3.7x10^10 Bq
Unit of Radioactivity
A = present activity
Exponential Decay Law:
What is the meaning of (A) in the formula?
(A is same with N)
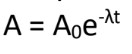
A0 = original activity
(Can also be Initial Activity)
Exponential Decay Law:
What is the meaning of (A0) in the formula?
(A0 is same with N0)
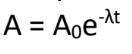
λ = disintegration constant / decay constant
(it’s not or, but over decay constant)
Exponential Decay Law:
What is the meaning of (λ) in the formula?
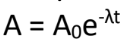
t = elapsed time
Exponential Decay Law:
What is the meaning of (t) in the formula?
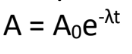
t ½ = Half-Life
Exponential Decay Law:
What is the meaning of (t ½ ) in the formula?