Unit 4 - Macro Economics Stephens
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/42
Earn XP
Last updated 1:47 PM on 5/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
1
New cards
aggregate
total of all (sum of all)
2
New cards
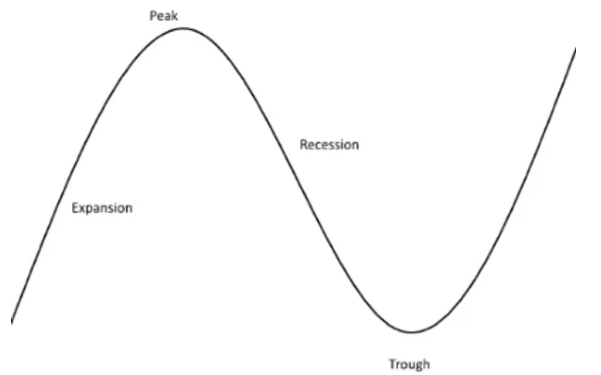
expansions
increased economic growth
(rising up on the business cycle)
(where we want to be)
(rising up on the business cycle)
(where we want to be)
3
New cards
peak
economic growth levels off
(tip of the business cycle)
(tip of the business cycle)
4
New cards
contraction
decreased economic growth
(going down on the business cycle)
(going down on the business cycle)
5
New cards
trough
recovery period
(bottom of the business cycle)
(bottom of the business cycle)
6
New cards
recessions
6 month decline in real GDP
7
New cards
inflation
increasing prices for goods and services
(normal in a growing economy)
(normal in a growing economy)
8
New cards
US economic goals
1 - growth
2 - low unemployment rates
3 - stable prices
2 - low unemployment rates
3 - stable prices
9
New cards
Federal Reserve Act
created the federal reserve bank
(1913)
(FED)
(1913)
(FED)
10
New cards
federal reserve bank
* board of governors
* 7 individuals nominated by President and approved by congress
* district banks
* 12 banks, 12 districts
* we live in district 7
* 7 individuals nominated by President and approved by congress
* district banks
* 12 banks, 12 districts
* we live in district 7
11
New cards
economic indicators
* GDP
* unemployment rate
* consumer price index (CPI)
* unemployment rate
* consumer price index (CPI)
12
New cards
GDP
measures the total value of all domestically produced goods/services
13
New cards
GDP equation
GDP=C+I+G+NX
c - consumer spending
I - investment (business)
G - government
NX - net exports (exports-imports)
c - consumer spending
I - investment (business)
G - government
NX - net exports (exports-imports)
14
New cards
real numbers
numbers adjusted for inflation
15
New cards
nominal numbers
numbers not adjusted for inflation
16
New cards
base year
equal to 1 or 100
used for chained dollars
used for chained dollars
17
New cards
chained dollars
$ chained into a base year
18
New cards
labor force
population 16 and older
19
New cards
unemployed population
16 or older actively seeking however unable to find employment
20
New cards
unemployment rate equation
unemployment rate=unemployed people/labor force
21
New cards
unemployment rate uses
* used as a major indicator of the business cycle
22
New cards
low unemployment rate
lower unemployment suggests expansions
23
New cards
high employment rate
rising unemployment suggests contractions
24
New cards
frictional unemployment
normal, people between jobs
25
New cards
structural unemployment
normal, unemployed because of market changes
26
New cards
seasonal unemployment
normal, expected due to seasonal changes
27
New cards
cyclical unemployment
caused by a downward movement in the business cycle, during a recession
28
New cards
natural unemployment rate equation
natural unemployment=frictional unemployment + structural unemployment
29
New cards
unemployment measuring
* the Bureau of Labor Statistics calculates this every month, gets media coverage
* unemployment in April 2023 was 3.4% (relatively low)
* unemployment in April 2023 was 3.4% (relatively low)
30
New cards
deflation
decrease in prices for goods and services
* usually caused by overproduction or decreasing demand
* not good long term for an economy
* usually caused by overproduction or decreasing demand
* not good long term for an economy
31
New cards
purchasing power
the ability to purchase goods and services with your $
* inflation causes decrease
* inflation causes decrease
32
New cards
groups harmed by inflation
* fixed incomes
* savers
* lenders
* savers
* lenders
33
New cards
groups helped by inflation
* some investors
* borrowers
* borrowers
34
New cards
demand pull inflation
will happen when aggregate demand increases
* increase in money supply
* increase in money supply
35
New cards
cost push inflation
will happen when productive resources increase in price
* productive resources (land, labor, capital)
* inflation causes inflation
* productive resources (land, labor, capital)
* inflation causes inflation
36
New cards
hyperinflation
excessive and increasing out of control, typically defined as 50% increase each month
37
New cards
consumer price index (CPI)
standard measurement of inflation
* calculated by the Bureau of Labor Statistics
* calculated by the Bureau of Labor Statistics
38
New cards
market basket
survey of prices of goods and services for atypical urban consumer (1982-84)
* products everyone would use (milk, eggs, gas)
* products everyone would use (milk, eggs, gas)
39
New cards
how countries control inflation
decrease the money supply, not popular for consumers/workers
* monetary policy, fiscal policy
* monetary policy, fiscal policy
40
New cards
monetary policy
decrease money supply (Federal Reserve Bank)
* used to control inflation
* used to control inflation
41
New cards
fiscal policy
increasing taxes
* used to control inflation
* used to control inflation
42
New cards
how countries deal with recessions
add money into circulation
* lower interest rates
* rates which banks loan money to the public
* open market operations
* buy bonds
* lower reserve ratio
* lowers money banks are required to hold
* lower interest rates
* rates which banks loan money to the public
* open market operations
* buy bonds
* lower reserve ratio
* lowers money banks are required to hold
43
New cards
business cycle
expansion, peak, contraction, trough