Diversity Exam 2: Animals
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
animal
multicellular, heterotrophic, internal digestion, movement and nervous systems
monophyletic
closest living relative to animals
choanoflagellates
cambrian explosion
large increase in diversity, seen in fossil record
~540 mya
establishment of basic body forms still seen today
land not yet colonized
punctuated equilibrium
evolution containing long intervals of relative stasis punctuated by short periods of rapid diversification
success of the cambrian explosion
increase in global O2
increase in ocean Ca2+
expansive continental shelf
evolution of hox genes (body plan changes)
extinction events
late oridivician: 85% all species, volcanism and anoxia
late devonian: 70% all species, ocean anoxia, global cooling flux
permian-triassic: 80% marine, 70% terrestrial, global warming, ocean acidification
triassic-jurassic: 70% all species, volcanism, global warming, ocean acidification
cretacous-paleogene: 75% all species, asteroid, bye all non avian dinosaurs
trends in animal evolution
centralization: of nervous system
cephalization: sensory organs concentrated towards anterior end
ordivician
modern spinal column, first fish
plants colonize land, then animals
fish evolution
early ordivician: first fish, armored plate evolution
late ordivician: bony jaws develop
two major lineages:
placoderms (bony fish ancestor)
acanthodians (shark ancestor)
devonian: shark and bony fish diversification, placoderms extinct by end of period, first lobe finned fishes evolve
end of triassic: bony fish diversify, extinction event
jurassic: body size increases, extinction event
cretaceous: closest ancestors of modern fish evolve
cretaceous-paleogene: radiation of bony fish
lobe finned fish
arose and diversified in devonian
first colonization of land end of devonian
led to evolution of tetrapods (amphibians, mammals, birds, crocs, squamates)
amphibians
early species fully aquatic, transition to terrestrial lifestyle
sarcopterygian ancestor (lungs, appendages with support away from body)
birds, crocs, reptiles diversification
first ancestors pennsylvanian period
sauropsid lineage
K-Pg extinction wiped our non avian dinosaurs
mammal diversification
first ancestors pennsylvanian period, synapsids
jurassic period: mammal lineage leading to modern
mammals forms
K-Pg extinction opened niches
homeostasis
maintaining a stable internal environment, requires energy
homeostasis parameters
temp, pH, blood glucose and pressure, heart and respiratory rates, behavioral feedback responses, [O2], [CO2], [Na+], [Ca+]
importance of thermoregulation
daily and seasonal temp variation can be extensive
temp affects rates of reactions (enzyme catalyzed and uncatalyzed rxns)
blood vessels and thermoregulation
vessels constrict or dilate based on temp
cold: vessels near surface constrict
warm: vessels near surface dilate
Q10 temp coefficient
measure of sensitivity of a reaction or physiological process to a change in temp (within a limited range)
can’t be extrapolated above/below the range
homeotherms
animals that keep a steady internal body temp
aka regulators
ex: birds, mammals
poikilotherms
animals that vary their body temp along with their environment
aka conformers
ex: frogs, lizards, fish
endotherm
animal gets heat primarily from internal sources (metabolism)
may or may not be successful at maintaining constant temp
ectotherm
animal obtains heat primarily from external sources
may have body temps higher or lower than external temp
thermoregulation small vs large body size
small: more behavioral options, move to microclimates
large: more structural and physiological, develop structures to help (adaptations)
microclimates
environments within a larger habitat that contain diff conditions
ex: shade, snow, roots, water depth
countercurrent heat exchange
in feet, cold and warm flow in opposite directions
surface and heat
larger surface = more heat lost
hibernation
state with low body temp and thermal conformity, most small mammals
heterotherms
homeothermic during summer, hibernate during winter
negative feedback regulation
stressor causes deviation from set point/range, physiology stabilizes system
positive feedback regulation
speeds up/amplifies process occurring
not typically involved in homeostasis
muscle function
convert energy from atp to mechanical movement
ex: move limbs, breathing, digestive movement, heart contraction
3 main types of muscles
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
skeletal muscles
attached by tendons to bones, packed with actin and myosin
troponin
cardiac muscles
shorter cells, branched, interlinked network
to decrease communication time
smooth muscles
actin and myosin arranged in loose network instead of bundles
locations: blood vessels, stomach, intestine, bladder, uterus
skeletal muscle anatomy
muscle fibers (cells) arranged into bundles (fascicles)
anchored to bone by tendon or directly fused on bone surface
voluntary locomotion, long cells with striations, adaptable
myofibrils
packaged into cells
contain myofilaments arranged into sarcomeres (actin and myosin)
sarcomere = contractile unit
t-tubules
cell membrane dips into cell
allow electric signal to travel deeper into the muscle cell
sarcoplasmic reticulum
modified smooth ER, calcium storage
myoglobin
oxygen storage within the cell
glycosomes
packets contain glycogen (sugar storage)
sarcomere structures
z line- boundaries of a sarcomere
m band/line - down middle of sarcomere
a band - dark band
i band - light band
h zone - no myosin heads (no actin)
z line
boundaries of a sarcomere
z = end of alphabet
m band/line
down middle of sarcomere
m = middle
a band/line
dark band
dArk
i band
light band
LIght
h zone
no myosin heads (no actin)
no Heads
titin
anchors myosin, elastic property, connects ends of filaments to z line
sliding filament theory
myosin pulling actin towards the middle
Ca released by SR, binds to troponin, twists tropomyosin, uncovers myosin binding site
myosin
chains twisted together, heads and tails
actin
two chains twisted, myosin head binding sites
interactions:
troponin = calcium receptor, unwinds+reveals binding sites
tropomyosin = twists so blocks binding sites at rest
innervate
to provide neural input
neuromuscular junction
synapse where a motor neuron axon makes contact w a muscle fiber
excitation
nerve impulse arrives at a neuromuscular junction, initiates an action potential
excitation-contraction coupling
electrical excitation of membrane leads to contractive activity by proteins
initiation of contraction
motor neuron is stimulated, sends signals towards muscle fibers
ACh released, diffuses acrpss hap
creates action potential in muscle fiber (across membrane)
ap spreads away from junction
cross bridge cycle
atp binds to myosin
atp hydrolysis (adp+p = activated conformation)
myosin head binds to active site
adp + p removed = power stroke
ending cross bridge cycle
ca ions transported back into SR, troponin twists tropomyosin, resting conformation
exoskeleton muscles
pull on interior surface
apodeme
part of exoskeleton projects inside body (what muscles attach to)
invertebrate muscles
asynchronous flight muscles, each excitation causes many contractions
catch muscle: adductor muscles able to sustain contraction forces closing the shell
hydrostatic skeleton
due to high fluid pressure inside
atp production
immediate (small amount stored in muscle)
glycolytic (glycolysis)
oxidative (citric acid cycle and ETC)
skeletal fiber types
slow oxidative
fast oxidative
fast glycolytic
slow oxidative
• slow myosin ATPase
• resists fatigue, high endurance
• thin (= little power)
• many capillaries
• red
fast oxidative
• fast myosin ATPase
• moderate sprinting/exercise
• thicker
• many capillaries
• red
fast glycolytic
• fast myosin ATPase
• anaerobic glycolysis
• depends on glycogen (short lived)
• intense, powerful movements
• large fibers
• few capillaries
• white/pale color
nervous systems basic functions
sensory input (receptors)
integration (thoughts, memories, decisions, sensation)
moros output (effector organs)
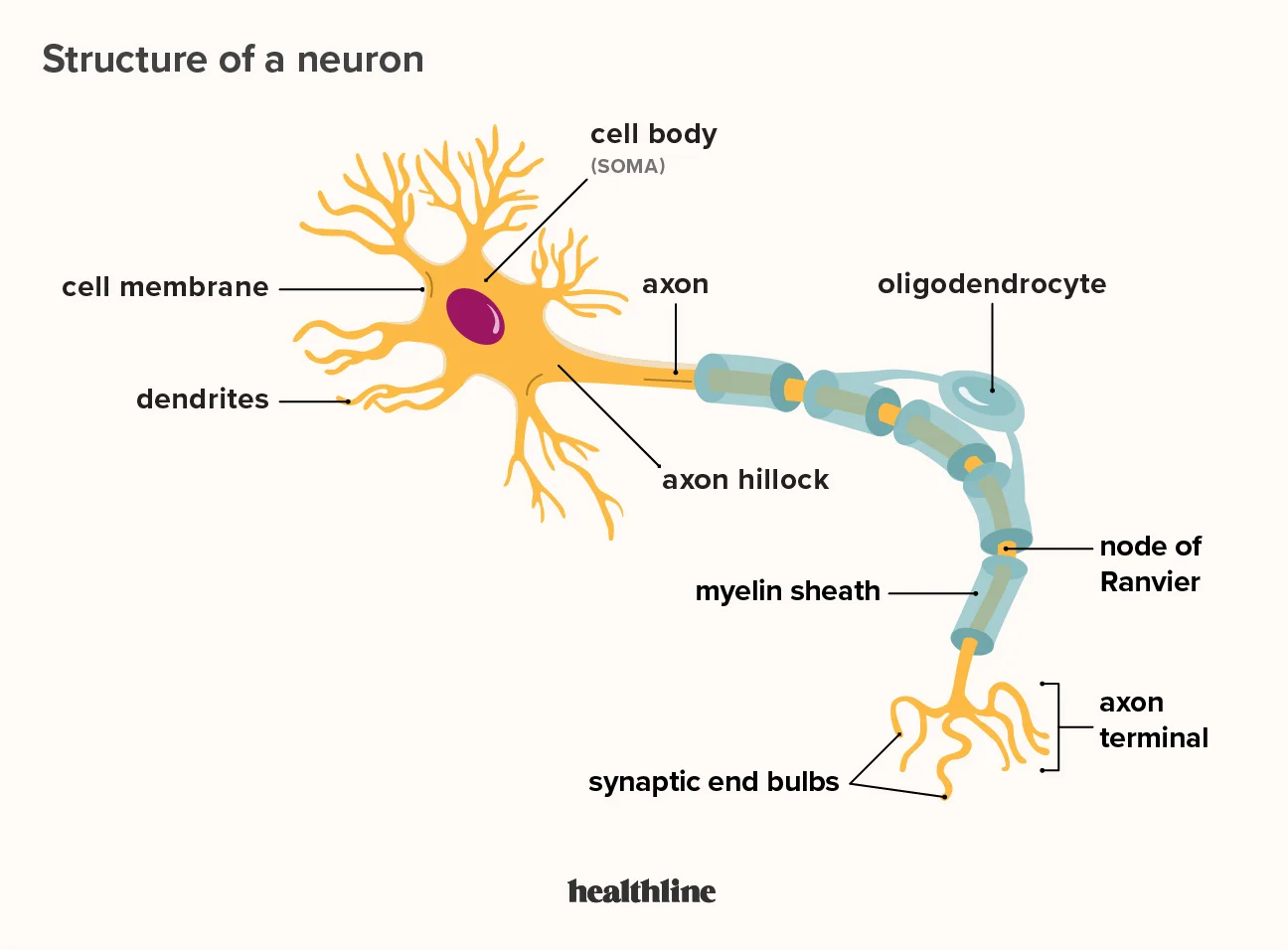
structure of a neuron
myelin
insulates, increases speed of transduction
neuron cell body
organelles, neurotransmitter synthesis
dendrites
receptive, high surface area
axon
variable size, conduction region, axon terminals
axon terminals
secretory region (secrete neurotransmitters)
excite or inhibit
resting membrane potential
living cells, ions separated against gradients
energy needed to separate
if separated = potential energy
voltage vs current
potential energy stored
flow of charge between points, released potential energy
negative potential established
Na/K pump:
3 Na out, high Na outside
2 K in, high K inside
differences in permeability: leak channels
100x more K leak channels than Na
gated channels
require specific signals (ligand, voltage)
voltage gated Na: activation and inactivation gates
graded potential
short distance signaling, variable strength, small region of membrane
current decreases with distance, stimulus opens ligand-gated channels
excitatory or inhibitory
initiate action potentials
converse at summation/trigger zone
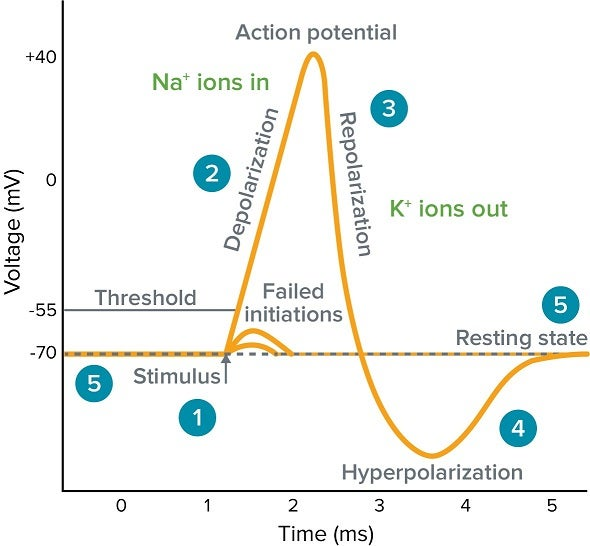
action potential
long distance signaling, constant strength
if summation potential strong enough
change in membrane potential
volate gated channels
inside of cell = more pos
doesn’t weaken with distance, all or nothing
action potential steps
resting state
depolarization
repolarization
hyperpolarization
myelinated fibers
prevent Na leaking, separates ionic attraction across membrane, increases conduction velocity
gaps between cells allows space for channel exchange
lipids = electric insulation
action potential graph
receptor cells transform stimuli into electric signals
transduction- conversion of energy from one form to another
1st step in receptor cells
graded potentials
potential is stronger with increased stimulation
2nd step in receptor cells
transmission: action potentials generated in nerves
stimulus energy relayed to integrative parts of nervous system for interpretation
2 types of receptor proteins
ionotropic: receptor protein is the ion channel
metabotropic: receptor protein relays signal through G protein mechanism to a channel, secondary messenger
receptor membrane proteins have high surface area = high sensitivity and response to stimuli
stretch receptors
mechanoreceptors, usually ionotropic
can be single neurons in simple systems, muscle spindle in skeletal muscle
further stretch = higher action potential
olfaction
metabotropic receptors
diversity of g protein couples receptor proteins (GPCRs) - one type per cell
oderants
chemicals detected by smell (chemoreceptors)
auditory systems
mechanoreceptors
sound waves > electric signals
high req waves → high pitch
low freq waves → bass/low pitch
human ear anatomy
external auditory canal- tympanic membrane (eardrum)
middle ear ossicles- oval window
diff pitches cause diff regions of basilar membrane to move
organ of corti- hair cells w stereocili, contact tectorial membrane
stereocilia move-neurotransmitters release onto neuron which generates ap - cochlear nerve - brain