PROTEIN ANALYSIS
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
Berzelius
Protein
In the earlier days, the complex nitrogen-rich substance found in cells of all animals and plants are not identified until ___ suggested the name “___”
Proteios = Primary
Protein came from the Greek word ___ which means ___
False.
Most of the 20 basic amino acids present in proteins were present from 1819 until 1904.
True or False.
Most of the 20 basic amino acids present in proteins were present from 1809 until 1914.
Proteins
They are the building blocks of the cell, which constitute the majority of its dry mass.
Answer: I, II, IV
III: should be nitrogen-rich substance
V: 20 basic amino acids
Which of the ff. describes proteins?
I. Product of transcription
II. Product of translation
III. Carbon-rich substance
IV. Contains the impact of data processed by nucleic acid
V. Has 21 basic amino acids
Chromatography
Martin and Synge (1942)
A technique which is now widely used to separate proteins.
This is developed by?
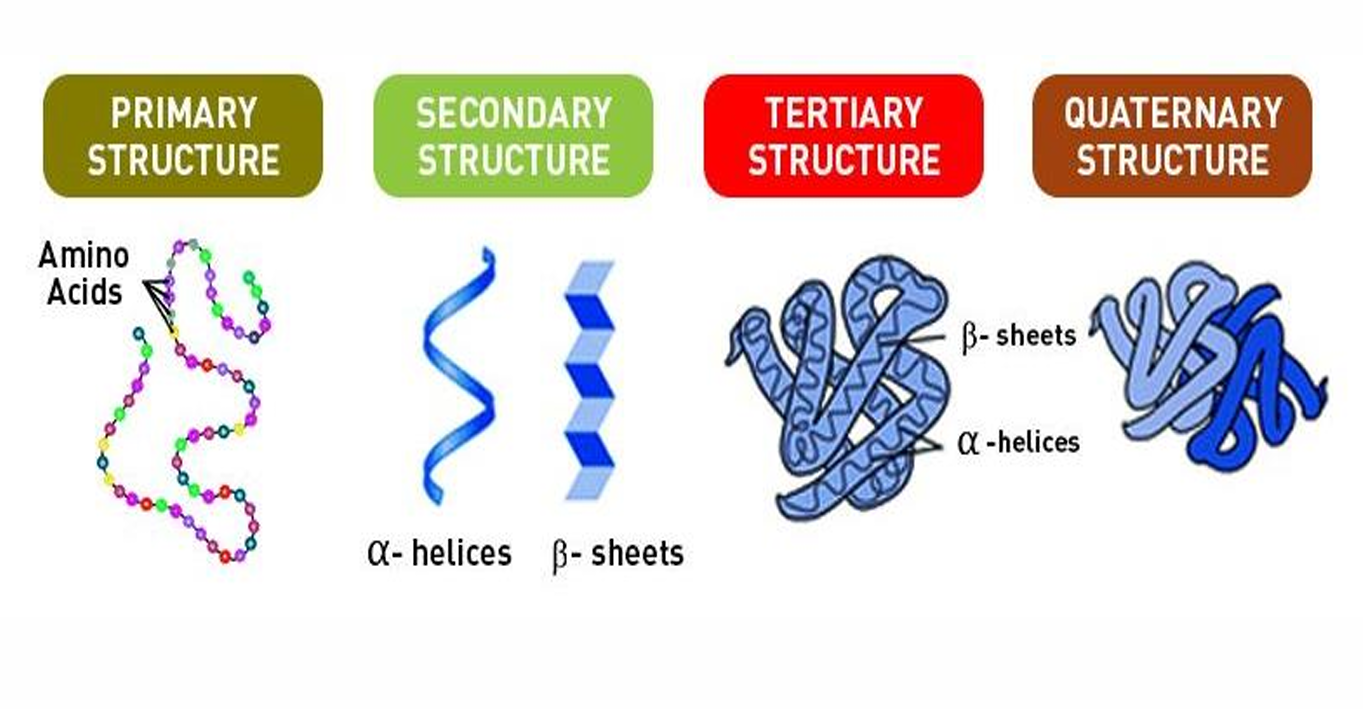
Primary structure
Secondary Structure
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
What are the different structures of proteins?
Primary Structure
This is composed of the sequence of a chain of amino acids.
Secondary structure
There is a hydrogen bonding in the peptide backbone, causing the amino acids to fold in repeating patterns.
a-helices
B-helices
What are the different patterns of secondary structure?
Tertiary structure
There is a 3-Dimensional folding of patterns of the protein due to the side chain interaction.
Quaternary structure
There is more than one amino acid chain.
Polymers
It is composed of covalently-linked amino acid residues and the carboxyl groups combined by peptide bonds.
Glycine
It contains a side chain of a single hydrogen.
Alanine
It contains a side chain of a methyl group.
Polypeptides
The amino acids form a long, linear chain, which is called?
Polypeptides → specific amino acid chain
It specifies the protein structure.
They share the same electrons
Peptide bonds release a water molecule because?
Proline
It doesn’t have an amino group.
Hydrogen bonds
Alpha helix and Beta sheets are held together by?
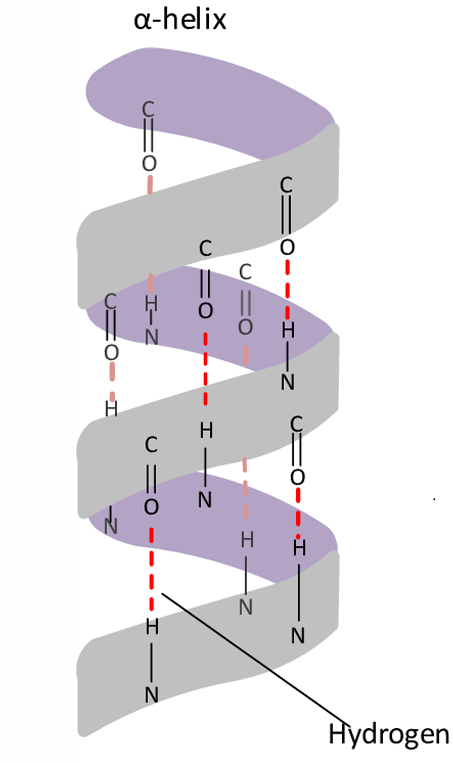
4th
Twist
In alpha helix, the hydrogen bonds form in every ___ amino acid and causes a ___ in the amino acid chain.
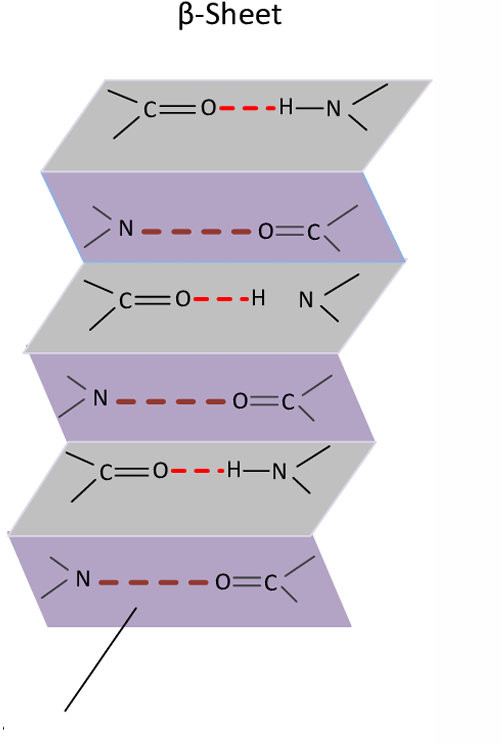
Pleats
Atoms
In beta sheets, the ___ are formed by the hydrogen bond between the ___ on the backbone of the polypeptide chains.
Tertiary structure
The protein molecule will bend and twist in a way that it could achieve the maximum stability and lowest energy state.
Quaternary structure
This is the association of two or more polypeptides into a multi-subunit complex. This is the assembly of individual polypeptides into a larger, functional clusters.
Hemoglobin (4 subunits: 2 alpha, 2 beta)
An example of quaternary structure
Sample Type
Location of Protein of Interest
Required Protein yield for the subsequent analysis to be performed
Method utilized
The procedure that may be used to achieve optimal isolation of proteins/ Protein Isolation Procedures depends upon:
Western blotting
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent (ELISA)
Gel shift assays (EMSA)
Reporter Assays
Mass Spectrometry and Immunoprecipitation
Proposed downstream applications for the quantification and identification of desired proteins.
Natural sources such as mammalian cell cultures
Tissues or bodily fluids
Overexpression in a model system such as:
Bacteria
Yeast
Insect or mammalian cells
Monoclonal antibodies from hybridoma cells
Plant cells used in agricultural biotechnology
Sources of proteins
Overexpression
This is the process where the gene are expressed at higher levels than normal within the cell or organism.
Naturally
Artificially induced
Overexpression can happen:
Produce large quantities of proteins
Monoclonal antibodies
Purpose of overexpression
Example
Mechanical disruption
Liquid homogenization
High-frequency sound waves
Freezing/thaw cycles
Manual grinding
Several methods are commonly used for physical lysis cells, including:
Require expensive equipment
Equipment is hard to use
Varying reproducibility
Protein denaturation or aggregation
Traditionally, physical techniques are used to disrupt cells, but there are disadvantages, such as?
Tissue disruption
Cell lysis
What are the first phases in cell fractionation?
To disaggregate the cells and break them open with minimal damage to the cellular fraction of interest
The goal of cell and tissue lysis
Properties of the source of sample
Choosing the best protein isolation method depends on the?
Physical methods
Heat treatment
Homogenization
Sonication
Chemical / Reagent-based methods
Treatment with detergent solution
Cell lysis have different methods. Cite examples.
Mechanical methods
It depends on the use of rotating blades to grind and disperse substantial amounts of complex tissue.
Waring blender
Polytron
What are commonly used for mechanical methods?
Waring blender
It is similar to the standard household blender
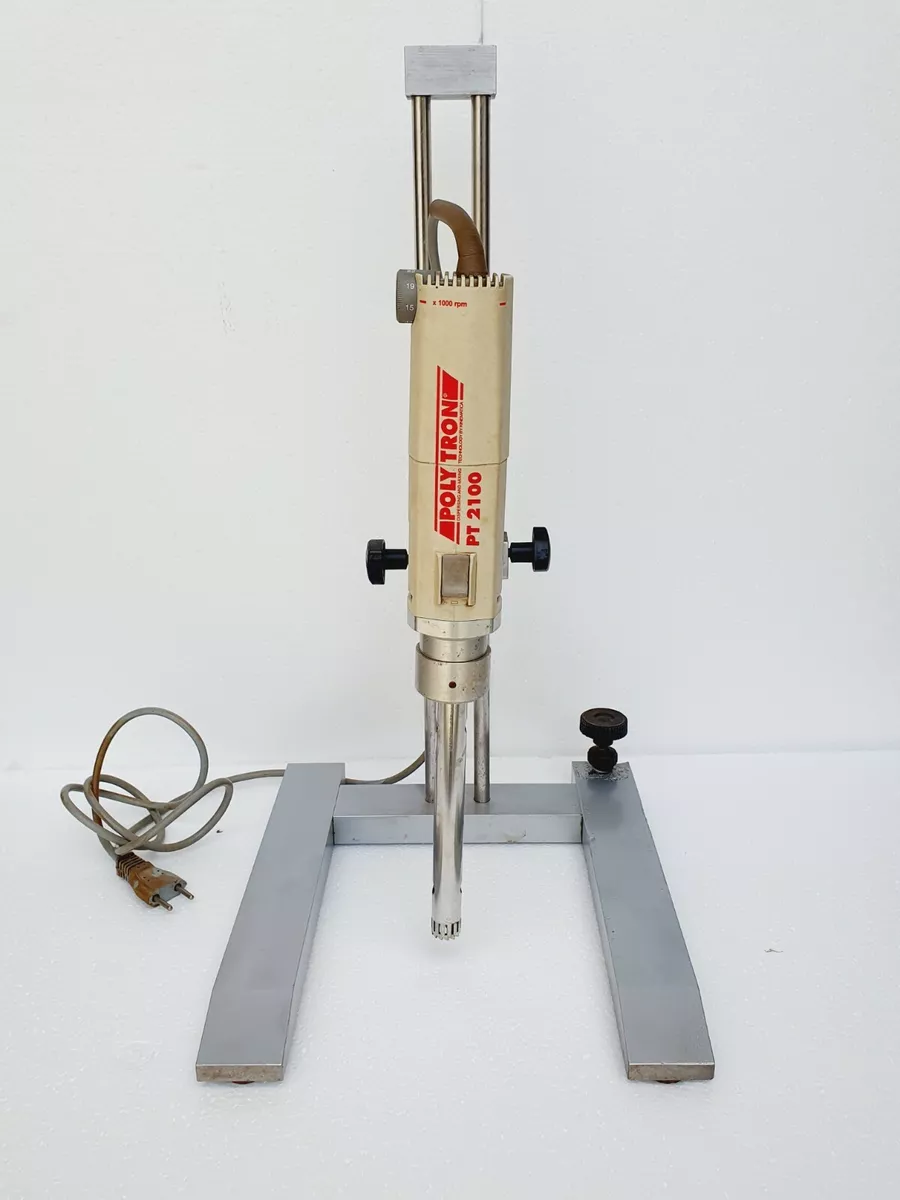

Polytron
It draws tissue into a long shaft containing rotating blades.
False.
In Polytron, the shafts vary in size to accommodate a wide range of volumes and can be used with samples as small as 1mL.
True or False.
In Polytron, the shafts vary in size to accommodate a wide range of volumes and can be used with samples as small as 1mm.
Liquid homogenization
It is the most commonly used technique for cell disruption.
Liquid homogenization
In this technique, cells are lysed by forcing the cell or tissue suspension through a narrow space, which is capable of shearing the cell membranes.
Dounce homogenizer
Potter-Elvehjem Homogenizer
French press
3 different types of homogenizers
Dounce homogenizer
It consists of a round glass pestle that is manually driven into a glass tube.
Potter-Elvehjem homogenizer
It consists of manually or chemical driven polytetrafluoroethylene pestle shaped to fit a rounded or conical vessel.
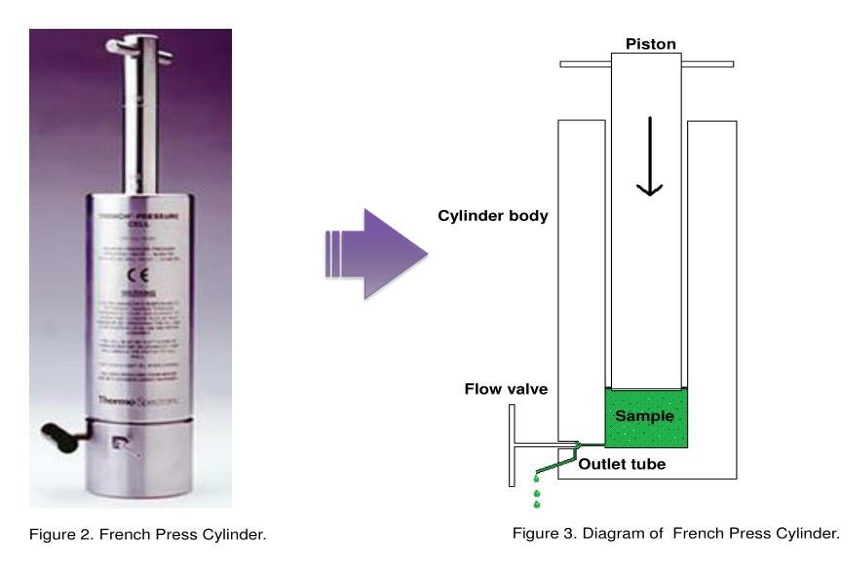
French press
It consists of a piston that is used to apply high pressure to a sample volume of 40-250 mL, forcing it through a tiny hole in the press.
40 - 250 mL
The sample volume in French press
French Press
The equipment is expensive, but the ___ is often the method of choice for breaking the bacterial cells mechanically
Freeze-thaw method
It is commonly used to lyse bacterial and mammalian cells.
Dry ice / ethanol bath
Room temp / 37 C
In Freeze-thaw method, the cell suspension is frozen in a ___/___ or freezer and then immediately followed by thawing at ___ temperature or ___.
Freeze-thaw method
This technique causes the swelling of the cells until they break as ice crystals.
The freeze-thawing process is repeated several times → lengthy
Disadvantage of freeze-thaw method
Recombinant proteins
Lysis
Although lengthy, freeze/thaw has been shown to release ___ ___ located in the cytoplasm of bacteria excellently and is recommended for the ___ of mammalian cells in some protocols.
Manual grinding
It is the most basic and common method used to disrupt cells.
Liquid nitrogen
Mortar and pestle
Manual grinding
First, the tissue needs to be frozen in ___ and then, crushed using a ___.
Tensile strength
Plant cells
Manual grinding
Because of the ___ of the cellulose and other polysaccharides comprising the cell wall, for instance of ___, ___ method is the fastest and most efficient way to access plant proteins and DNA.
Sonication
This method uses pulsed, high-frequency sound waves to agitate and lyse cells, bacteria, spores, and finally diced tissues.
Probes
Vapor bubbles
Shock waves
Sonication
Mechanical energy released from the ___ initiates the formation of microscopic ____ causing ____ to radiate through the sample.
Volumes
Sonication is best suited for?
The type of cell used
The frequency depends on?
Microscale cell disruption
It is often accomplished through chemical and enzymatic methods or combinations of the two.
Rapid, gentle, efficient, and reproducible → high protein yield
Extracts total protein or subcellular fractions
Disrupts lipid membrane and cell wall
Components are removed for downstream analysis
High conc. of salt and detergents incompatible with protein assays and mass spectrometry
The characteristics of reagent-based methods for lysing cells
Lysozyme (200 ug/mL)
It can be added to digest polysaccharide components of yeast and bacterial cell walls, making the cells easier to lyse.
Glass beads
An alternative to lysozymes wherein the use of this method will facilitate the crushing of cell walls. This edition is commonly used with yeast cells.
Increases
DNase
RNase
Glass Beads
The viscosity of a sample typically ___ during lysis due to the release of material that can be removed by adding ___ and ___ to avoid interfering with the protein target.
Protease inhibitors
However, in all of this, proteolysis can be a problem whenever cells are manipulated; this can be avoided by adding ____ to all samples due for lysis.
False.
Unlike nucleic acids, proteins do not have a generalized purification method.
True or False.
Unlike nucleic acids, proteins have a generalized purification method
Chromatography
Electrophoresis
Purification techniques of proteins wherein they are used to separate proteins into different bands depending on whether the goal is for preparatory step or for quantitative analysis.
Liquid Chromatography
Fast protein LC
High-Performance LC
The types of chromatography that can be used for protein purification, depending on the goal (preparatory or quantitative analysis).
Hydrophobic interaction column chromatography
Size-exclusion chromatography
Affinity chromatography
It is possible to use the following techniques either as a single step or a sequential connected step:
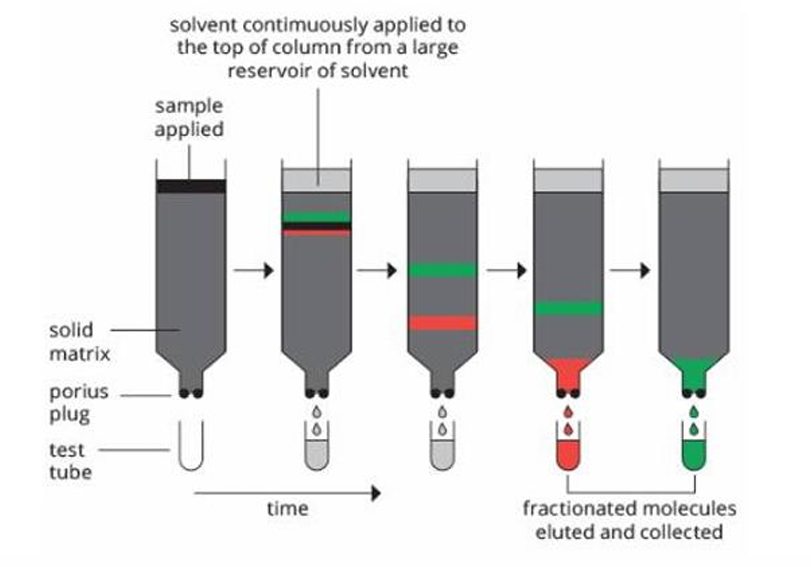
Column chromatography
It is a primary protein purification method in use in most laboratories.
Cylindrical column → porous solid matrix
Solvent → pumped
Matrix → 2
Column Chromatography
A combination of proteins in a solution is added to the surface of a ___ loaded with a ___ submerged in a solvent.
After that, a large amount of ___ through the column is ___ through the column.
Due to their association with the ___ , separated proteins are deluded ___ distinct levels, and they can be obtained individually as they flow from the bottom.
Charge
Hydrophobicity
Size
Ability to attach to specific chemical components (depending on matrix selection)
In column chromatography, proteins are separated according to?
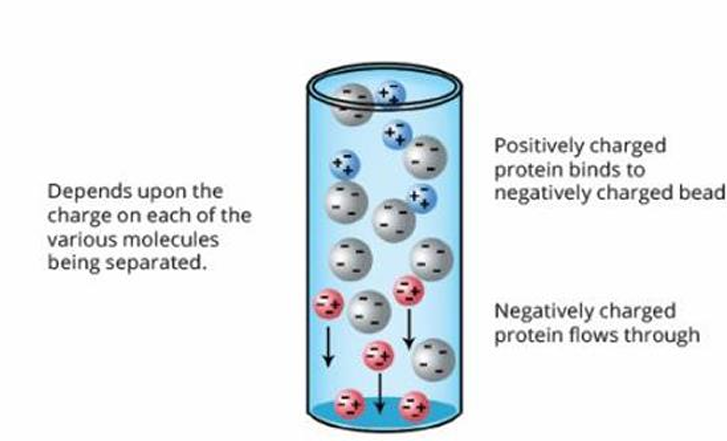
Ion-exchange chromatography
Columns of ion exchange are filled with tiny beads holding either positive or negative charges that retard proteins of the opposite charge.
pH
Ionic strength
In Ion-Exchange Chromatography, the interaction of protein and matrix relies on the ___ and ___ of the fluid moving down the column.
Binds to negatively charged beads
Flows through
Ion-exchange chromatography
Positively-charged protein
Negatively charged protein
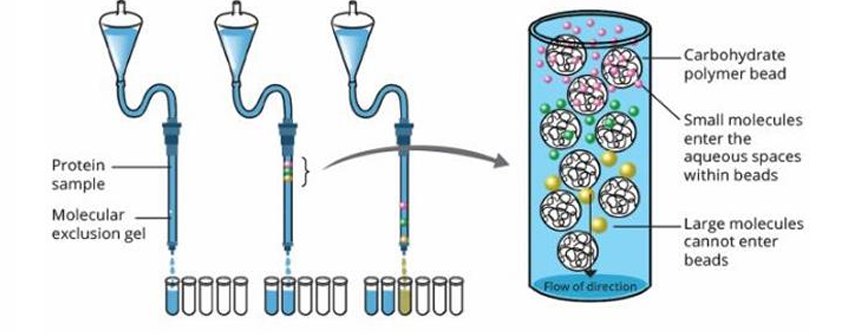
Gel-filtration chromatography
It separates proteins by size.
Postponed and moved through the column
Wiped out of the column
In gel filtration filtration:
Protein molecules tiny enough to reach the bead
Proteins that cannot enter the beads
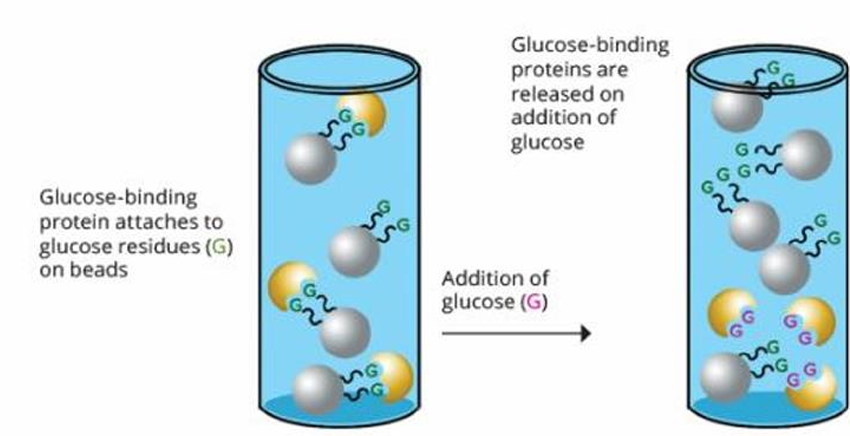
Affinity chromatography
It is contained in a matrix covalently pair with a molecule that interacts specifically with the protein of interest.
pH shift
Concentrated salt solutions
Affinity chromatography
Proteins that attach specifically to such a column can eventually be produced through a ___ or ____, and these are extremely purified.
Attaches → glucose residues
+ Glucose → Released
In affinity chromatography, the glucose-binding protein attaches to ___ residues on beads. Upon addition of glucose, the glucose-binding proteins are ___.
Colum Chromatography
What protein separation by chromatography?
Ion-Exchange Chromatography
What protein separation by chromatography?
Gel-filtration Chromatography
What protein separation by chromatography?
Affinity Chromatography
What protein separation by chromatography?
Western blot
It is used to detect antibodies to specific epitopes of antigen subspecies and confirm the specificity of antibodies detected by screening tests like ELISA.
Immunoblot
Other term for Western blot
Electrophoretically
Molecular weight
Membranes
Antibodies
In the Western blot technique, proteins are separated ___ according to their ___, transferred to ___, and identified through labeled ___.
Enzyme Immunoassays
They are similar to Western blot in a way where they use antibodies to detect antigens, but they are detected in microtiter plates (in vivo) than absorbent membranes.
Sensitivity
Specificity
But cannot be quantitative
Lateral flow techniques provide?
Sample preparation
Electrophoresis
Transfer
Blocking
Antibody incubation
Detection
Steps in immunoblotting
Linear state
In sample preparation, the proteins from fold state will turn into?
Electrophoresis
Migration of proteins based o their molecular weight
Membrane
In transfer, the proteins travel from gel to?
Blocking
It is done to prevent nonspecific binding of antibodies, and to cover the empty spaces of the membrane.
Antibody incubation
Primary and Secondary antibodies are added to the membrane
Detection
The membrane is treated with a substrate specific to the enzyme linked to the secondary antibody.
Loading buffer
Linearized protein → negative charge → size
Sample Preparation
A ____ is added to the sample to separate the macromolecules in the sample. This will result in ___ protein with a ___ charge proportional to their ___.