Reptile Laboratory Animal Medicine – Key Vocabulary
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Set of key vocabulary flashcards covering reptile biology, husbandry, clinical techniques, diseases, and surgery as presented in the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
# 1 reason reptiles are seen in practice
Diseases related to poor husbandry
Nutrition
Improper housing
Lighting
Temperature
Ectotherm
An animal that relies on external heat sources to regulate body temperature.
Preferred Optimal Temperature Zone (POTZ)
The range of environmental temperatures in which a reptile’s metabolic functions operate most efficiently.
Fossorial
Referring to organisms that primarily live underground.
Anesthesia/Surgery
Patient prep
Normal respiratory rate for most reptiles is 10-20 bpm IPPV should be done 4-6 times a minute
Anesthetic monitoring
As snakes become anesthetized, relaxation progresses from cranial to caudal
During recovery motor function returns in the opposite direction
The righting reflex is lost early during anesthetic induction
In snakes when the tongue is pulled from the sheath & retracts indicates surgical plane
If tongue withdrawal is lost they are too deep
celiotomies
Surgical procedures that involve opening the abdominal cavity for examination or treatment.
Salmonellosis
most recognized reptilian zoonosis
Zoonotic significance 1st reported in 1963 when 7 mon. infant contracted the disease from a pet turtle.
Over 2000 serotypes – some host specific
Symptoms in humans = abdominal pain, cramps, diarrhea, dysentery, nausea, vomiting, fever. In young children, meningitis, brain abscess.
Organism shed in feces intermittently
Ecdysis
The process of shedding the outer layer of skin; occurs in one piece in snakes and patches in lizards.
Dysecdysis
Abnormal or difficult shedding of the skin, often due to poor husbandry such as low humidity.
R lung is > half the body length
L small non-functional (85% smaller)
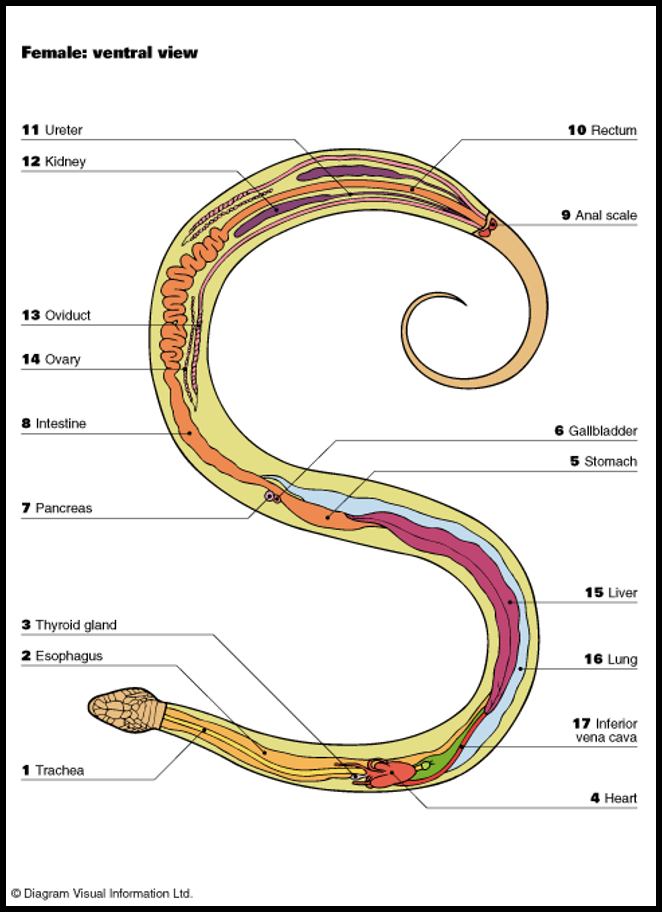
Viviparous
Describes animals that give birth to live young instead of laying eggs.
Oviparous
Describes animals that lay eggs, with embryonic development occurring outside the mother's body.
Ovoviviparous
Describes animals that produce eggs that hatch within the body, giving birth to live young.
Vomeronasal Sense
(Jacobson’s organ)
Detects particles of odor transmitted from the tongue
Aids in detecting prey
Clinical Techniques
Medication Administration
IV
–Tail vein
–Heart
–Palatine vein
SC
–Between scales (easier when coiled and can see skin folds)
IM
–Epaxial muscles
–Lateral muscle groups
–Needle is placed between the scales
ICe (intracoelomic)
–Avoid anatomical structures, use lower quadrant
–Fluids given ICe should be warmed
Gila Monster
Only poisonous lizard in the US
Lizard Eyes
Movable eyelids/nictitating membrane
Stationary eyelids/clear spectacle
Chameleons—Eyes move independently
Lizard Eyes
Visible as an opening in most species
Tympanic membrane
Clear
Scaled and not visible
Autotomy
The voluntary release of the tail as a defensive mechanism; common in many lizard species.
Chromatophore
Pigment-containing cell in reptile skin that allows color change for camouflage or communication.
Parietal Eye
Light-sensitive ‘third eye’ on the top of the head in some lizards, aiding hormone production and thermoregulation.
Cloaca
Common chamber in reptiles that receives fecal, urinary, and reproductive products before elimination.
Coprodeum
The anterior portion of the cloaca that stores feces.
Urodeum
Middle section of the cloaca that receives urinary waste (and reproductive products in females).
Proctodeum
Final cloacal chamber leading to the vent for elimination.
Turtle order
Chelonia
Turtle
aquatic or semi aquatic
Exception is the box turtle
Tortoise
terrestrial
Terrapins
semiaquatic hard-shelled
Hemipenes
Paired copulatory organs located in the base of the male lizard and snake tail.
Cloacal Probing
Technique for sexing snakes by measuring the depth a probe can be inserted into the hemipenal pockets.
Celiotomy
Surgical incision into the coelomic cavity of reptiles (equivalent to laparotomy in mammals).
Intracoelomic (ICe) Injection
Administration of fluids or drugs directly into the coelomic cavity.
Metabolic Bone Disease (MBD)
Skeletal disorder caused by calcium/phosphorus imbalance, vitamin D3 deficiency, or insufficient UVB light.
Salmonellosis
Zoonotic bacterial infection commonly carried and intermittently shed by reptiles, especially turtles.
Inclusion Body Disease (IBD)
Serious viral disease in boas and pythons characterized by neurologic signs and intracytoplasmic inclusions.
Paramyxovirus
Respiratory virus of snakes that can cause pneumonia and neurologic signs.
Pentastomiasis
Parasitic infection of the reptile respiratory tract caused by tongue worms (Pentastomids).
Gout
Condition in which uric acid crystals accumulate in organs or joints, often from dehydration or high-protein diets.
Dystocia
Difficulty in laying eggs or live young; often called egg binding in reptiles.
Paraphimosis
Prolapse of hemipenes that cannot be retracted, leading to swelling and tissue damage.
Shell Rot
Infection of turtle or tortoise shell scutes; classified as dry (fungal/bacterial) or wet (hemorrhagic, bacterial).
Aural Abscess
Pus-filled swelling behind the tympanic membrane of turtles, often due to vitamin A deficiency.
Stomatitis
Inflammation of the oral cavity (“mouth rot”), frequently caused by bacterial infection secondary to stress or injury.
Tail Whip
Defensive behavior in which lizards use their tails as weapons to strike predators or handlers.
Thermal Gradient
A range of temperatures within an enclosure that allows reptiles to thermoregulate behaviorally.
Ultraviolet B (UVB) Light
Wavelength of light (290-320 nm) required for cutaneous synthesis of vitamin D3 in reptiles.
Ventilation (in husbandry)
Air movement within an enclosure that helps regulate temperature and humidity while preventing respiratory disease.
Ectoparasite
Parasite such as mites or ticks that lives on the external surface of the host.
Nuchal Bone
Median bone at the anterior margin of a turtle’s carapace.
Carapace
Dorsal (upper) portion of a turtle or tortoise shell.
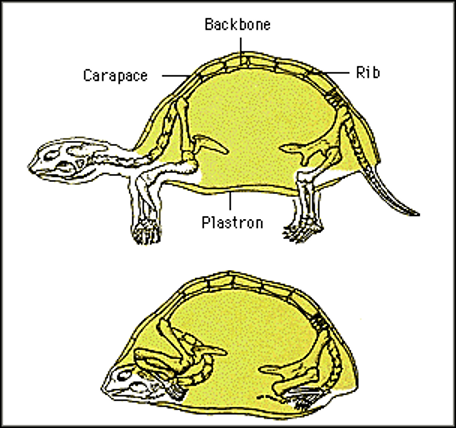
Plastron
Ventral (lower) portion of a turtle or tortoise shell.
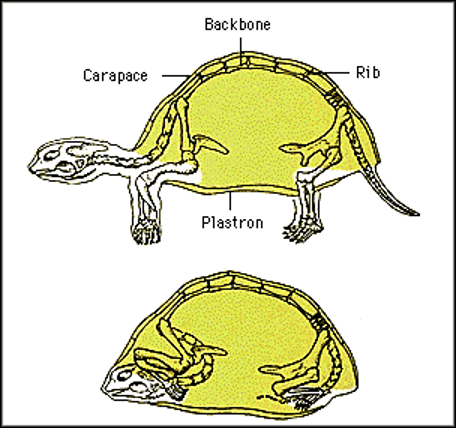
Scute
Keratinized scale covering the bony plates of a turtle shell.
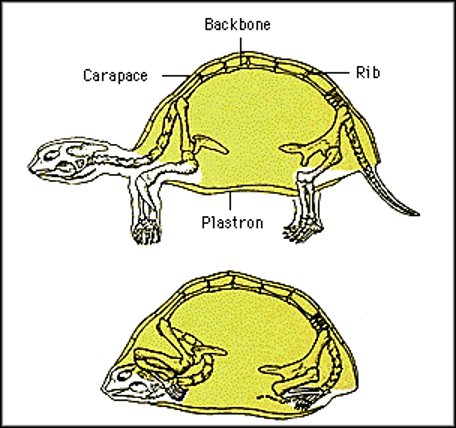
Jugular Vein (Chelonians)
Preferred site for venipuncture in turtles and tortoises because of easier access and larger size.
Subcarapacial Sinus
Blood collection site located at the dorsal midline beneath the anterior carapace of chelonians.
Cardiocentesis (Snakes)
Blood sampling technique in which a needle is inserted directly into the heart under restraint or anesthesia.
Ventral Tail Vein
Common venipuncture site along the midline of the underside of a reptile’s tail.
Ketamine
Injectable dissociative anesthetic widely used in reptiles, though often requiring higher doses than in mammals.
Telazol
Combination anesthetic (tiletamine + zolazepam) that provides rapid induction useful for intubating reptiles.
Propofol
Ultra-short-acting injectable anesthetic increasingly favored for induction in reptiles.
Righting Reflex
Ability of a reptile to flip itself from dorsal to ventral recumbency; loss indicates deepening anesthesia.
Autogenous Heat (Endothermy)
Internal heat production; absent in reptiles, which are ectothermic.