10. rabies
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what shape are rhabdoviridae? are they naked or enveloped viruses?
bullet shaped
enveloped
what type of genome do rhabdoviridae have?
non-segmented RNA
what 5 structural proteins are encoded in the genome?
N: nucleocapsid
encapsulates genome; forms ribonucleocapside (RNP)
P: phosphoprotein
cofactor for polymerase
M: matrix protein
G: glycoprotein
binding
L: polymerase
stuttering (?)
what are the general steps in the virus’s life cycle?
attachment: receptor/virus interaction
virus entry: G protein
uncoating and RNP release
transcription
replication (genomic RNA)
assembly: M protein
budding or release
what is a reservoir host?
host that is capable of sustained intra-species maintenance of a variant within a geographic area (maintain viruses in population)
not “sub-clinical” or chronic shedders
how is a susceptible host different from a reservoir host?
susceptible hosts do not maintain viruses in the population → infection ends in host
what factors influence rabies incubation period?
severity of exposure
proximity to brain
species of animal
variant of virus
how does rabies spread throughout the body?
nerves innervating skeletal muscles → travels up CNS to brain → spread along nerves to salivary glands, skin, cornea & other organs
what are the two forms of rabies?
furious: aggressive, unprovoked attacks
paralytic (aka “dumb”): depressed
what demographic makes up a large portion of fatal human rabies cases?
children under 15 years old (~40%)
(outside of the US) what is the main source of rabies transmission to humans?
dogs
what is the main source of rabies in the US?
wild mammals (bats, raccoons, skunks, foxes, etc.); mongooses (in Puerto Rico)
how is a direct fluorescent antibody test (DFAT) used to diagnose rabies?
microscopic detection of viral antigens using a fluorescent conjugate with antibodies to RABV
test brain tissue
gold standard for rabies testing
diagnostic for rabies
how is immunohistochemistry used to diagnose rabies?
detects RABV antigens
similar sensitivity as DFAT
can use formalin-fixed tissues
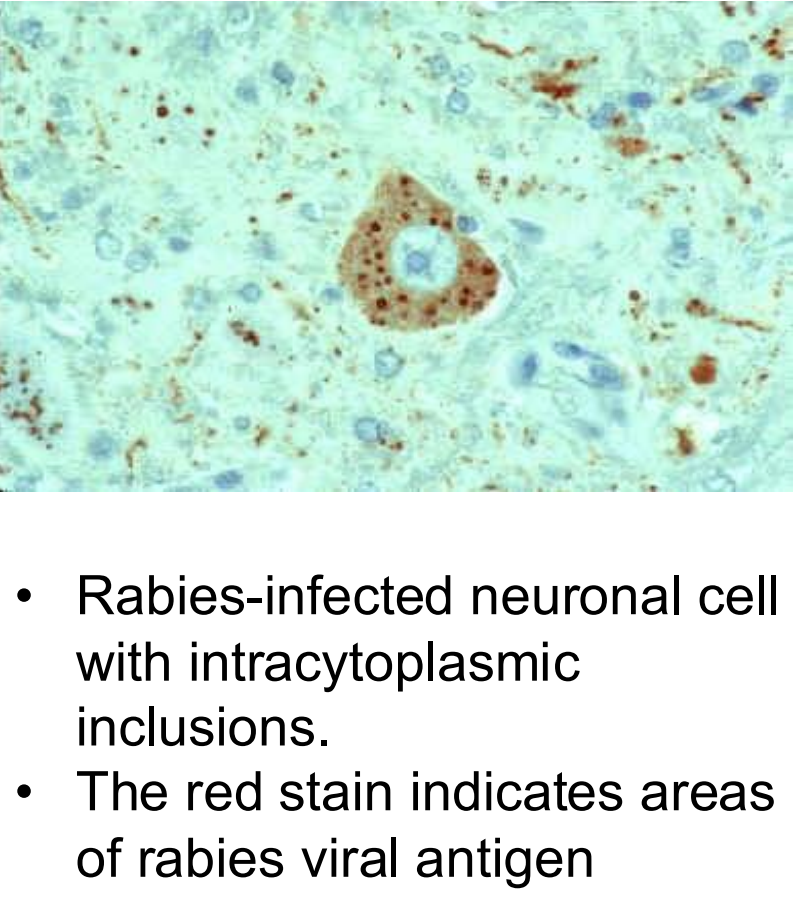
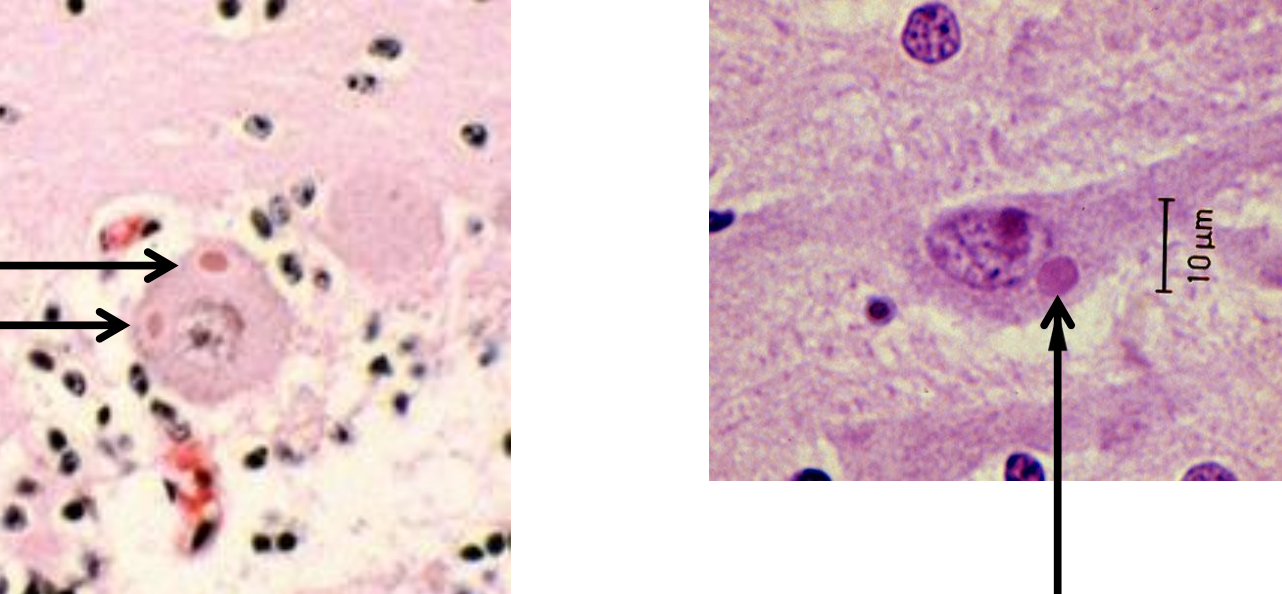
what are negri bodies? how are they interpreted diagnostically?
inclusion bodies where viral replication and assembly happens during infection
histopathologic signature of rabies but NOT definitive for diagnosis (highly suggestive)
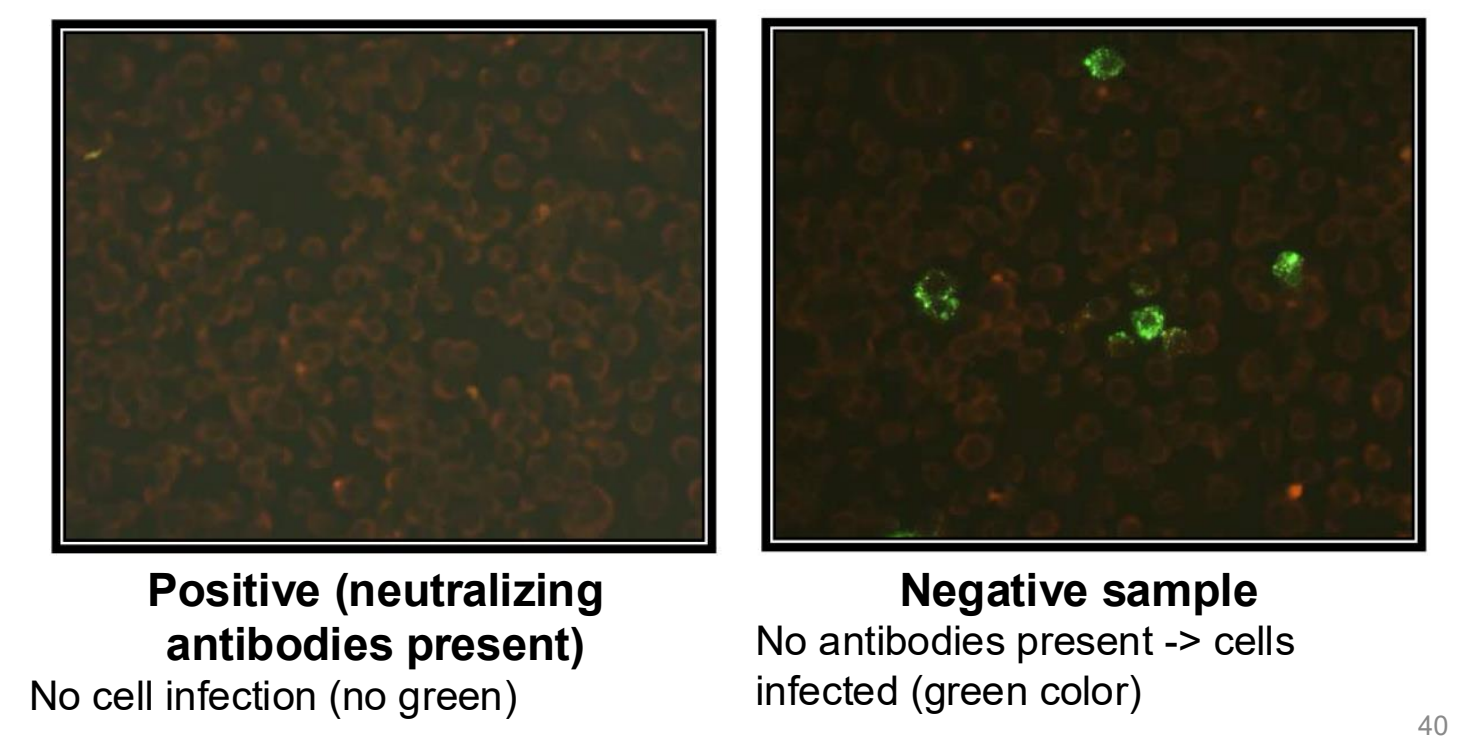
how is a rapid fluorescent focus inhibition test (RFFIT) used to diagnose rabies?
detection of neutralizing antibodies using live RABV, cell culture, and fluorescent conjugates
positive = neutralizing antibodies present; no cell infection
negative = no antibodies present; cells infected
(important for rabies testing)
how is RT-PCR used to diagnose rabies?
can be used for diagnosis and characterization of lyssaviruses (rabies genus)
useful when samples are not suitable for DFAT
primer targets usually for N gene (most conserved)