Habitats, Ecosystems, and Energy Flow in Ecology
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Habitat
The place where a plant or animal lives.
Community
A group of plants and animals that live together in an area.
Ecosystem
The community of plants and animals and their environment.
Ecology
The study of ecosystems.
Rockpools
An example of a habitat.
Habitat Study
To study a habitat, we make observations and collect information about the plants, animals and their environment.
Mapping an Ecosystem
The first step in studying habitats and their communities is to make a simple map of it.
Environmental Factors
Factors that include temperature of the air, soil and any water present, light intensity, aspect (the direction that the site faces), and wind speed.
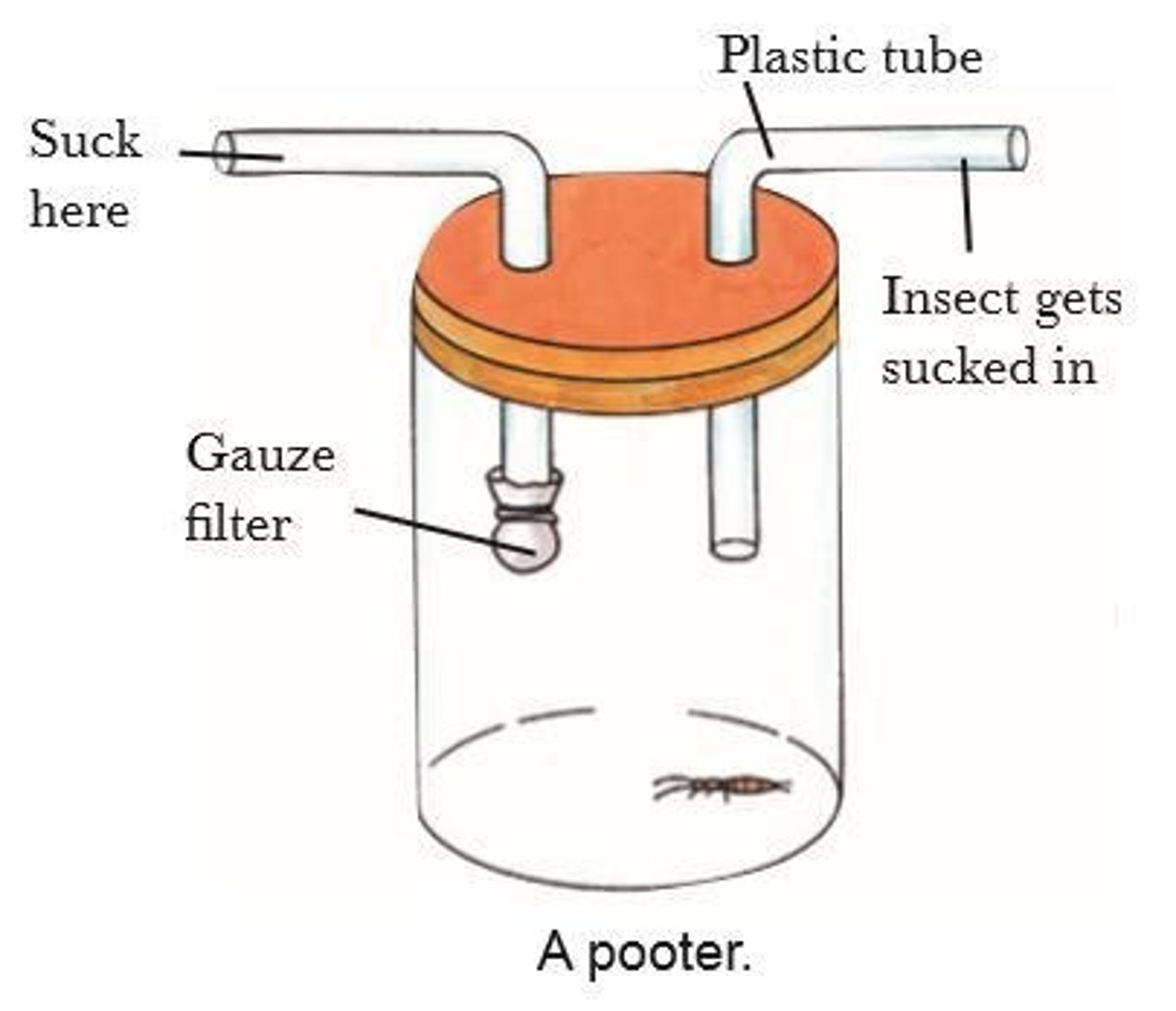
Pooter
A jar with two rubber tubes used to collect small insects.
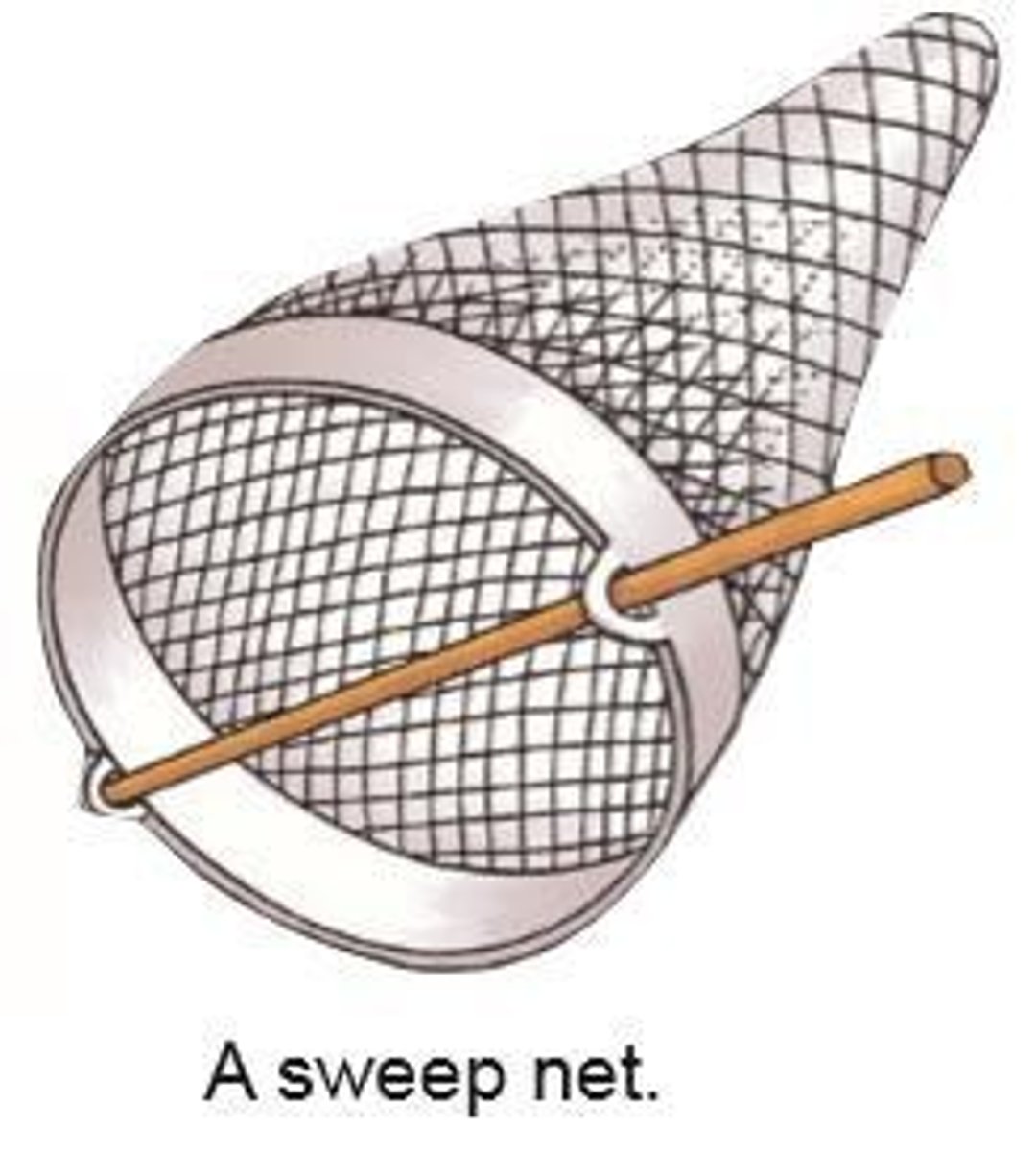
Sweep Net
A net moved gently through long grass and hedges to collect insects.
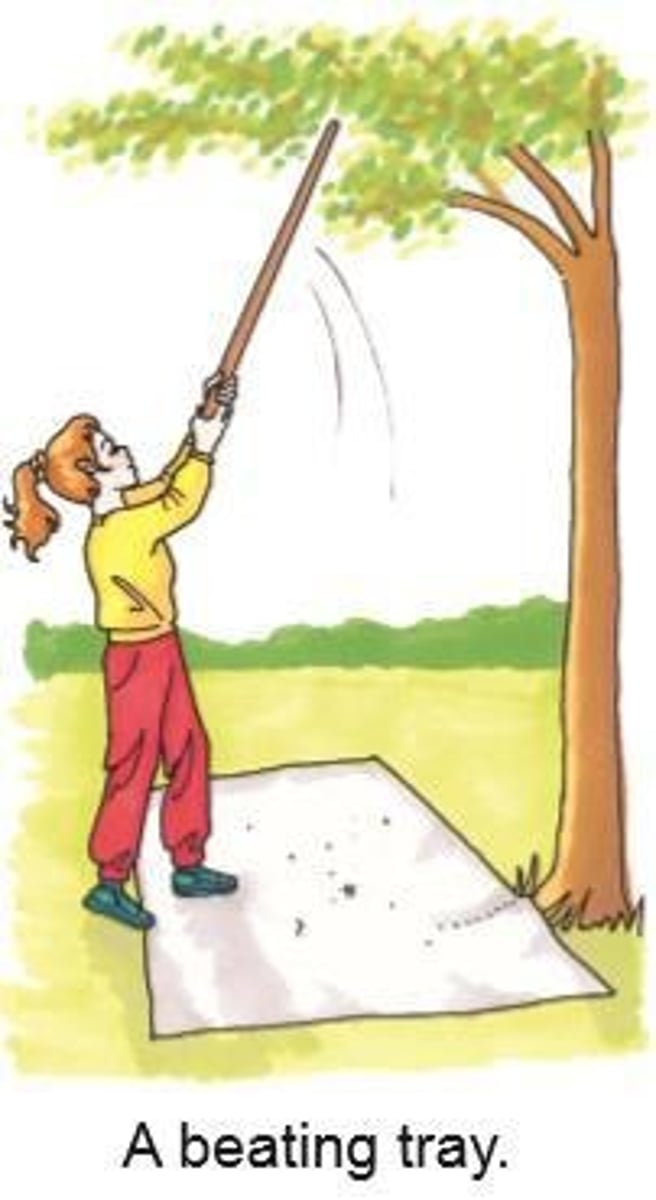
Beating Tray
A tray used to collect insects from trees.

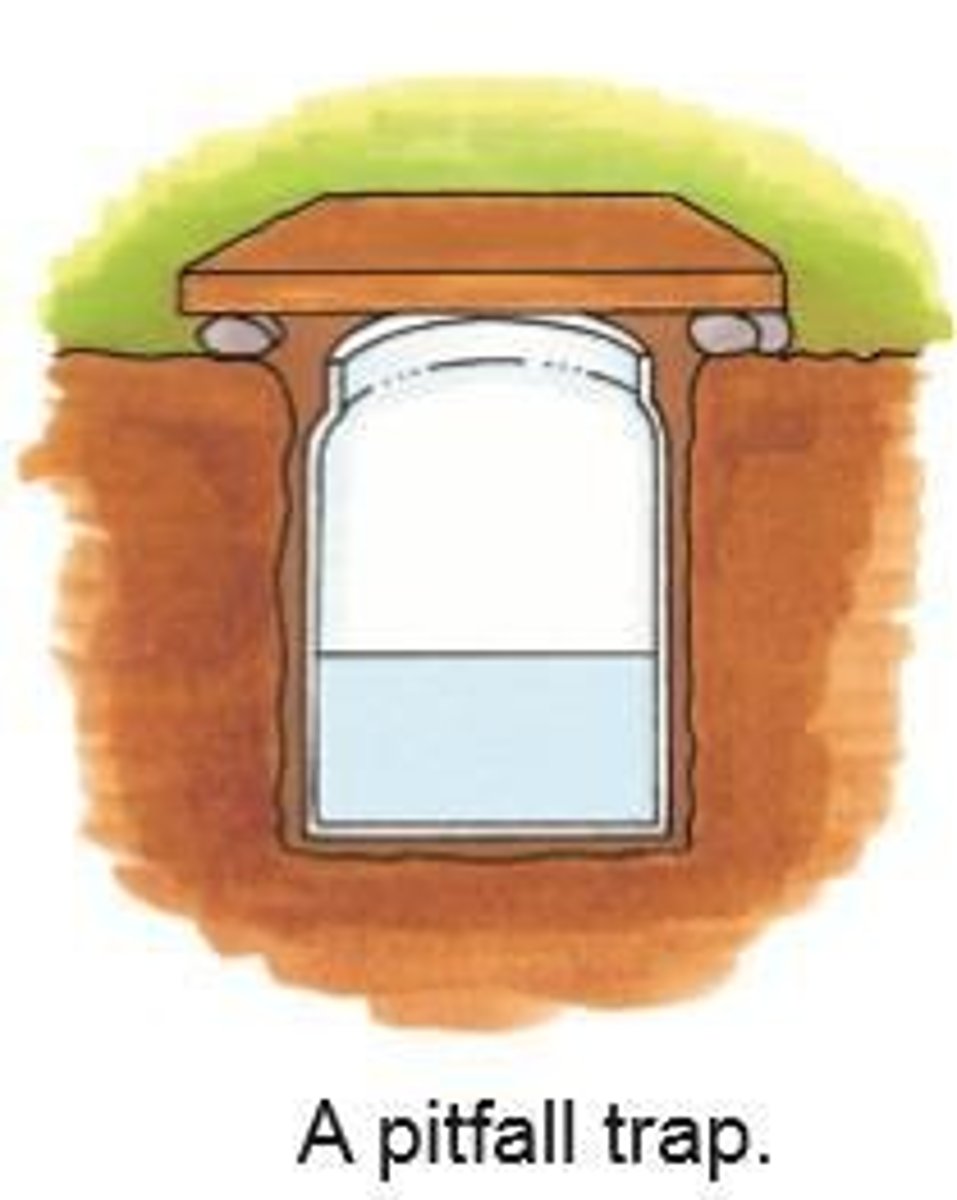
Pitfall Trap
A jar used to collect crawling insects.
Identifying Unknown Species
You can use a book with illustrations or a key to identify any species you do not know.
Quadrat
A square frame used to sample plants within a study area.
Sample Areas
Small areas within the study area used to estimate plant presence.
Relationships Within Ecosystems
Includes adaptation, competition, and interdependence.
Adaptation
A characteristic that improves the chances of an organism surviving within its habitat.
Earthworm adaptations
The long, narrow, slimy body allows the worm to burrow in the soil.
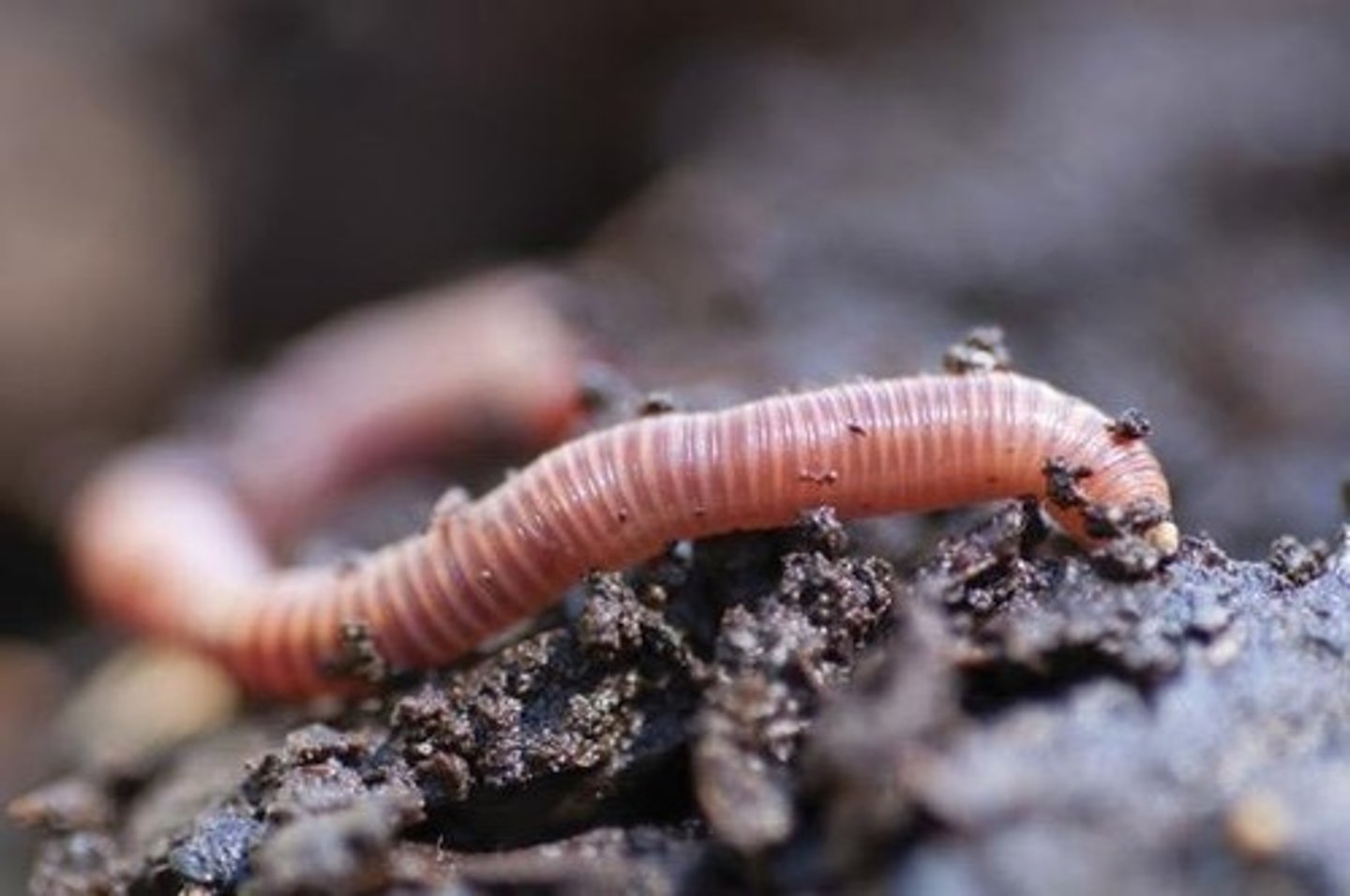

Earthworm behavior
Living under rocks and quickly burrowing into the soil help earthworms to avoid being eaten by predators.
Competition
Competition occurs between members of a community whenever there is a limited supply of a resource that they need.
Cactus competition
Cactus plants in a desert compete for water because there is a limited supply, but they do not compete for sunlight because there is plenty of sunlight.
Interdependence
The way that living organisms rely on each other is called interdependence.
Flow of Matter Through Ecosystems
Matter flows between living and non-living parts of ecosystems.
Respiration in ecosystems
When plants and animals respire they release carbon dioxide and water back to the environment.
Decomposition
When they die they are broken down by fungi and bacteria, releasing elements such as carbon and nitrogen into the air and soil.
Flow of Energy Through Ecosystems
The sun is the main source of energy on Earth.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis allows plants to obtain energy from the sun.
Energy transfer in food chains
When plants are eaten the energy they contain passes on to other organisms.
Energy release by respiration
Plants and animals release energy from food by respiration.
Chemical energy conversion
Respiration converts chemical energy into other forms.
Energy forms in animals
In animals the chemical energy in food may be converted into heat, motion, chemical and sound energy.
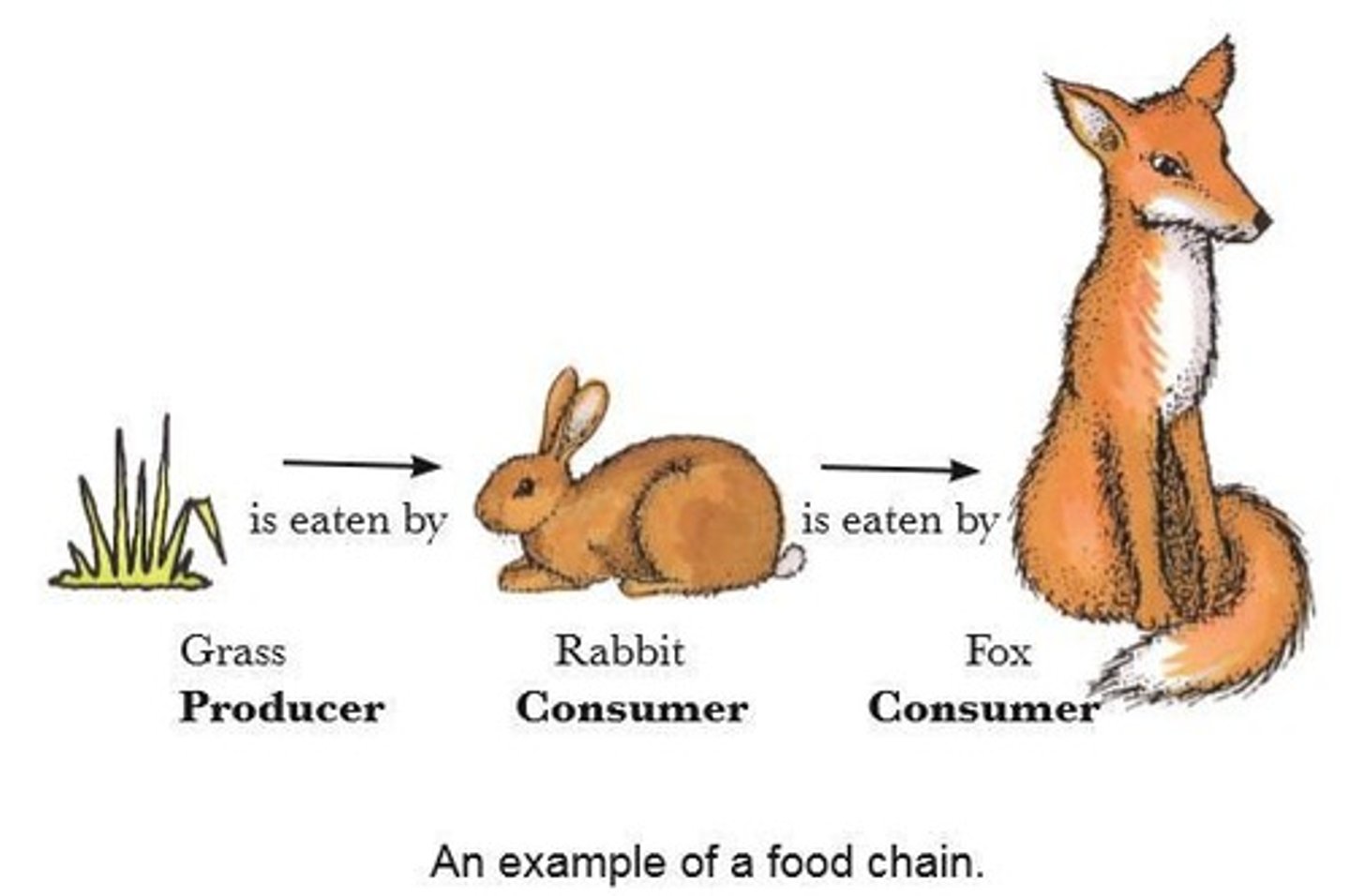
Food Chain
A food chain is a sequence of organisms where each one is eaten by the next.
Energy transfer in food chains
Each time an organism is eaten, the matter and energy it contains passes to the organism that eats it.
Producers
Producers are organisms that can make their own food using sunlight by photosynthesis.
Example of a producer
In this food chain, grass is the producer.
Consumers
Consumers are organisms that obtain their food by eating other living organisms.
Example of consumers
In this food chain the rabbit and the fox are consumers.
Decomposers
A decomposer is an organism that feeds on dead or decaying matter.
Examples of decomposers
Many types of bacteria and fungi are decomposers.
Function of decomposers
Bacteria and fungi break down dead matter and make it available for other living organisms to use.
Predators and Prey
A predator is an organism that hunts and kills another organism for food.
Definition of prey
The prey is the organism that is hunted.
Example of predators and prey
In this food chain the thrush and sparrow hawk are predators and the slug is prey.
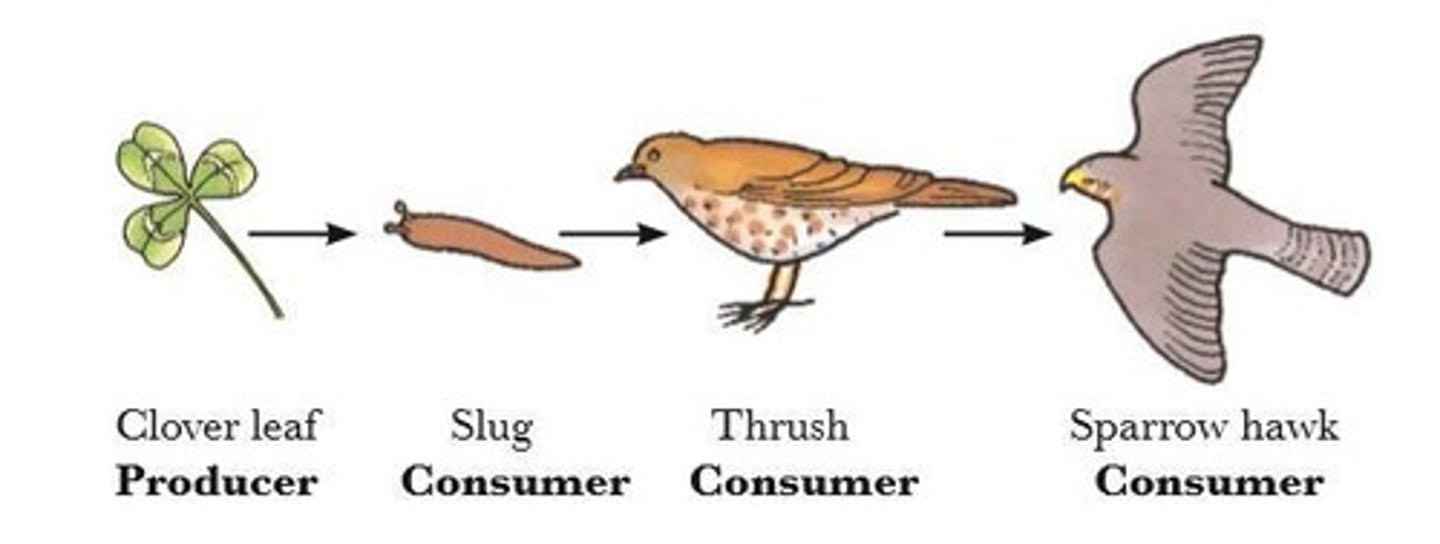
Energy Transfer in a Food Chain
In a food chain there are usually a lot of organisms at the start of the chain and very few at the end.
Energy transfer efficiency
This is because only 10% of the total available energy is passed on to the organisms at the next stage.
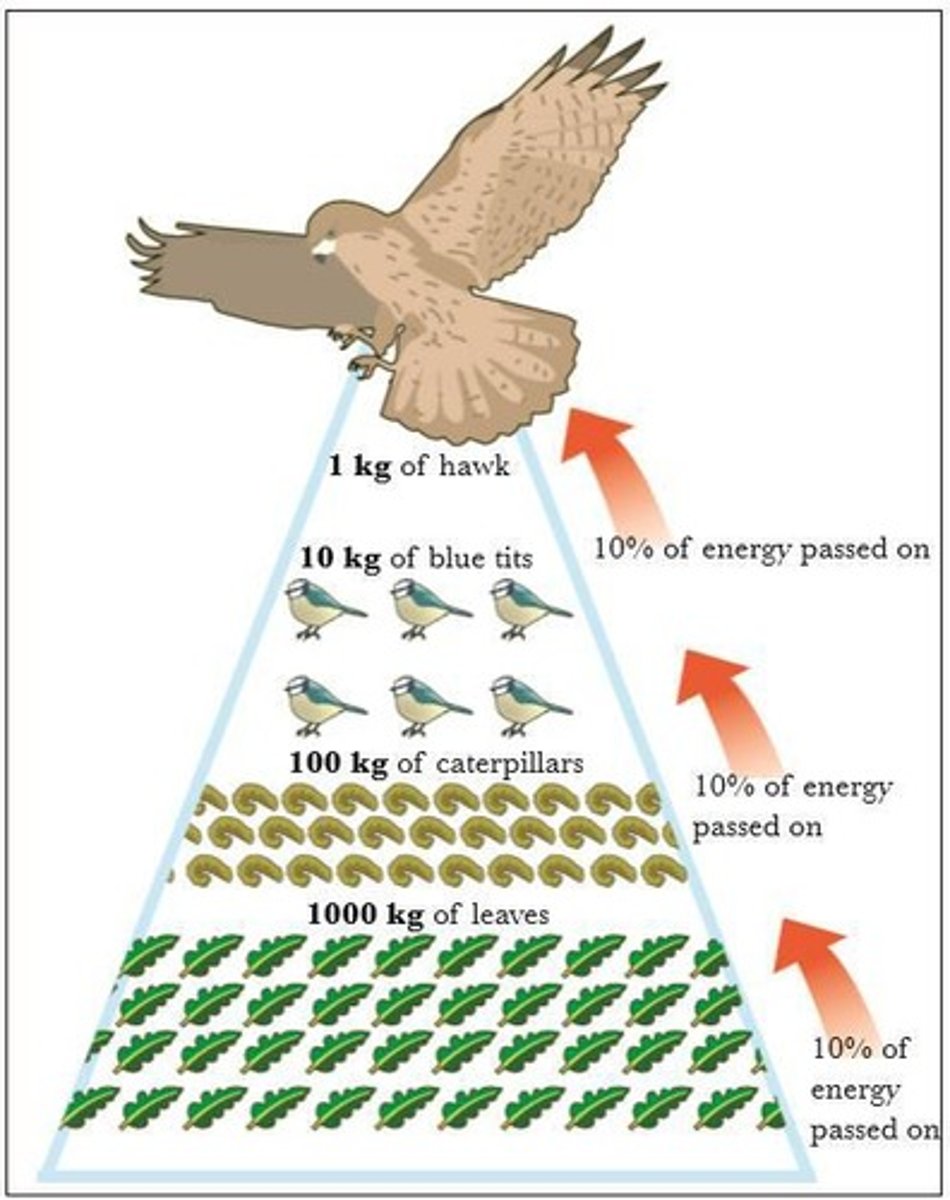
Energy loss in ecosystems
The other 90% is used for activities such as movement and respiration, or is released as heat.