Amino Acids
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Alanine Abbreviations
Ala or A
Arginine Abbreviations
Arg or R
Asparagine Abbreviations
Asn or N
Aspartic Acid Abbreviations
Asp or D
Cysteine Abbreviations
Cys or C
Glutamic acid Abbreviations
Glu or E
Glutamine Abbreviations
Gln or Q
Glycine Abbreviations
Gly or G
Histidine Abbreviations
His or H
Isoleucine Abbreviations
Ile or I
Leucine Abbreviations
Leu or L
Lysine Abbreviations
Lys or K
Methionine Abbreviations
Met or M
Phenylalanine Abbreviations
Phe or F
Proline Abbreviations
Pro or P
Serine Abbreviations
Ser or S
Threonine Abbreviations
Thr or T
Tryptophan Abbreviations
Trp or W
Tyrosine Abbreviations
Tyr or Y
Valine Abbreviations
Val or V
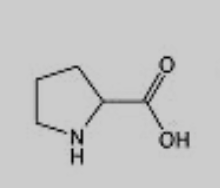
What amino acid is this?
Proline
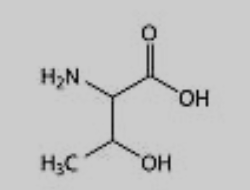
What amino acid is this?
Threonine
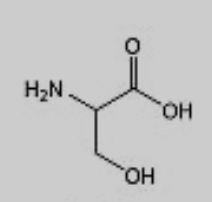
What amino acid is this?
Serine
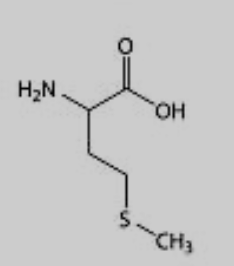
What amino acid is this?
Methionine
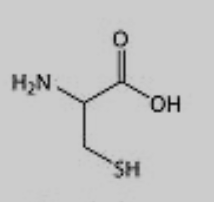
What amino acid is this?
Cysteine
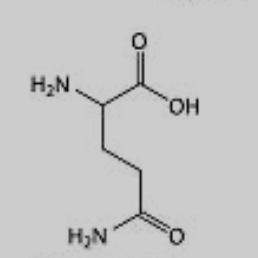
What amino acid is this?
Glutamine
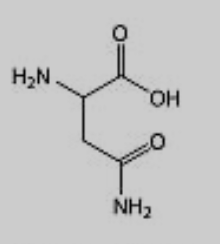
What amino acid is this?
Asparagine
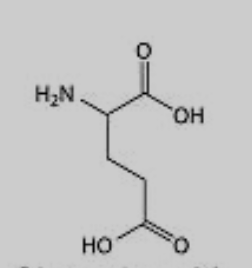
What amino acid is this?
Glutamic Acid
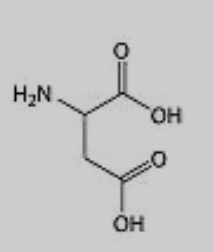
What amino acid is this?
Aspartic Acid
What amino acid is this?
Histidine
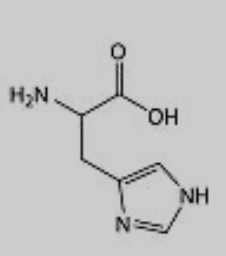
What amino acid is this?
Arginine
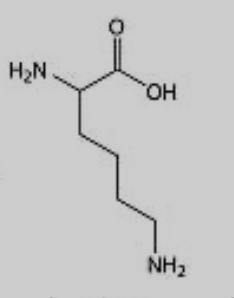
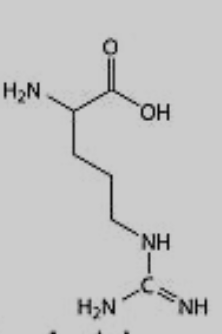
What amino acid is this?
Lysine
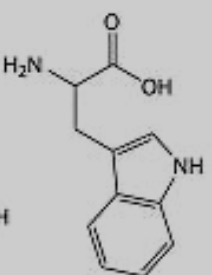
What amino acid is this?
Tryptophan
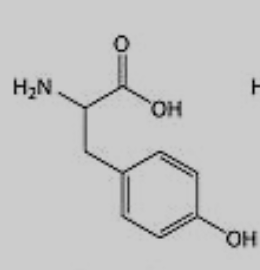
What amino acid is this?
Tyrosine
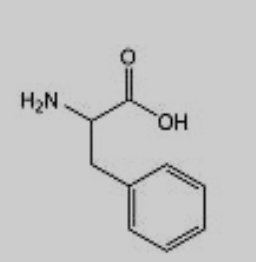
What amino acid is this?
Phenylalanine
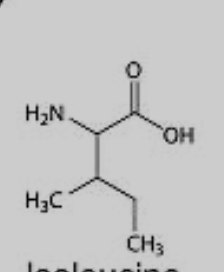
What amino acid is this?
Isoleucine
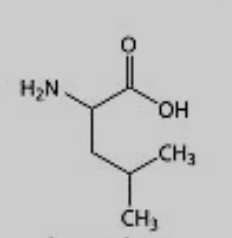
What amino acid is this?
Leucine
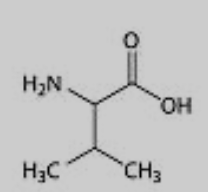
What amino acid is this?
Valine
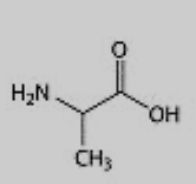
What amino acid is this?
Alanine
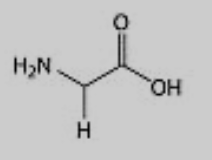
What amino acid is this?
Glycine
What is proline known to do?
-disrupt alpha helices
-because of its set angle it does beta turns
What are the redox signals? Which is better than the other and why?
methionine and cysteine
methionine is the primary redox signal because it can go back and forth between its reduced and oxidized state in response to oxidizing envronments. cysteine is not ideal because it can oxidize twice, the second of which is not reversible so it will kill the protein/enzyme in highly oxidative environments
What amino acids do pi stacking? What is it used for?
typically phenylalanine and tryptophan
the side chains for these are considered non polar but the electron pi system is slightly polar and needs to be stabilized in a completely nonpolar environment. pi stacking is done to help stabilize these electrons
Which amino acids are beta branched?
isoleucine, valine, and threonine
What is cysteine good for?
making disulfide bonds (cystine)
good and easily made nucleophile (because pka is within 1 of physiological pH)
Which amino acid is gamma branched?
leucine
What is the main thing that aspartic acid and glutamic acid do?
They are in basic form in the body, so they give a natural negative charge and are great H bond acceptors
**they don’t act as acid/base in the body except in a lysosome where the environment is so acidic
What is histidine good to do?
acid base catalysis
okayyy nucleophile in base form but this is rare
Which amino acids are aromatic?
phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan
Nucleophiles
-cysteine is the best one that is typically going to be used
-serine and lysine are good but they are hard to make
-histidine is an okayyy nucleophile
Electrophiles
-there are no natural electrophiles
-the closest are aspartic and glutamic acids since an enzyme can be used to put a LG in place of the oxygen which would then make it a good electrophile
What amino acids can be phosphorylated? Which are stable/unstable? What is the purpose?
-anything with an -OH can be phosphorylated and is stable (serine, tyrosine, threonine). these are used for regulation
-cysteine, aspartic acid, and glutamic acid can be but they are unstable. these are used for timing mechanisms since they won’t stay phosphorylated long