CLIN PATH: EXAM #2 (DERM - LEC I)
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Skin
________ is the most accessible organ of the human body
adnexal structures
Skin is distinct from mucosa in that it contains ________________ such as the eccrine units that exude sweat and the folliculosebaceous units that produce hairs and oils
Epidermis
______________ – superficial, tough, protective
• Stratified epithelium (keratinocytes)
• Melanocytes, exocrine sweat glands open here
• Has 5 layers
Dermal
__________ – epidermal junction
•Undulating, basement membrane
Dermis
___________ – semi-fluid, binds the body together
• Nerve endings, oil & sweat glands, hair follicles, blood & lymph vessels, connective tissue
Melanocytes and Langerhans cells
________________________ are dendritic cells that are intercalated among the keratinocytes of the epidermis
Melanocytes
__________________, which are positioned in the basal layer, synthesize a reddish-brown biochrome, melanin
Langerhans cells
_______________ share a similar arborized morphology (to Melanocytes) but are positioned in the midspinous layer
Langerhans cells
________________ are bone marrow–derived antigen-presenting cells
connective tissue gel
The dermis consists of a ___________________ composed largely of proteins and mucopolysaccharides
collagen types I and III, and a network of elastic microfibrils
The Dermis is composed of ________________________ is also woven throughout the full dermal thickness
Dermis
Fibrocytes are ubiquitous, and there are also mast cells and dendritic immune cells arrayed throughout the ________
Macule
________________:
• Area of increased or decreased pigmentation WITHOUT elevation or depression
• <1 cm
• Not palpable
• In superficial layers only
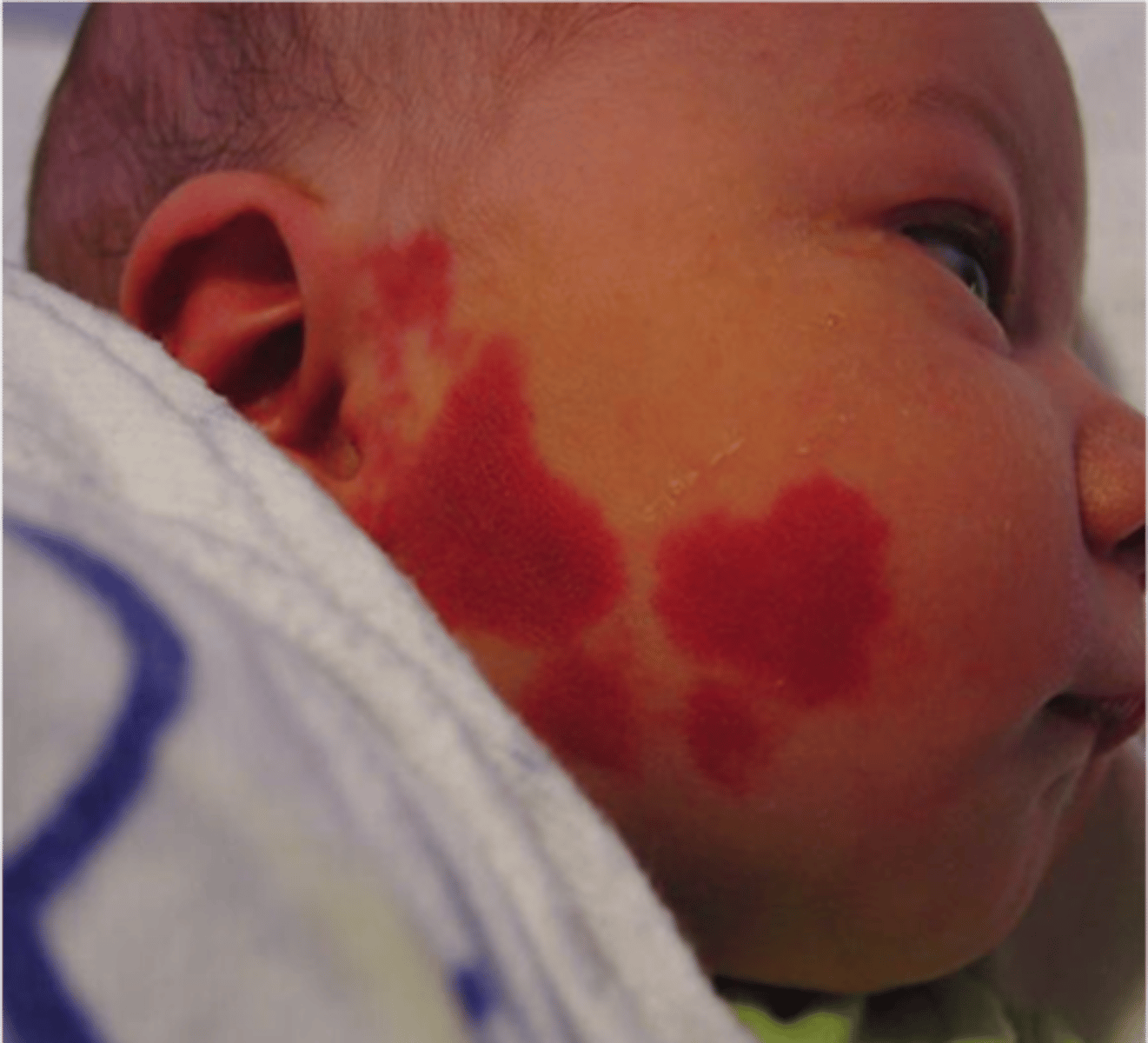
Patch
__________________:
• Macular type lesion
• Circumscribed
• >1 cm in diameter
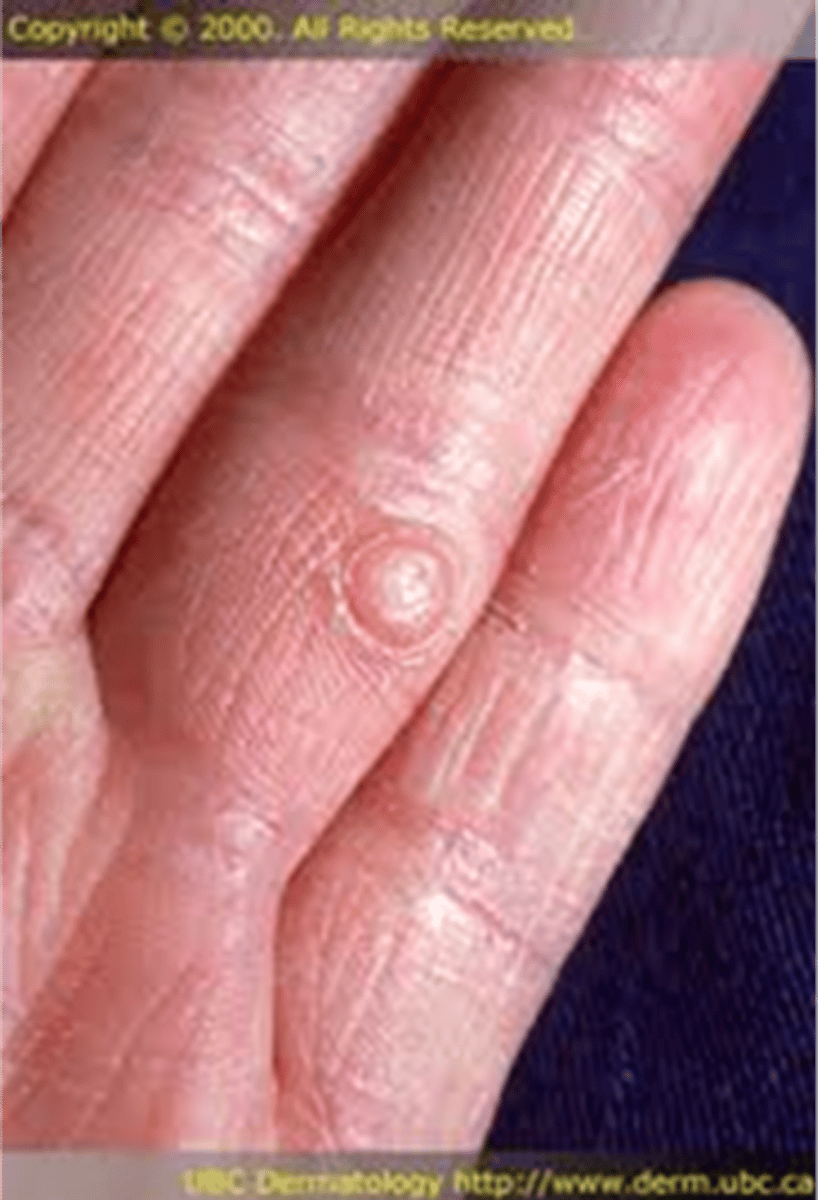
Papule
____________________:
• Superficial, solid lesion
• <0.5 cm in diameter
• Often occur in clusters
• Can accompany rashes
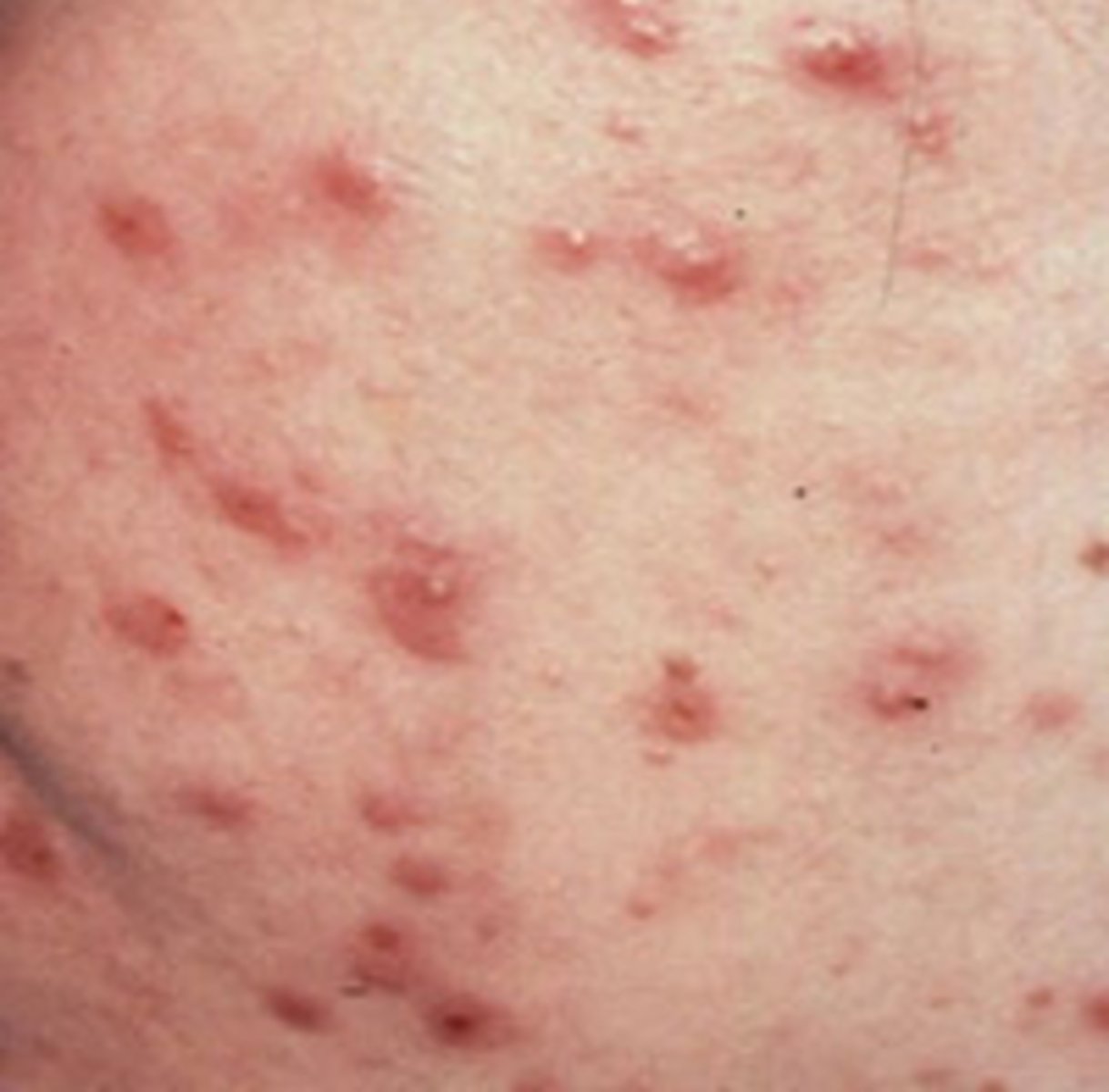
Papule
_________________:
• Inflammation
• Infected/ abraded skin
• Accumulated secretions
• Infection
• Disseminated histoplasmosis
• Hypertrophy of skin cells
• Acne
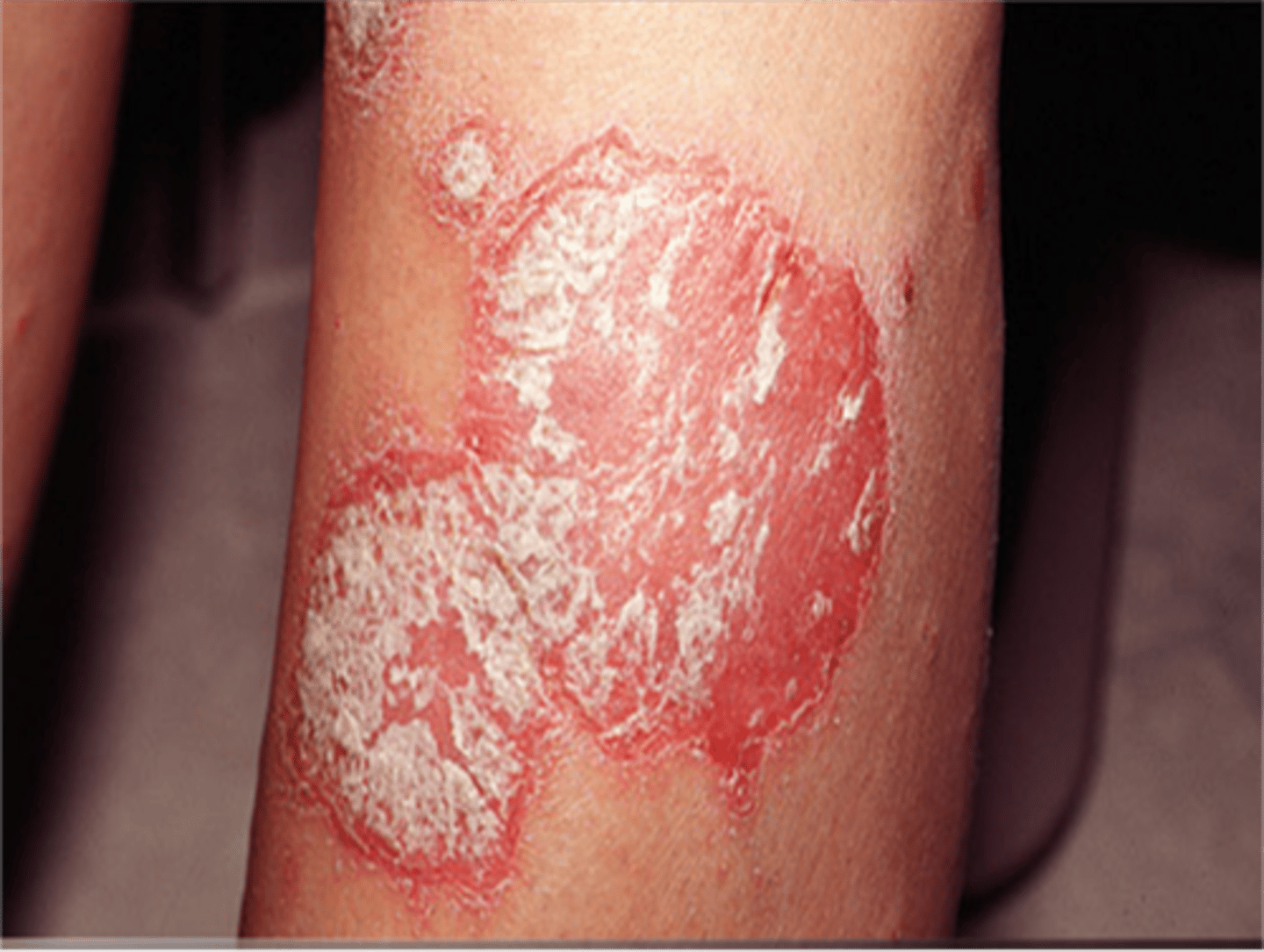
Plaque
______________:
• Plateau-like elevation with a surface area > it's height
• Frequently forms by a confluence of papules
• >1 cm in size
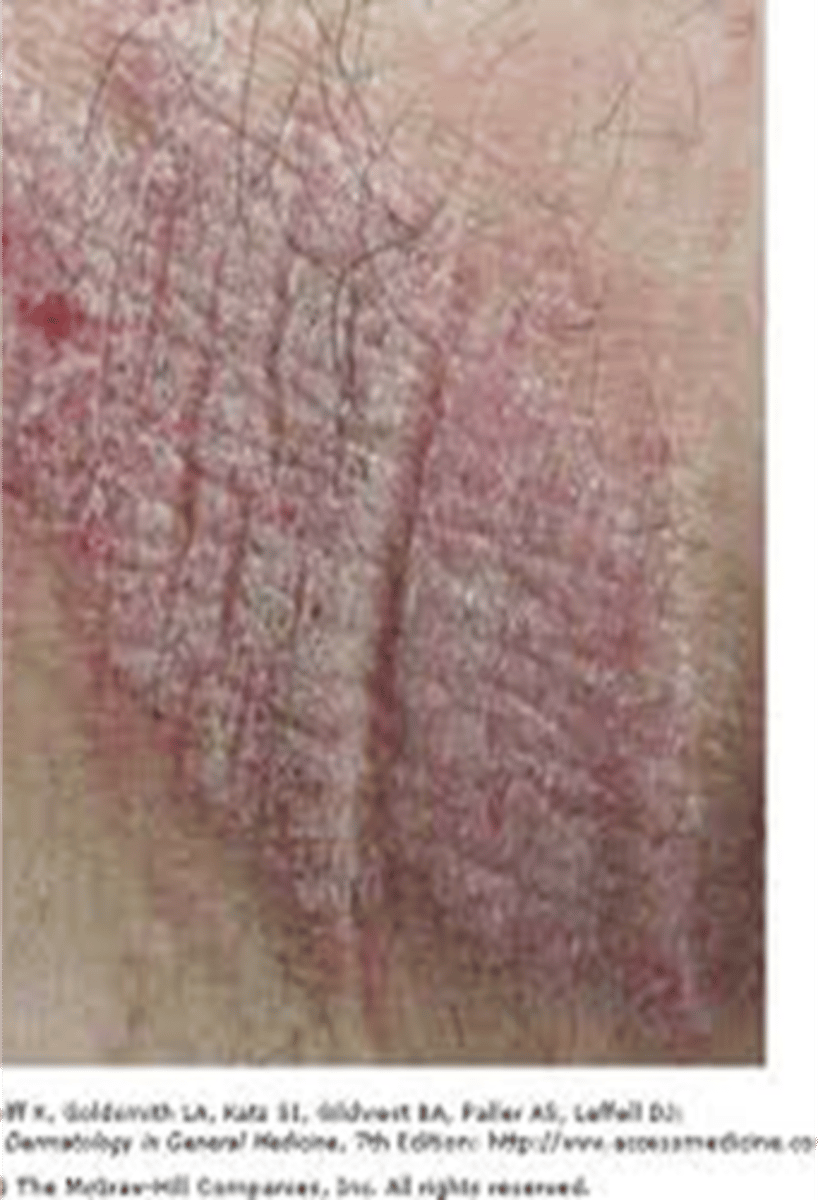
Lichenification
____________ – the surface is rough & thickened
•Accentuates the normal skin lines
•Resembles a tree bark
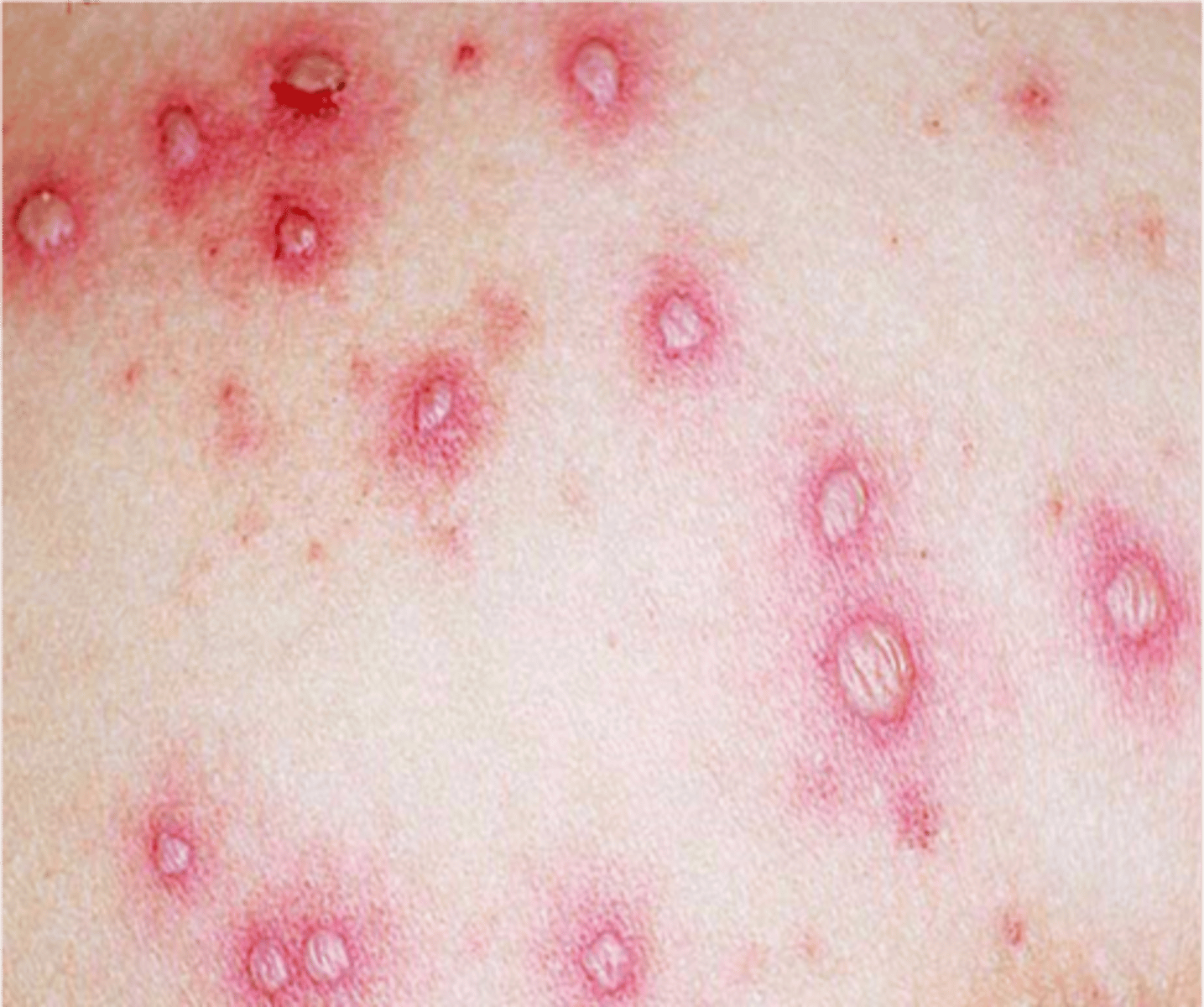
Vesicle
• Small fluid filled lesion on or below the skin
• Circular lesions
• <1 cm in diameter
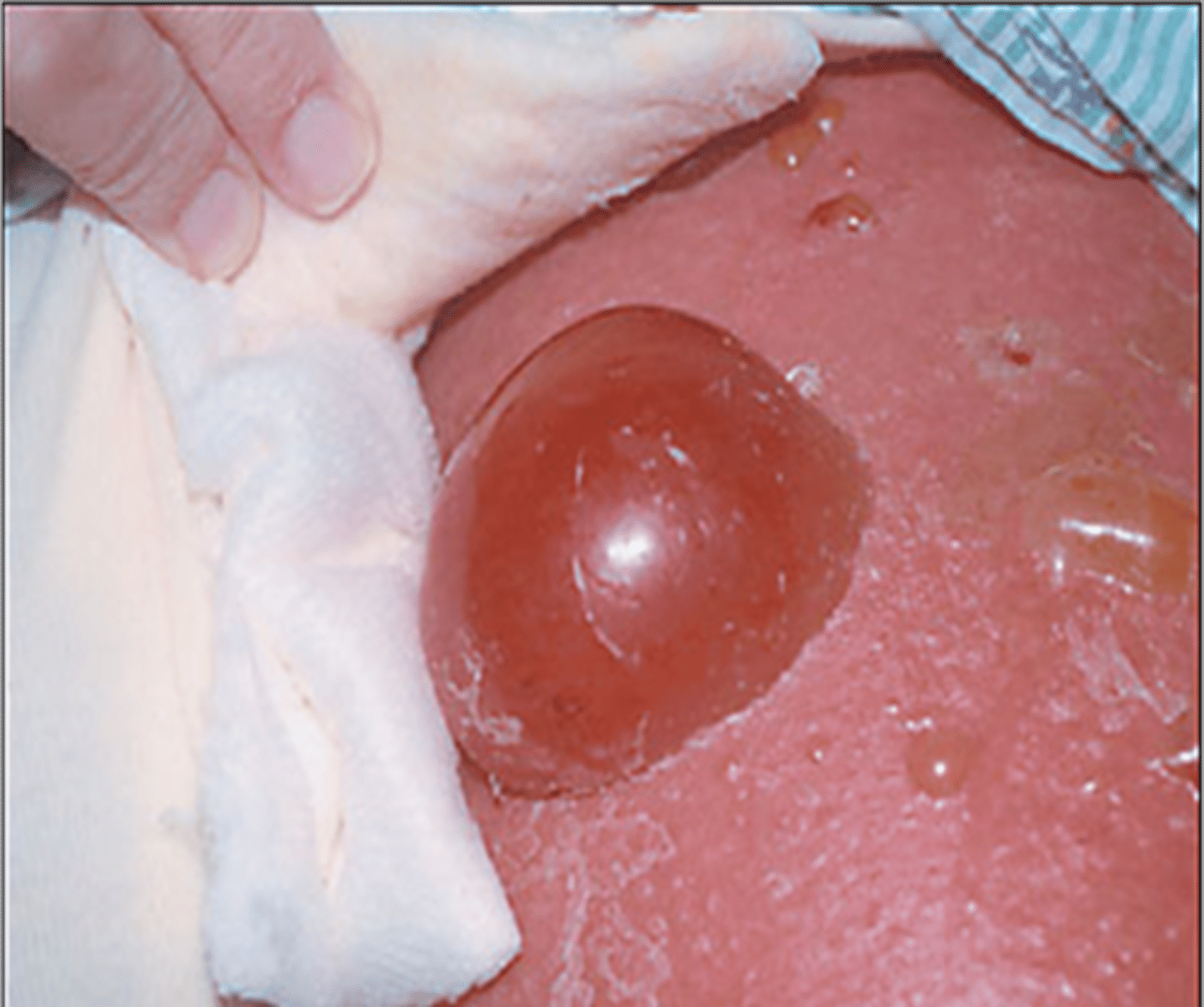
Bulla
•Circumscribed collection of free fluid
•> 1 cm
pustule
•A vesicle or bulla containing purulent fluid is known as a _________
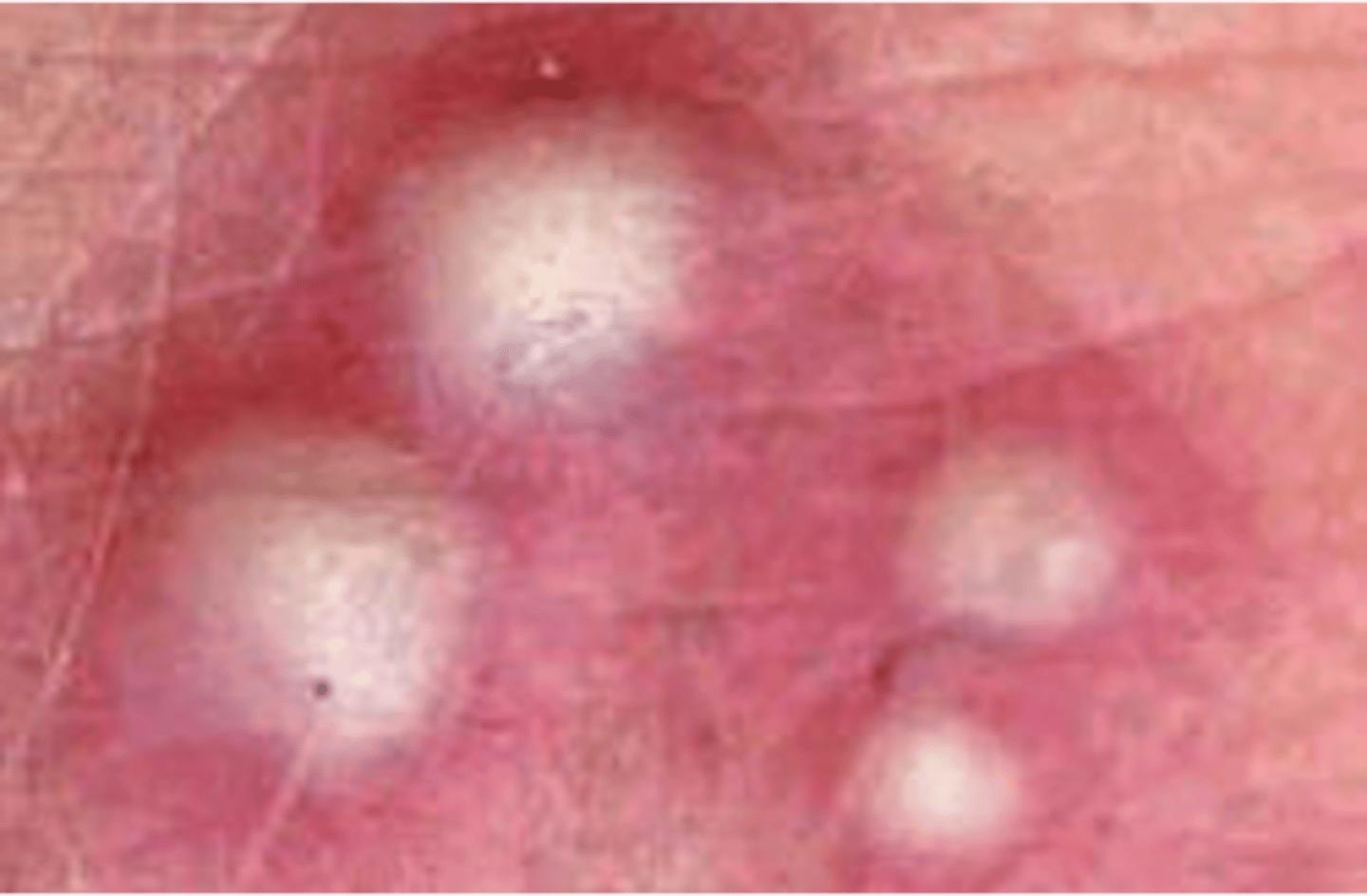
pustule
___________________:
•Superficial skin cavity containing purulent exudate
•May be yellow, white, green-white, or hemorrhagic
blisters
Both vesicles and bulla are called _________
Blisters (Vesicle or Bulla)
When the epidermis separates from the dermis, a pool of lymph and other body fluids collect between the 2 layers while the skin re-grows from underneath. What is this called?
Blisters (Vesicle or Bulla)
Etiology of __________________:
•Chemical or allergic rxn
•Physical injury (heat, frostbite, friction)
nodules
____________:
• Solid, circular lesion
• > 1 cm
• Usually invades the epidermis & lower dermis
Wheal
_________________ (AKA: urticarial exanthem, urticaria)
- Rounded, or flat topped, edematous plaque
- Well demarcated
- No scaling
- No epidermal involvement
- Color varies
- Shape: round, oval, gyrate, annular or serpiginous
Wheal
An allergic response to allergens such as drugs or insect bites will appear as what kind of skin response?
Darier's sign
_______________:
•Gentle rubbing or stroking of the lesions, is followed by local itching, erythema and weal formation within 2-5 min

Dermatographism
___________________:
• "writing on the skin”. It is a very common localized hive reaction.

Cyst
_______________:
•Encapsulated lesion filled with fluid or semisolid material
•Elevated, circumscribed, palpable
•An enclosed sac with a distinct membrane lining
•
Abscess
________________: A collection of pus
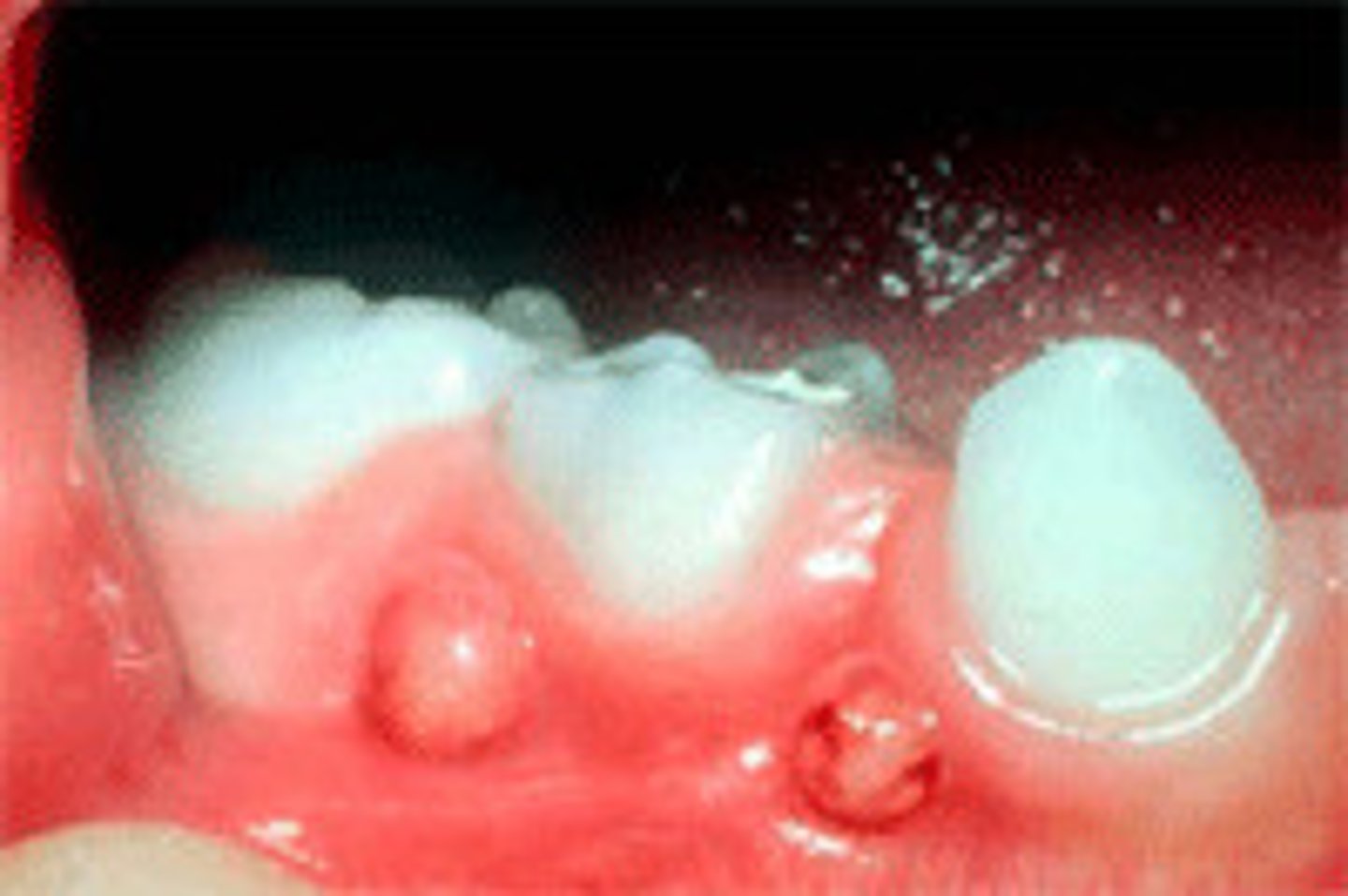
Crusts
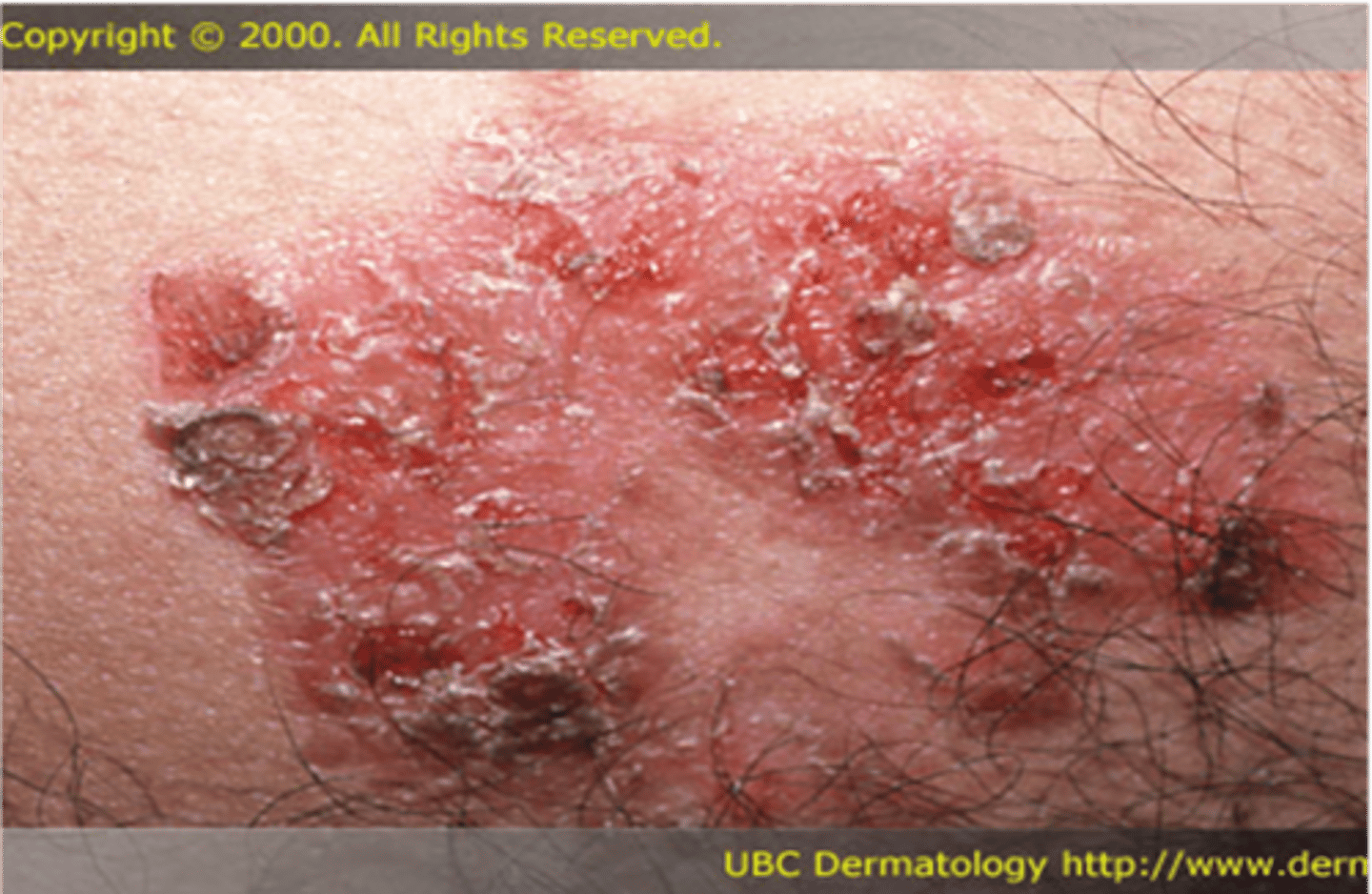
________________:
•Dried serum or exudates on the skin surface
•Blood appears brown
•Serum is honey colored
•Pus is a combo of yellow & green
•Present after blisters rupture
Scales (Desquamation)
_______________:
• Abnormal areas of stratum corneum
•An increased rate of epidermal cell proliferation
•May be adherent or loose, large sheet-like areas or tiny particles
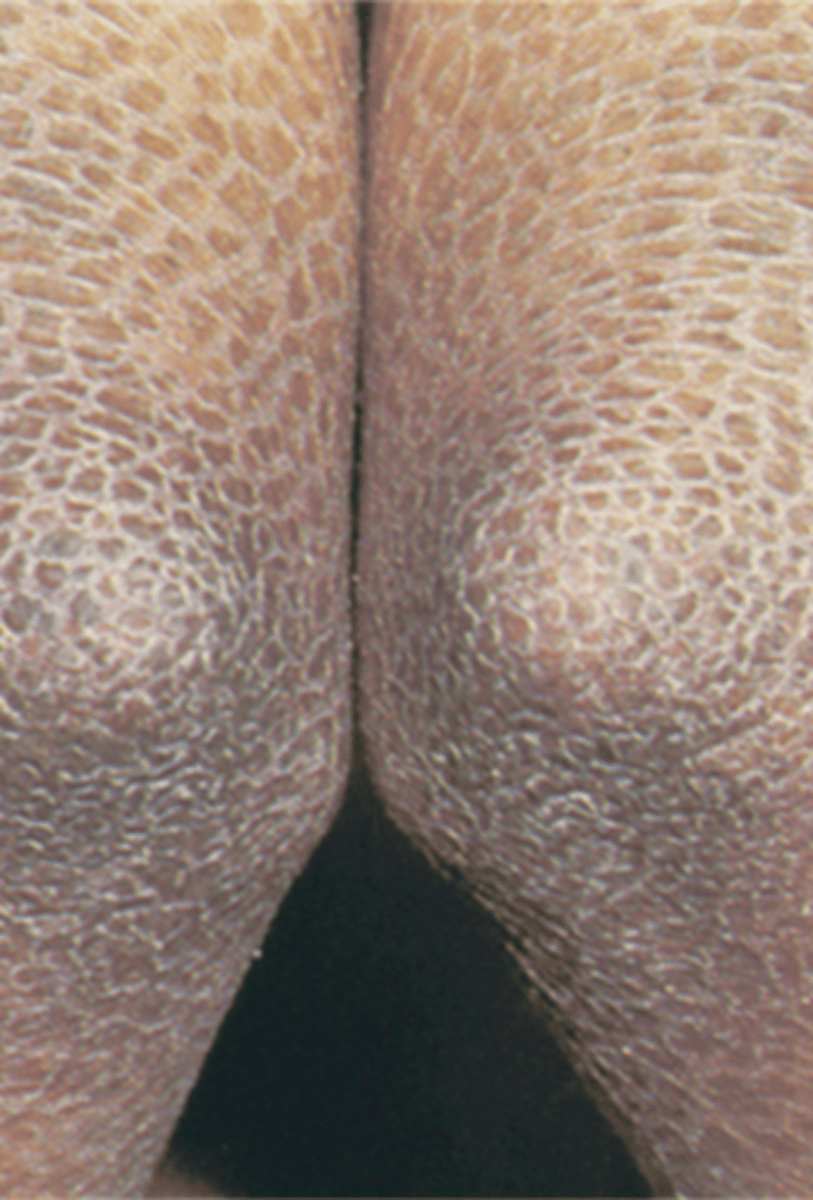
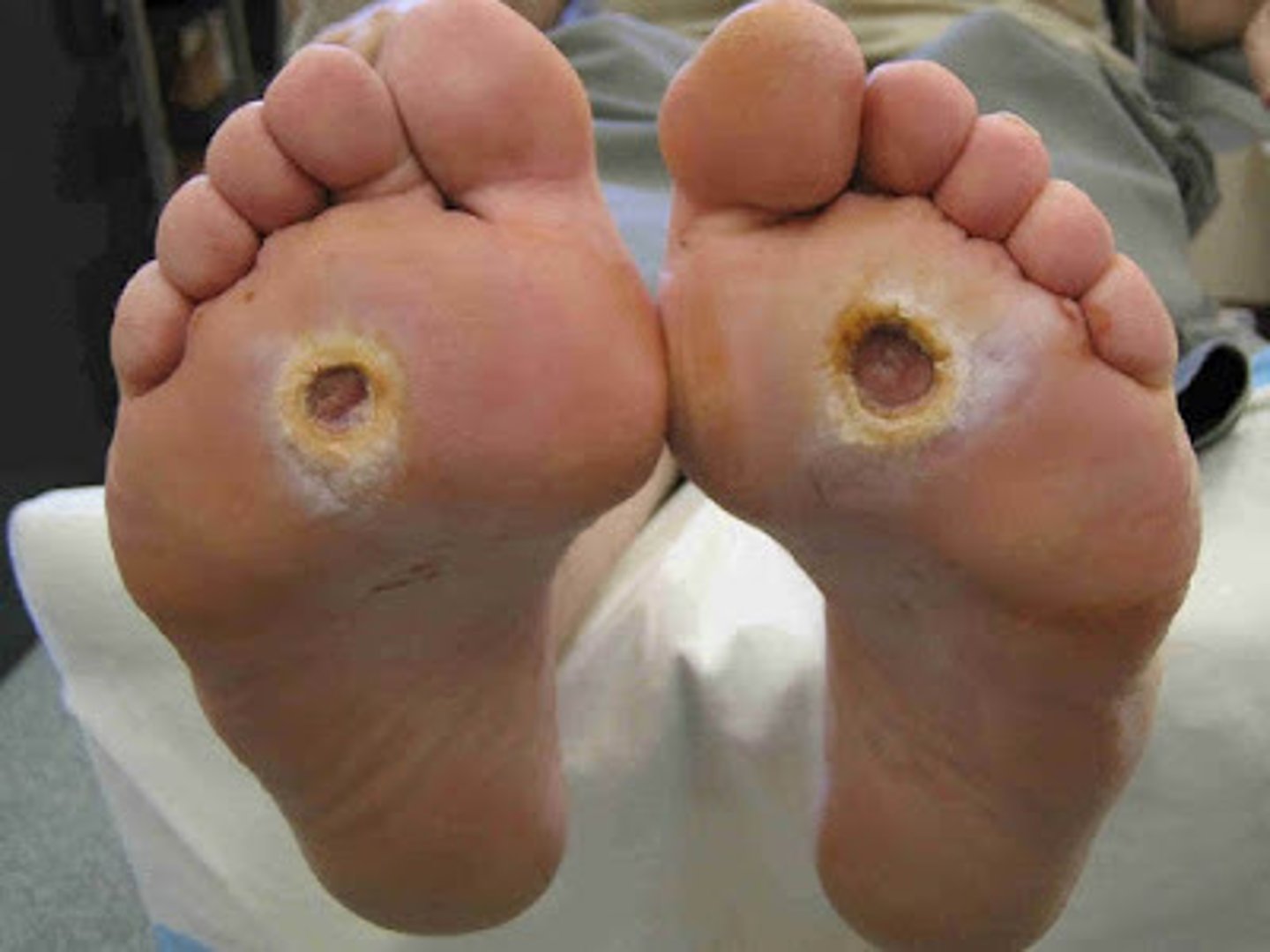
Erosion
_____________:
•Skin defect with loss of epidermis only
•Heals w/o a scar
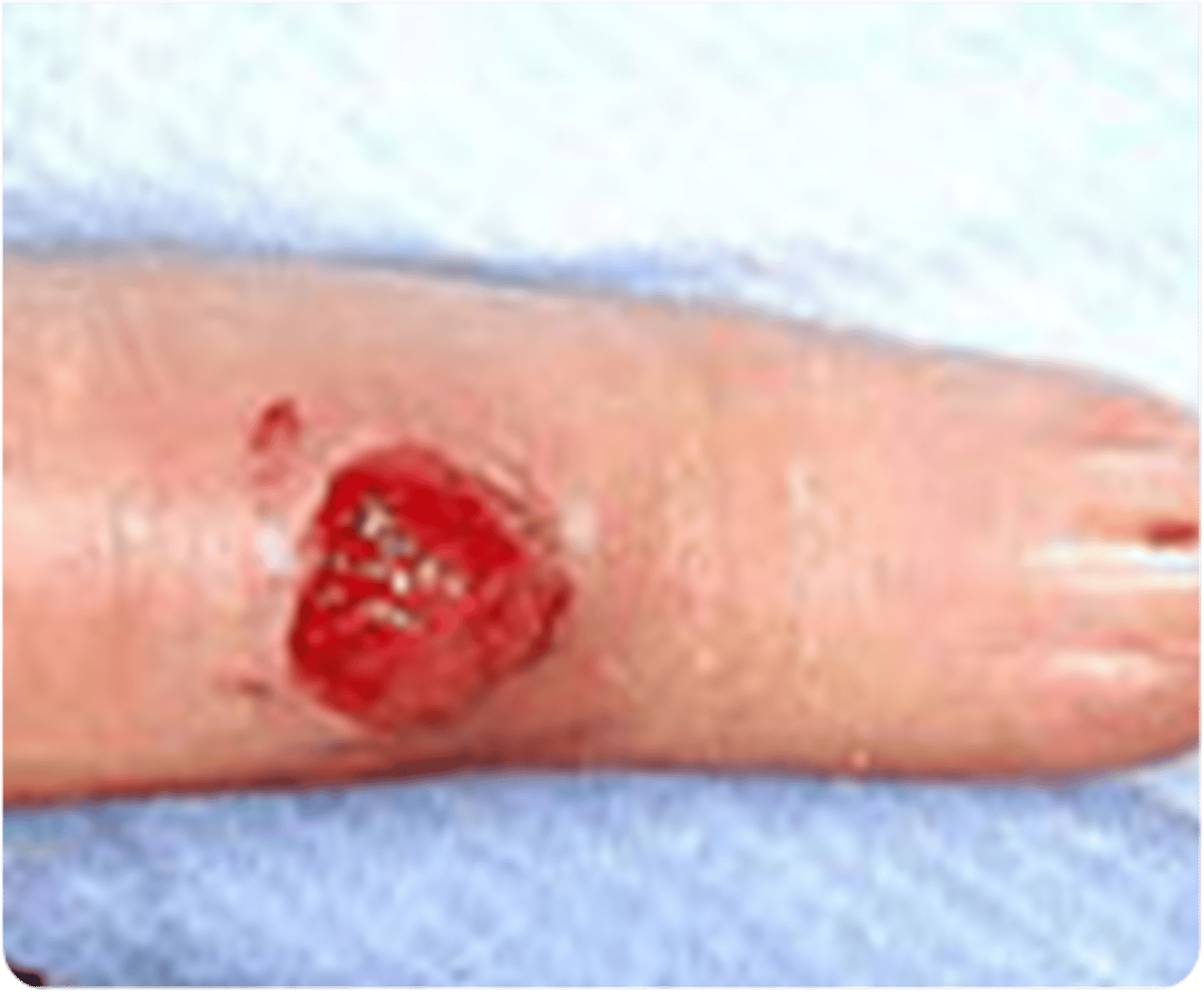
Ulcer
•Skin defect with a loss of epidermis & upper layer of the dermis
•May extend into lower layers
•Always heals with scar tissue
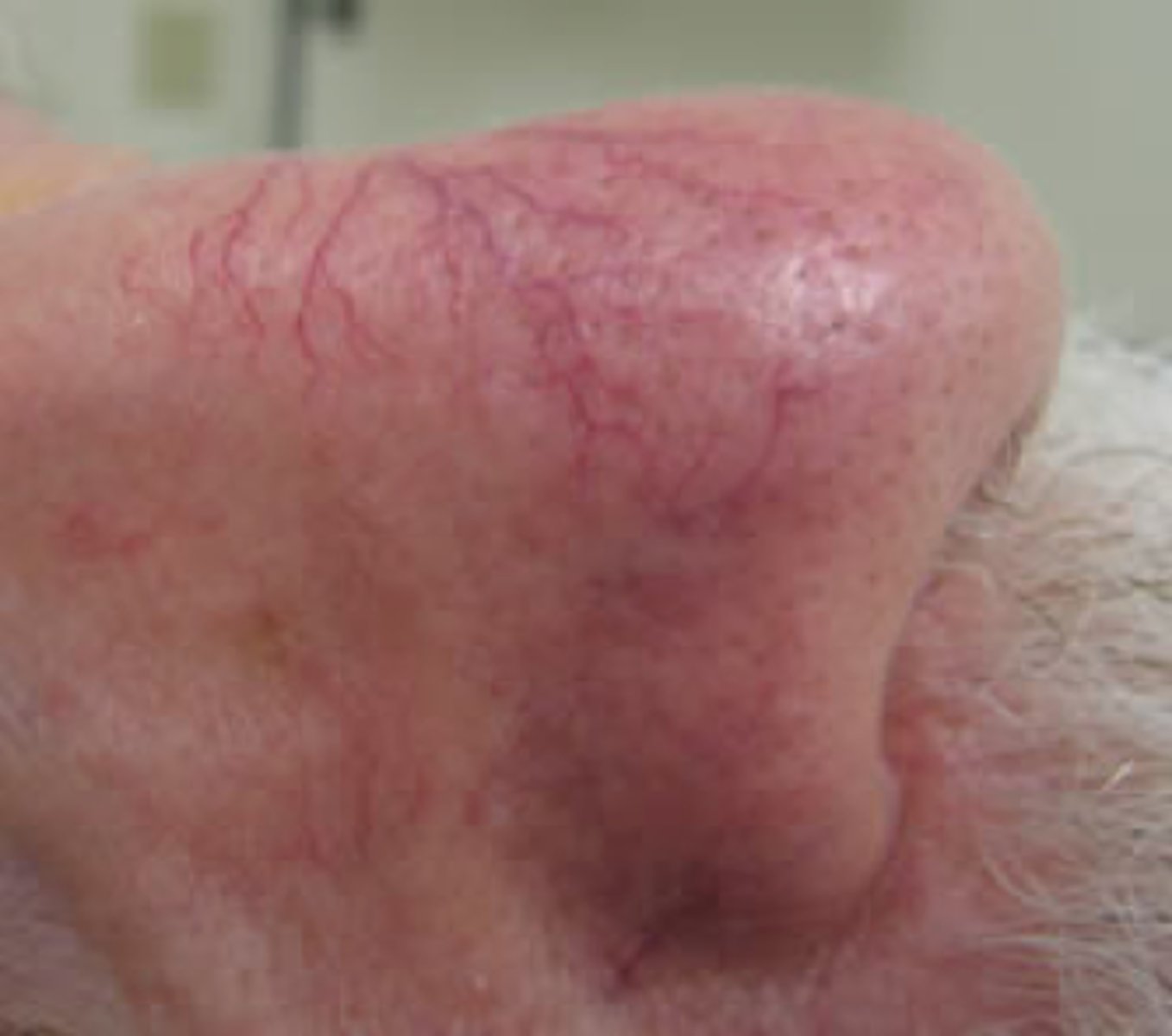
Telangiectasias
__________________:
•Small enlarged blood vessels near the surface of the skin
•Usually mms in size
•On nose, cheeks & chin
•
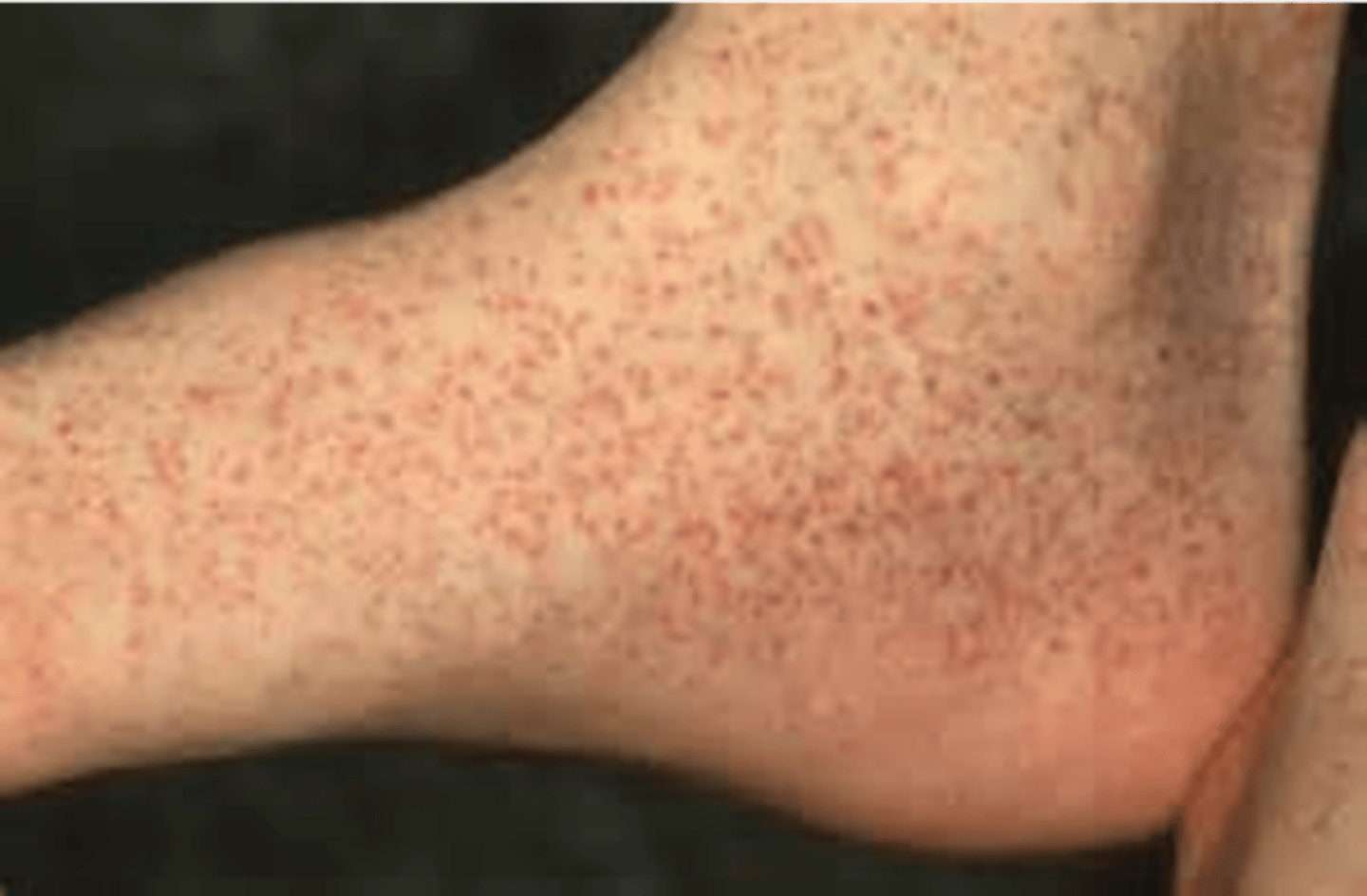
Petechiae
•One petechia
•Small red or purple spot on the body
•< 3 mm
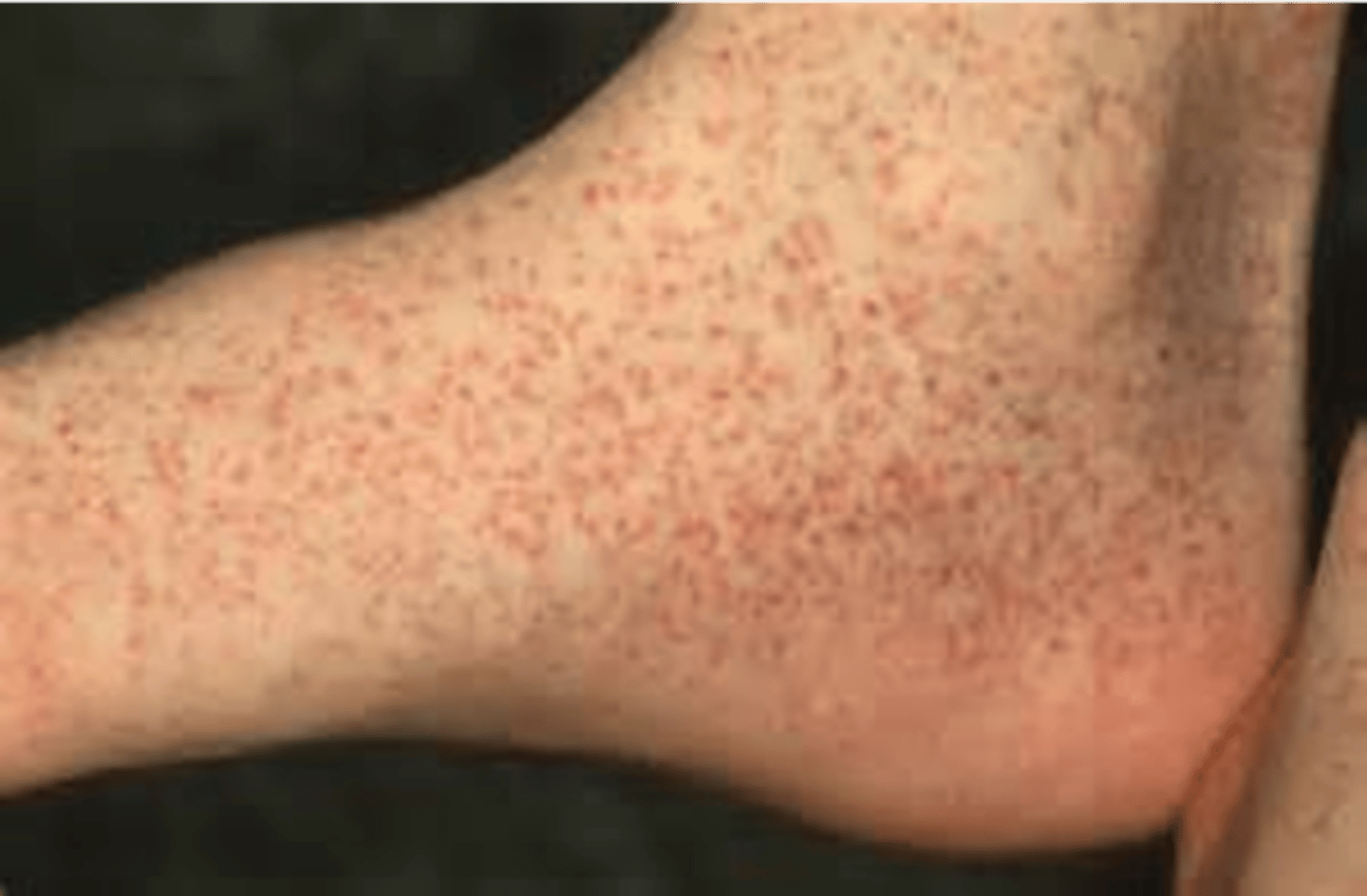
Petechiae
•Etiology:
•Minor hemorrhage (broken capillary)
•Thrombocytopenia
•↓ platelet function
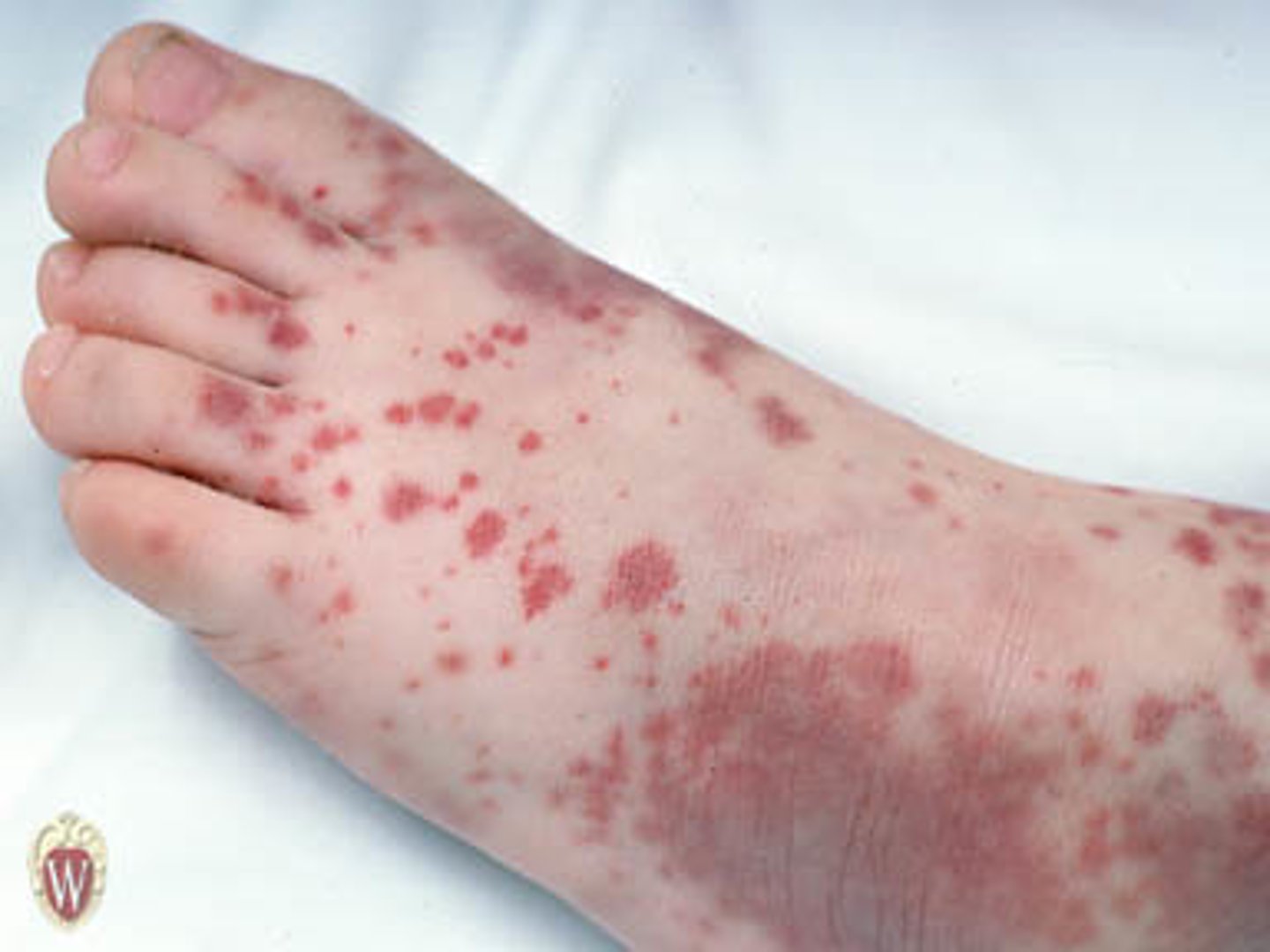
Purpura
_________________:
•Larger red or purple discolorations on the skin 3mm-10mm
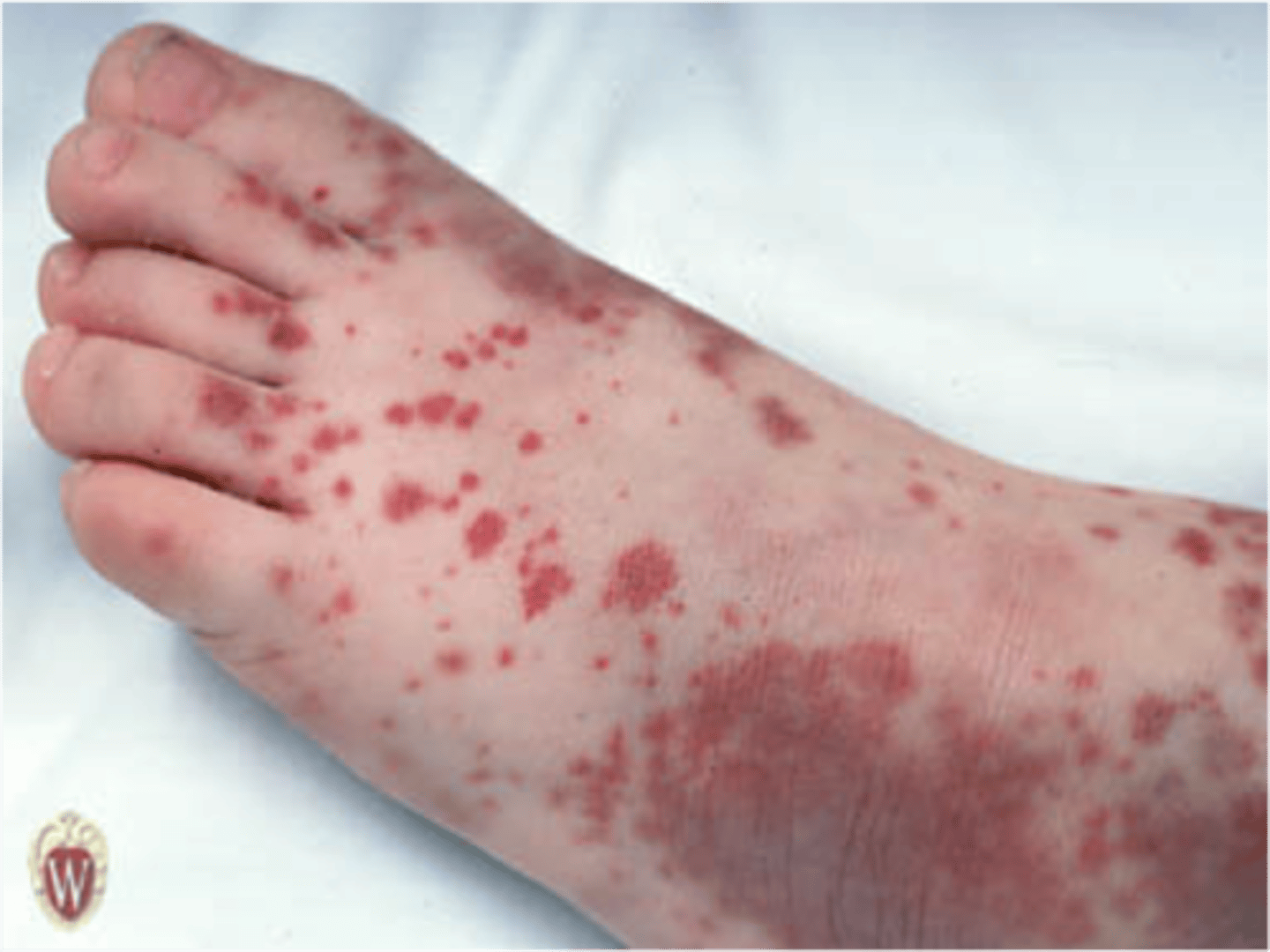
Purpura
______________ Etiology:
•Bleeding under the skin
Ecchymosis
________________:
•Capillary damage allows blood to extravasate into surrounding tissues
•> 1 cm in diameter
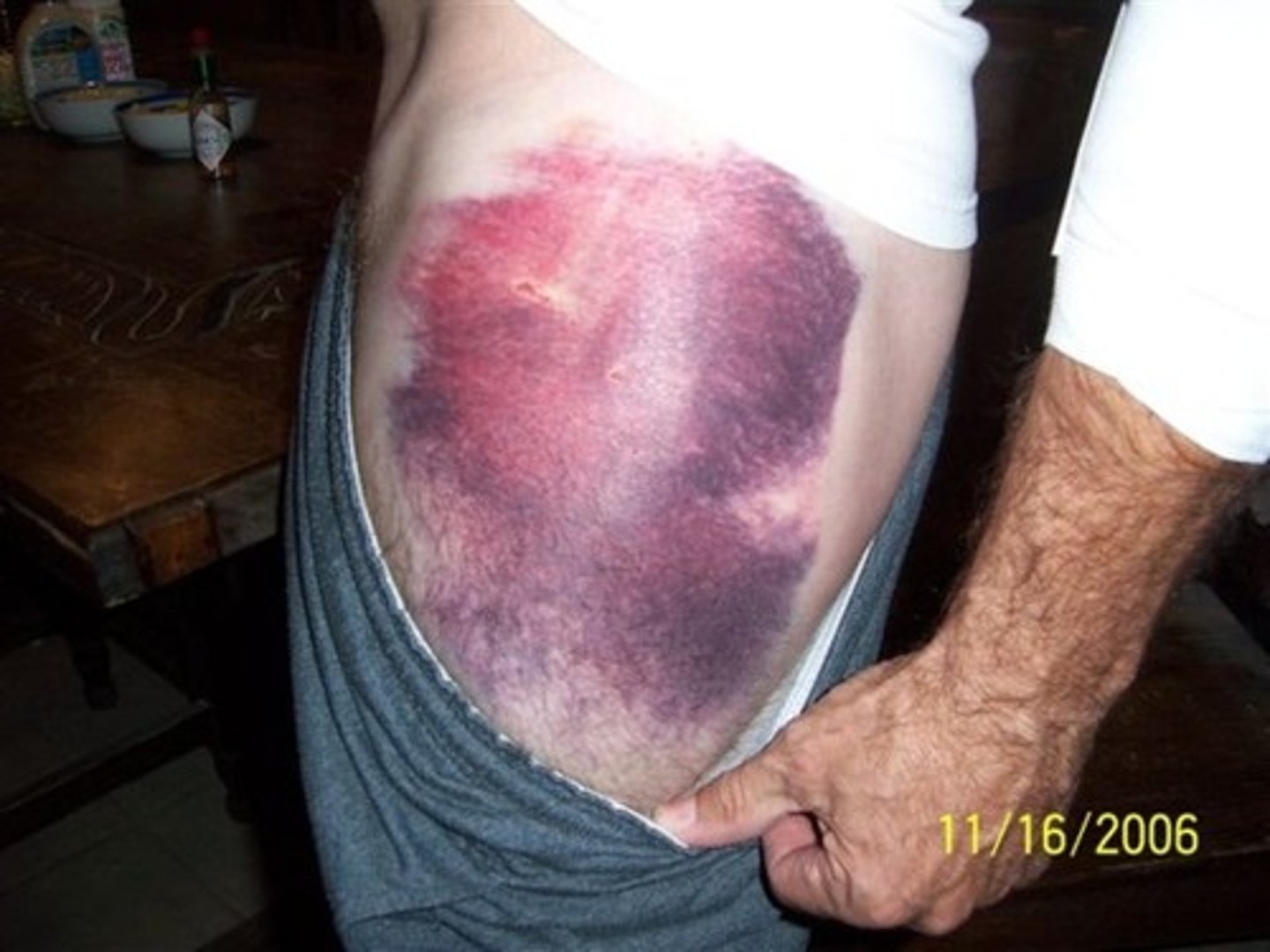
Ecchymosis
_________________: Etiology:
•Usually blunt trauma
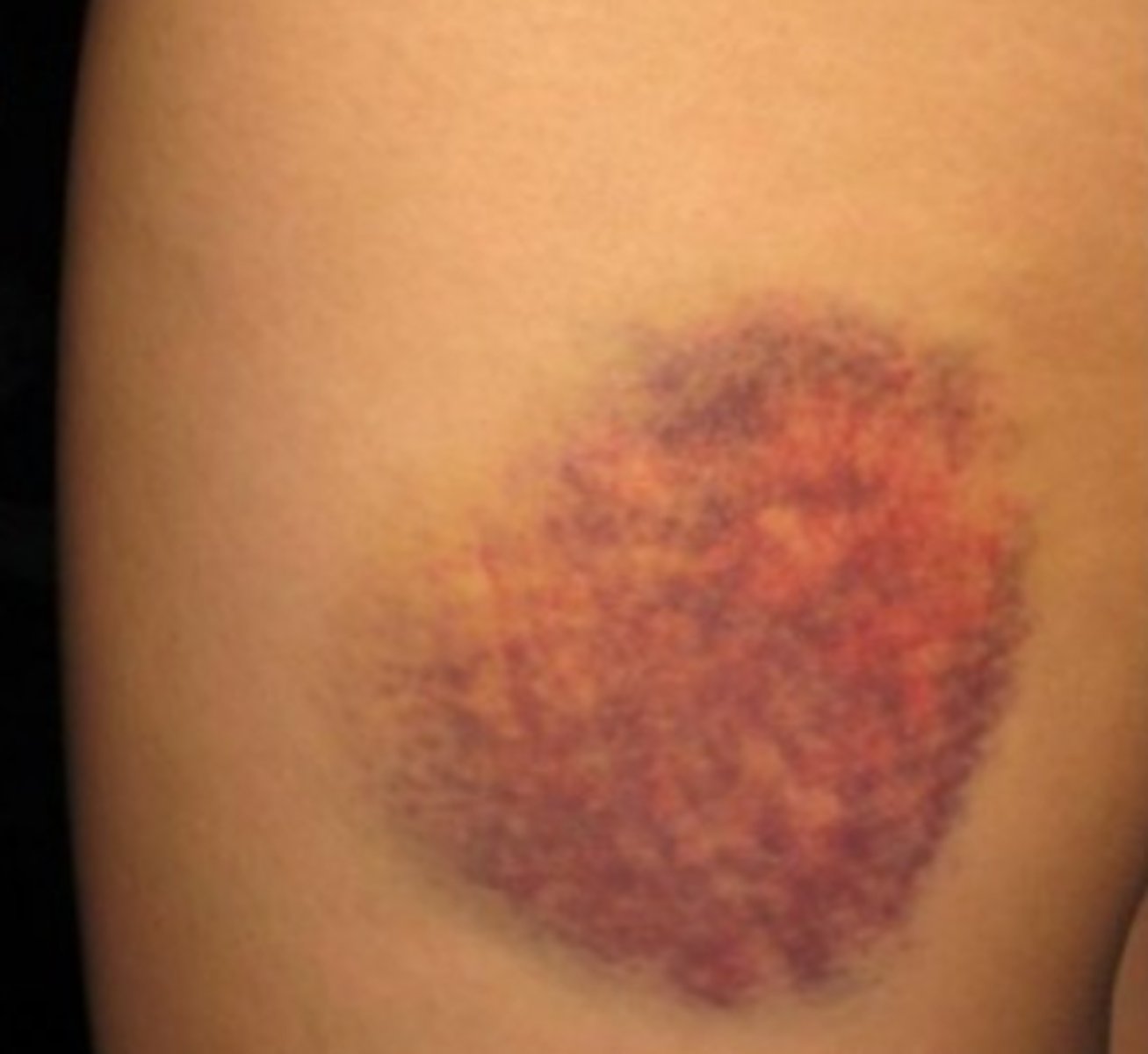
Petechiae, Purpura, and Ecchymosis
________________ do NOT blanch with pressure
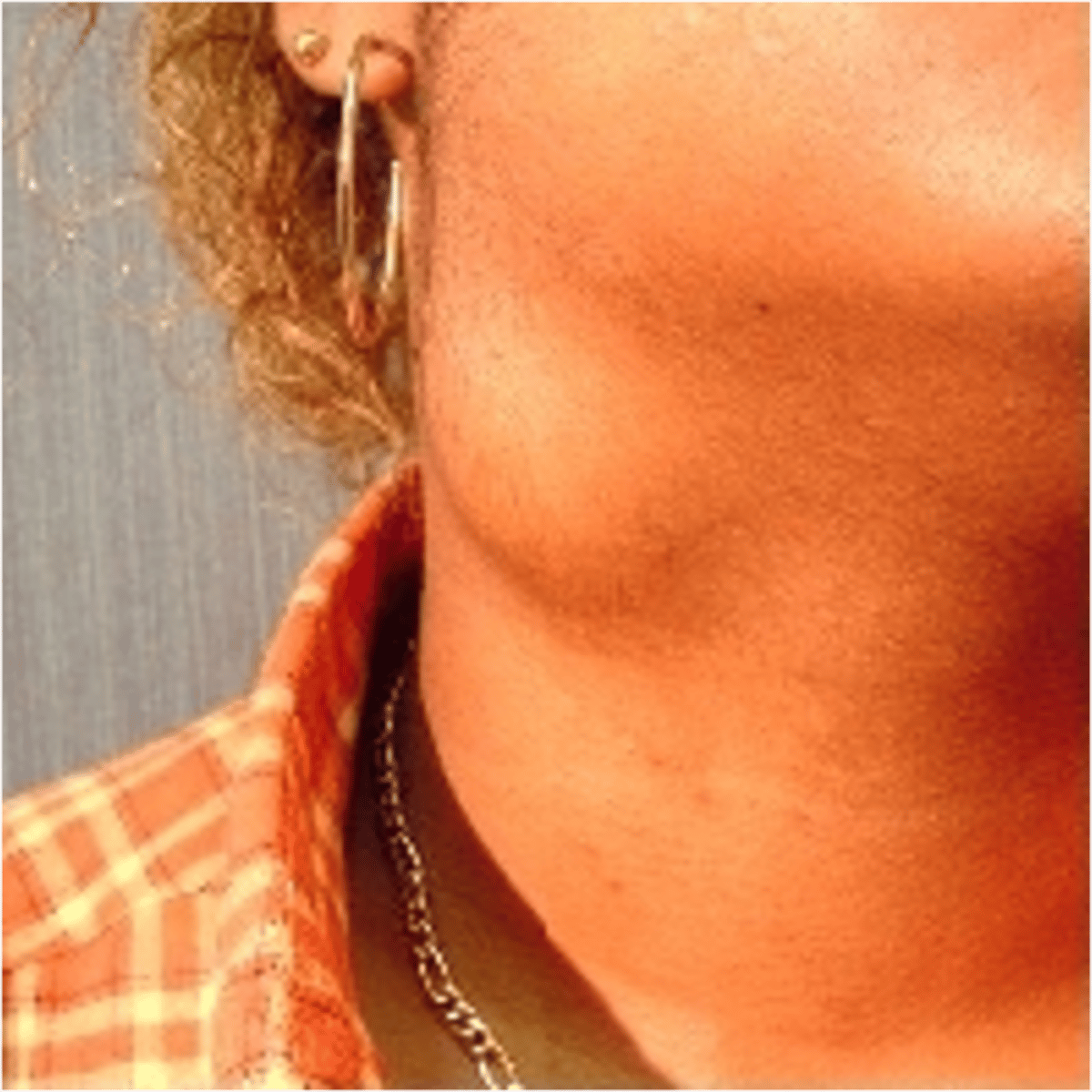
Tumor
________________:
•Solid lesion with elevation & depth
•Usually involves epidermis & dermis, possibly SC tissue
•> 2 cm in diameter
•+/ - pigmentation
Perivascular dermatitis
________________:
• Perivascular inflammatory infiltrate w/o significant epidermal involvement
• EX: hives
Spongiotic dermatitis
_______________:
•Associated with intercellular epidermal edema (spongiosis)
• EX: allergic contact dermatitis
Psoriasiform dermatitis
_________________:
• Associated with epidermal thickening from elongated rete ridges
• EX: psoriasis
Interface dermatitis
_______________:
•Cytotoxic rxn that affects the dermis and epidermis
•Characterized by vacuoles and lymphocyte infiltrates
• EX: lichen planus
Vesiculobullous dermatitis
_______________:
• Intradermal or subepidermal cleavage
• EX: bullous pemphigoid
Vasculitis
__________________:
• Damage to cutaneous vessel walls
• EX: leukocytoclastic vasculitis
Folliculitis
_______________:
• Rxn directed against colliculo-sebacous units
• EX: acne folliculitis
Nodular dermatitis
_________________:
• Nodular or diffuse dermal infiltrate w/o significant epidermal changes
• EX: cutaneous sarcoidosis
Panniculitis
___________________:
• Involves the sc fat
• erythema nodosum
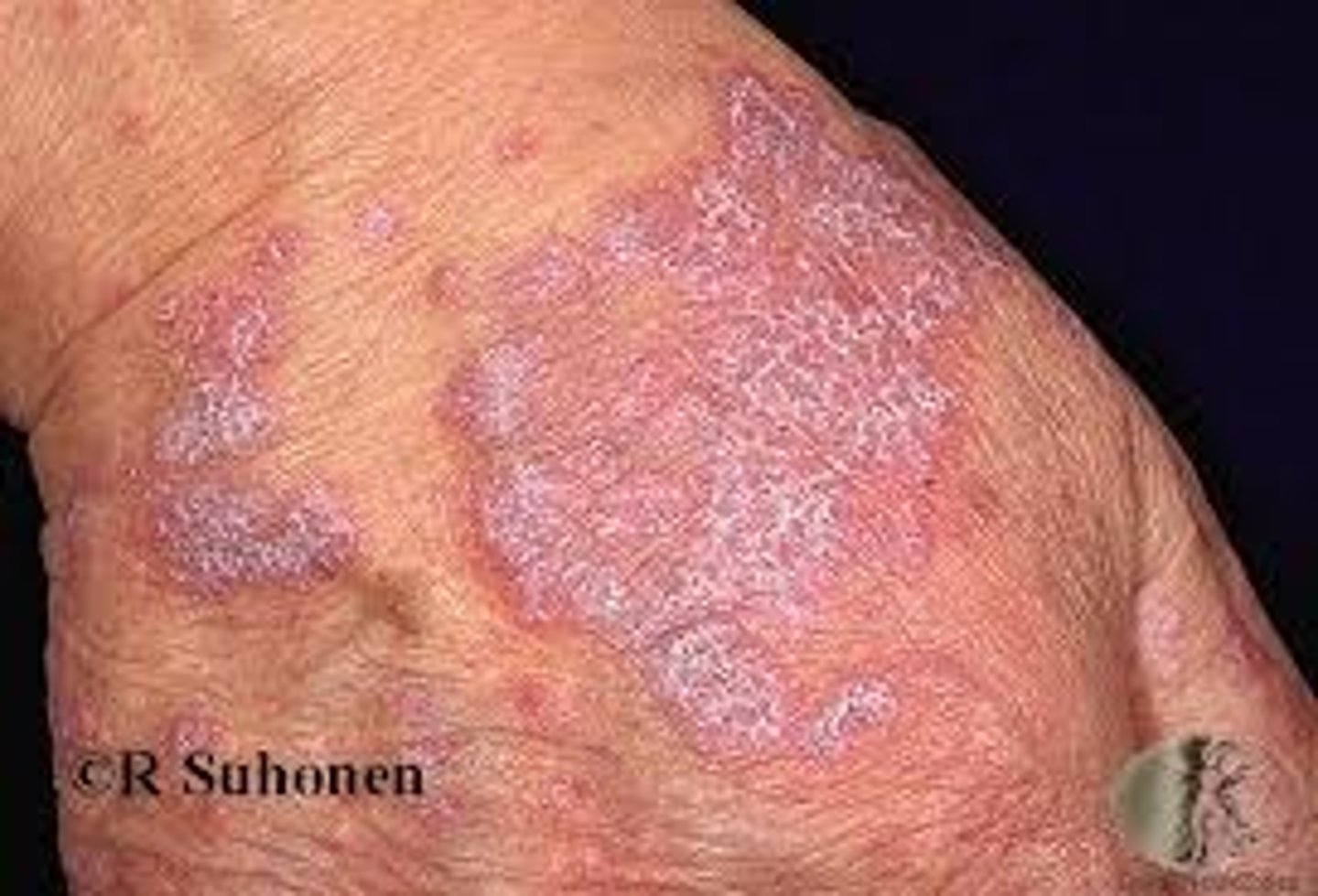
Psoriasis
____________________:
• Commonly affects the nail bed and matrix, yielding pitted or markedly thickened dystrophic nails.
• Mucosal surfaces are spared.
______________:
• "Squirting dermal papillae" (Migration of neutrophils from the dermal papillae into the overlying epidermis)
psoriatic arthritis
Only extracutaneous manifestation of psoriasis is ________________: a deforming, asymmetric, oligoarticular arthritis that can involve small or large joints.
Interface dermatitis
________________:
• Inflammatory skin disease in which the junction between the papillary dermis and epidermis is obscured.
Interface dermatitis
_________________:
• Lymphocytes attack the basal layer of epidermis causing vacuolar change in the basal cells or necrosis of basal keratinocytes.
Interface dermatitis
________________:
•Lichen Planus (chronic interface dermatitis)
•Erythema Multiforme (acute interface dermatitis)
vacuolar change
Lymphocytes attack the basal layer of epidermis causing _____________ in the basal cells or necrosis of basal keratinocytes.
vacuoles
Injury to basal keratinocytes and other structures produces tiny ___________ along the dermoepidermal junction, on both sides of the basal lamina
T-cell mediated damage to keratinocytes and remodeling of the basement membrane zone
The pathophysiology of many of the diseases in which interface dermatitis occurs is similar. What is it?
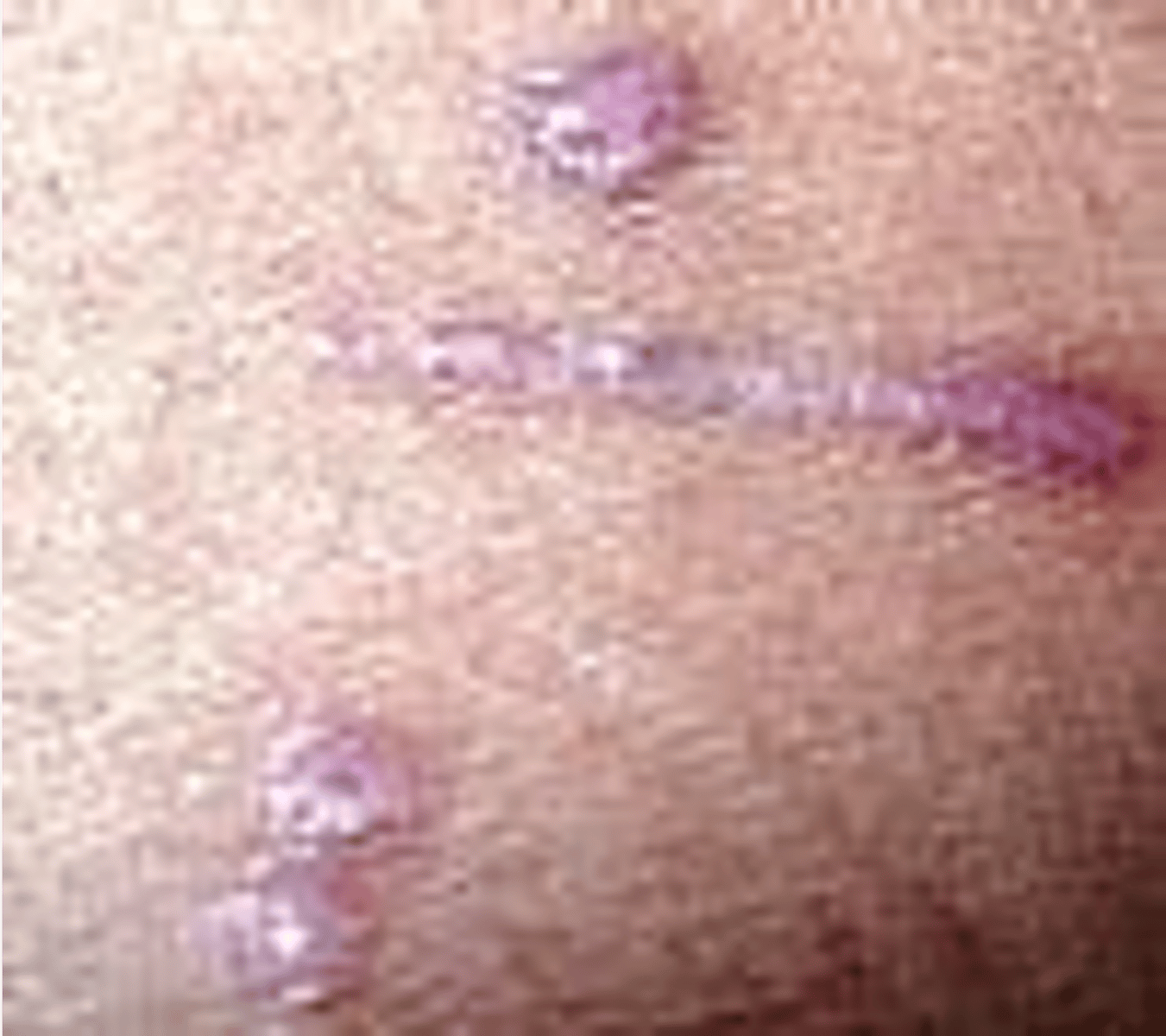
Lichen planus
______________:
•Develops in adulthood
•Women > men
• Etiology: mostly unknown
Drugs that cause Lichen planus
________________:
•Therapeutic gold
•Antimalarial agents (Quinine, Chloroquine)
•Penicillamine (cupramine)
•Thiazide diuretics
•Antibiotics (Tetracycline, Isoniazid, Streptomycin)
•Anticonvulsants (Carbamazepine, Phenytoin)
Lichen planus
________________: Begins with a dense infiltrate of T lymphocytes in the papillary dermis & superficial dermis:
• Keratinocytes & melanocytes are damaged
Lichen planus
_________________:
•Vacuoles appear in the lower epidermis
•Colloid bodies are also present
•Mature lesions are composed of CD8 cytotoxic T cells
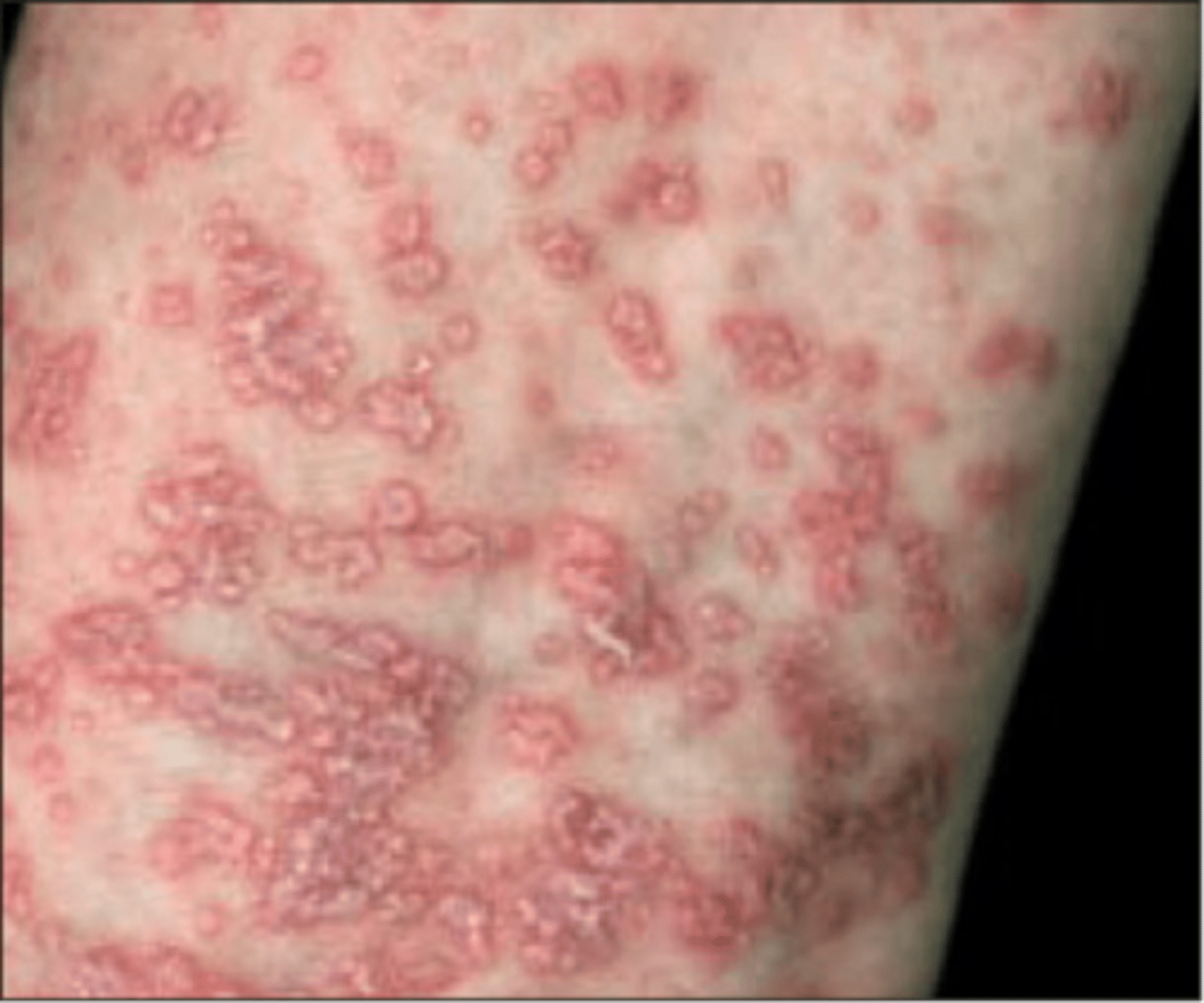
Erythema Multiforme
_______________: A cell mediated immune rxn that results in necrosis of epidermal keratinocytes
Erythema Multiforme
_____________ Etiology:
•HSV infection
•Rxn to meds
•Idiopathic