I HATE THIS CLASS KILL ME.
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sugoi!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
periodicity
organization of the periodic table
atomic radius
size of atom
what rows are periods
horizontal - like an x axis
what rows are groups
vertical - like a y axis
what are groups based on
valence electrons
what happens as you go down a table
each group gives you another shell
why does atomic radius get bigger as you go down and left
down - you add shells / left - atomic radius decreases when going right because we are moving within a shell and each element gains a proton
ionization energy
energy required to remove an electron from the atom . it will always be an electron for the outermost shell
electronegativity
ability of atoms to hold electrons tightly
dmitri mendeleev
father of the periodic table
mendeleev’s periodic table
he put elements in rows by increasing atomic weight and in columns by reactions . it was missing spots for unknown elements
current periodic table
made by henri moseley . they are in rows by increasing atomic number
horizontal rows
periods labeled 1-7
vertical columns
groups labeled 1-18
main categories
non metals, metals, metalloids
metal characteristics
good conductor of heat and electricity, shiny, ductile, malleable, chemical property has a corrosive reaction with water
non-metals
bad conductors, not ductile or malleable, brittle, dull, most are gases
metalloids
characteristics of metals and non metals
groups
elements have similar characteristics . same number of valence electrons and form same kind of ions
hydrogen
belongs to its own family . it is a diatomic and reactive gas and also an alternative fuel source
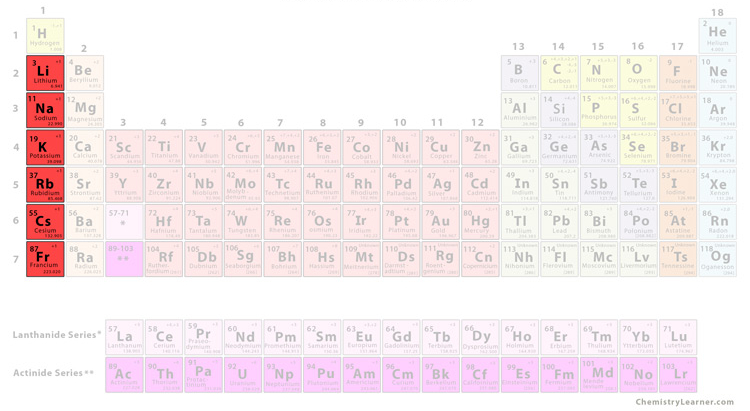
what group is this
alkali metal
alkali metal characteristics
very reactive and soft
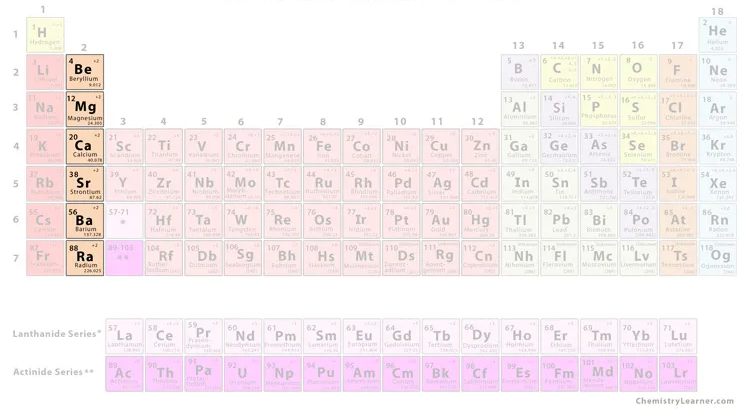
what group is this
alkaline earth metals
alkaline earth metals characteristics
reactive
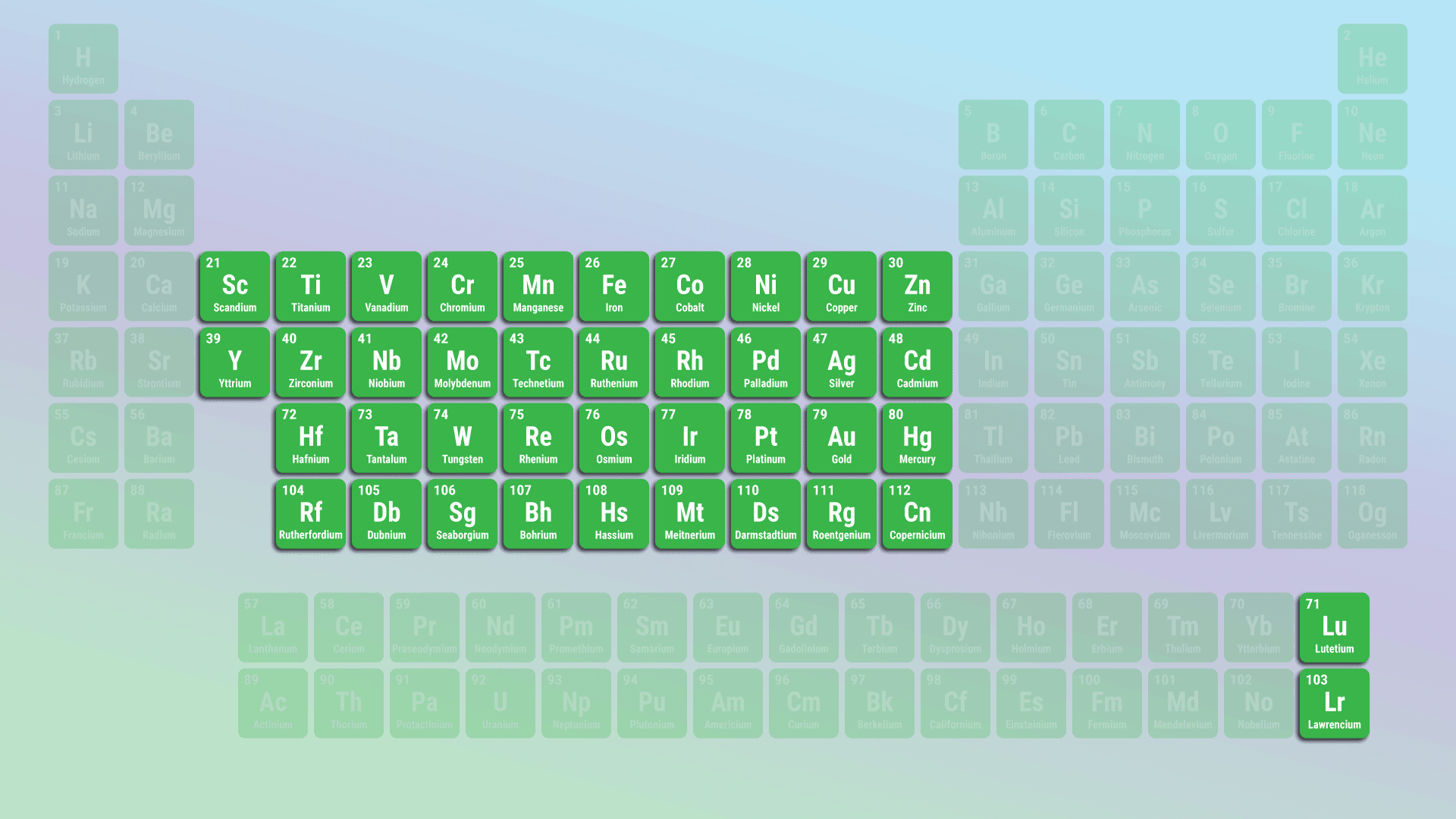
what group is this
transition metals
transition metals characteristics
less reactive and have multiple ionization states
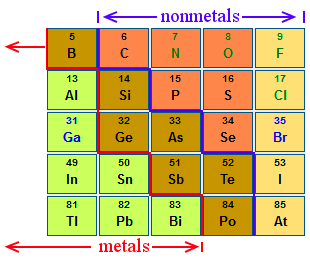
what group is this
metalloids
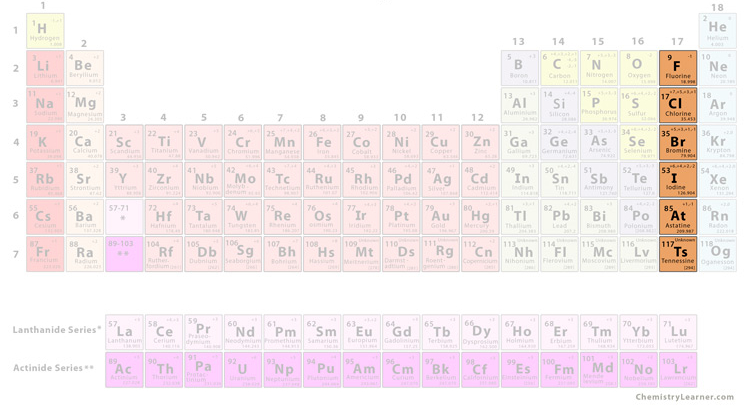
what group is this
halogen
halogen characteristics
very reactive,, found combined with other elements in nature
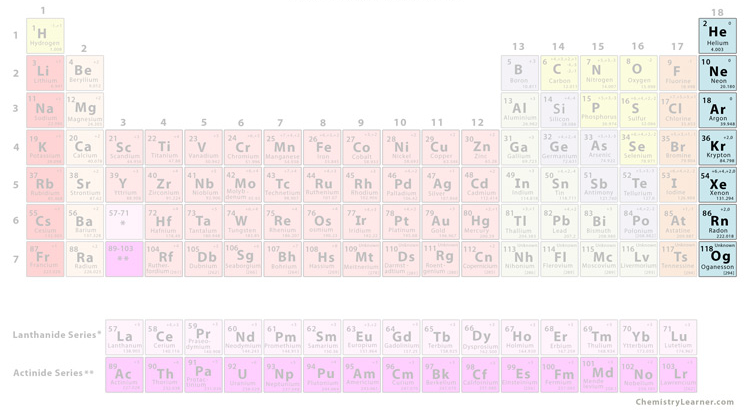
what group is this
noble gases
noble gases characteristics
not reactive at all, has full outer electron shell
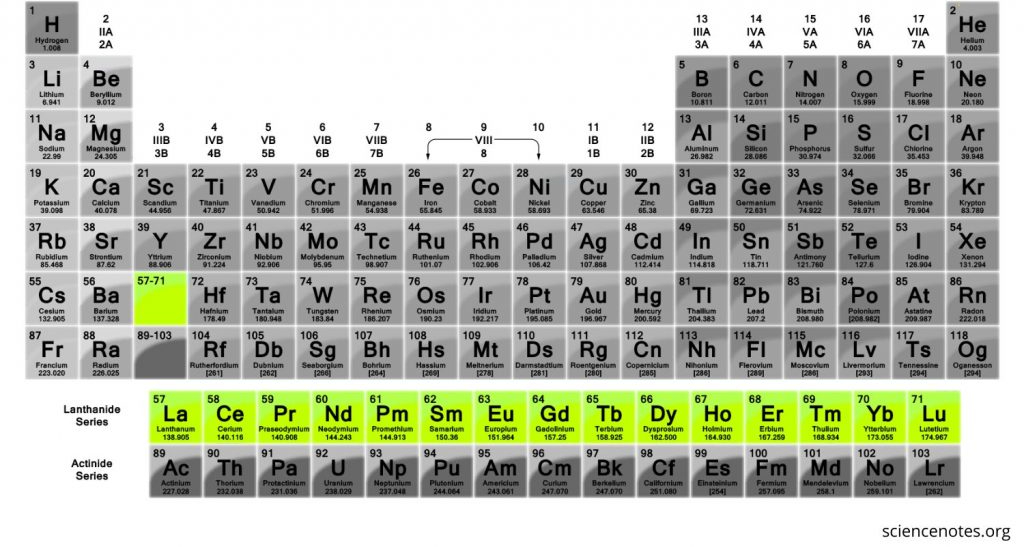
what group is this
lanthanide series
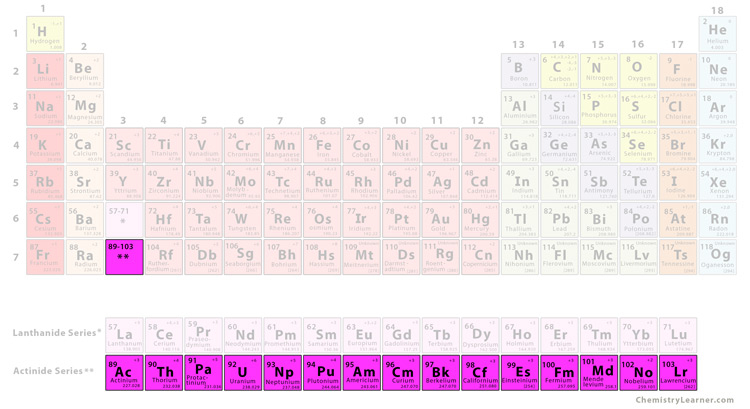
what group is this
actinide series
how does size of a metal determine the reactivity of the atom
the bigger the atom, the farther the electrons are from the nucleus, making the attraction weaker