4.2.2 Low Vision Aids
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Px eligible for Low vision Aids
Reduced VA
Reduced field
Don’t need to be registered as SI or SSI
Likely from progressive conditions such as AMD, Glaucoma, DR, Retinitis Pigmentosa - peripheral field loss
Group 1 - SSI
Worse VA than 6/120 (3/60)
Group 2 - SSI
VA 6/120 or better, but worse than 6/60
& contraction of their VF
Group 3 - SSI
VA 6/60 or better
With clinically significant contracted VF which is functionally impairing Px
E.g bitemporal hemianopia
Group 1 - SI
VA of 6/120 to 6/60 with Full Field
Group 2 - SI
VA between 6/60 and 6/24
& moderate contraction of VF
Group 3 - SI
6/18 or better, with marked field defect
e.g homonymous hemianopia
Certificate of Vision Impairment (CVI) - completed by Ophthalmologists
Info regarding details of disorder, VA, fields and difficulties the px is having
Name, address, DOB
Establishes the Ophthalmologist believes the requirements are met - formally classifies Px as SSI/SI
Starts the process of registration
5 copies - Px, Local Authority, Px’s GP, Hospital notes, Epidemiological analysis e.g Moorfields
Home visit to see the environment/look at modifications
Referral of Visually Impaired Patient (RVI) - completed by non-ophthalmologist clinic staff to refer
Info about px condition, problems with daily life
Only Hospital staff can complete this
Must have consent of px to refer
For Px where registration is not appropriate
Referred to social services due to struggling with eyesight
Simply flags the px to local authority to see if the px can be assessed for any help
4 copies - Social S, Px, Px GP. Hospital file
Low Vision Leaflet (LVL)
Self-referral leaflet to the Social Services
Local opticians who can give to px who are struggling
Where can Low vision services provided?
Hospital eye departments - recommend low vision aids - advice on contrast, lighting and daily tasks
Community Optometry Low vision Services
Charities - RNIB - counselling - training in the use of aids
Rehabilitation services - Local authority - rehab training for daily tasks, mobility and orientation support, home assessments and adaptations
Guide Dogs for Blind association - apply for a guide dog
Uni Eye Clinics
Assistive Technology
BlindSquare – App describes environment and announces points of interests/streets/specified points as you travel
iDentifi – Voiceovers objects in the camera screen - recognises objects and brands so helps with grocery shopping
Be My Eyes – App matches visually impaired user with sighted volunteer for help - free unlimited calls - real time assistance
SeeingAI - narrates the world around the px - helps with reading, describing photos and identifying products
VoiceVista - helps VI Px with their surroundings - audio navigation app - gives directions and helps find places - has a sound beacon which helps stay on route
Reverse contrast
Increasing size on the screen
Kindle - contrast and size of print
Large Print Books
No change in posture/distance
Simple, no training req.
Less conspicuous
Disadvantages
Limited in size
Reduces contrast
Deciding between monocular or binocular MAG
If VAs are similar then Bino. is preferred
VA’s are not similar use Monocular - use the best VA eye
Design of Magnifiers may force it the be used monocularly
What option do we have to hence distance mag
Telescope is the only useful aid
In some cases you can move closer e.g TV
When using a distance telescope does the Px need to wear specs?
Can be used with or without specs
Largest FOV is obtained when exit pupil is closest to the eye
What Rx does the Px wear for Hand MAG?
Distance RX
Spectacle Microscope
e.g px is -4.00 and needs 3x mag
MAG = F/4
F = +12.00DS
Take into account Rx
Final Lens = +8.00DS
What is the FOV for telescopes?
Restricted at 7 degrees - 1 degree = 1cm viewed at 57cm
Difficult to walk around and view - good for spotting tasks such as Bus numbers and watching TV
Adv of telescopes
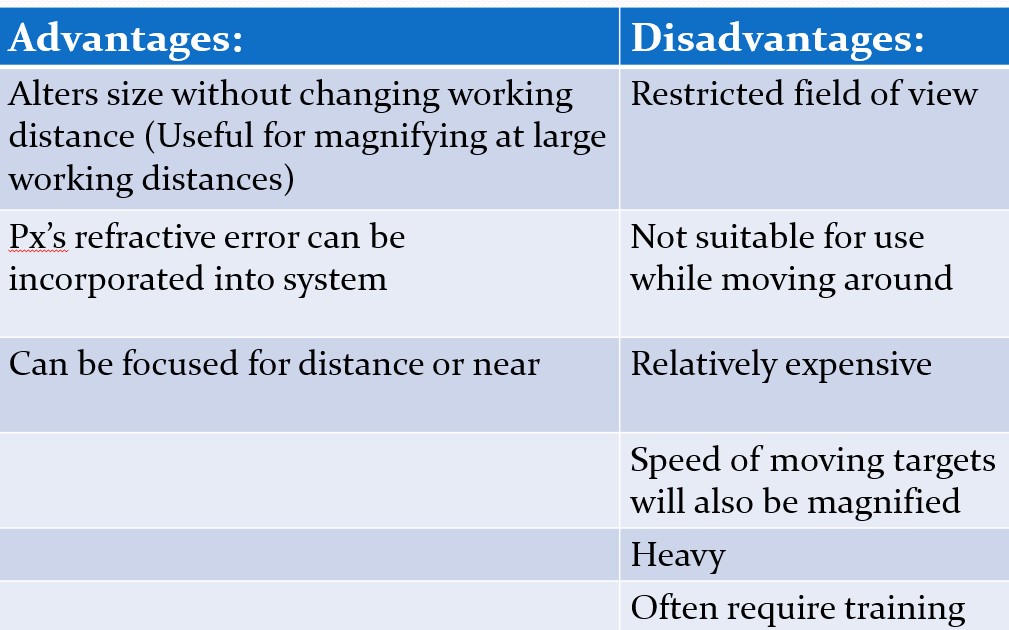
Types of telescopes
Keplerian - img is inverted - prism used to rotate the lens - greater mag
Galilean - no prism
Pros of Near Telescopes
Increased WD compared to Spec Mag
Cons of Near Telescopes
When compared to spec microscope;
Worse FOV
Cosmetically poor
Costly
Heavier
Hand Magnifiers
Best Known LVA - easy to use
Widely available
Higher power = smallest lens diameter
What happens at the FP of the magnifier?
MAG is greatest
FOV is smallest
Parallel rays of light emerge - no need to accommodate
Summary of Hand Magnifiers
Plus lenses - increase retinal image size via RDM
Allows Px to adopt a closer WD
If object is placed at anterior FP of lens - Distance Rx
If object is closer than Anterior FP - Reading Rx/ Near ADD
Advantages of Hand MAGs
Discrete
Easy to use
Portable
Lightweight
Convenient for brief tasks e.g labels
Inexpensive
Can use internal illumination
Used with distance Rx
Disadvantages of Hand Mags
Handling - require a hand + needs to be steady
Restricted FOV
Can cast shadows over object
In a stand magnifier why is the object to lens distance LESS than the FP of the lens?
Provides a better quality image c less aberrations
Diverging light leaves the mag - Px must accommodate / Reading ADD
ADV of Stand Magnifiers
Accurate WD
Hands free
Contains internal illumination
DisAdv of Stand Magnifiers
May require special reading specs
Stand can prevent assess to object
Flat surface required
Can be more bulky than hand mags
What would be the power for a low powered stand mag?
around 4x mag
What would be the power for a med/high powered stand mag?
from 4 to 20x mag
z closer to 0
Dome Magnifier
Advantages;
Great for instantly enlarging text on a book
Rests on the page – does not have to be held up by the patient.
Disadvantages;
Can be somewhat heavy & fiddly – not ideal for patients with arthritis etc.
Spectacle Rx
Advantages;
High Plus Rx may replace a magnifier
Hands free
Disadvantages;
Lenses are heavy
Galilean over Keplerian?
Lighter, shorter and cheaper
Keplerian over Galilean
Widens FOV, better quality img than Galilean
Non-Optical LVA
Tints - Dark for albinism or RP, yellow for CS in AMD
Caps/Visors to reduce glare
Typoscopes - flat sheet of card or plastic that helps isolate a line - improves contrast and helps maintain place when reading text
Extra illumination for AMD, Glaucoma, DR, RP
CCTV
Variable high levels of magnification
Reverse contrast
Reduced visual crowding
Improved illumination
Up right view posture - reduces neck and back strain compared to other LVAs
Desktop systems/hand held units
COST
Learning curve
Portability