Study of matter - flashcards
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
important key words that seem unfamiliar; complete with must-know notes in same folder :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Isotope
Atoms of the same element but with different amounts of neutrons.
have similiar or even identical chemical behavior, but may have differing physical properties (density, radioactivity, etc)
isotopes can be stable or unstable
written using isotope notation
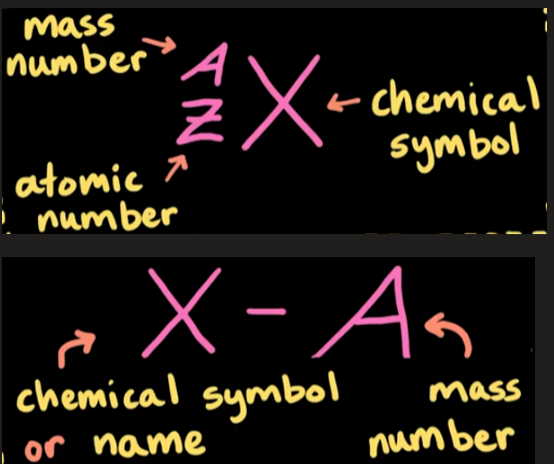
Allotrope
Different forms of the same element, where the atoms are arranged in distinct ways
differing physical and chemical properties (ie, conductivity)
carbon: diamond, graphite, graphene, fullerene
Molecule
2 or more atoms that are held together by (most commonly) covalent bonds
sizes range from diatomic molecules to complex macromolecules
Compound
Substance composed of two or more different elements that are chemically bonded together
ionic, covalent or metallic bonds
have fixed ratios depending on the atoms
need chemical methods to break the bonds
Mixture
Combination of two or more substances, where each substance retains its own chemical properties
no chemical bonds between the substances, meaning that they can be separated by physical means
Homogeneous mixtures
Mixtures uniform in composition and appearance throughout
solution
alloy
gaseous mixtures
colloids
Solution
Homogeneous mixture where a solute is dissolved in a solvent
can be separated by physical processes like evaporation or filtration
Alloy
Homogeneous mixture of metals
Gaseous mixture
Homogeneous mixture of gas
distribute uniformly
most commonly separated by distillation or fractional distillation, chromatography and absorption
Colloids
Homogeneous or heterogeneous mixtures depending how well the other substance is distributed throughout the other one.
for example whipped cream has two distinct phases (gas, liquid) which makes it heterogeneous, but milk is also a colloid, but homogeneous since the fat that it contains is well uniformly distributed throughout
for homogeneous colloids, ways of separation include
ultrafiltration
centrifugation
electrophoresis (separated using an electric field)
for heterogeneous colloids, ways of separation include
filtration and sieving
settling and decantation
centrifugation
Suspensions
Heterogeneous mixture where solid particles are dispersed throughout a liquid or gas, undissolved
can be separated by means of:
filtration
decantation
centrifugation
evaporation
magnetism
Heterogeneous mixtures
Mixtures not uniform and as such, the individual components can be seen and distinguished from one another
suspensions
colloids
emulsions
mechanical mixtures
Emulsion
Heterogeneous mixture that is a subtype of colloids, where the dispersed phase and continuous phase are both liquids
may be so unstable that separates over time
can be separated by means of
centrifugation
decantation
heating breaks the emulsion
addition of emulsifying agent, destabilizing the emulsion
filtration in some cases
Mechanical mixtures
Heterogeneous mixtures where the components are physically distinct and can be easily separated by filtration
Distillation
Way of separating homogeneous mixtures by utilizing differences in the boiling points of the components
Evaporation
Way of separating homogeneous mixtures by utilizing difference in boiling points or the volatility (vaporization ability)
Fractional distillation
Way of separating homogeneous mixtures with close but not the same boiling points, may include multiple steps
Chromatography
Way of separating homogeneous or heterogeneous mixtures based on their different ways of moving from stationary to mobile phases (move at different rates through a tube)
Ultrafiltration
Way of separating homogeneous mixtures where semi-permeable membrane is used to separate particles based on size (water purification)
Centrifugation
Using centrifugal force to separate components of a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture based on density (spinning at high speeds to separate)
Filtration, sieving
Way of separating heterogeneous mixtures by utilizing differences in particle size
Settling and decantation
Way of separating heterogeneous mixtures by the settling of particles over time based on density
Magnetic seperation
Used to separate heterogeneous mixtures’ components when one is magnetic
Crystalline solid
Solid substance with a regular repeating structure (ie, diamond, NaCl)
Amorphous solid
Solid substance with no organized pattern in its lattice (glass)
Changes of state where energy is absorbed
Melting
Vaporization
Sublimation
Changes of state where energy is released
Freezing
Condensation
Deposition