Psychophysics
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is Weber’s Law?
Weber’s Law states that the smallest change in a stimulus that can be perceived, the just noticeable difference (JND), is proportional to the intial stimulus.
What are aspects associated with classical psychophysics?
Absolute thresholds (is there anything there?)
Difference thresholds (is there any difference?)
Scaling (Estimation of stimulus intensity - how much)
Multidimensional scaling
What is classical psychophysics theory?
Supra-threshold stimuli (strong stimuli) the relation between stimulus strength and experienced magitude. eg. what’s the relation between experienced loudness and actual dB
Near-threshold stimuli (weak stimuli) sensory limits (hearing tests)
The discrimination threshold and Weber’s law
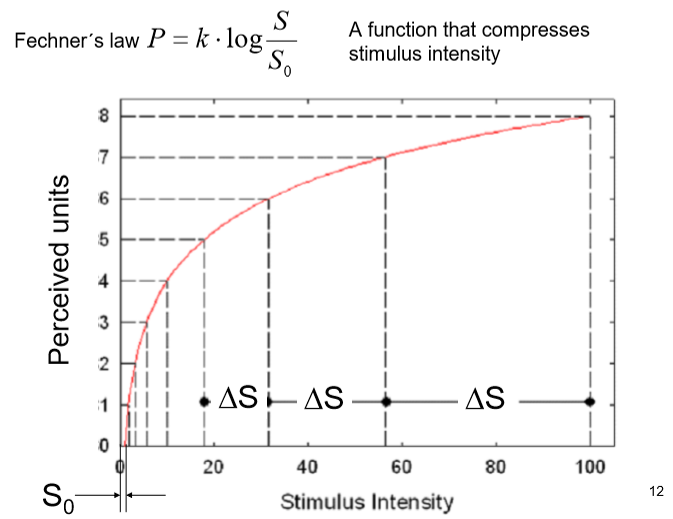
the idea that to obtain 75% correct discriminations, stmuli must differ by a constant %, not a constant amount.
Fechner’s law
if a stmulus is multiplied by a fixed factor, the corresponding perception is altered in additive constant amounts.
Why is there no ideal thresholds?
Threshold varies from trial to trial
Random neural firing (noise) - if there is inner noise then participants can’t distinguish it from a weak stimulus
Stim-magnitude varies between trials
Name 4 types of scaling methods
Magnitude estimation - estimate the sensory magnitude with a number
Ratio estimation - estimate a number by how much stronger a test stimulus is compared to a standard.
Ratio production - the inverse of ratio estimation
Magnitude matching/adjustment - with a number: adjust a stimulus to match a number
What is the YES-NO paradigm?
respond yes if you perceive something and no if you perceive nothing
results in bias (how liberal or conservative a person is answering)
proportion false alarms (FA) at catch trials gives an estimation of guessing frequency
What is the two-alternative-forced-choice (2AFC) paradigm?
2 stimuli is presented, one has to be chosen and guessing if necessary.
liberated by the bias from the YES-NO paradigm
could result in systematic bias though or time-order effects
Method for threshold measurements - Method of constant stimuli
A range of stimuli from very hard to relatively easy are selected.
pick them uniformly and this will be the constant stimuli set.
Decide answering format yes/no etc
Test each stimuli many times (20-25) in random order
Calculate the % of yes and no responses at each level
Fit the psychometric function
What is the high threshold theory (HTT)
assumes that all events above threshold are detected
but threshold is influenced by trial-to-trial variability
all catch trials are below threshold but occasionally lead to false alarms due to guessing
What are the problems associated with HTT
correction for guessing is far from perfect
predicts linear relations between hits and false alarms (ROC-curve) but the actual relations are often curves!!!!!! not straight lines.
Assumptions of the Signal Detection Model
assumes that there is no absolute threshold
assumes that there is always noise present in the environment
assumes that the noise can be internal or external and varies randomly
Procedure for SDT
Participants are repeatedly presented to same S+N (weak signal + Noise) and N (no signal only noise) stimuli in random order.
For each observaation (x) a decision has to be made whether x is a signal + noise (SN) or just noise (N)
The ROC curve
receiver operating characterisitics
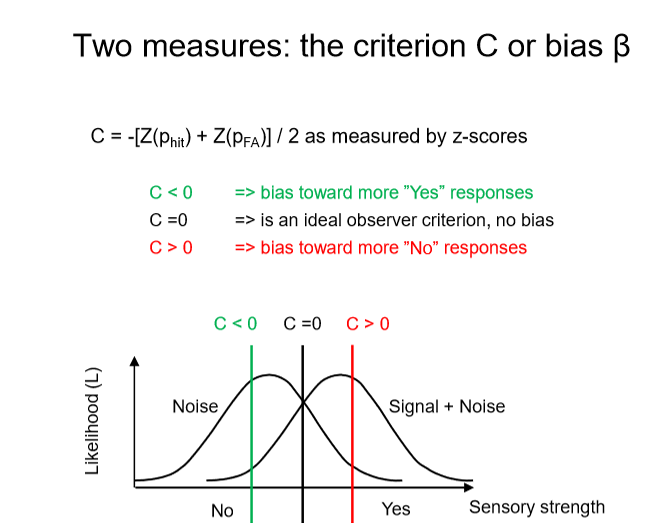
plot hits against false alarms for all criterions C
what is d-prime
is useful when a researcher wishes to find out whether sensitivity is actually changed or whether a person is simply more willing to say Yes under some conditions than others
SDT and the criterion