Quiz 2 Study Guide
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Joints and Muscles Quiz Study Guide
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
Fascicle Arrangement
The organization of muscle fibers that affects a muscle's range of motion and power.
Parallel Muscles
Muscles with fascicles running parallel to the long axis, allowing for extensive range of motion but less power (e.g., sartorius).
Pennate Muscles
Muscles with fascicles attaching obliquely to a central tendon, providing greater power but limiting range of motion (e.g., rectus femoris).
Convergent Muscles
Muscles where fascicles converge from a broad area to a single tendon, offering versatility in movement (e.g., pectoralis major).
Circular Muscles
Muscles arranged in concentric rings, useful for closing openings (e.g., orbicularis oris).
Agonist
The primary muscle responsible for generating a specific movement (e.g., biceps brachii for elbow flexion).
Antagonist
The muscle that opposes the movement of the agonist (e.g., triceps brachii for elbow extension).
Synergist
A muscle that assists the agonist by providing additional force or reducing unwanted movement (e.g., brachialis).
Fixator
A muscle that stabilizes the origin of the agonist, enabling it to function more effectively (e.g., shoulder girdle muscles).
Axial Muscles
Muscles located on the head, neck, and trunk.
Appendicular Muscles
Muscles associated with the limbs.
Occipitofrontalis
A muscle with two bellies; frontal raises eyebrows, occipital pulls scalp backward.
Orbicularis Oculi
A muscle that closes the eye (blinking, squinting).
Orbicularis Oris
A muscle that closes and protrudes the lips (kissing muscle).
Levator Labii Superioris
A muscle that elevates the upper lip (smiling).
Zygomaticus
Muscles that elevate the corners of the mouth (smiling).
Depressor Anguli Oris
A muscle that lowers the corners of the mouth (frowning).
Temporalis
A muscle that elevates and retracts the mandible (chewing).
Masseter
A muscle that elevates the mandible (chewing).
Sternocleidomastoid
A muscle that flexes the neck and rotates the head.
Trapezius
A muscle that elevates, retracts, and rotates the scapula.
External Intercostals
Muscles that elevate ribs during inhalation.
Internal Intercostals
Muscles that depress ribs during forced exhalation.
Pectoralis Major
A muscle that adducts and medially rotates the arm.
Diaphragm
The prime mover for inhalation, contracts to enlarge the thoracic cavity.
Rectus Abdominis
A muscle that flexes the vertebral column.
External Obliques
Muscles that flex and rotate the vertebral column.
Rhomboideus Major
A muscle that retracts and elevates the scapula.
Infraspinatus
A muscle that laterally rotates the arm.
Deltoid
A muscle that abducts the arm.
Biceps Brachii
A muscle that flexes the elbow and supinates the forearm.
Triceps Brachii
A muscle that extends the elbow.
Gluteus Maximus
A muscle that extends and laterally rotates the thigh.
Sartorius
A muscle that flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates the thigh.
Biceps Femoris
A muscle that extends the thigh and flexes the knee.
Tibialis Anterior
A muscle that dorsiflexes and inverts the foot.
Gastrocnemius
A muscle that plantarflexes the foot and flexes the knee.
Calcaneal Tendon
Connects the gastrocnemius and soleus to the heel bone, aiding in plantarflexion.
Flexion
a decrease in the joint angle from anatomical position
Ex. If you bend your elbow
Extension
a return to anatomical position of a part of the body that was flexed
Hyperextension
extension of the part of the body beyond anatomical position
Abduction
movement of the limbs in the coronal plane away from the body
Adduction
the return of the part of the body to the anatomical position after abduction
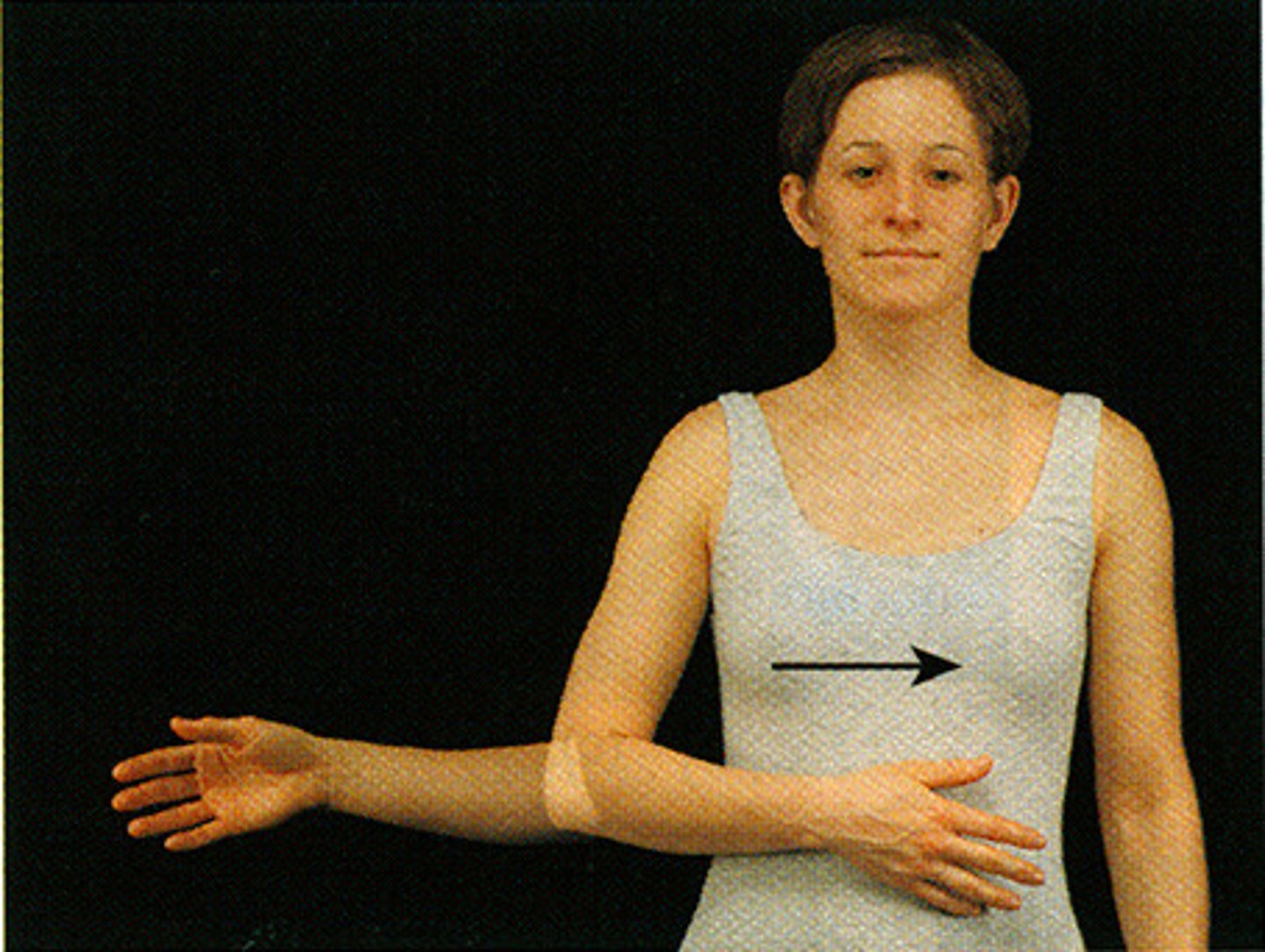
Rotation
circular movement of a part of the body
Supination
lateral rotation of the hand
Pronation
medial rotation of the hand
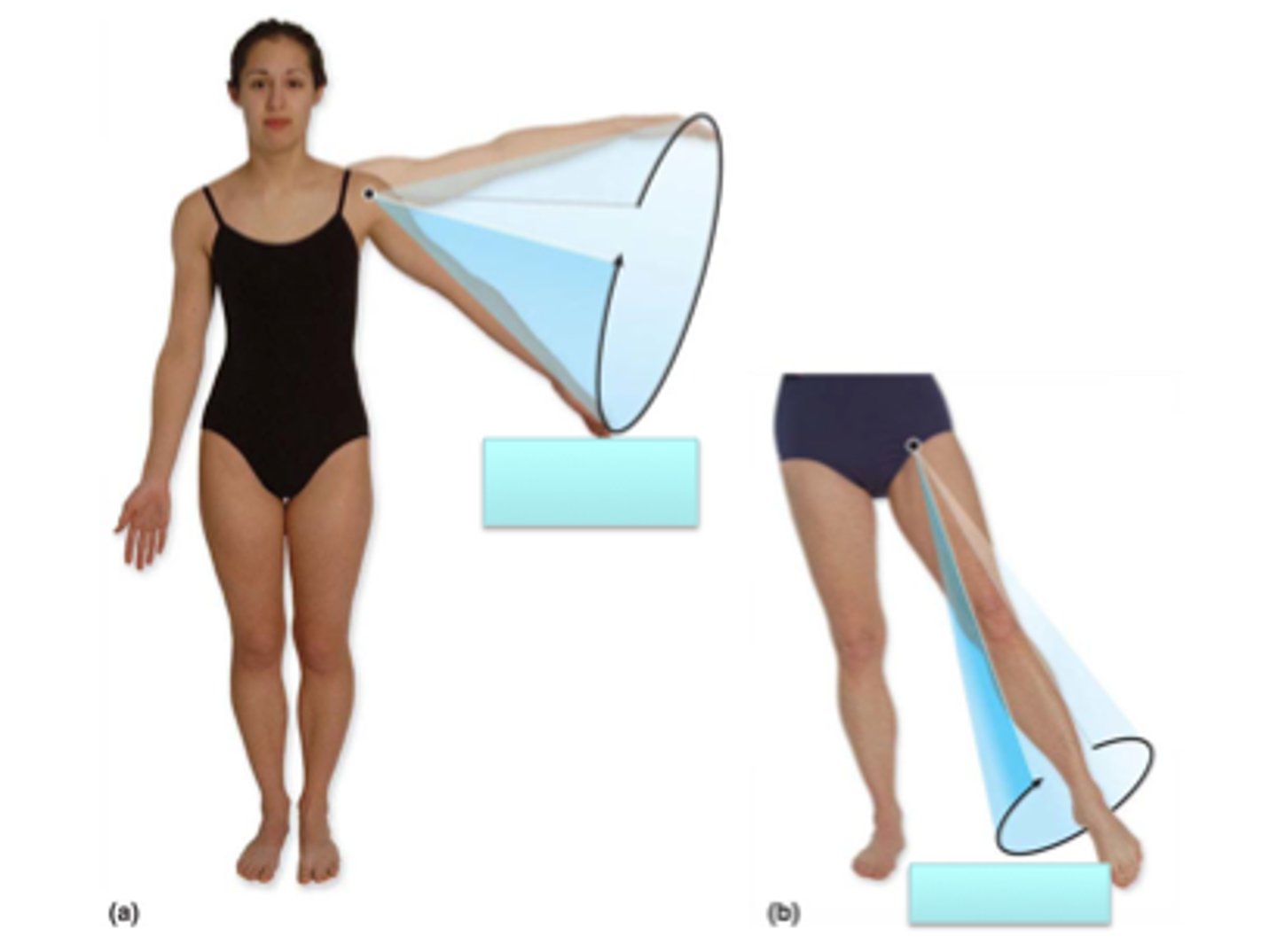
Circumduction
movement of a muscle in a conical shape
Protraction
a horizontal movement in the anterior direction
Retraction
the reverse of protraction
Elevation
to move in a superior direction
Depression
movement in the inferior direction
Inversion
move the feet inward so that the soles are facing each other
Eversion
turning the soles of the feet outward
flexion
What action is this?
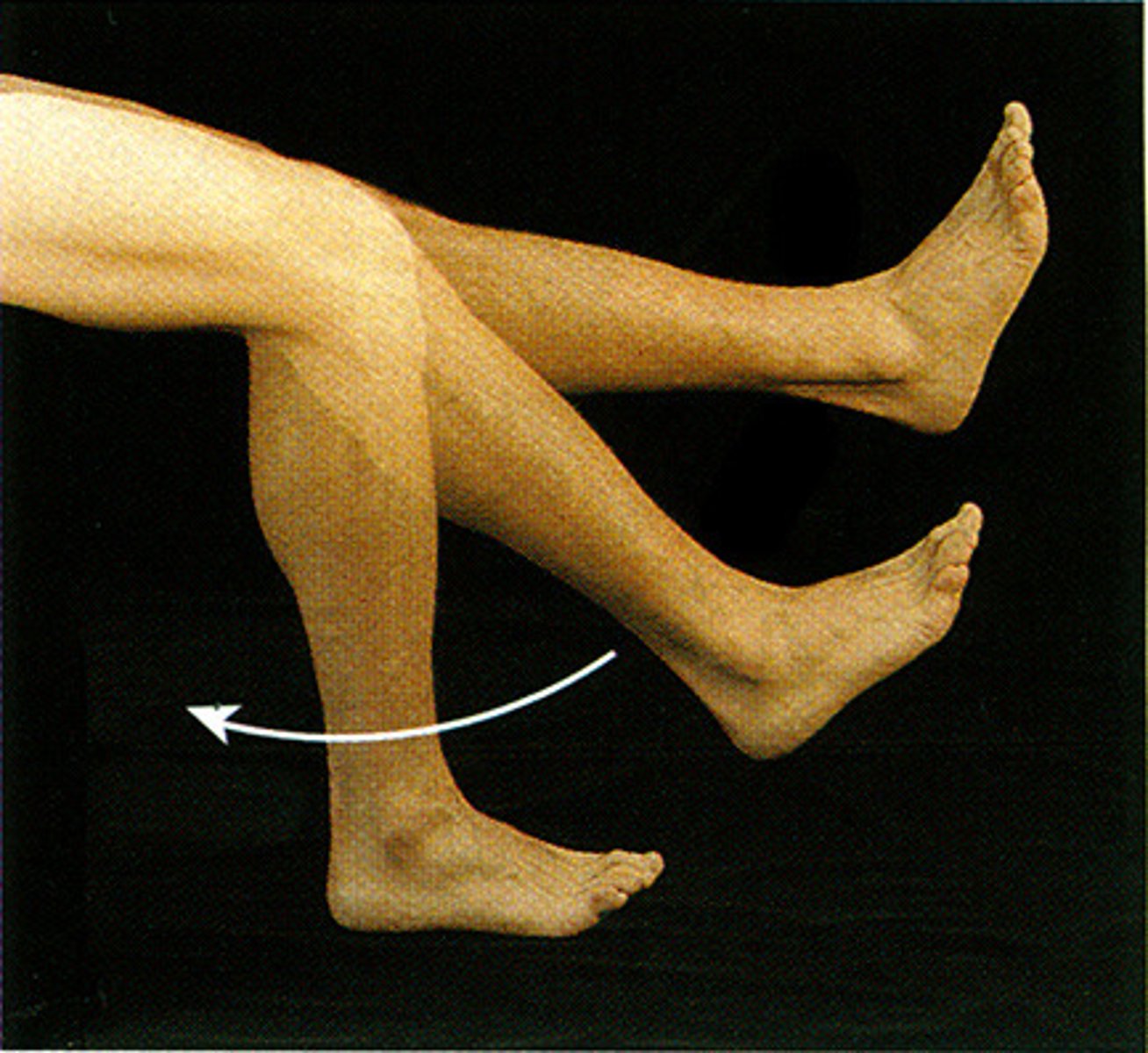
extension
What action is this?
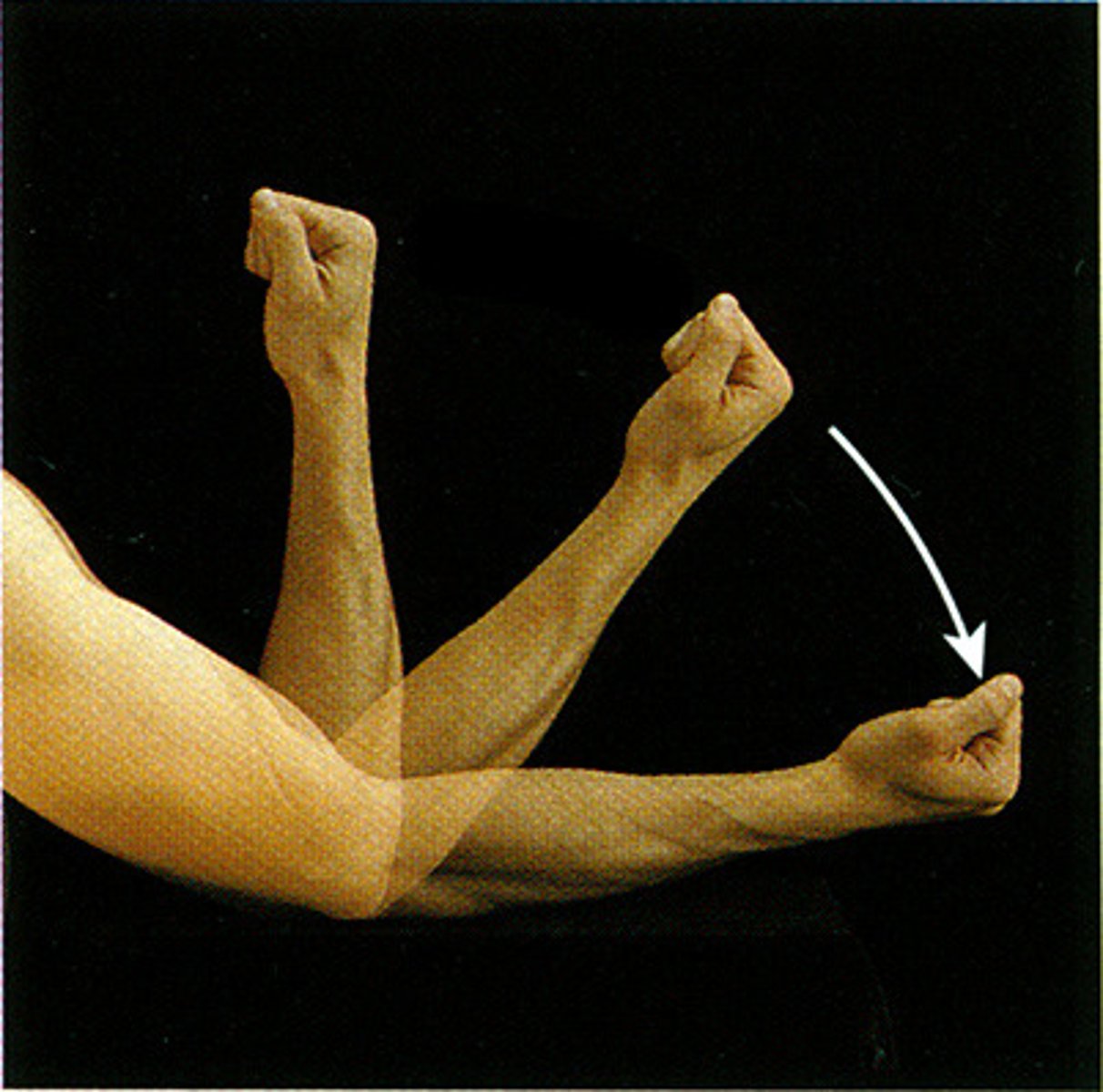
circumduction
Rotation
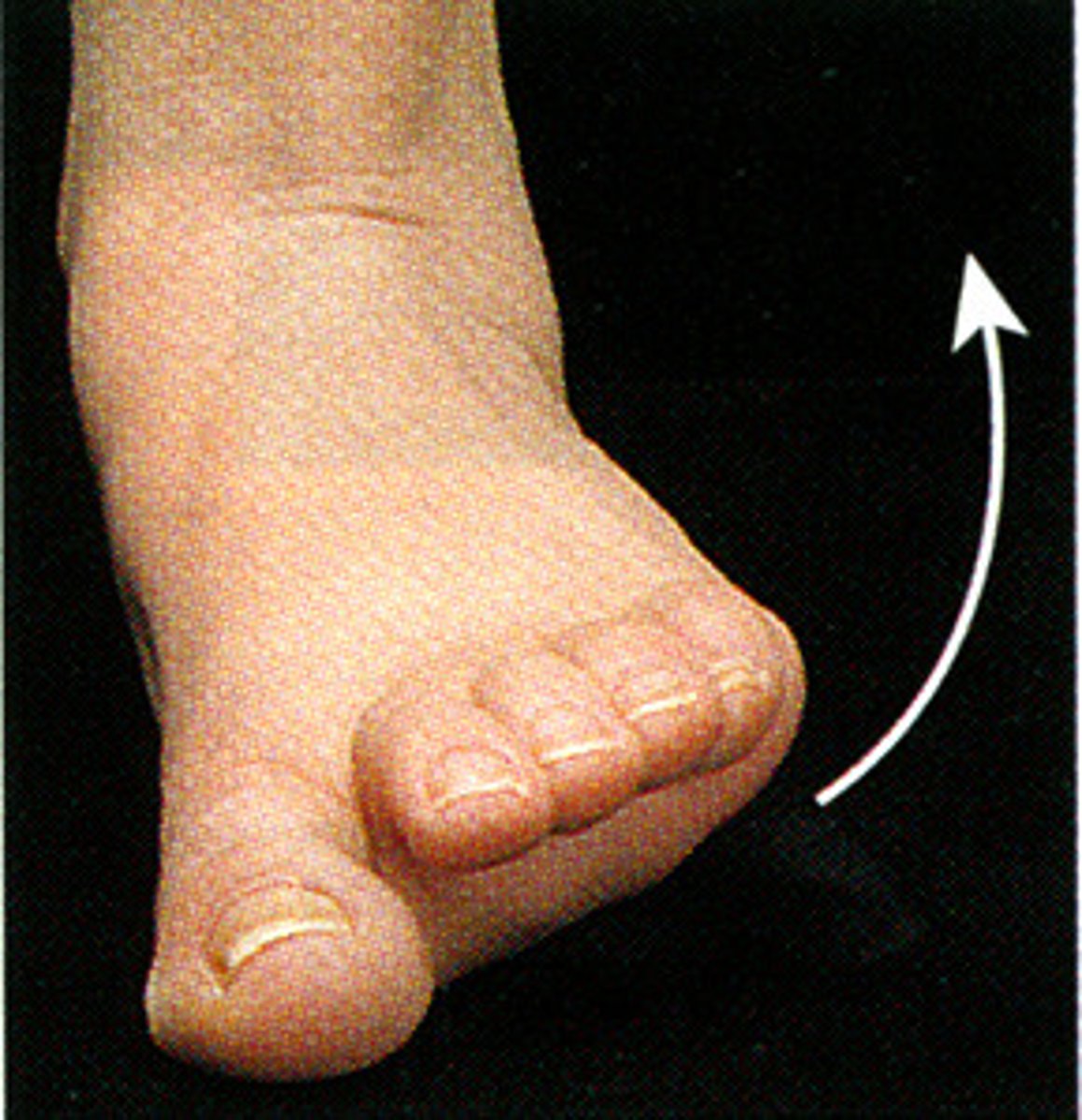
eversion
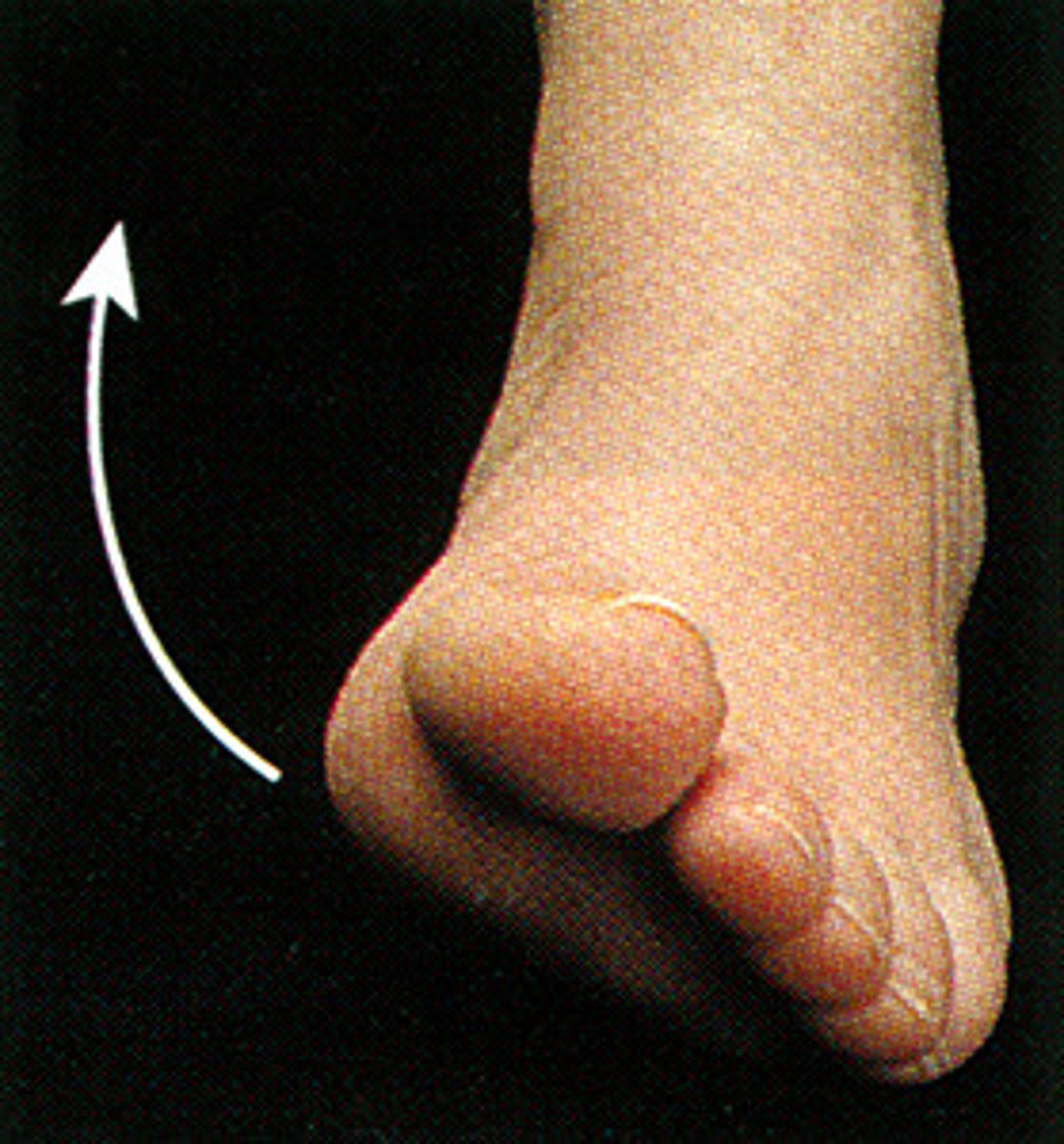
inversion
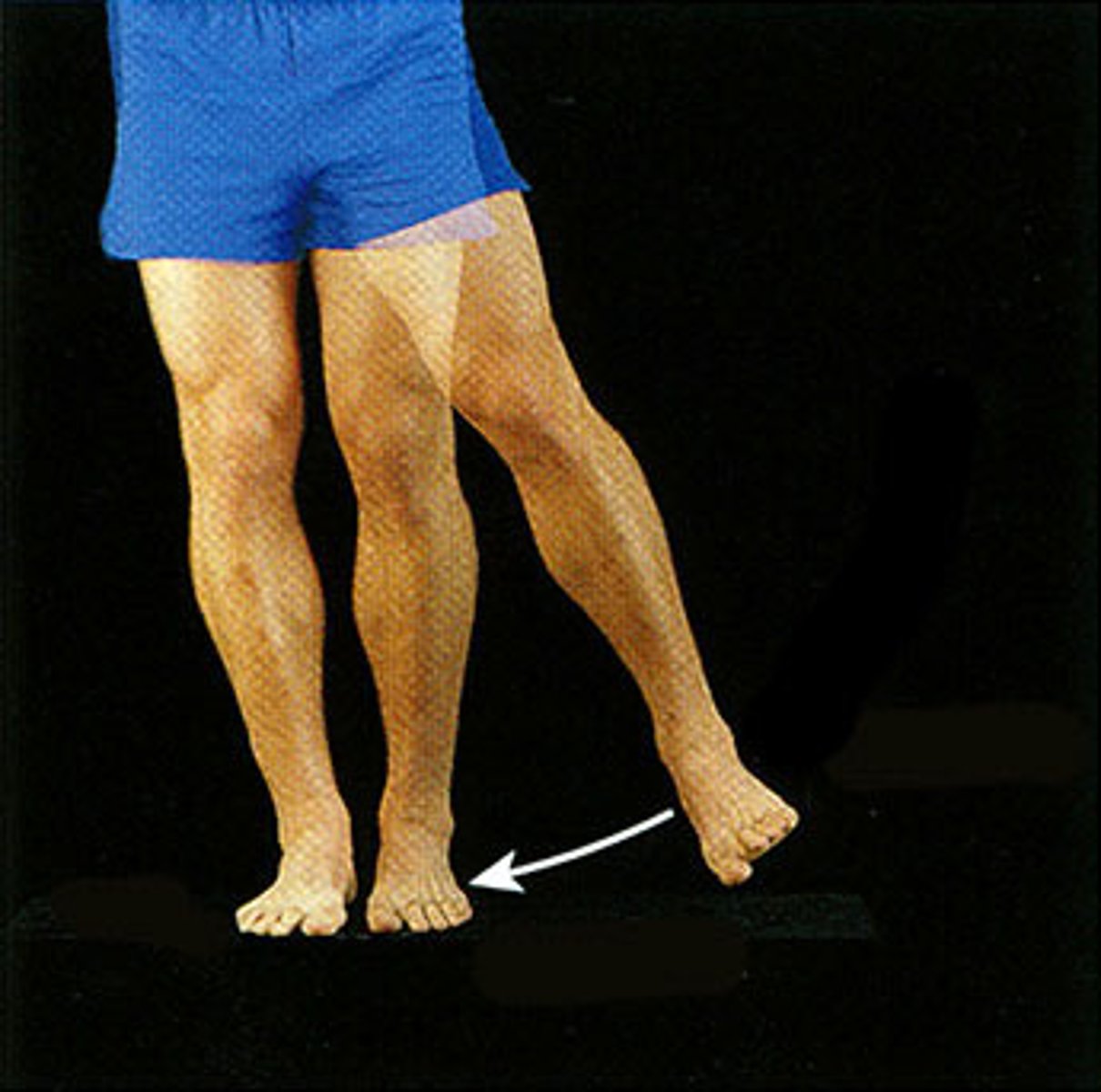
adduction
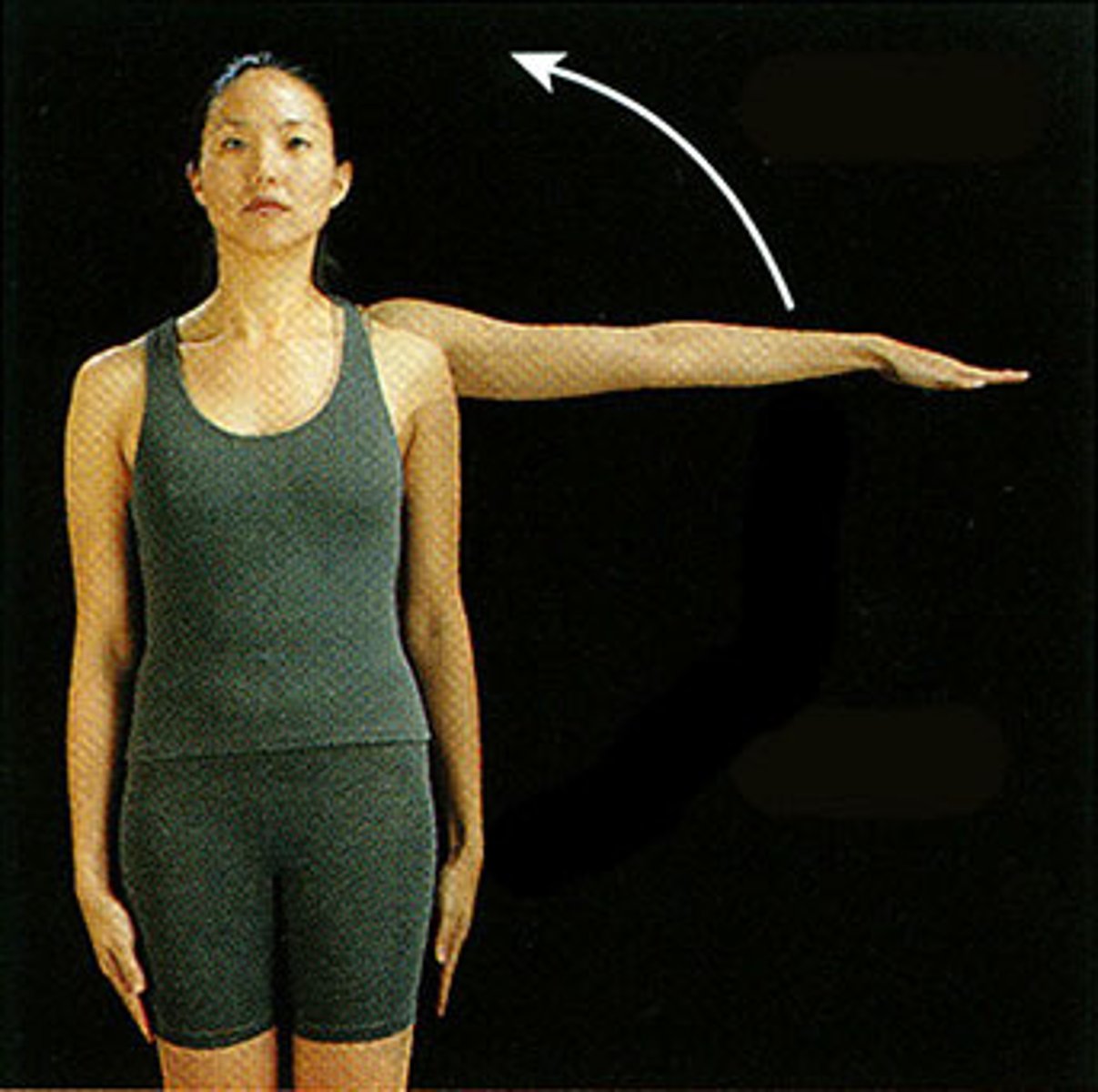
abduction
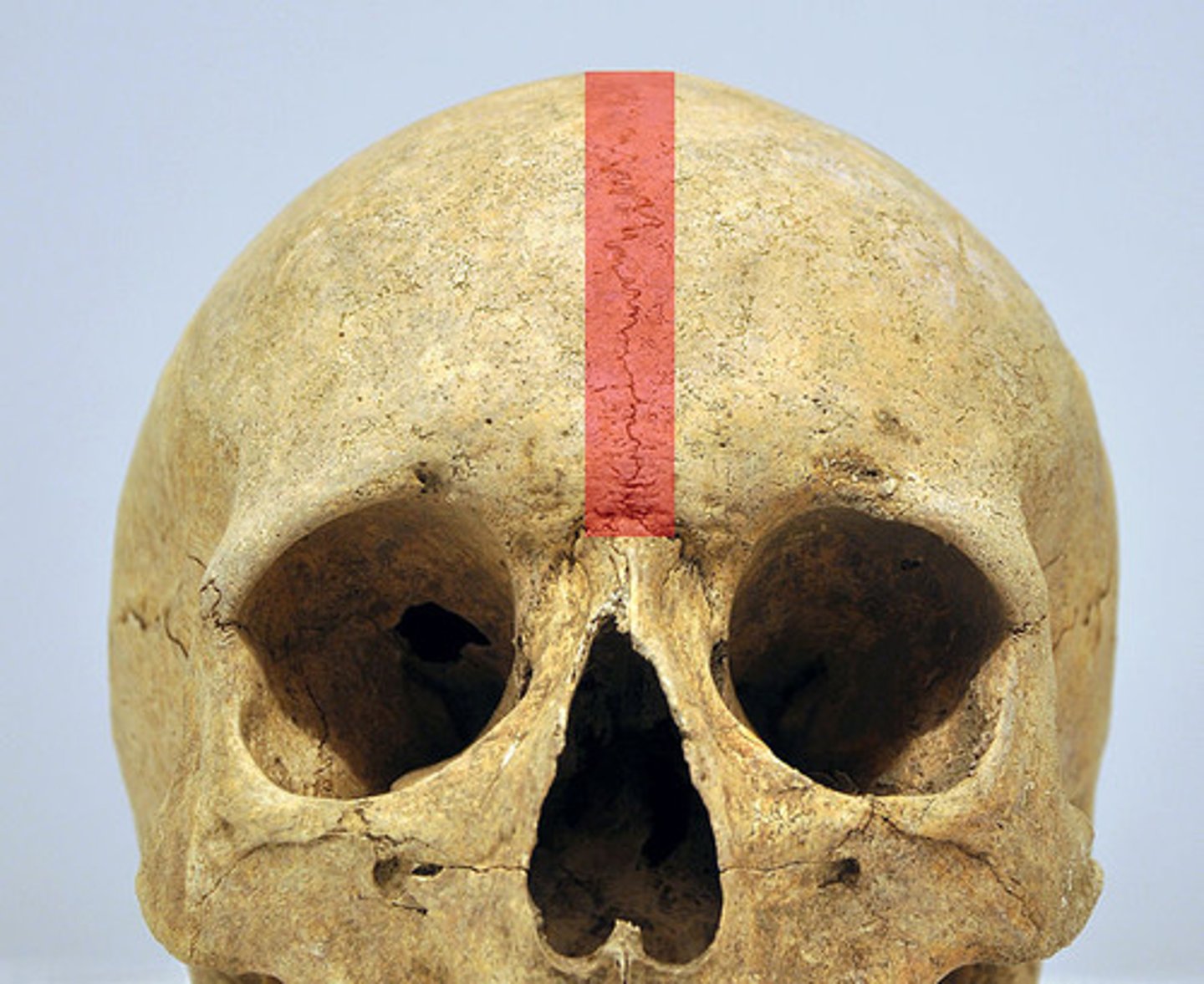
synarthrosis
Bones that join together and are held in place with threads of collagen, form a joint that is called a(n) ___________
amphiarthrosis
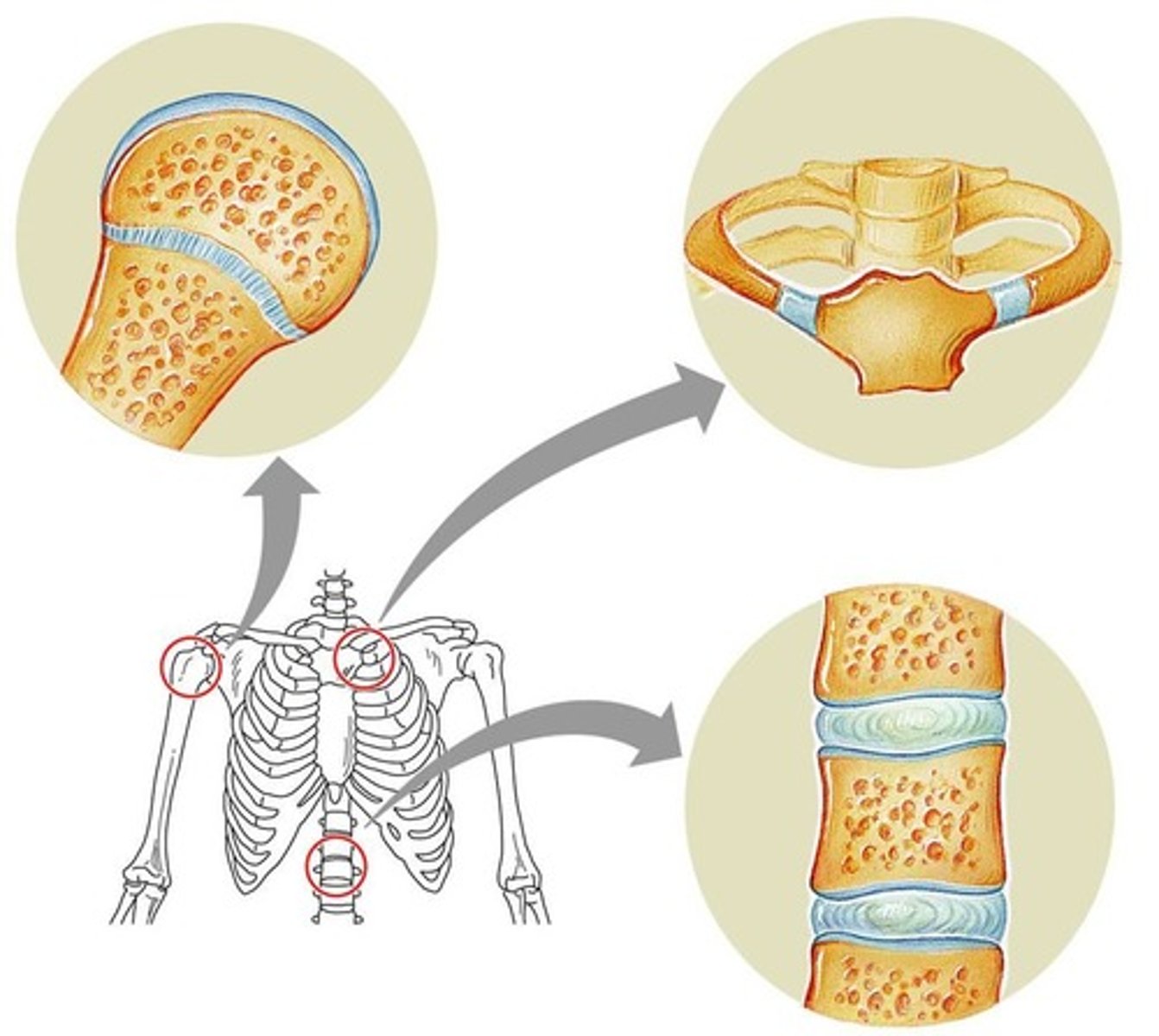
Bones joined together with cartilage between the ends of the bones, form a joint called a(n) _____________
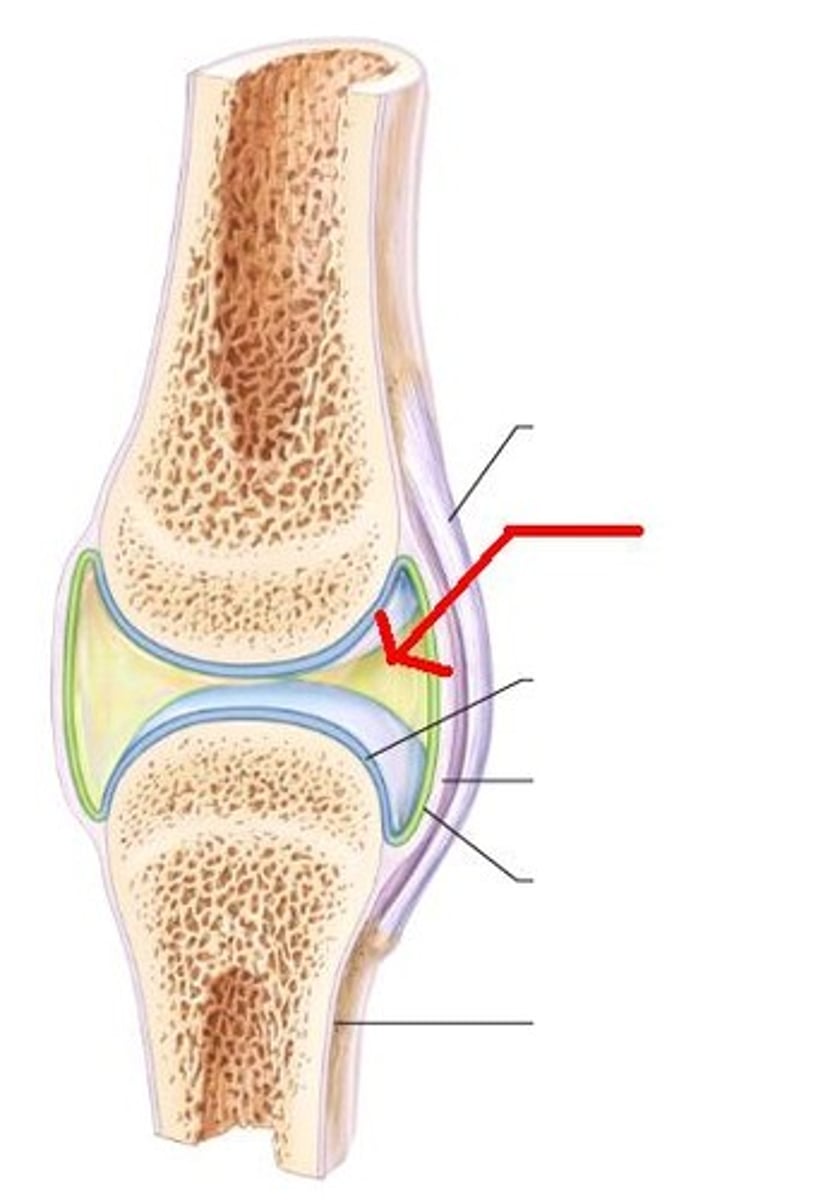
synovial
The most complex joints are called _____________ joints. They display varying amounts of mobility.
synostosis
When two bones join together and fuse so that no visible separation occurs, it is referred to as a(n) ___________or bony joint.
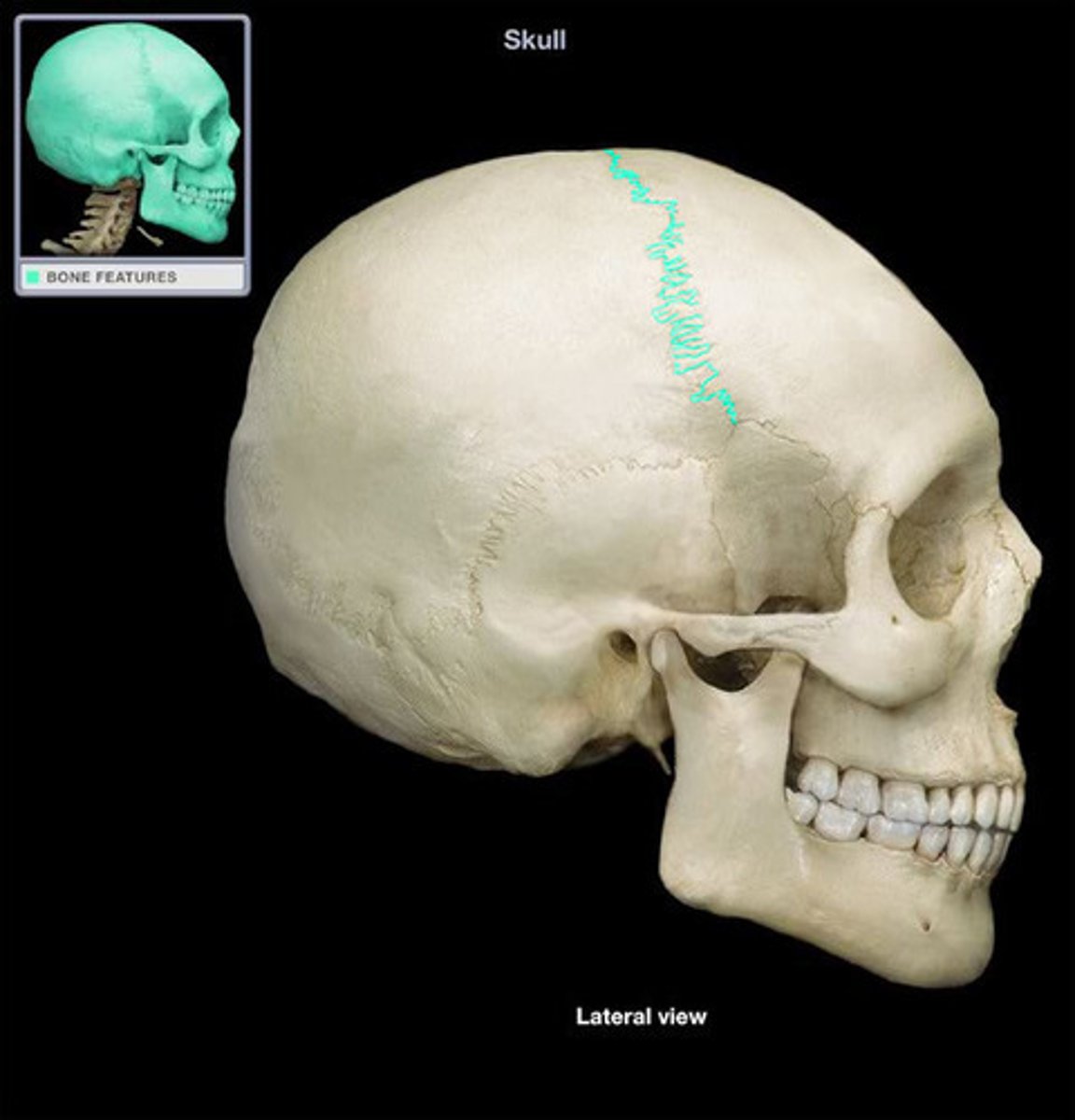
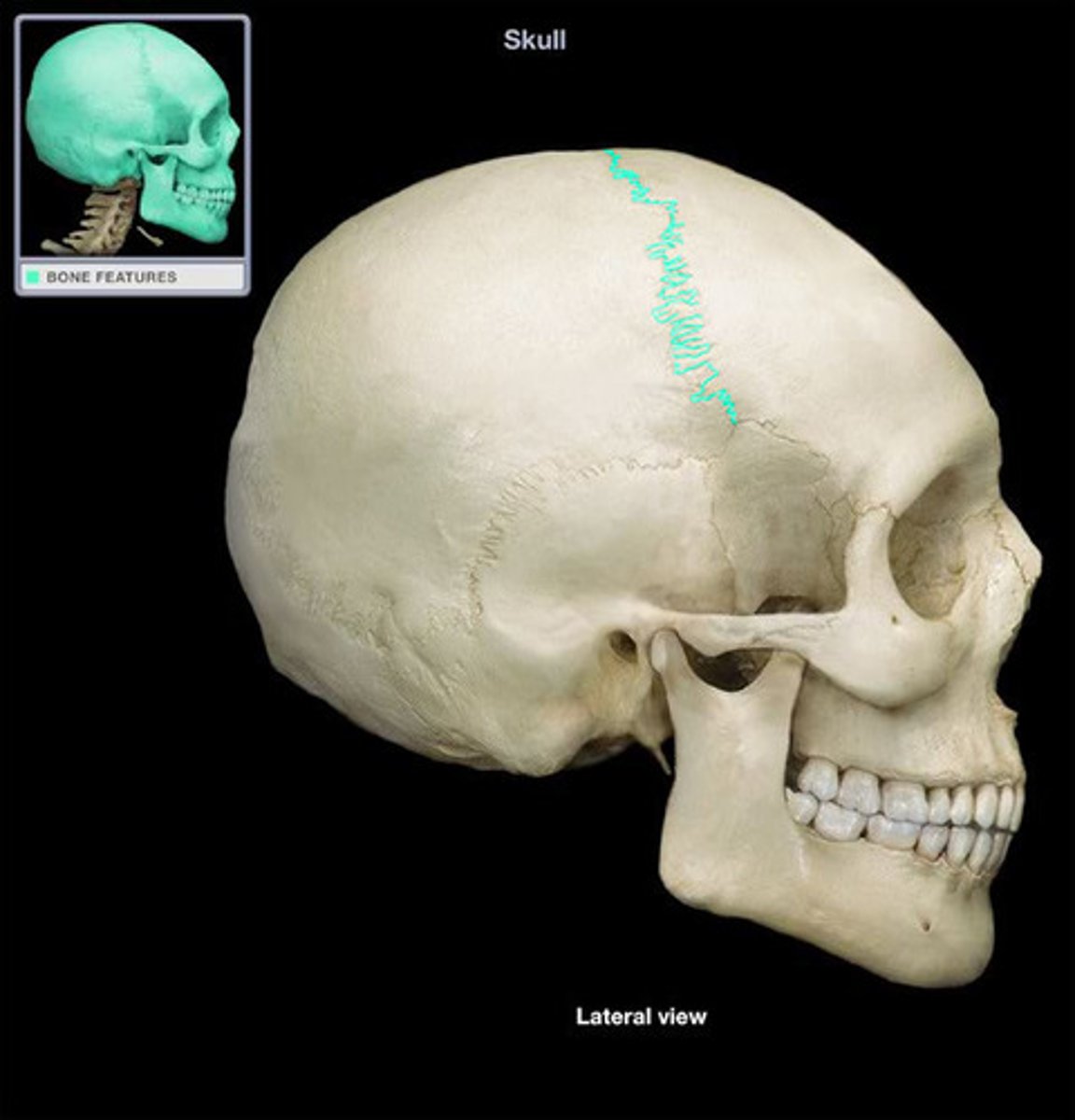
suture
A ____________ is a fibrous joint between two skull bones.
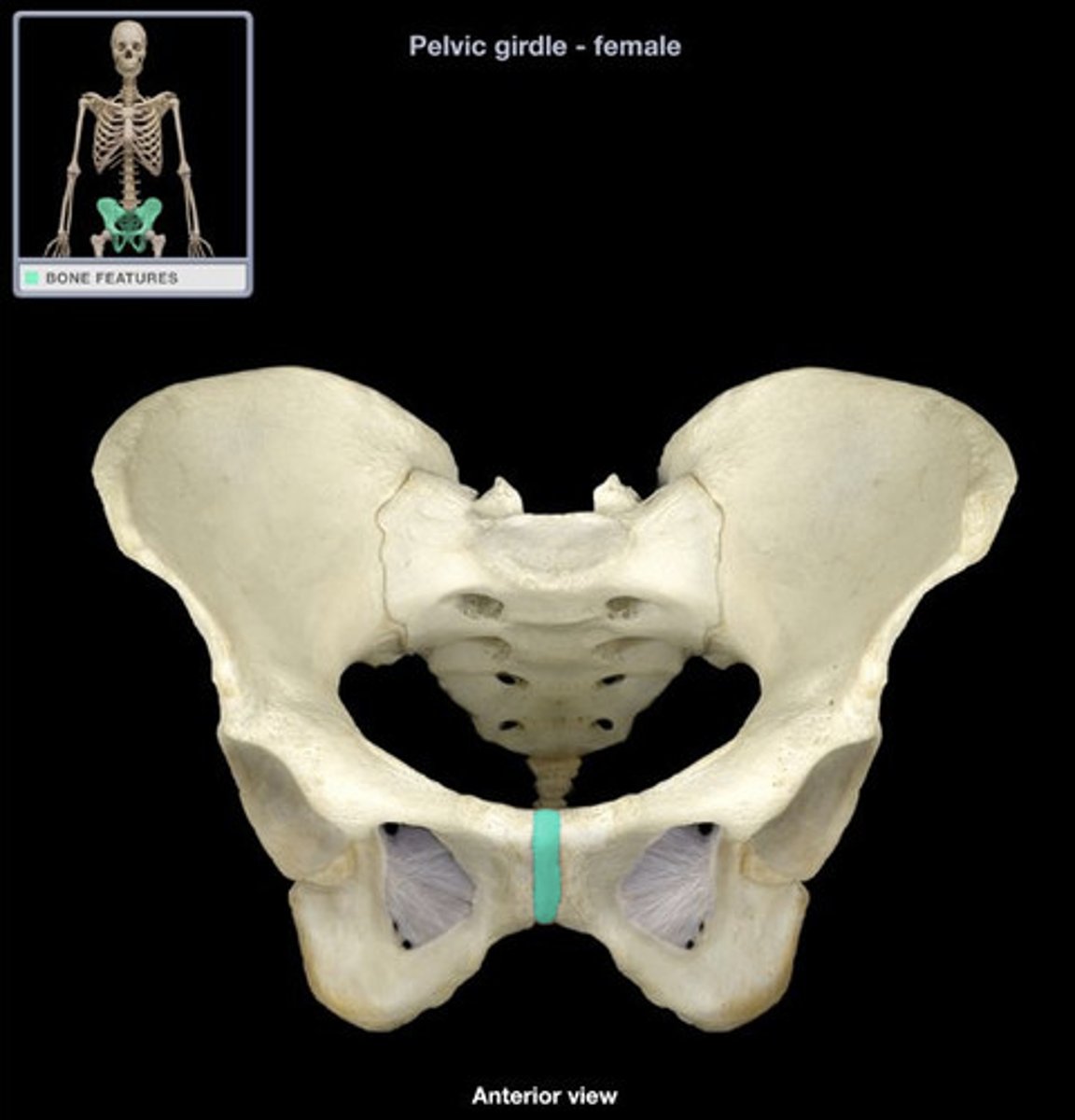
symphysis
The pubic _________________ is a cartilaginous joint in the anterior pelvis
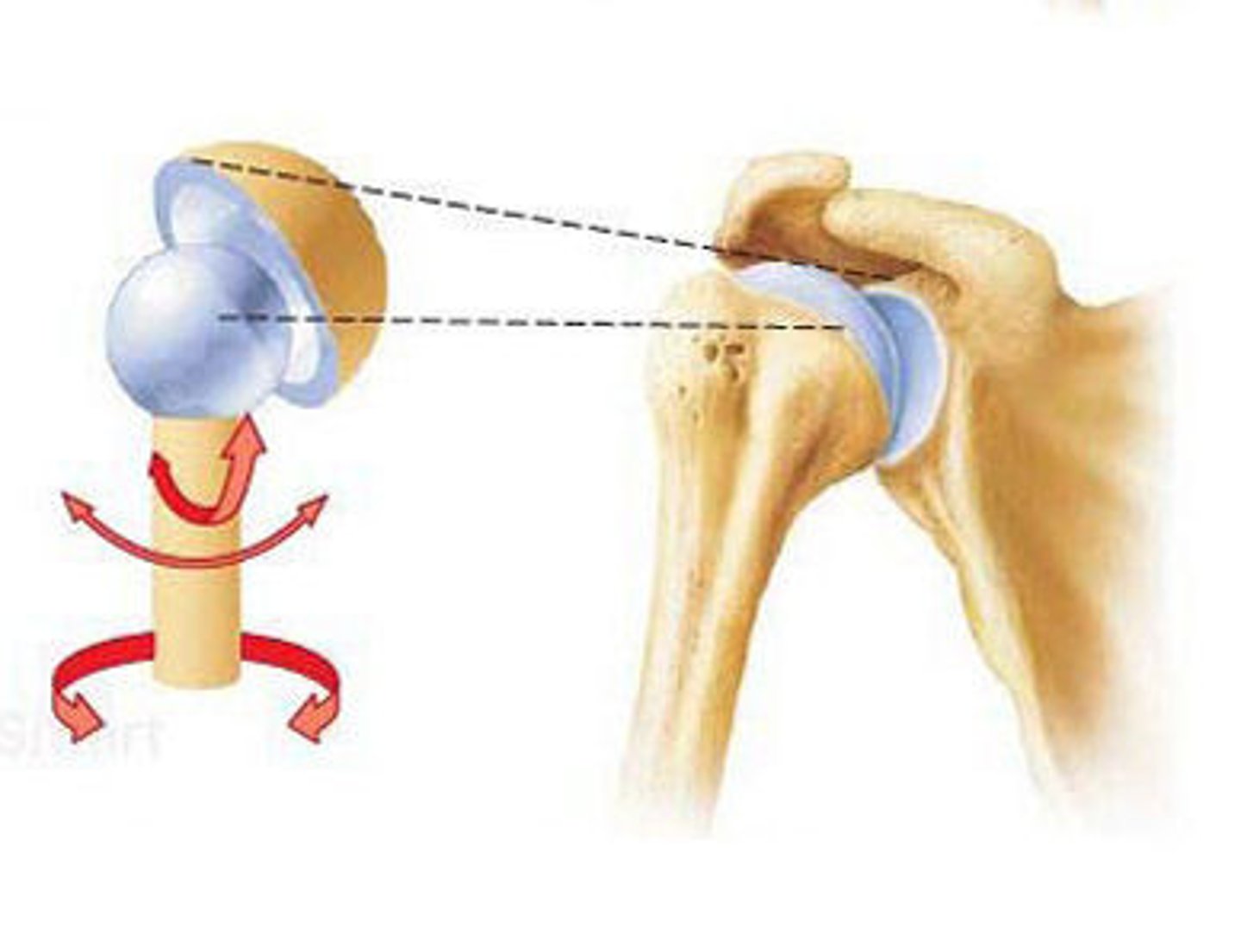
ball-and-socket
The synovial joint with the highest degree of movement is called a ________________ joint.
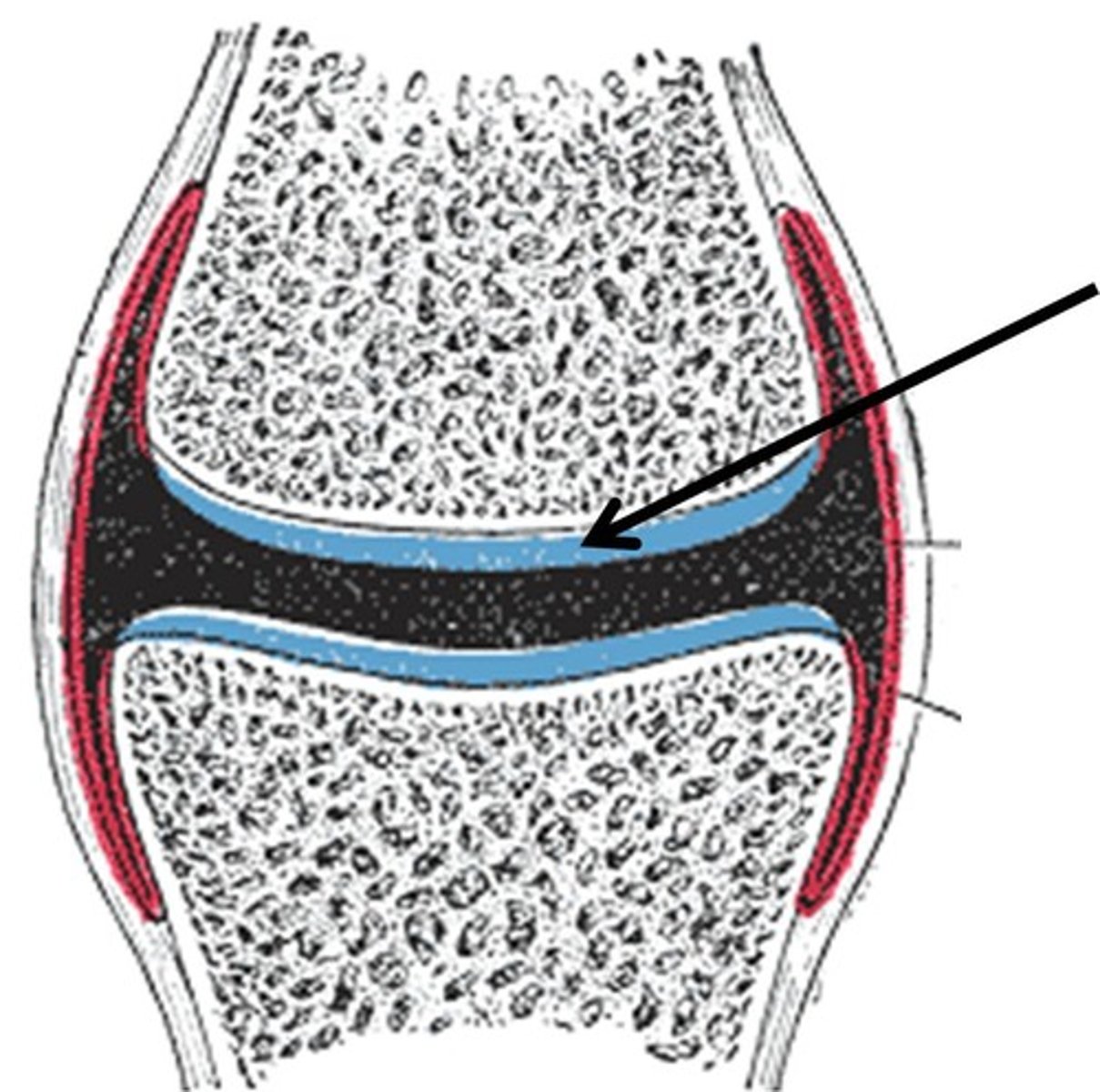
articular cartilage
The opposing surfaces of bones that are connected via synovial joints, are covered with a thin layer of _________________
synovial fluid
Between the articular surfaces, a thin cavity is filled with ______________, which acts to lubricate the joint surface and nourish the tissues of the internal joint surface
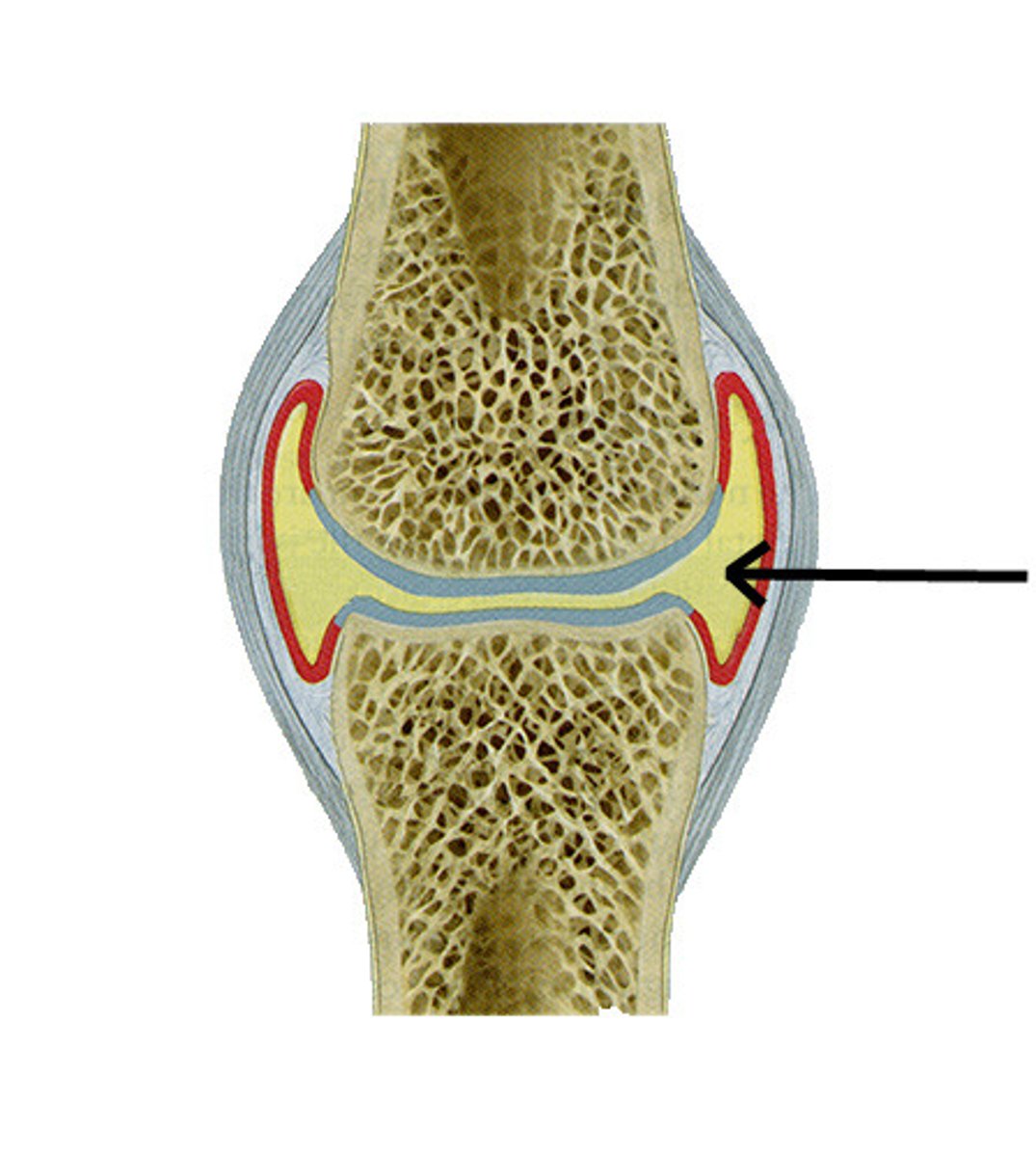
joint capsule
The _____________ maintains the boundary of the joint and contains the synovial fluid.
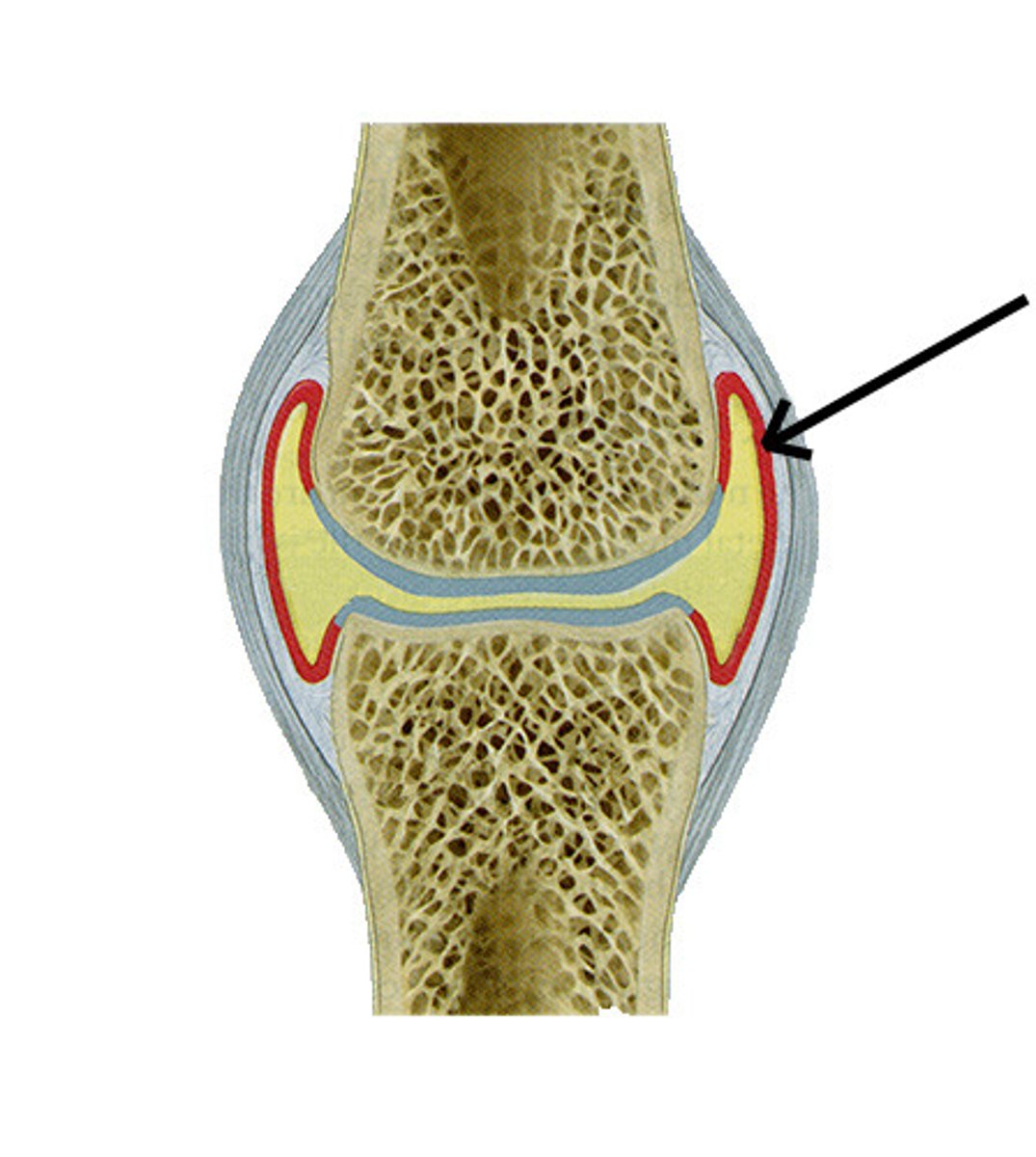
fibrous
The outermost layer of the joint capsule is the ____________ capsule, which is continuous with the periosteum, and provides support to the joint
synovial membrane
The deeper portion of the capsule is the _____________________, which contains cells that synthesize the synovial fluid.
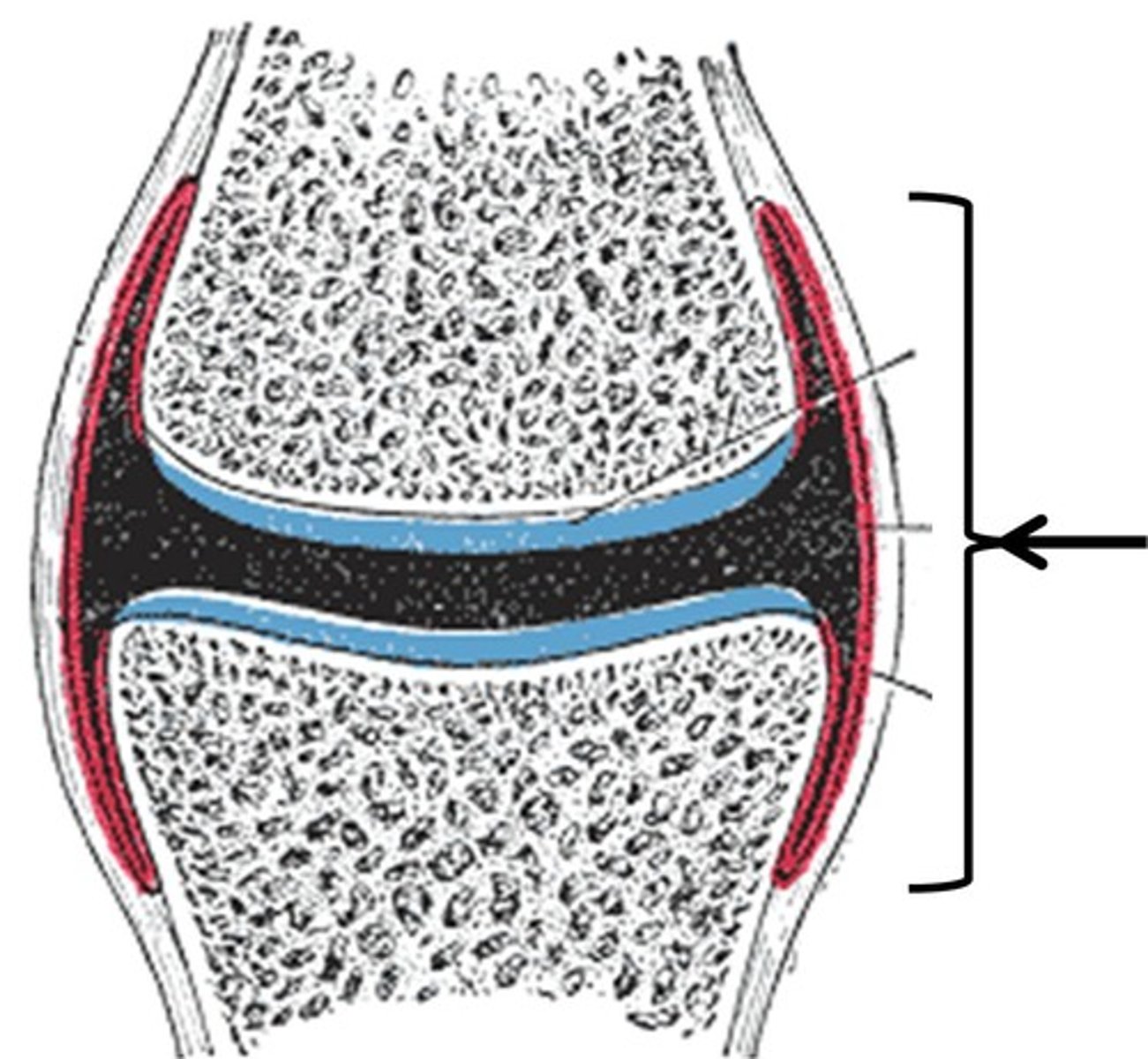
meniscus
An example of fibrocartilage that provides additional padding and stability to the joint, is the ___________ of the knee
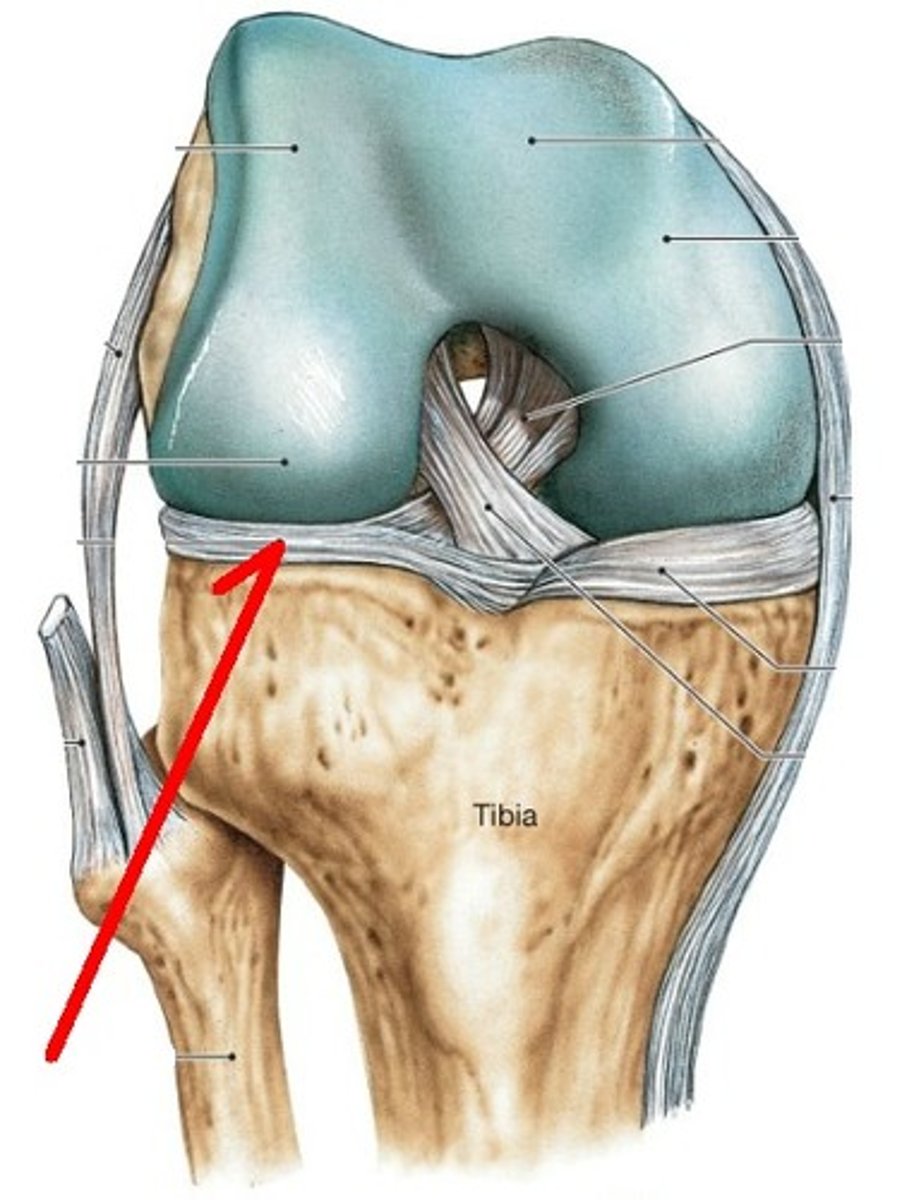
Diarthrosis
freely movable joints; also known as synovial joints
Muscle Tissue
Specialized tissue for contraction, enabling movement, posture maintenance, and heat production.
Excitability
The ability of muscle tissue to respond to stimuli, typically from motor neurons.
Contractility
The ability of muscle tissue to shorten forcefully when stimulated.
Extensibility
The ability of muscle tissue to stretch without being damaged.
Elasticity
The ability of muscle tissue to return to its original length after stretching or contracting.
Skeletal Muscle
Muscle attached to bones, responsible for voluntary movement, with multiple peripheral nuclei and striations.
Cardiac Muscle
Muscle found in the heart, responsible for pumping blood involuntarily, with one or two central nuclei and intercalated discs.
Smooth Muscle
Muscle located in the walls of hollow organs, responsible for involuntary movement, with a single central nucleus and no striations.
Fascicle
A bundle of muscle fibers surrounded by perimysium.
Muscle Fiber
The basic cellular unit of muscle, surrounded by endomysium and containing myofibrils.
Myofibril
Rod-like units inside muscle fibers that contain sarcomeres.
Sarcomere
The functional unit of contraction in muscle tissue, containing thick (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments.
Endomysium
Connective tissue surrounding each muscle fiber.
Perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding each fascicle.
Epimysium
Connective tissue that covers the entire muscle organ.
Tendon
Connective tissue that connects muscle to bone, transmitting force.
Sarcolemma
The plasma membrane of the muscle cell.
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum that stores calcium ions in muscle fibers.
Mitochondria
Organelles that provide energy for muscle contraction.
Thin Filaments
Composed of actin, part of the myofilament structure in muscle fibers.
Thick Filaments
Composed of myosin, part of the myofilament structure in muscle fibers.
Transverse Tubules
Invaginations of the sarcolemma that allow electrical impulses to reach deep into the muscle fiber.
Z Disc
The boundary of each sarcomere.
I Band
The region of the sarcomere that contains only thin filaments (actin).
A Band
The region of the sarcomere containing thick filaments (myosin) with some overlap of thin filaments.