Fields Unit 1 Vocab
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
im fucked
Last updated 6:50 AM on 9/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
1
New cards
Politics
The process of influencing the actions and policies of government
2
New cards
Government
The rules and institutions that make up the system of policy making
3
New cards
Equal Access Act of 1984
Legislation passed in 1984 to ensure students have equal access to extracurricular activities and clubs in public schools, regardless of their religious or political affiliations.
4
New cards
Board of Education of Westside Community Schools v. Mergens
**Issue:** Can public schools deny equal access to religious student groups?
**Holding:** No, public schools must allow religious clubs if they allow other non-curricular clubs.
**Significance:** Upheld the Equal Access Act, protecting students' First Amendment rights to freedom of religion and speech in public schools.
**Holding:** No, public schools must allow religious clubs if they allow other non-curricular clubs.
**Significance:** Upheld the Equal Access Act, protecting students' First Amendment rights to freedom of religion and speech in public schools.
5
New cards
Democracy
system of gov where power is held by the people
6
New cards
Natural Rights
The right to life, liberty, and the property, which the gov cannot take away
7
New cards
social contract
people allow their gov to rule over them to ensure an orderly and functioning society
8
New cards
Montesquie belief in government
* Advocated for the separation of powers
* Believed in a system of checks and balances
* Ideas influenced the creation of modern democratic governments
* Believed in a system of checks and balances
* Ideas influenced the creation of modern democratic governments
9
New cards
Hume belief in government
* Advocated for limited government intervention.
* Argued for the protection of individual rights and order without excessive control.
* Emphasized the importance of consent and voluntary cooperation in governance.
* Argued for the protection of individual rights and order without excessive control.
* Emphasized the importance of consent and voluntary cooperation in governance.
10
New cards
American political culture
set of beliefs, customs, traditions, values that Americans share
11
New cards
1st part of DOI “Preamble”
“When in the Course of human events, it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bands which have connected them with another . . .”
Set the stage for the argument that the British government was no longer legitimate.
Set the stage for the argument that the British government was no longer legitimate.
12
New cards
2nd part of the DOI
“Life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness
13
New cards
3rd part of the DOI
List of grievances against the King of England.
Mainly included charges against misrepresentation in gov.
Mainly included charges against misrepresentation in gov.
14
New cards
4th part of DOI
Denunciation of the British people (how US will be separate)
15
New cards
5th part of DOI
Pledge by the signers to each other to protect “our Lives, our Fortunes, and our Sacred Honor.”
16
New cards
Popular Sovereignty
The principle of political power resting with the people, who have the right to govern themselves through elected representatives and participate in decision-making.
17
New cards
republicanism
A system in which the government’s authority comes from the people.
18
New cards
inalienable rights
rights that gov cant take away (pursuit of happiness are among those inherent, self-evident rights)
19
New cards
The Pursuit of Happiness
The belief that individuals should be able to achieve their goals through hard work, sacrifice, and their own talents
20
New cards
Liberty
social, political, and economic freedoms
21
New cards
Participatory Democracy
Theory that widespread political participation is essential for democratic gov (EX: ACLU, NRA, AARP)
22
New cards
Civil Society Groups
An Independent association outside the gov control
23
New cards
Pluralist theory
Theory of democracy that emphasizes the role of groups in policy making process
24
New cards
Elitist Theory
Theory of democracy that elites (rich people) have a disproportionate amount of influence in the policy making process
25
New cards
Political institutions
structure of gov including Executive, Legislative, and Judiciary powers
26
New cards
Constitutional Republic
A democratic system with elected representatives in which the constitution is the supreme law
27
New cards
Constitution
document that sets out fundamental principles of gov and establishes the institutions of gov
28
New cards
Republic
a gov ruled by representatives of the people
29
New cards
Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union
A governing document that created a union of thirteen sovereign states in which the states, not the union, were supreme
30
New cards
Unicameral
A one-house legislature
31
New cards
Bicameral
A two-house legislature
32
New cards
Shays’s Rebellion
a popular uprising against gov of Massachusents
33
New cards
AoC Article I
Names the Union as “The United States of America.”
34
New cards
AoC Article II
Provides that states retain sovereignty not delegated to the national government.
35
New cards
AoC Article III
Creates a “league of friendship” for defense and security.
36
New cards
AoC Article IV
protects equal treatment and freedom of movement for citizens.
37
New cards
AoC Article V
Allocates one vote in Congress for each state.
38
New cards
AoC Article VI
Gives the national government the power to declare war.
39
New cards
AoC Article VII
Gives states the power to assign military ranks
40
New cards
AoC Article VIII
Expenditures by the United States will be paid with funds raised by state legislatures.
41
New cards
AoC Article IX
Gives Congress the power to declare war and peace, appoint tribunals for crimes on the seas, regulate the post office, appoint a president, and request requisitions from the states. Nine states are required to consent to declare war
42
New cards
AoC Article X
Allows a “committee of the states” to exercise the powers of Congress when Congress is not in session
43
New cards
AoC Article XI
Provides that Canada may join the Union.
44
New cards
AoC Article XII
Provides that the Confederation accepts the war debt.
45
New cards
AoC Article XIII
Provides that amendments require approval of all state legislatures.
46
New cards
US Constitution Article I
Creates a bicameral legislature, establishes requirements for serving in the House of Representatives and Senate, lists expressed powers of Congress, and allows for implied powers.
47
New cards
US Constitution Article II
Creates the presidency, establishes requirements for office, lists expressed powers of the executive.
48
New cards
US Constitution Article III
Creates a Supreme Court and provides that Congress may establish lower federal courts.
49
New cards
US Constitution Article IV
Sets forth the relationships between states.
50
New cards
US Constitution Article V
Establishes the process for amending the Constitution.
51
New cards
US Constitution Article VI
Establishes that the Constitution, federal laws, and treaties are the supreme law of the land.
52
New cards
US Constitution Article VII
Describes how the Constitution will be ratified.
53
New cards
US Constitution Article Preamble
Sovereignty comes from the people, and the Constitution will create a “more perfect Union.”
54
New cards
Virginia Plan: Structure of Legislature
Bicameral
55
New cards
Virgina Plan: Apportionment
**Lower House:**
* Number of seats apportioned by state population.
* Members directly elected by citizens.
\
**Upper House:**
* Number of seats apportioned by state population.
* Members elected by lower house (from list supplied by state legislatures).
* Number of seats apportioned by state population.
* Members directly elected by citizens.
\
**Upper House:**
* Number of seats apportioned by state population.
* Members elected by lower house (from list supplied by state legislatures).
56
New cards
Virgina Plan: Powers
Legislature has strong powers, including the ability to veto state laws.
57
New cards
NJ Plan: Structure of Legislature
Unicameral
58
New cards
NJ Plan: Apportionment
**Legislature:**
* Equal representation for states regardless of state population. Members appointed by the states.
* Equal representation for states regardless of state population. Members appointed by the states.
59
New cards
NJ Plan: Powers
Legislature has similar power as under the Articles of Confederation but can also levy taxes and regulate commerce.
60
New cards
Great Compromise: Structure of Legislature
Bicameral
61
New cards
Great Compromise: Apportionment
**House of Reps:**
* States represented according to population.
* Members directly elected by citizens.
\
**Senate:**
* States represented equally (two senators per state).
* Members appointed by state legislatures.
* States represented according to population.
* Members directly elected by citizens.
\
**Senate:**
* States represented equally (two senators per state).
* Members appointed by state legislatures.
62
New cards
Great Compromise: Powers
* Legislature has broad powers over commerce and the ability to make laws as necessary.
* House of Representatives has the “power of the purse” to levy taxes.
* House of Representatives has the “power of the purse” to levy taxes.
63
New cards
Virginia Plan: Summarized
A plan of government calling for a three-branch government with a bicameral legislature, where more populous states would have more representation in Congress
64
New cards
NJ Plan: Summarized
A plan of government calling for a three-branch government with a bicameral legislature, where more populous states would have more representation in Congress
65
New cards
Constitutional Convention
a meeting attended by state delegates in 1787 to fix the Articles of Confederation
66
New cards
Writ of habeas corpus
the right of people detained by the government to know the charges against them
67
New cards
bill of attainder
when the legislature declares someone guilty without trial
68
New cards
ex post facto laws
laws punishing people for acts that were not crimes at the time they were committed
69
New cards
Grand Committee
a committee at the constitutional convention that worked out the compromise on representation.
70
New cards
Great (Connecticut) Compromise
An agreement for plan of go that drew upon both the Virginia and NJ plans; settled issue of state rep by calling for a bicameral legislature with HOR apportioned proportionately and Senate apportioned equally.
71
New cards
3/5 compromise
Agreement reached by delegates at the Constitutional Convention that a slave would count as 3/5 of a person in calculating a state’s rep
72
New cards
Compromise on Imporation
Congress could not restrict the slave trade till 1808
73
New cards
Executive Branch (Lawmaking power)
* Executes laws.
* Works to shape legislative agenda.
* Has power to veto legislation.
* Nominates judges to the federal judiciary.
* Nominates key executive branch officials.
* Gives State of the Union Address.
* Works to shape legislative agenda.
* Has power to veto legislation.
* Nominates judges to the federal judiciary.
* Nominates key executive branch officials.
* Gives State of the Union Address.
74
New cards
Legislative Branch (Lawmaking power)
* Writes nation’s laws.
* Can override a presidential veto.
* Determines number of Supreme Court justices.
* Creates lower courts.
* Can override a presidential veto.
* Determines number of Supreme Court justices.
* Creates lower courts.
75
New cards
Judicial Branch (Lawmaking power)
* Interprets contested laws.
* Can declare both federal and state laws unconstitutional.
* Can declare both federal and state laws unconstitutional.
76
New cards
Executive (National Security and Foreign Policy Responsibilities)
* President acts as commander in chief of the military.
* Sets foreign policy agenda.
* Negotiates treaties.
* Sets foreign policy agenda.
* Negotiates treaties.
77
New cards
Legislative (National Security and Foreign Policy Responsibilities)
* Declares war.
* Senate ratifies treaties.
* Senate ratifies treaties.
78
New cards
Executive (Oversight Responsibilities)
**Oversees federal bureaucracy.**
79
New cards
Legislative (Oversight Responsibilities)
* House issues articles of impeachment; Senate holds impeachment trials (over president, executive branch officials, and federal judges).
* Budget authority and oversight over executive branch agencies. Senate confirms judicial nominees.
* Senate confirms key executive branch officials.
* Budget authority and oversight over executive branch agencies. Senate confirms judicial nominees.
* Senate confirms key executive branch officials.
80
New cards
Judicial (Oversight Responsibilities)
May declare executive branch actions in conflict with the Constitution
81
New cards
Seperation of powers
a design of gov that distributes powers across institutions in order to acoid making one branch too powerful on its own
82
New cards
checks & balances
a design of gov in which each branch has powers that can prevent other branches from making policy
83
New cards
federalism
divides power between the national and state governments
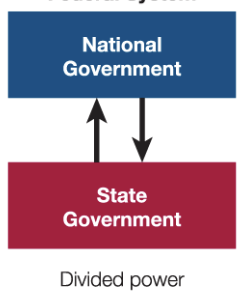
84
New cards
expressed or enumerated powers
authority specifically granted to a branch of the government Constitution
85
New cards
necessary and proper or elastic clause
language in Article I, Section 8 granting Congress the powers necessary to carry out its enumerated powers.
86
New cards
supremacy clause
constitutional provision declaring that the constitution and all federal laws and treaties are the supreme law of the land
87
New cards
amendment
the process by which changes may be made to the constitution
88
New cards
Federalist
* Supporters of the Constitution
* Advocated for Strong National Government
* Included wealthy merchants and southern plant owners
* Advocated for Strong National Government
* Included wealthy merchants and southern plant owners
89
New cards
Antifederalists
* Opposers of the Constitution
* Advocated for Strong State Government
* Included rural areas, more farmers and shopkeepers
* Advocated for Strong State Government
* Included rural areas, more farmers and shopkeepers
90
New cards
Federalist Papers
A series of 85 essays written by Hamilton, Madison, and Jay that lay out the theory behind the constitution
91
New cards
Faction
group of self-interested people who use gov to get what they want → tramples over other’s rights
92
New cards
Fed 10
Essay in which Madison argues that dangers of factions can be mitigated by a large republic and republican gov
93
New cards
Fed 51
Essay in which Madison argues that separation of powers and federalism will prevent tyranny
94
New cards
Brutus 1
Antifed paper arguing that the country was too large to be governed as a republic and that constitution gave too much power to national government
95
New cards
Step 1: Amendment Proposed by
2/3 Votes in both house and congress OR Constitutional congress called by 2/3 States
96
New cards
Step 2: Amendment Ratified By
3/4 of 50 States legislatures OR 3/4 of State constitutional conventions
97
New cards
Unitary System
a system where the central government has all of the power over subnational governments.
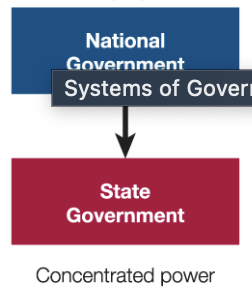
98
New cards
Confederation
system where the subnational governments have most of the power.
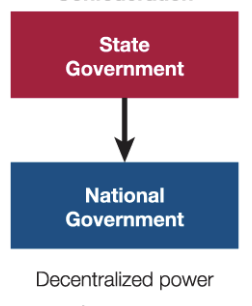
99
New cards
Enumerated or expressed powers
powers explicitly **granted to the national governmen**t through the constitution (AKA Expressed Powers)
\
Includes:
* Coin money
* Declare war
* Raise and support armed forces
* Make treaties
* Provide for the naturalization of citizens
* Regulate interstate and foreign trade and trade with indian tribes
\
Includes:
* Coin money
* Declare war
* Raise and support armed forces
* Make treaties
* Provide for the naturalization of citizens
* Regulate interstate and foreign trade and trade with indian tribes
100
New cards
exclusive powers
powers only the national government may exercise