N245: Disorders of the Bladder and Lower Urinary Tract
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Micturition
Urination

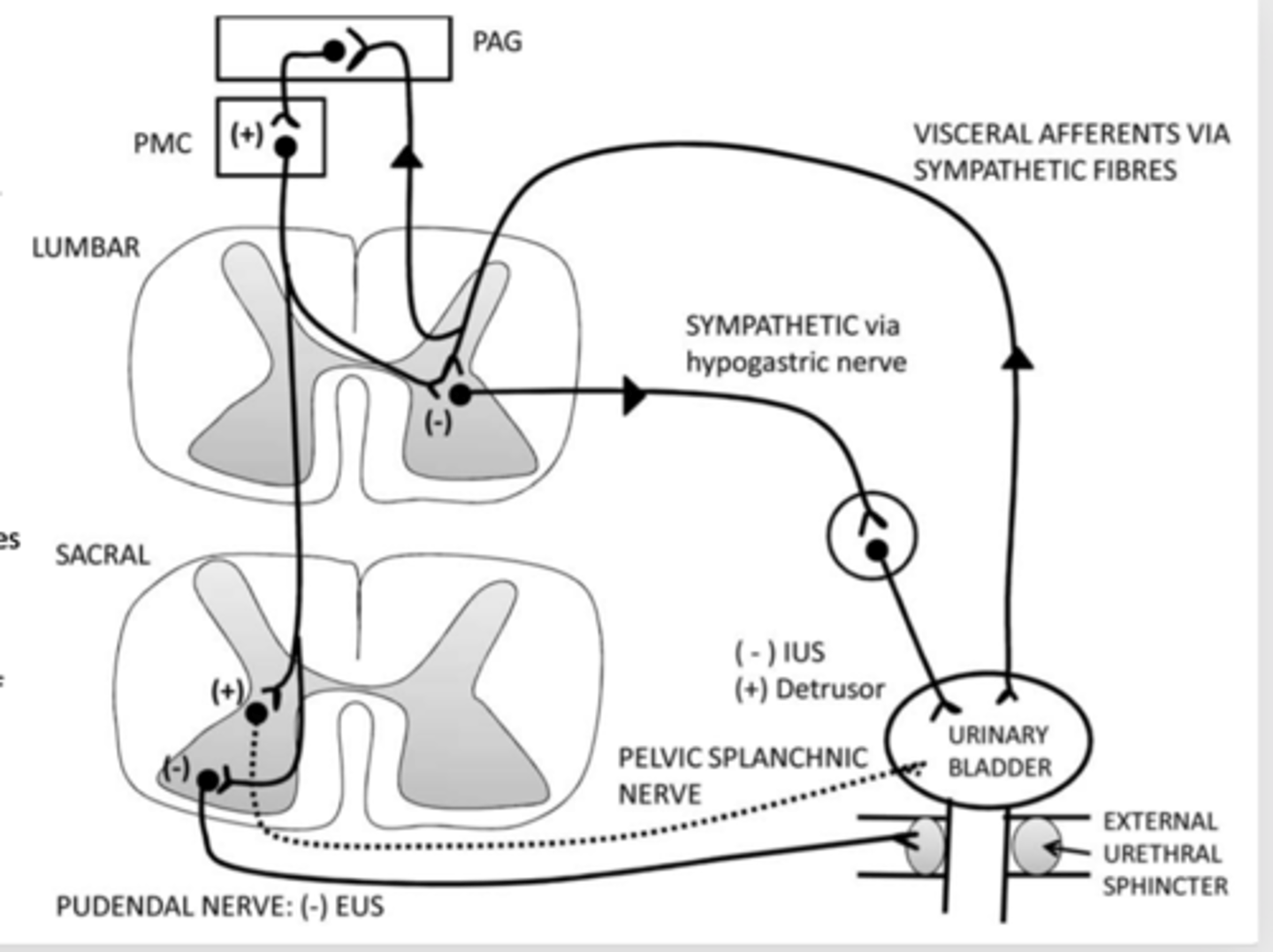
What causes micturition?
Stretch receptors in the bladder send signals to the spinal cord --> send signals to the brain
How do we control micturition?
Control over micturition involves the prefrontal cortex and the motor cortex
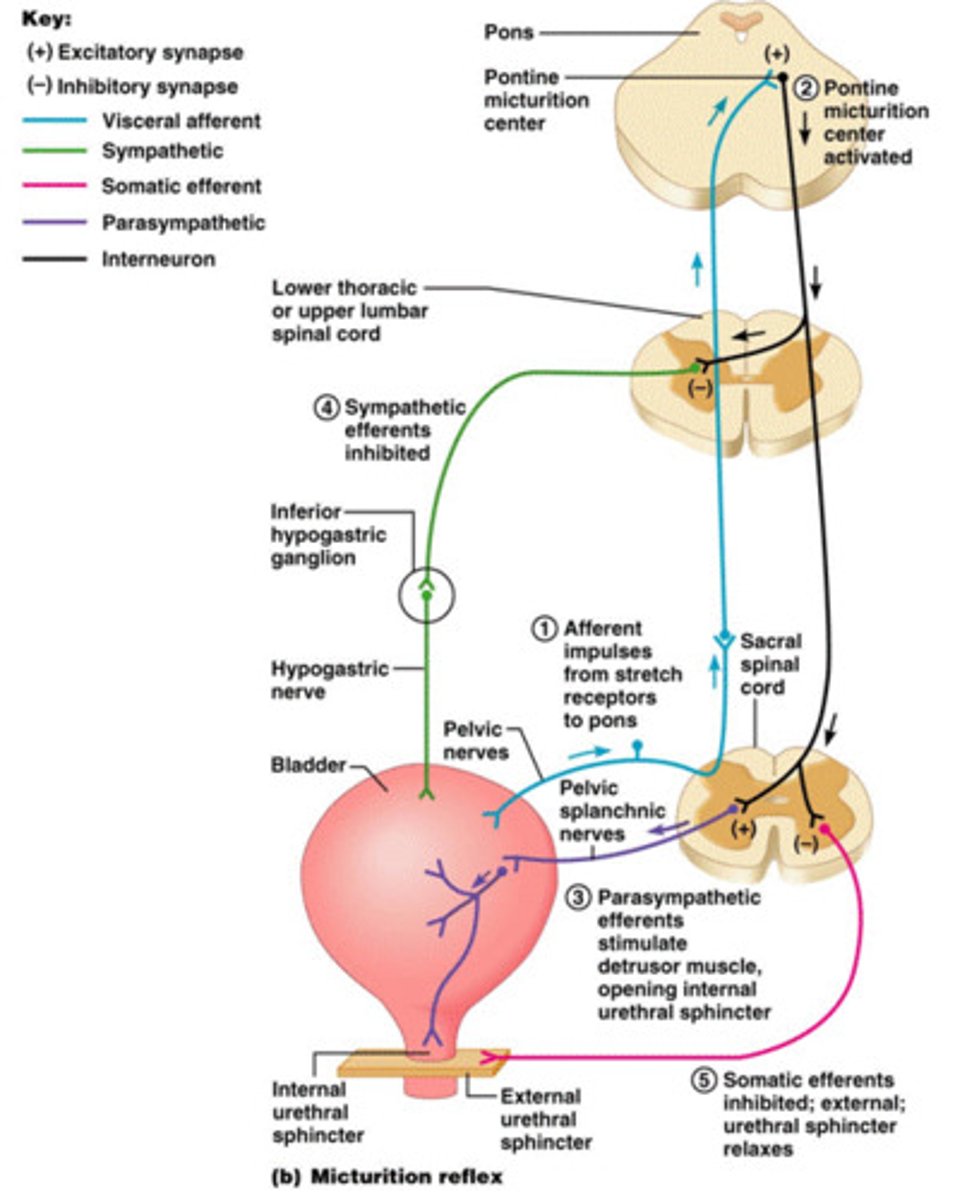
What does potty training do?
Potty training teaches children to sense and control their urinary bladder
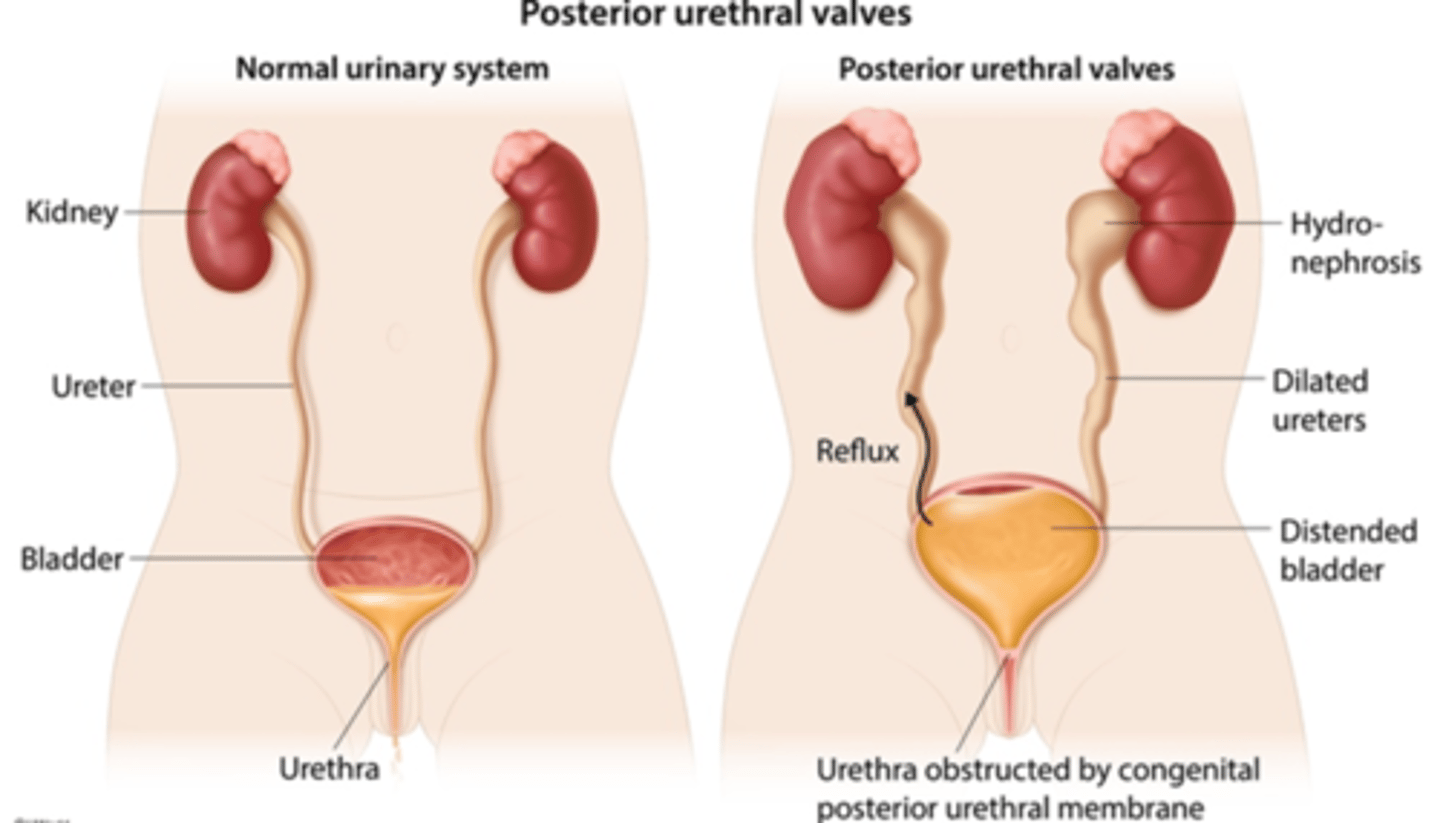
Causes of urinary obstruction
STDs, constipation, bladder tumors
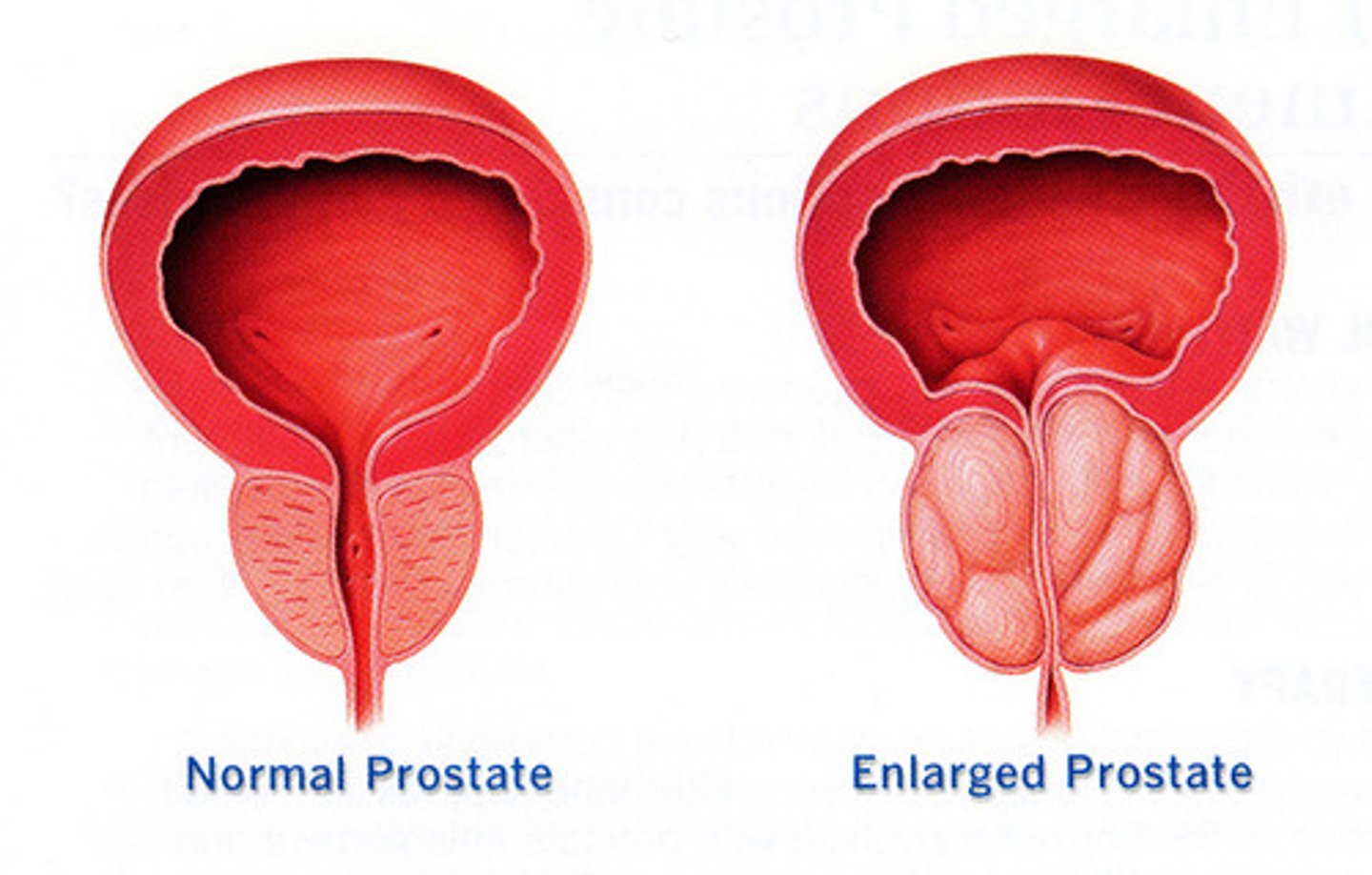
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
A benign growth of cells within the prostate gland, develops in 90% of men over 80 yrs old
Early stages of urinary obstruction
Bladder compensates for obstruction --> muscle hypertrophy, frequent and urgent urination
Later stages of urinary obstruction
Detrusor muscle cannot contract --> urine retention --> increased frequency of urination
Trabeculae
Hypertrophied smooth muscle in the bladder --> develops due to obstruction
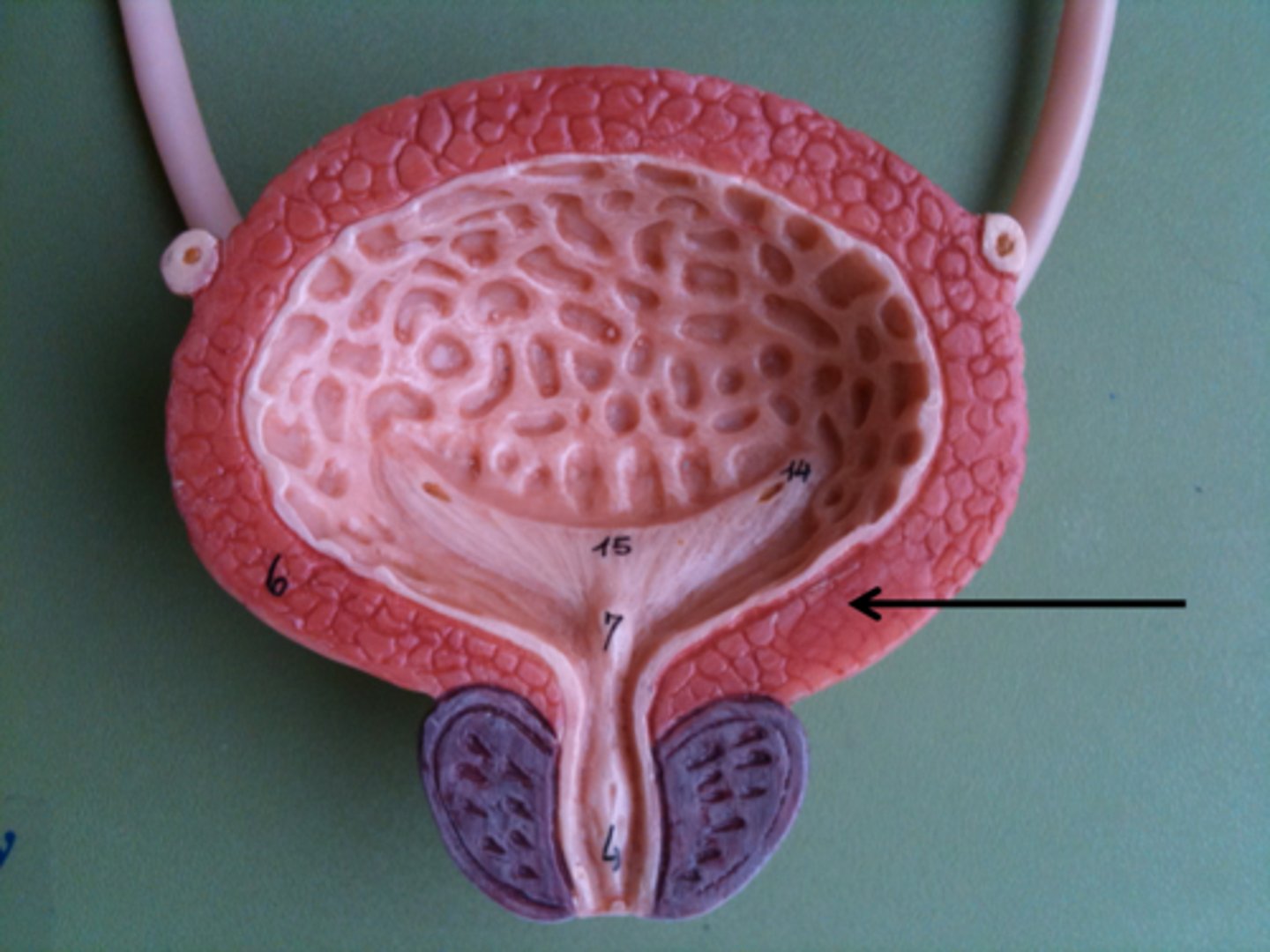
Cellules
Small pockets of mucosal tissue
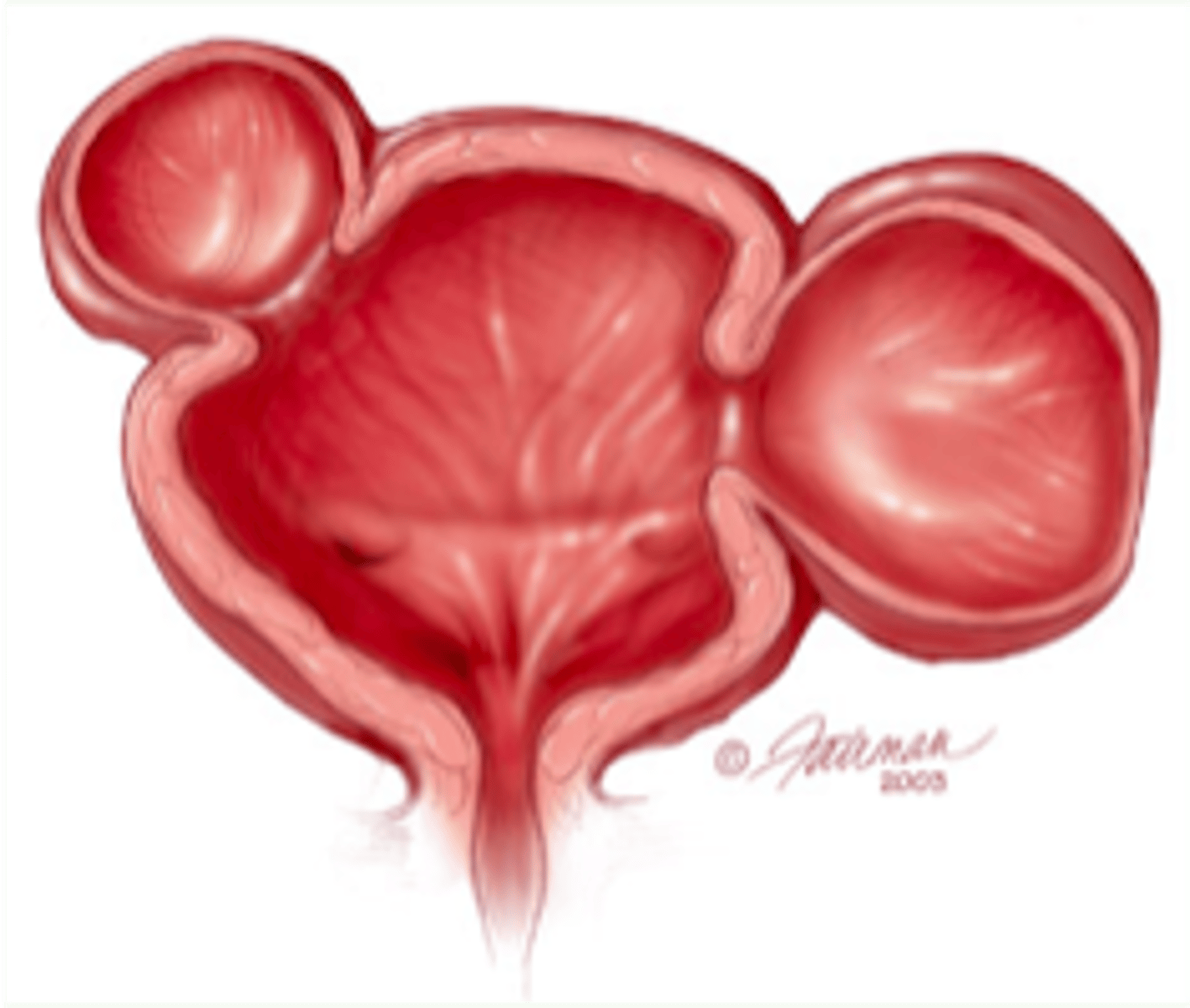
Diverticula
Abnormal pockets/protrusions in the urinary bladder wall --> develops due to obstruction
Incontinence
Inability to control urination

Enuresis
Involuntary urination by child age older than 4 years
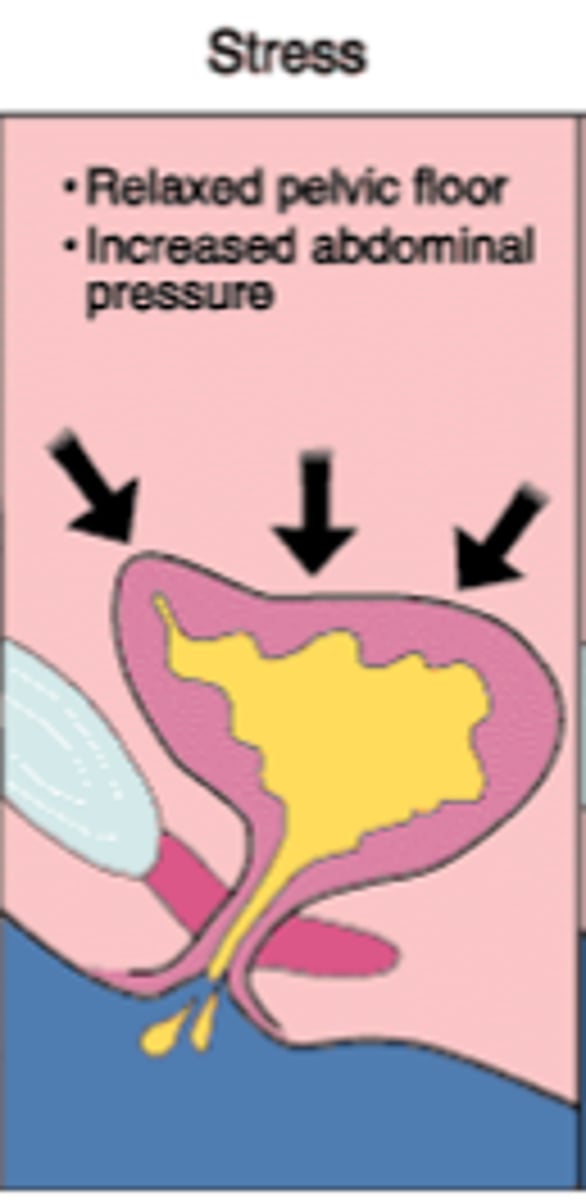
Stress incontinence
Relaxed pelvic floor muscle + increased abdominal pressure --> involuntary urination when coughing laughing, sneezing, running --> puts pressure (stress) on the bladder --> urination
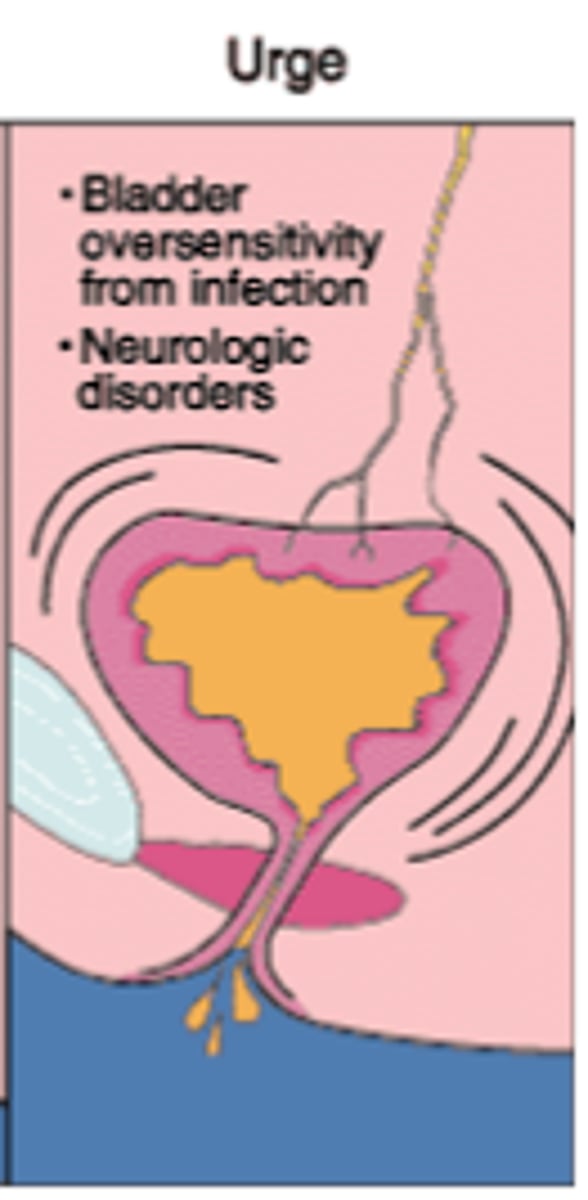
Urge incontinence
Bladder hypersensitivity --> sudden urge to urinate --> involuntary urination
Overflow incontinence
Full bladder --> small leaks because the bladder simply cannot hold anymore
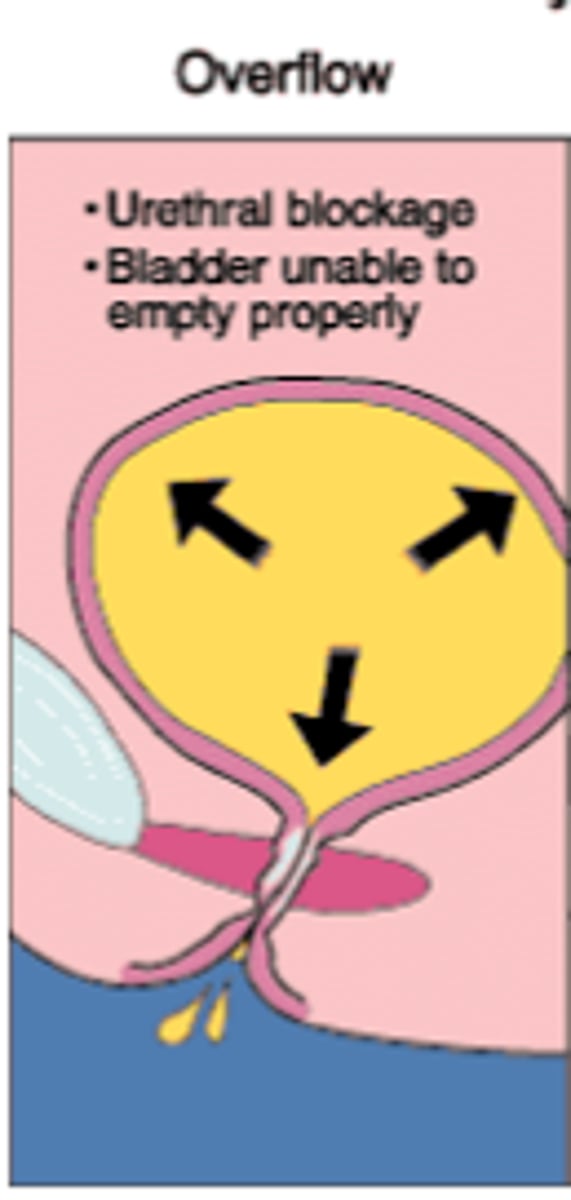
Retention
The inability to empty the bladder
What are some causes of retention?
Spinal injury/anesthesia --> prevents micturition reflex from firing
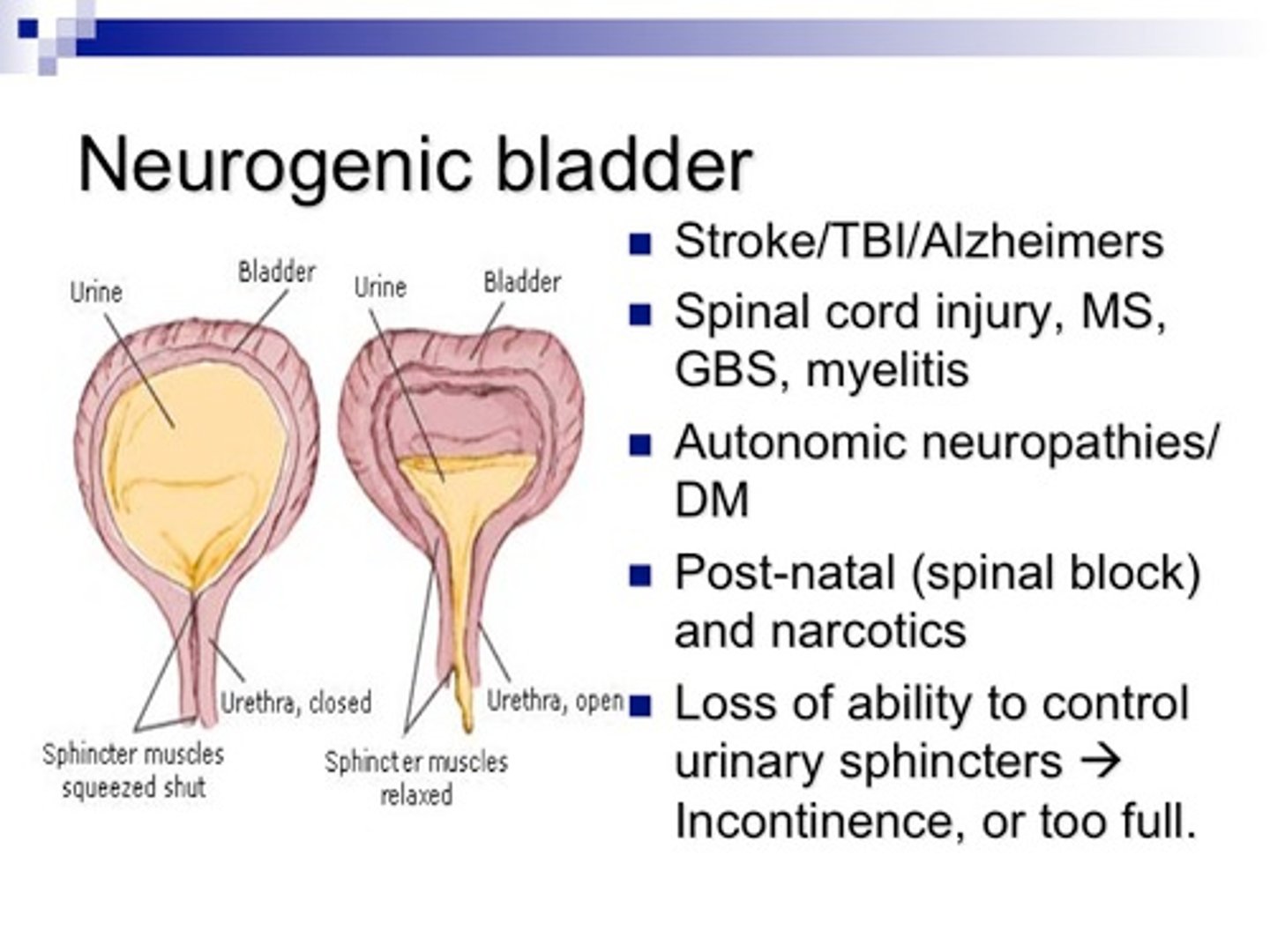
Neurogenic bladder disorders
Disorders that interfere with the neural control over the ability to keep urine in the bladder (spastic) or pee urine out (flaccid)
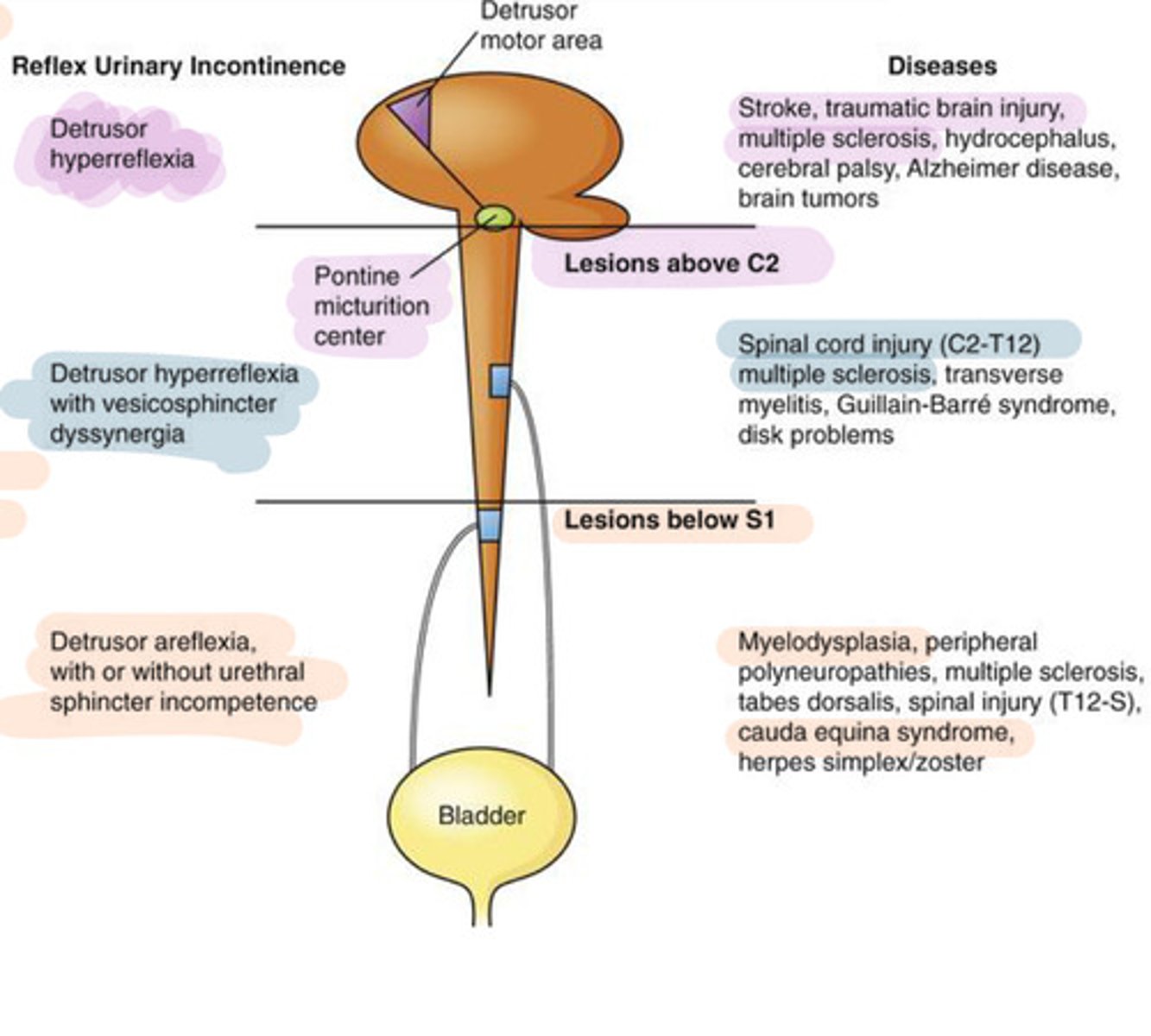
Causes of neurogenic bladder disorders
Stroke, Parkinson, MS, spinal cord injuries
Spinal shock
Spinal cord injury --> lack of neural transmission/stimulation --> bladder cannot contract --> catheter is needed to prevent retention
Spastic bladder
What: The inability of the bladder to store urine (brain cannot halt urination anymore)
Cause: Spinal injury above T12
S+S: Involuntary urination
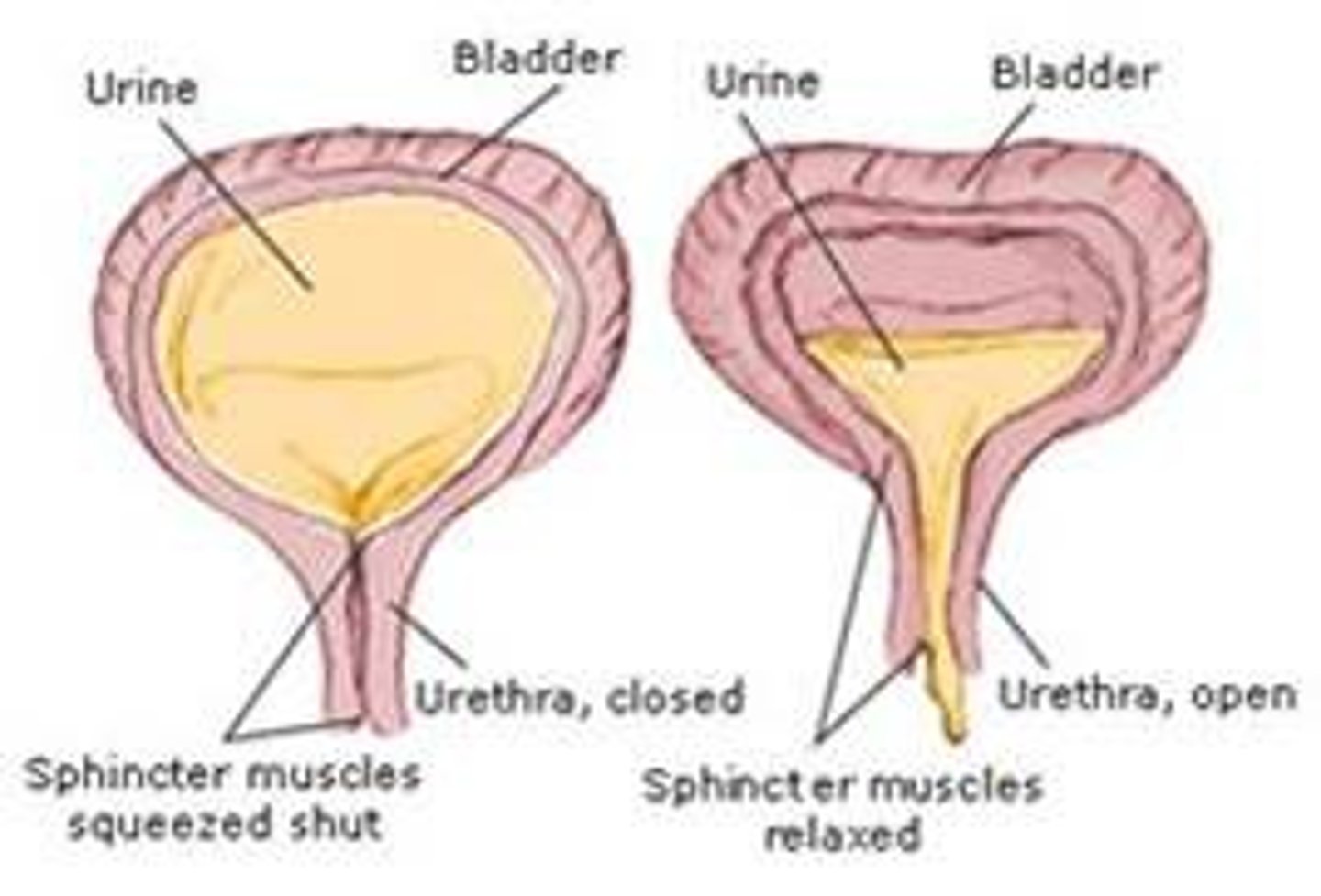
Flaccid bladder
What: The inability of the bladder to empty urine
Causes: Spinal injury below T12
S+S: Urine retention
Treatment for neurogenic bladder disorders
1. Prevent overdistention
2. Prevent UTIs
3. Prevent renal damage
4. Prevent harmful social stigma
Non-urologic conditions that lead to urinary bladder problems
"DIAPPERS"
D - Dementia
I - Infection
A - Atrophic vaginitis
P - Pharmaceuticals
P - Psychological
E - Endocrine (diabetes)
R - Restricted mobility
S - Stool impaction
Treatment for incontinence
Catheters, medicines, surgery, KEGELS

Characteristics of bladder cancers
Multiple tumors, often malignant --> metastasizes to pelvic lymph nodes, liver, and bone
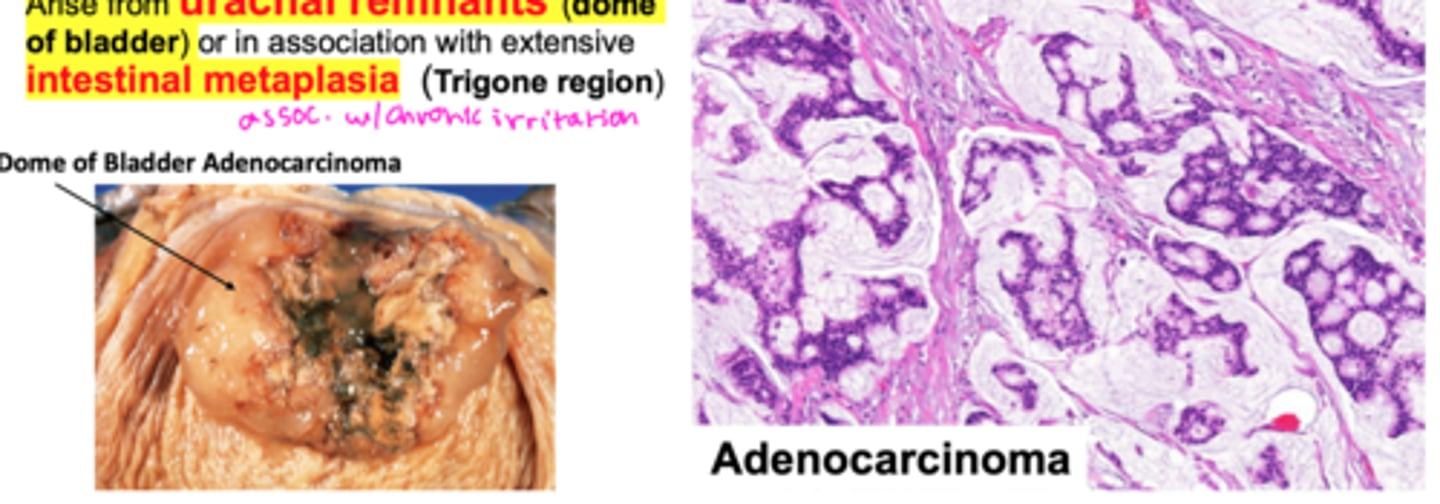
Early S+S of bladder cancers
Hematuria, dysuria, UTIs
Causes of bladder cancers
Exposure to chemicals, smoking, UTIs

Treatment of bladder cancers
Surgery, chemo, radiation, photoradiation