Skull Lab anatomical concepts and development
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Foramen
Round opening/hole/passage in bone
Fissure
nature division/narrow passage (slit-like) through bone
Fossa
bony depression or hollow space formed by various structures (including bone)
Meatus
tube-like channel extending within bone
Sulcus
crevice or groove in bone (typically due to adjacent blood vessels, nerves, etc.)
Sinus
air-filled bony cavity (lined with mucous membrane)
Crest/Line/Ridge
raised and/or prominent bony processes
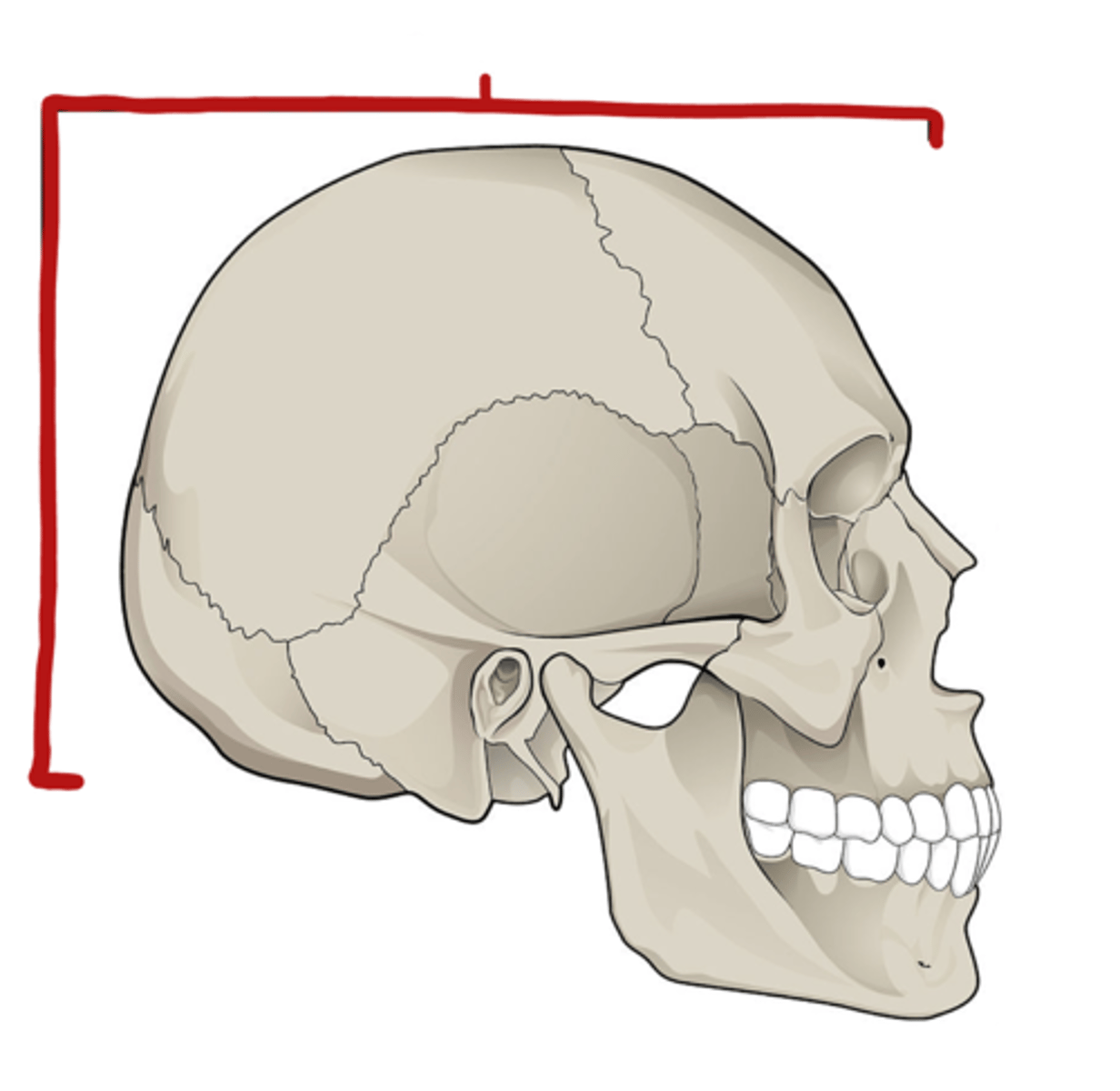
Name of skill division marked
Neurocranium (braincase, cranial vault)
Function of Neurocranium
Protection of brain
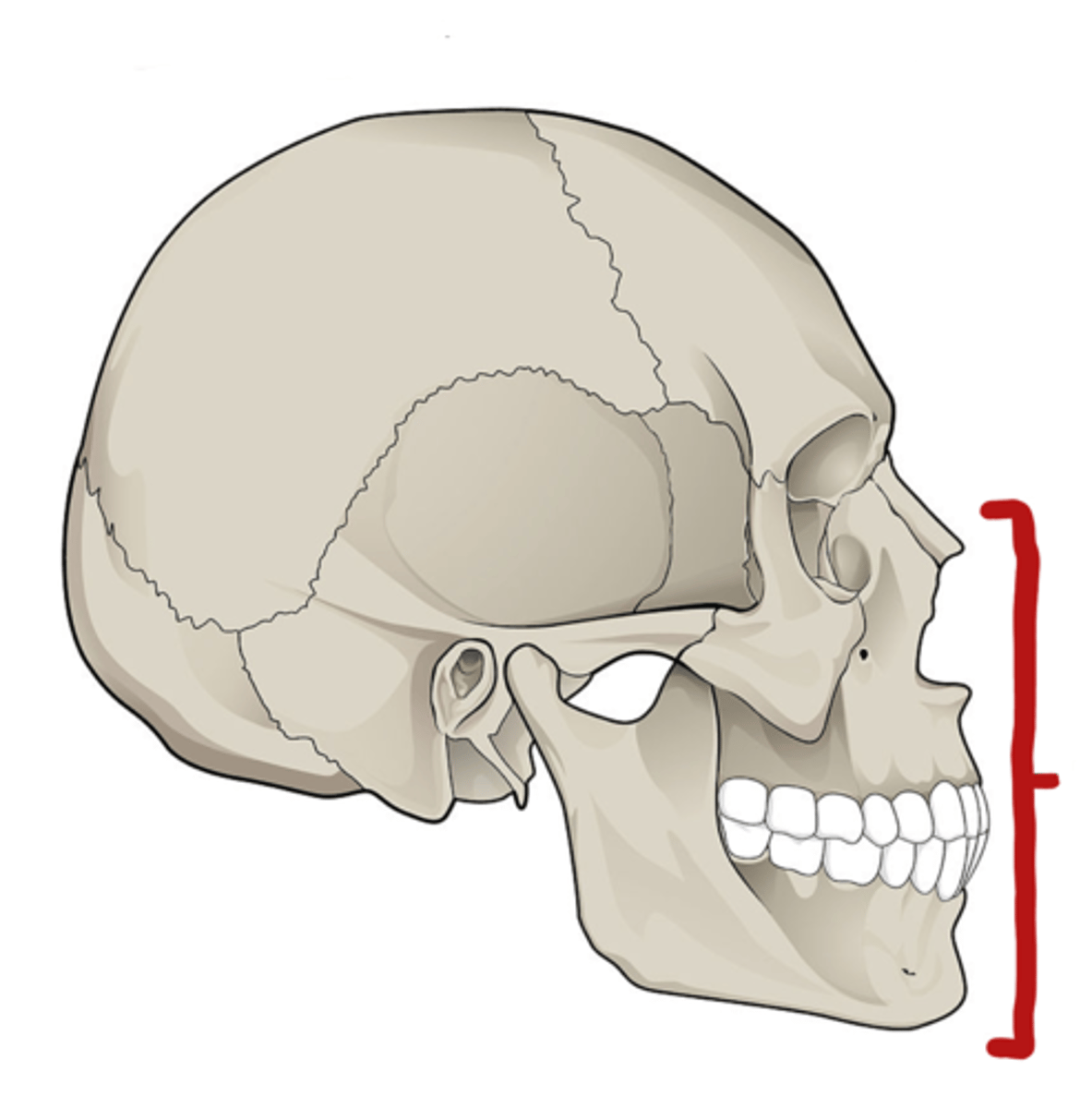
Name of skill division marked
Visceral cranium (facial skeleton)
Function of the visceral cranium
- gives a characteristic shape to the human face
- protection of delicate organs of the face
- provides a bony surface for attachment of facial muscles
- contains many foramina for the passage of neuro structures
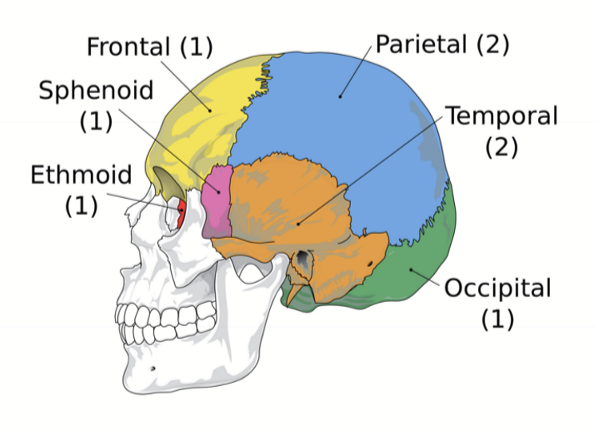
what bones make up the neurocranium?
- 1 Frontal bone
- 1 Ethmoid bone
- 1 Sphenoid bone
- 1 Occipital bone
- 2 Temporal Bones
- 2 Parietal Bones
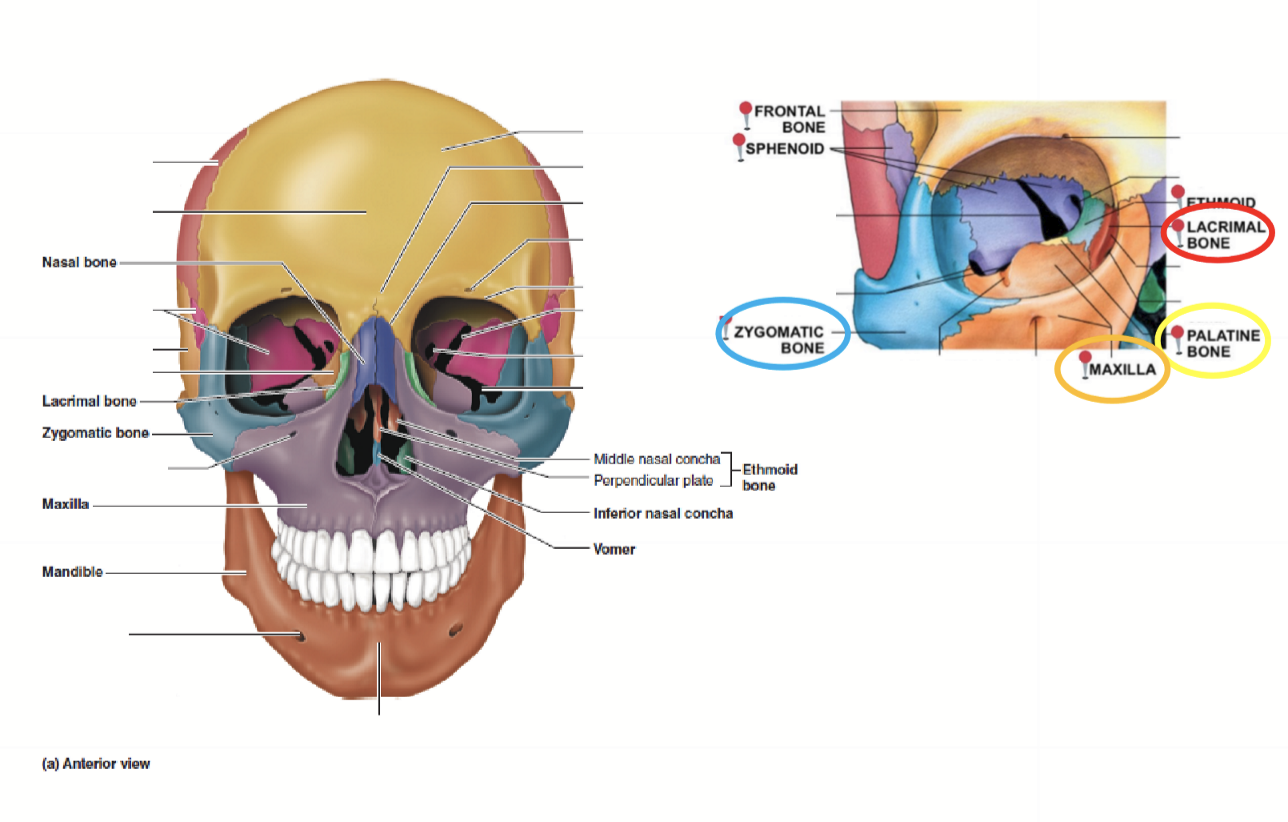
What bones make up the Visceral Cranium?
1 mandible, 1 vomer, 2 maxillae, 2 palatine, 2 zygomatic, 2 nasal, 2 lacrimal, 2 inferior conchae
What features of the neurocranium allow it to protect the brain?
- layered composition of bones allows a force to radiate over a larger surface area
- Joints at articulations are immoveable (i.e. sutures)
- Inernal bone structures are trianfulated to support the contents of the neurocranium (i.e. buttress of the skull)
~ protection of the brain is also facilitated by meninges~
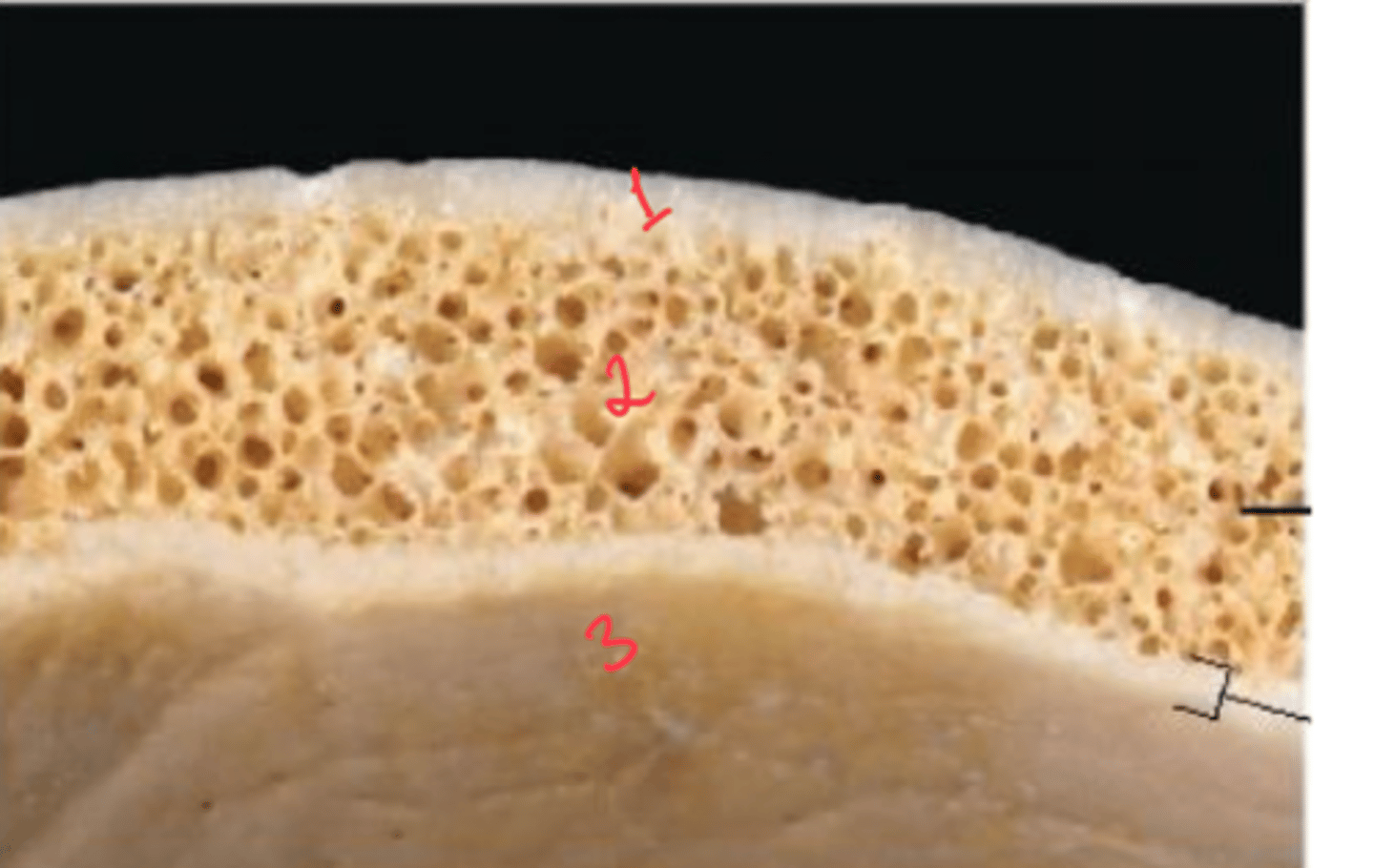
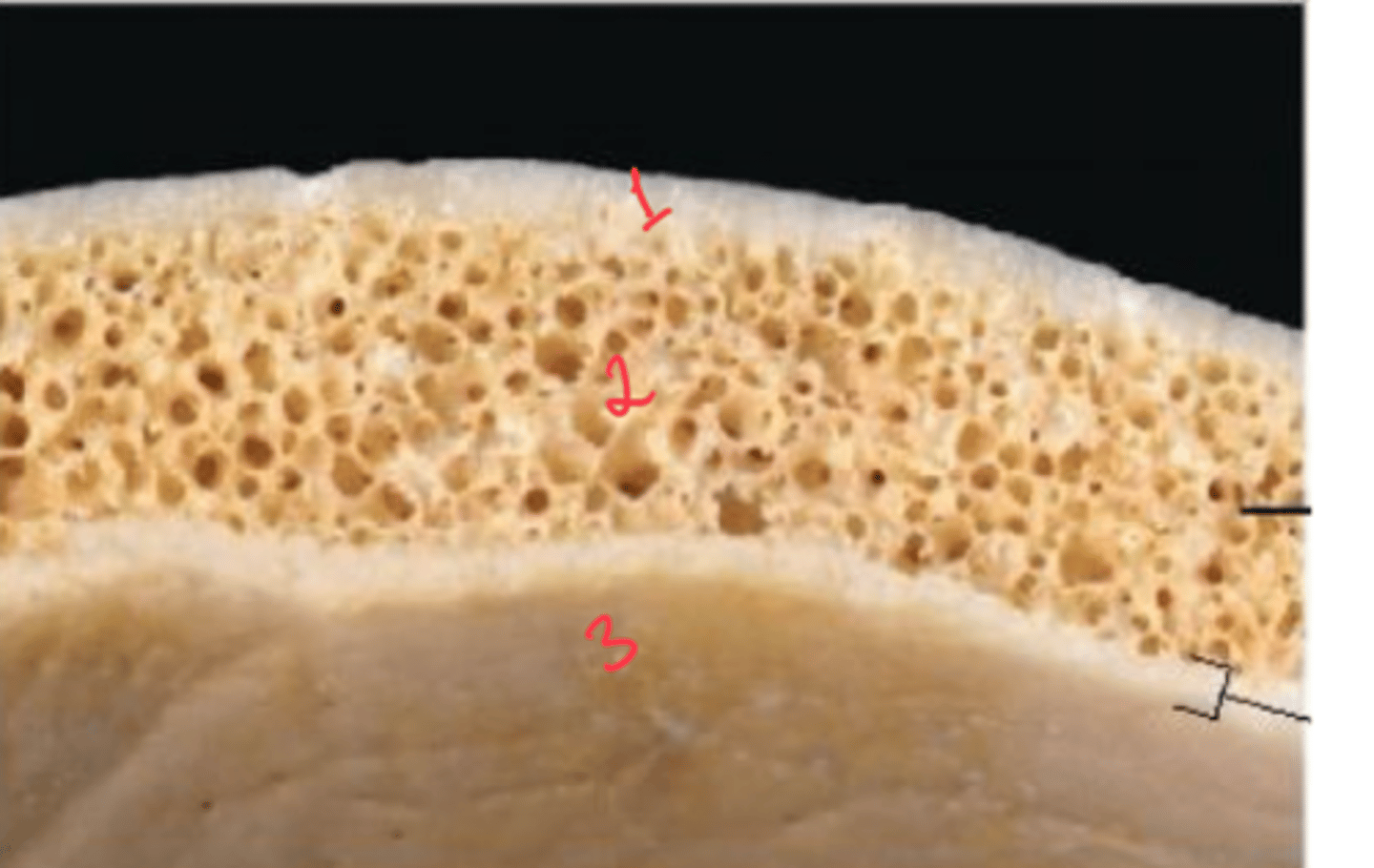
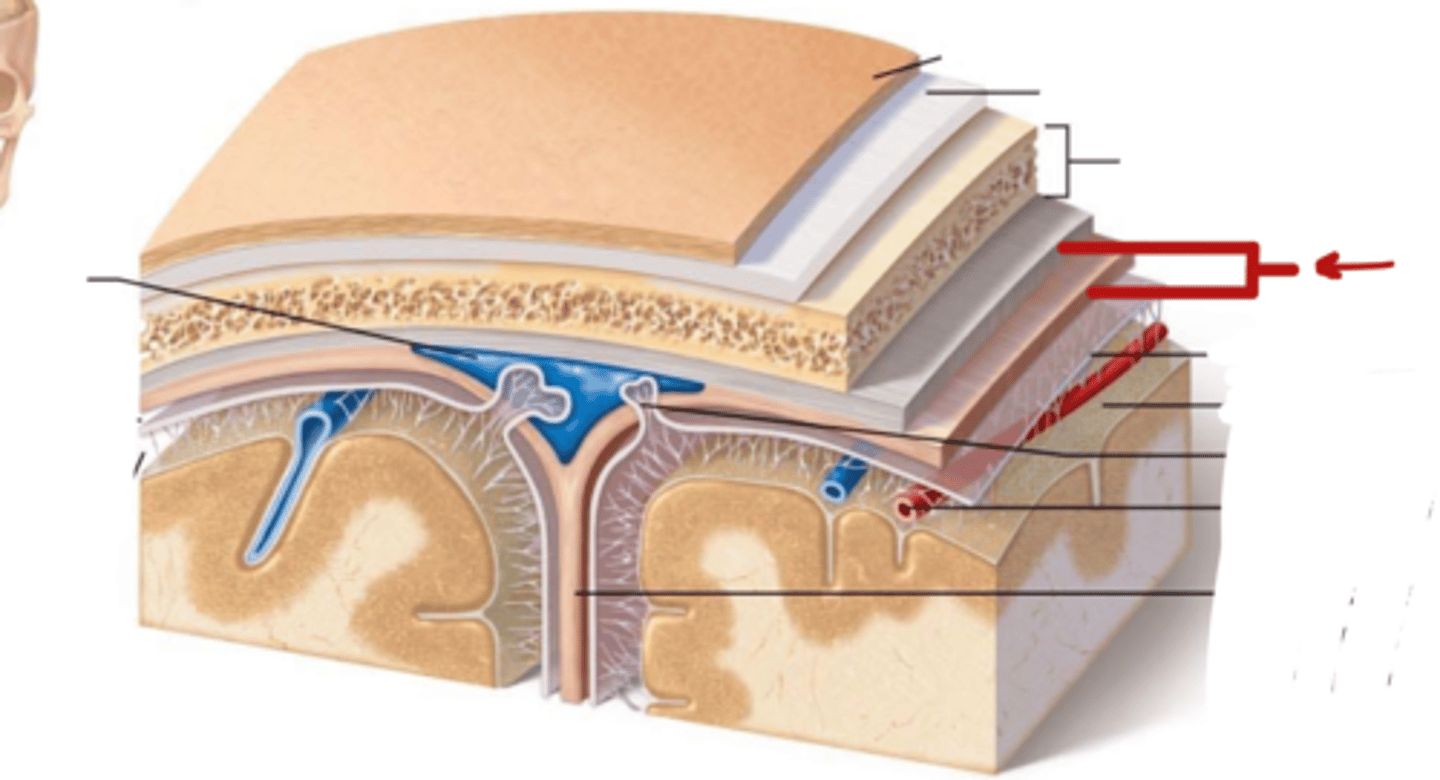
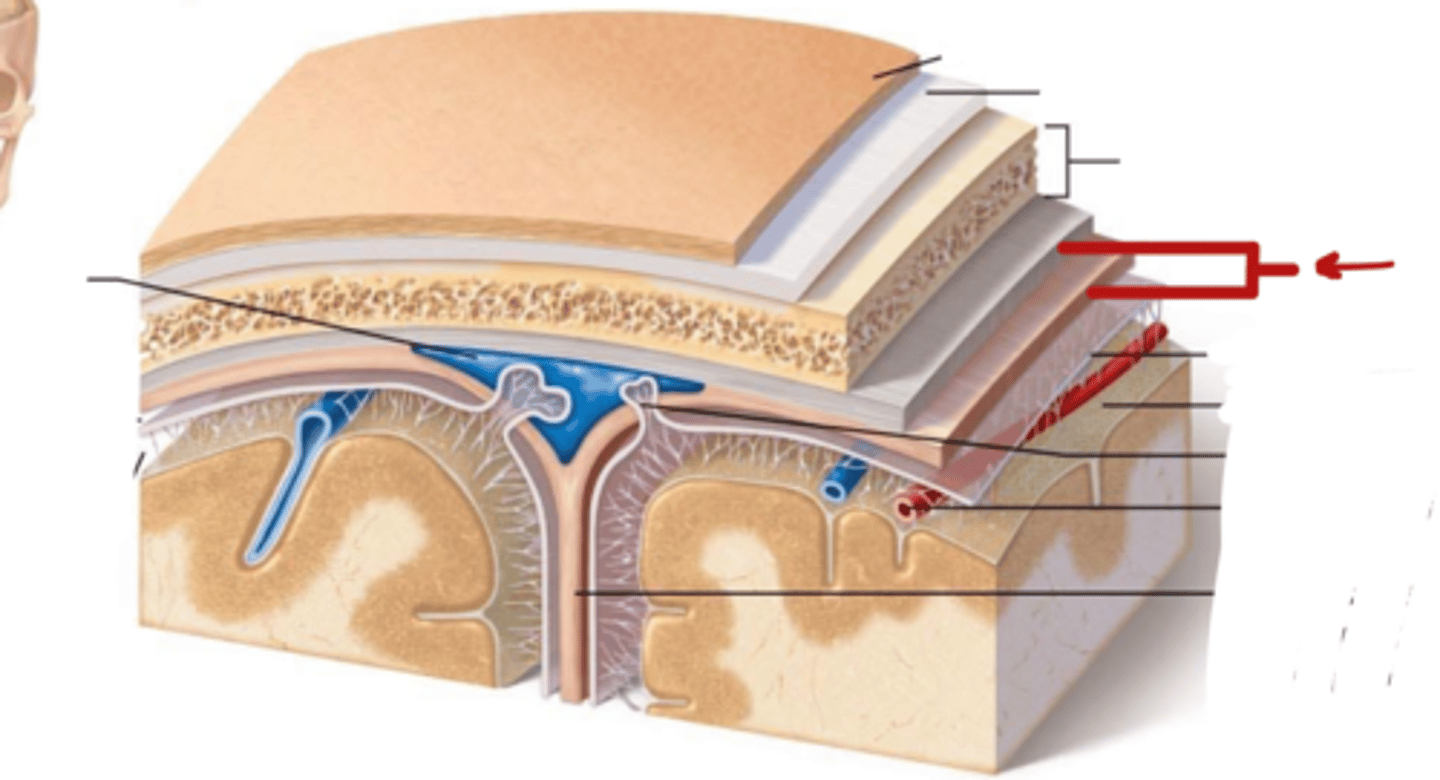
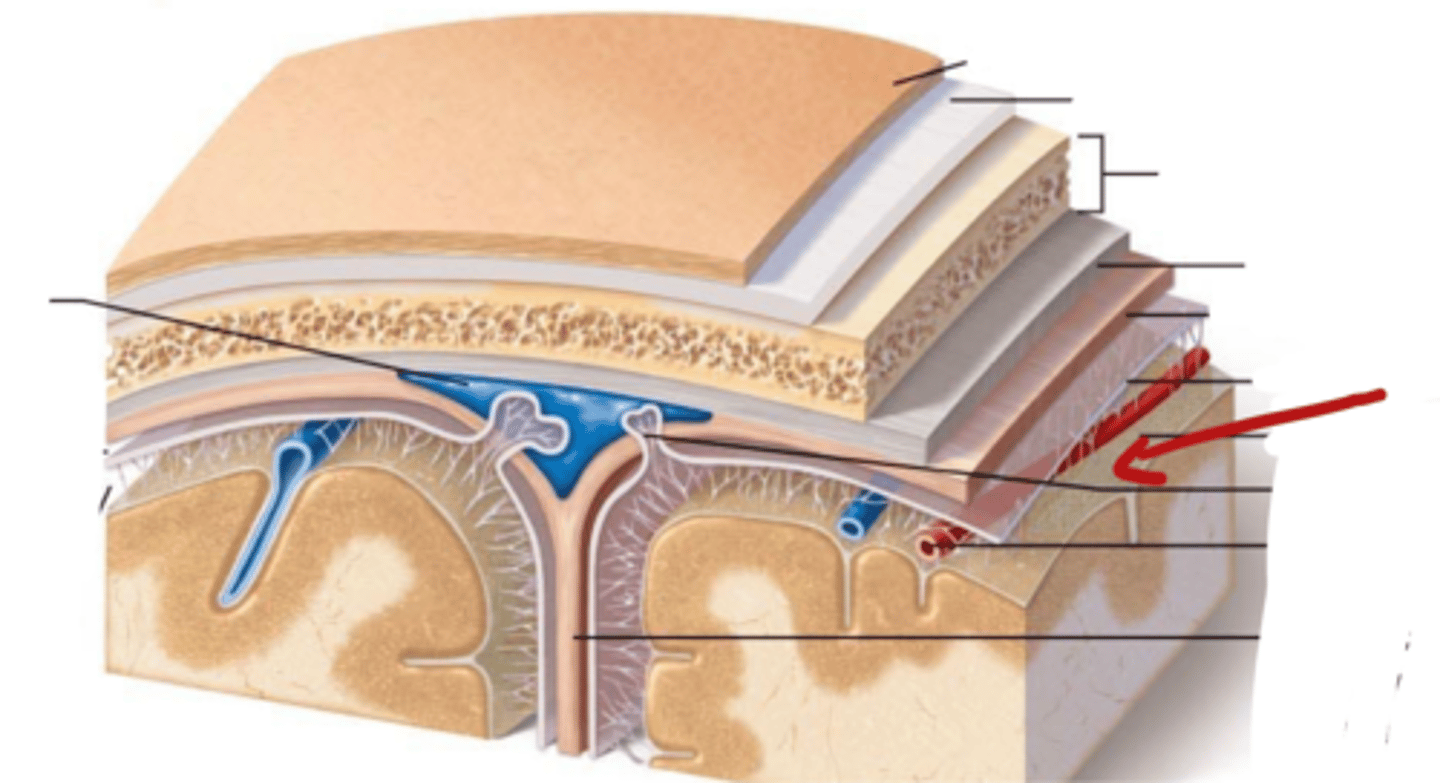
What are the Layers of bone in skull?
1. Outer table: compact bone
2. Diploe: Spongy bone
3. Inner table: compact bone
what are cranial sutures? what are they made up of?
immoveable joints, made up of fibrous connective tissue
do sutures contain diploe?
no, this makes the skull thinner and more susceptible to injury in these areas
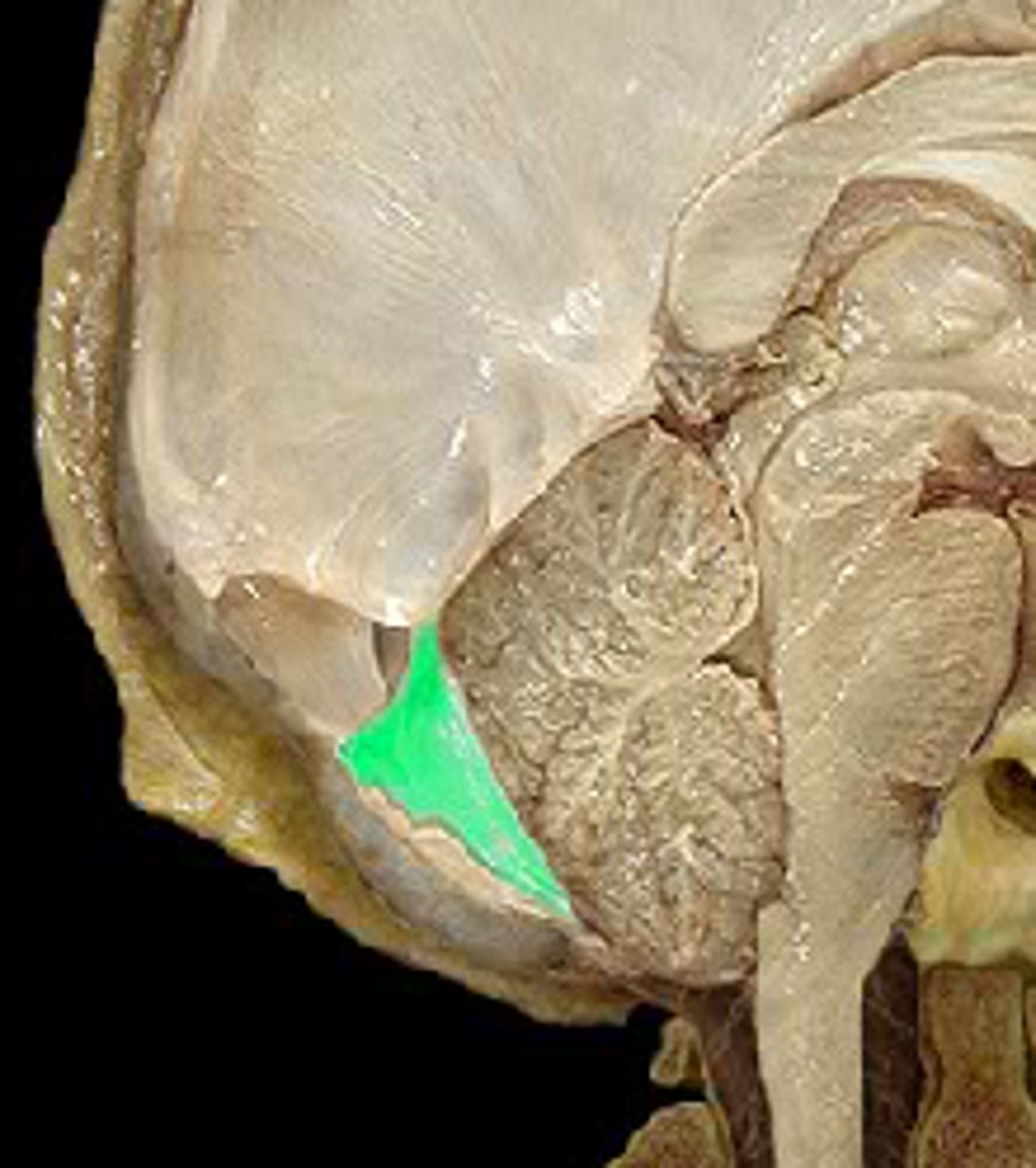
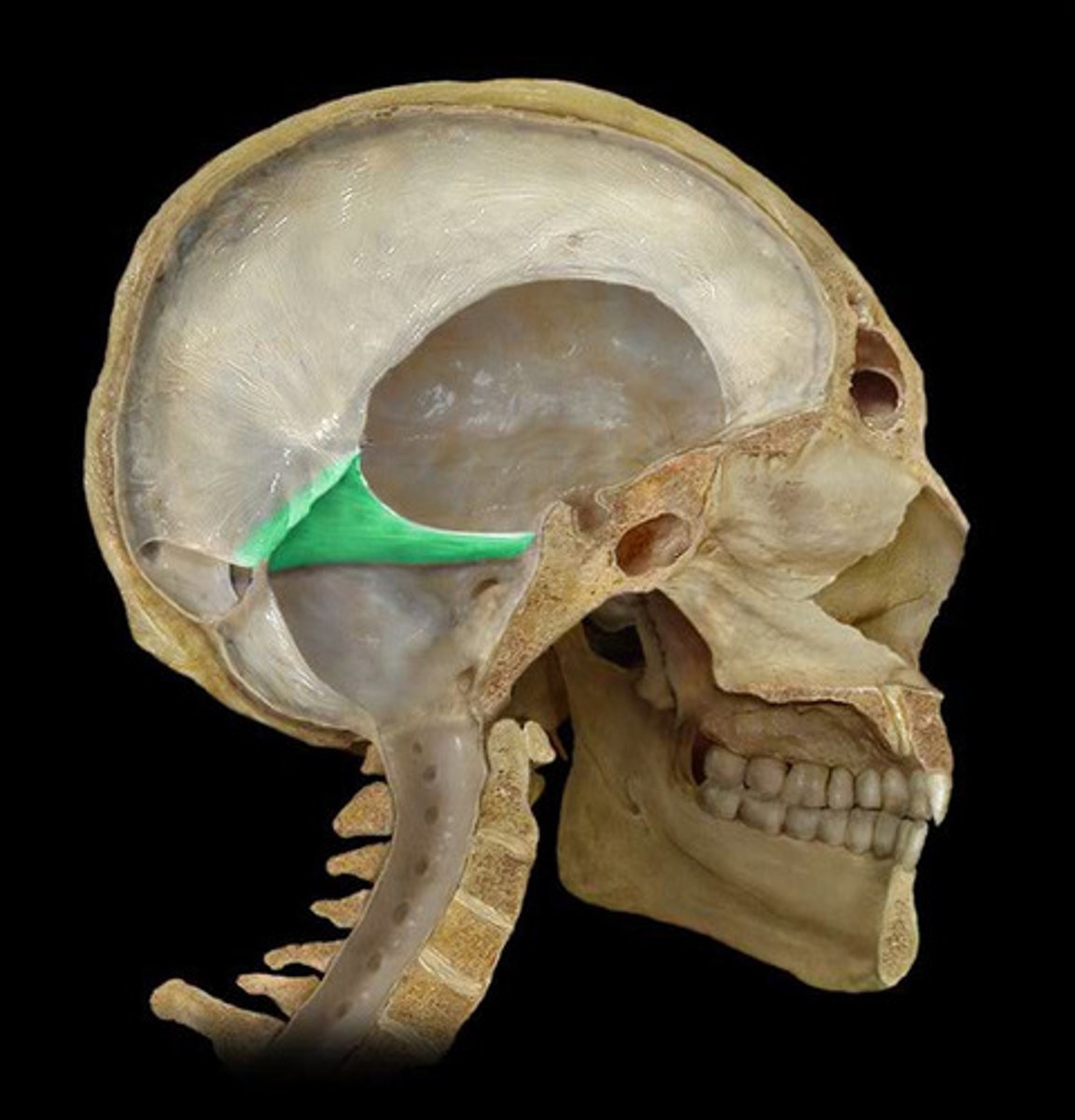
Structure of the Skull
Triangulated to support contents of neurocranium
Formed by lesser wings of sphenoid bone and petrous portion of the temporal bones
What are the meninges?
what is the meninges function?
membranous layers of connective tissue that cover the brain (and spinal cord)
(in between the skull and brain)
- protect the brain and spinal cord from mechanical
- provide a framework for vasculature
what are the three meninges layers?
what are the spaces associated with these layers?
(all in order! from external to internal)
~ Epi-dural space (potential space)
1. Dura Mater
~ Sub-dural Space (potential space)
2. Arachnoid Mater
~ Sub-arachnoid space (real space)
3. Pia Mater
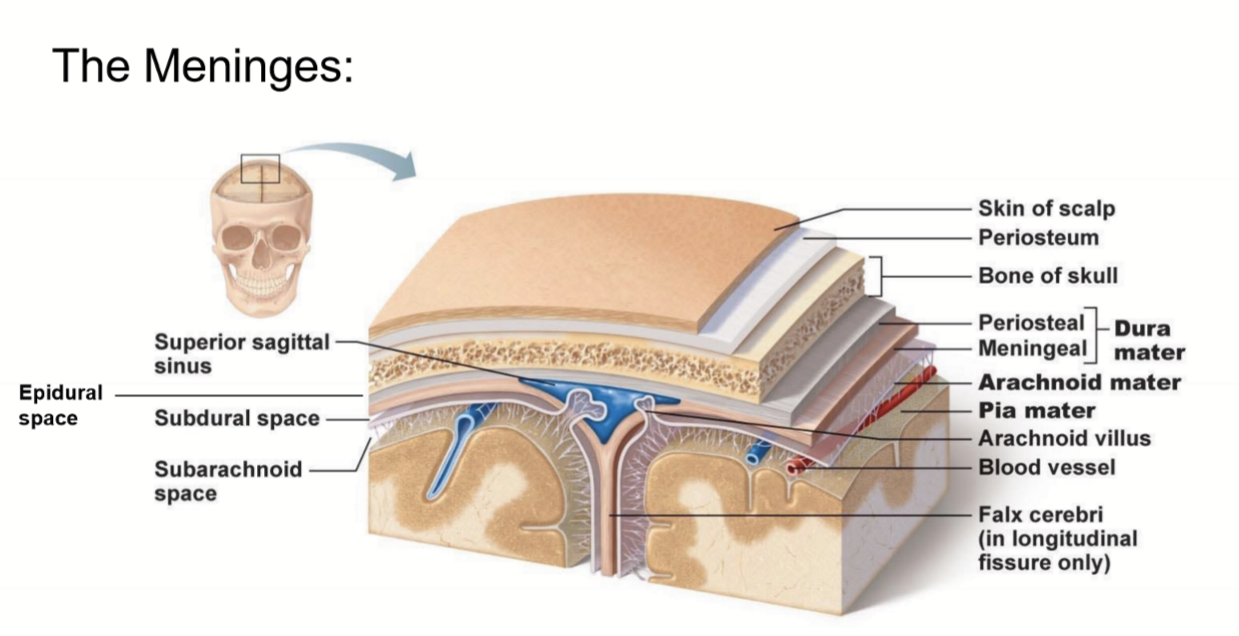
Describe the Dura Mater
- what is it made of?
- outer periosteal layer and inner meningeal layer
- thick, fibrous, strong (DICT)
- Vascular
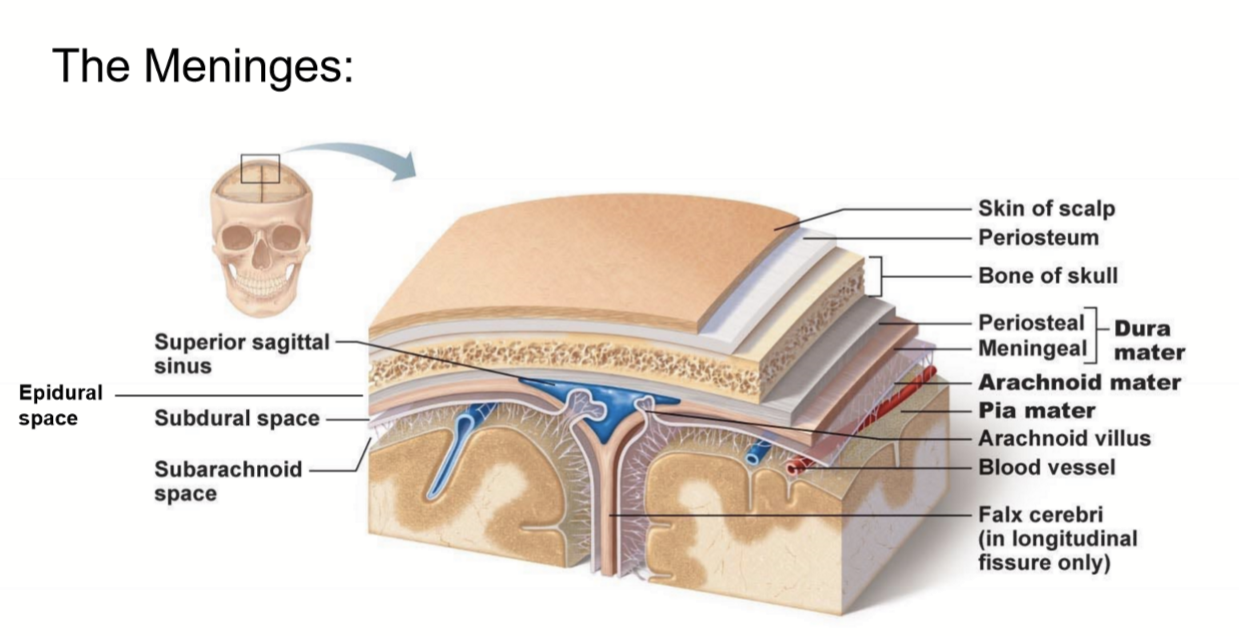
Describe the Arachnoid Mater
- What is it made of?
- thin (LCT)
- Avascular
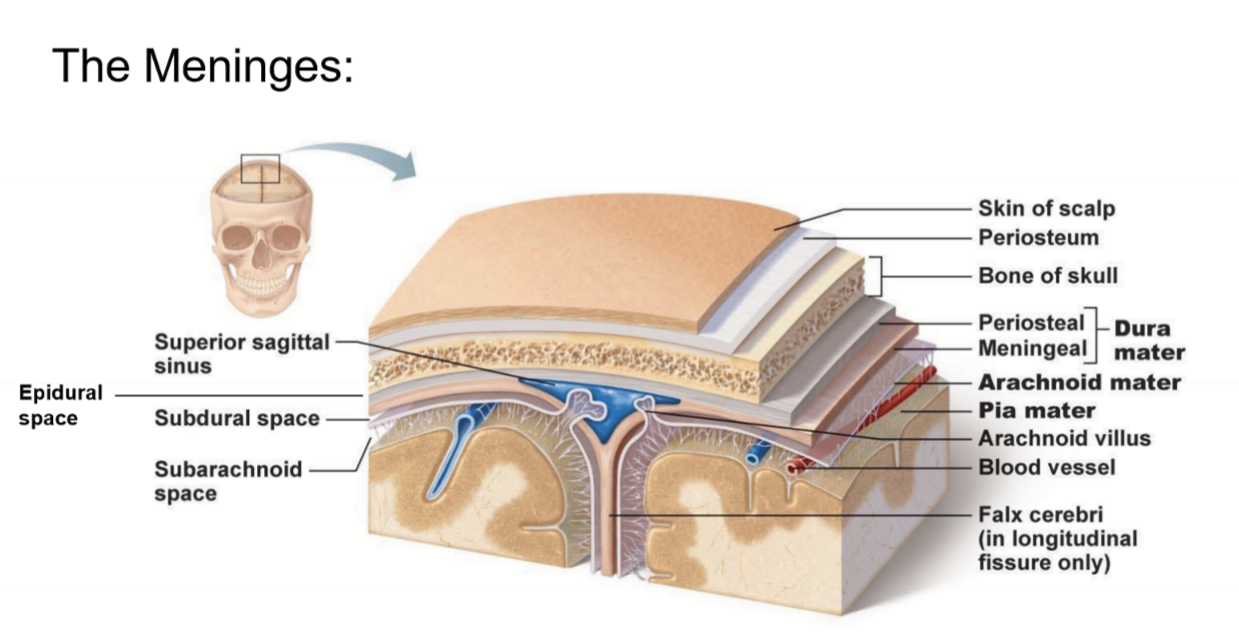
what is in the sub-arachnoid space, where is it
located in between the arachnoid mater and pia mater
contains Cerebral Spinal Fluid
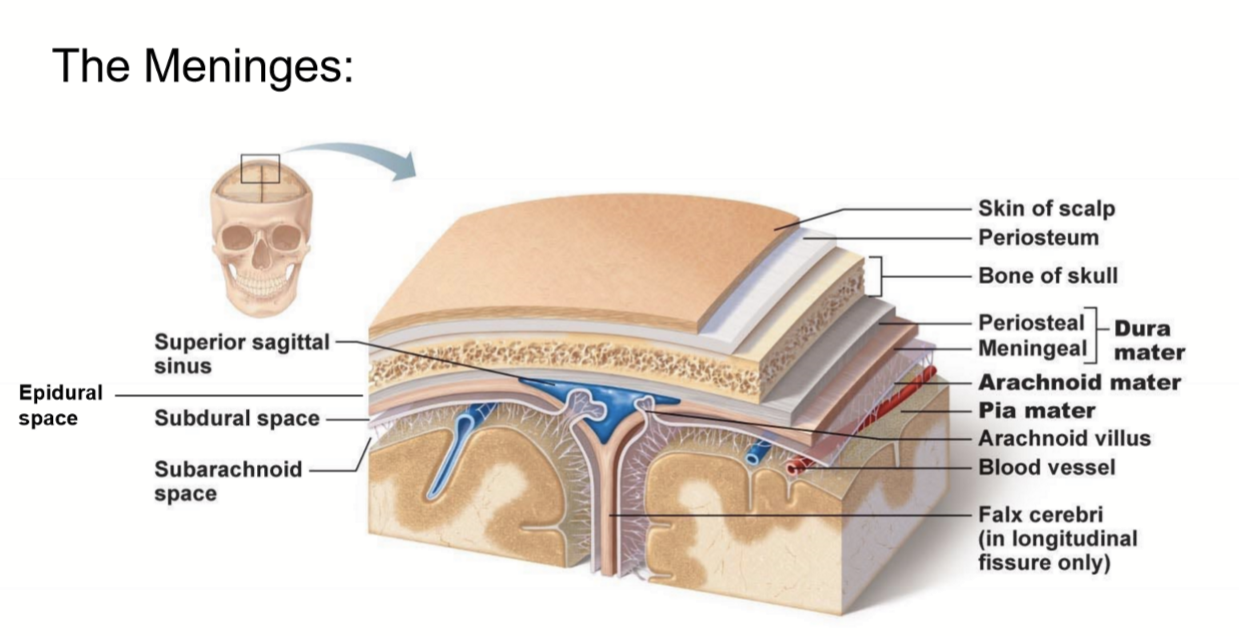
Describe the Pia Mater
Tightly adhered to brain and spinal cord
very thin
vascular
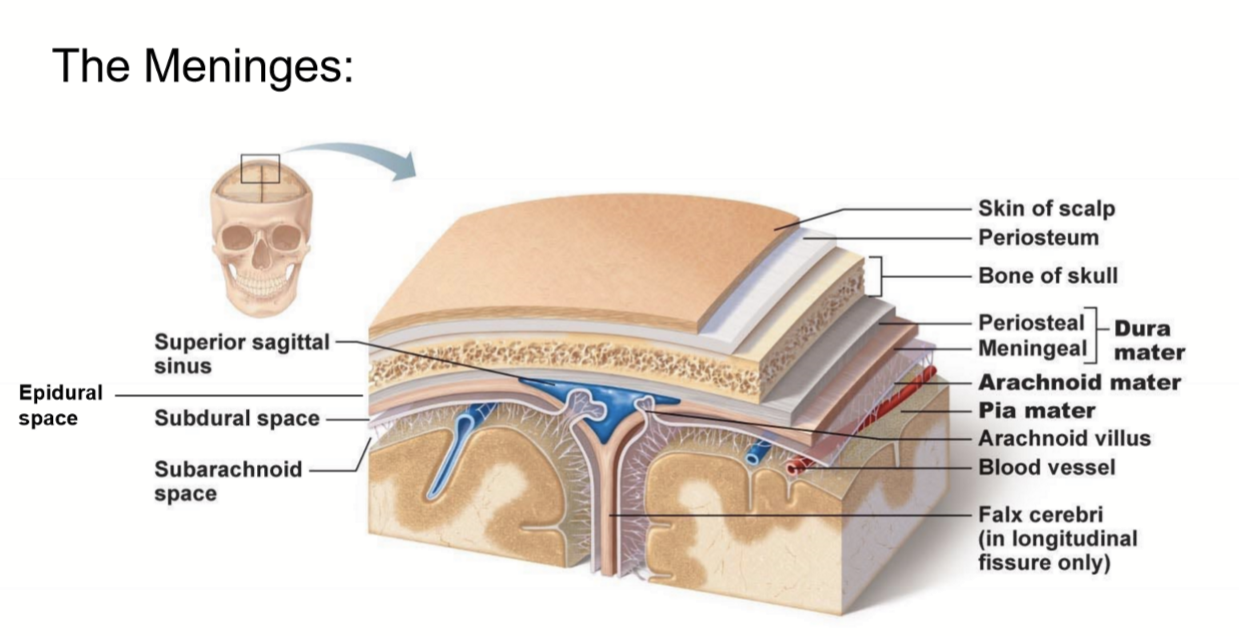
Dura Mater
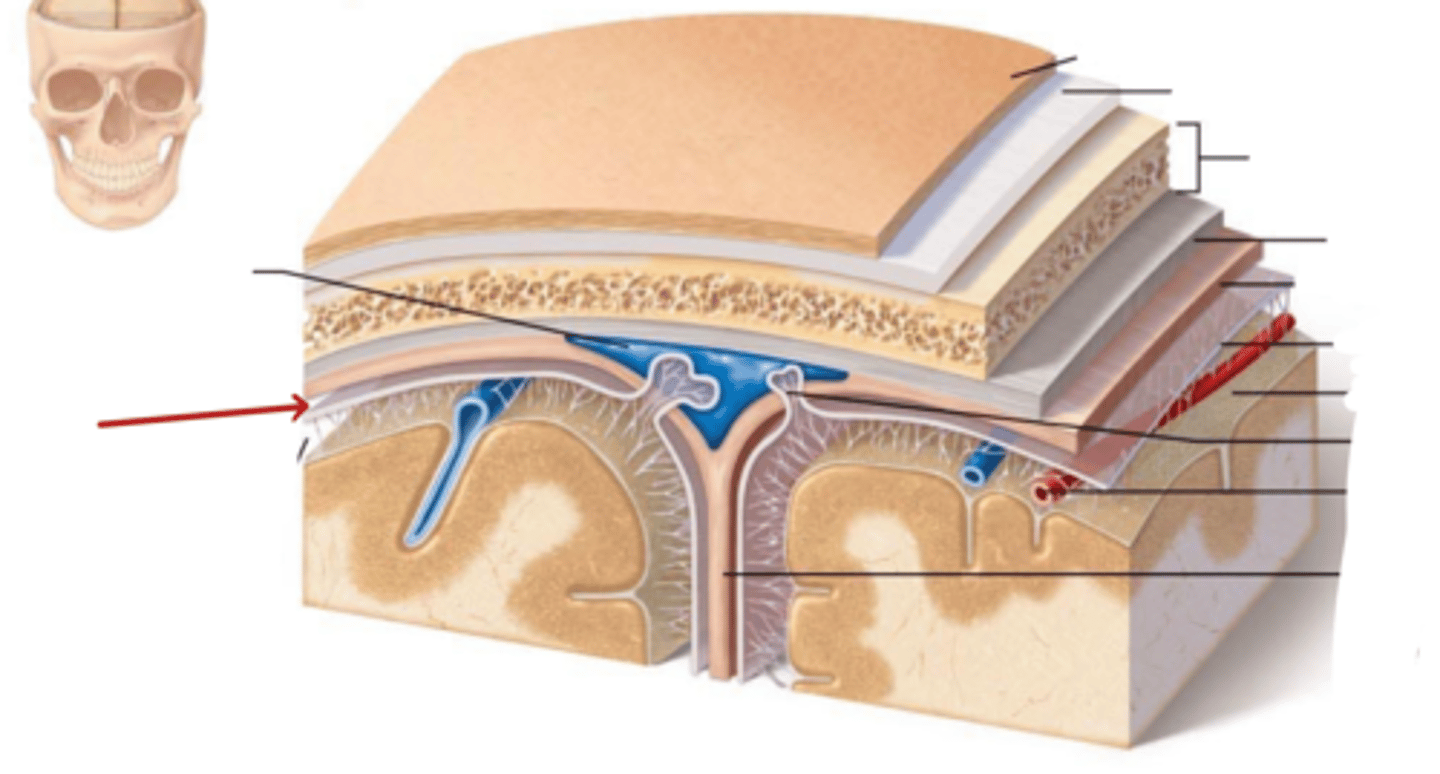
Sub-dural Space
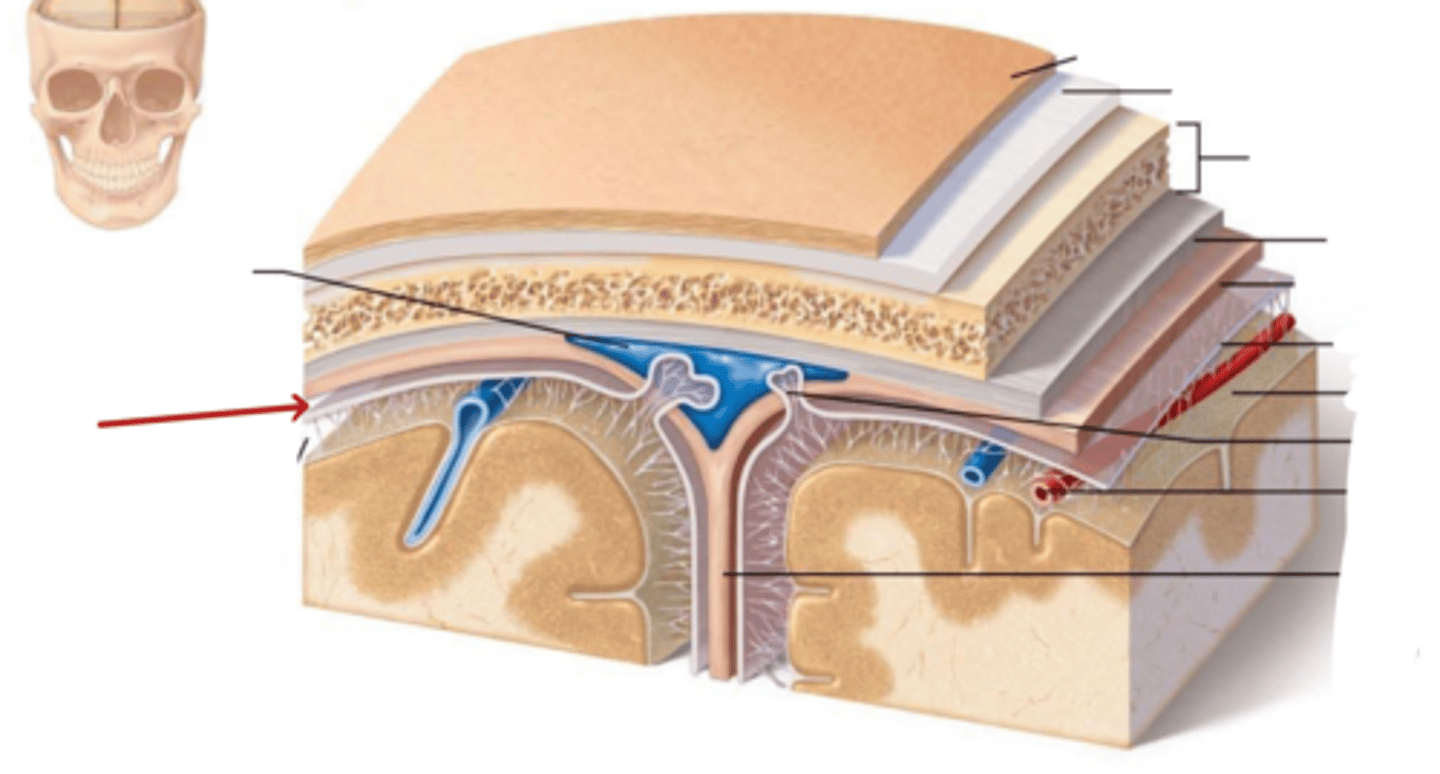
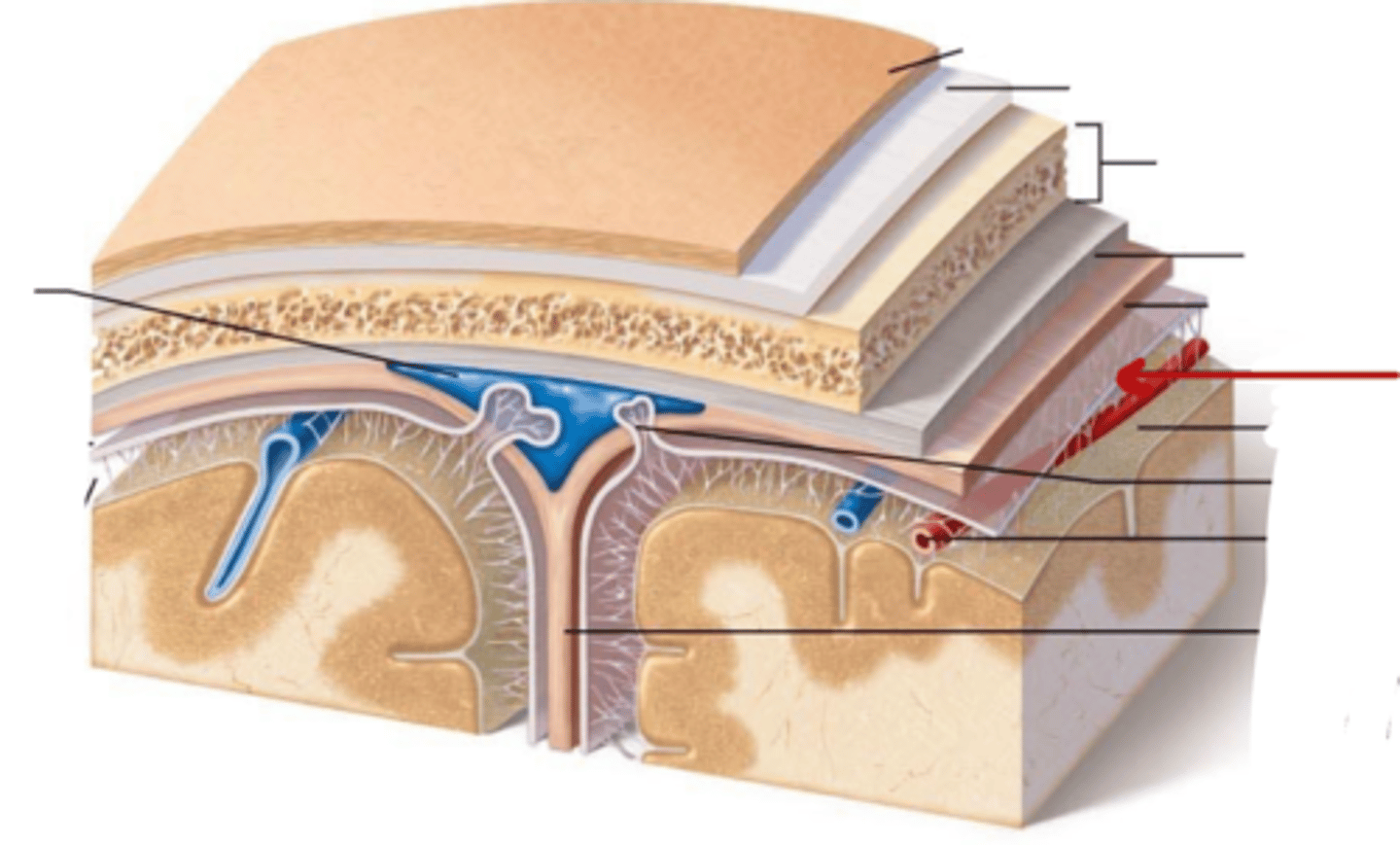
Arachnoid Mater
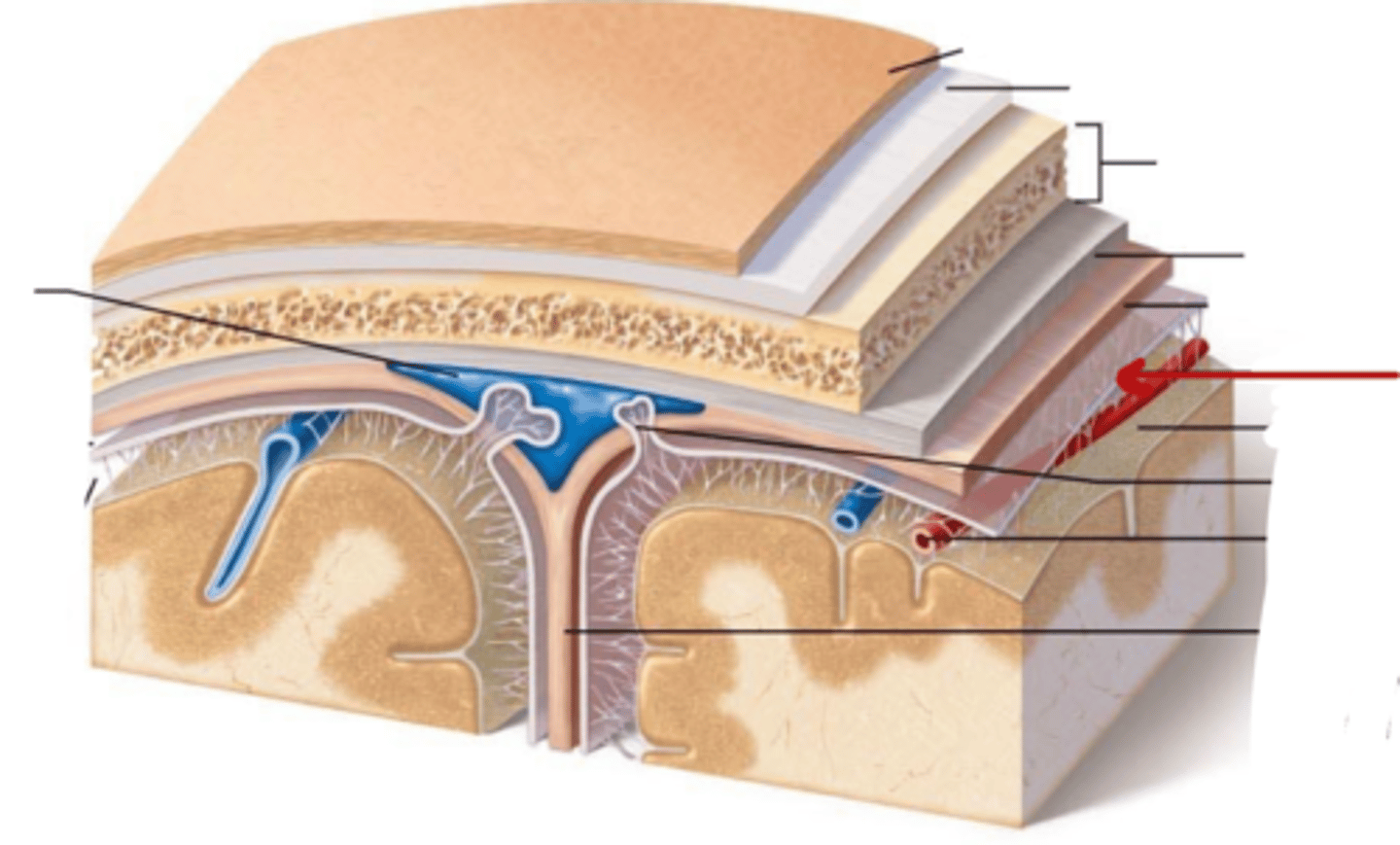
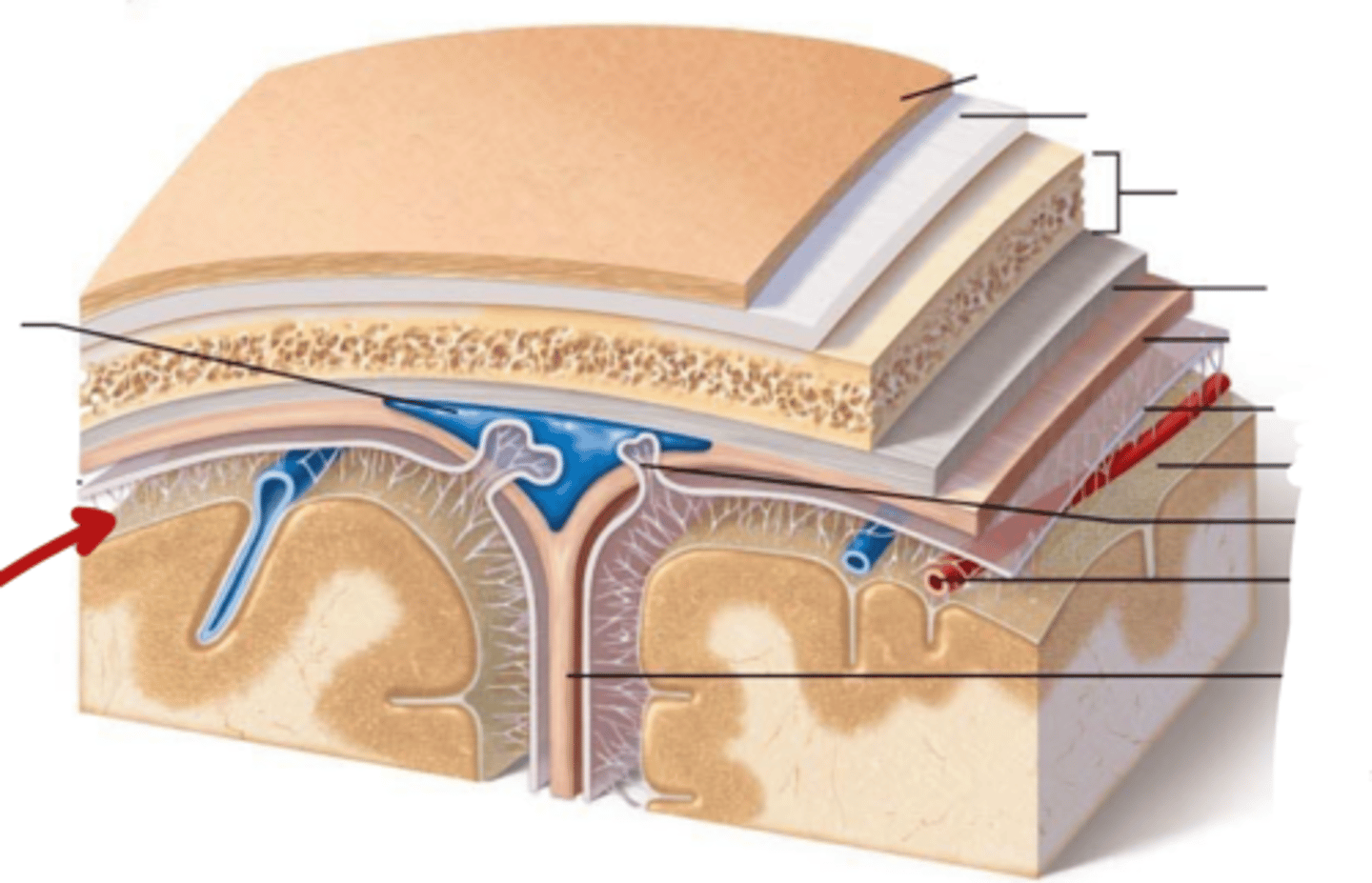
Sub-Arachnoid Space
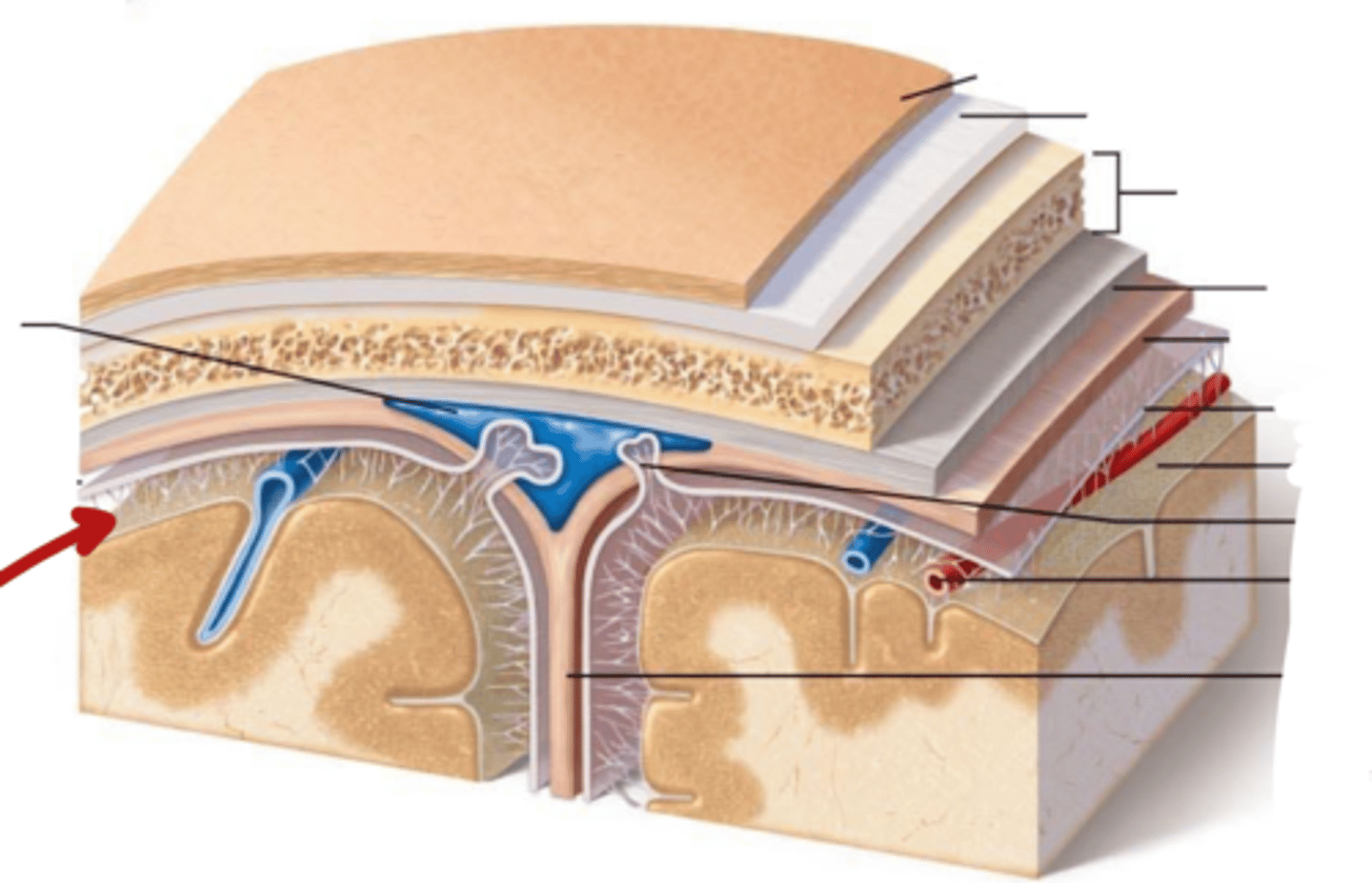
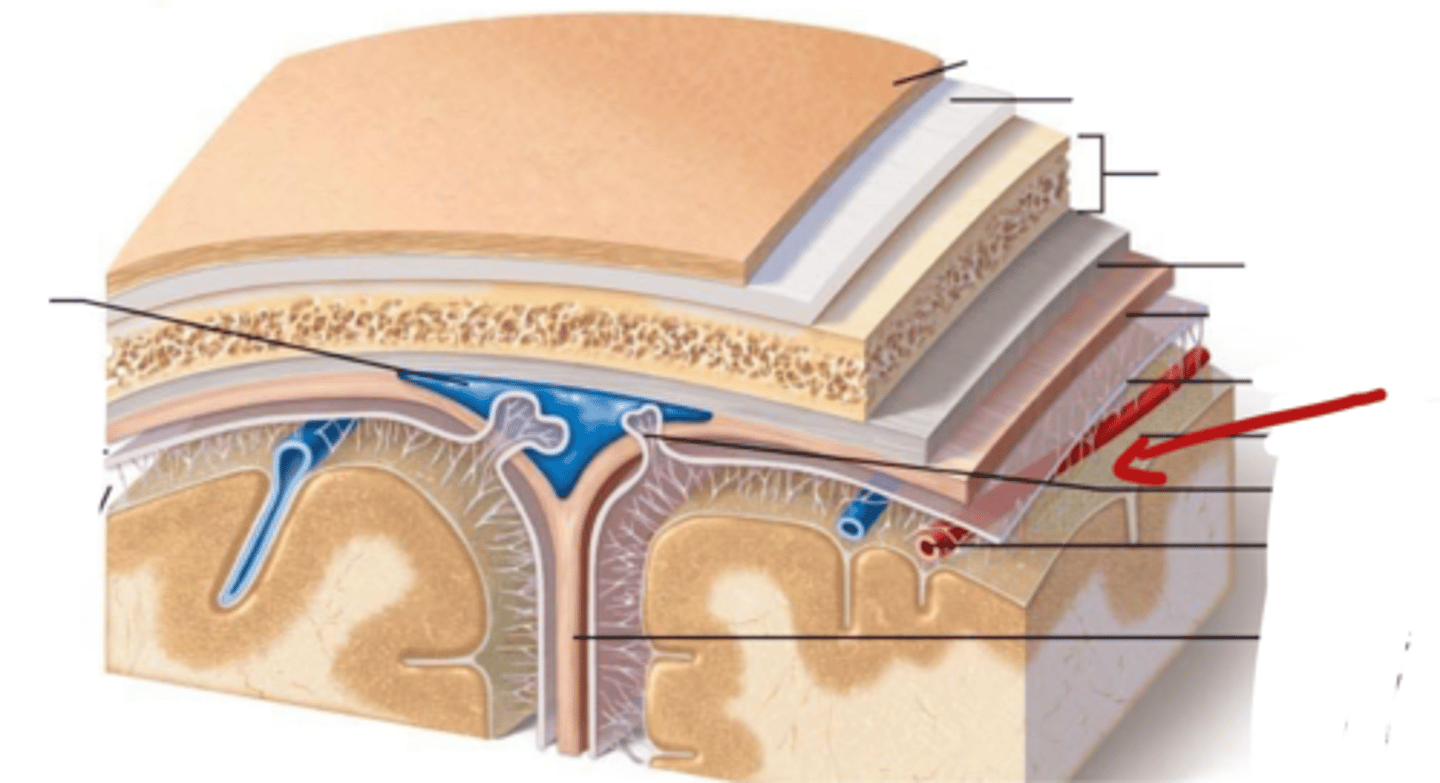
Pia Mater
What are the Dural folds?
Membranes that divide the cranial cavity into compartments and support the brain and spinal cord
-- 2 large folds: Falx Cerebri and Tentorium Cerebelli
-- 2 small folds: Falx Cerebelli and Diaphragma Sellae
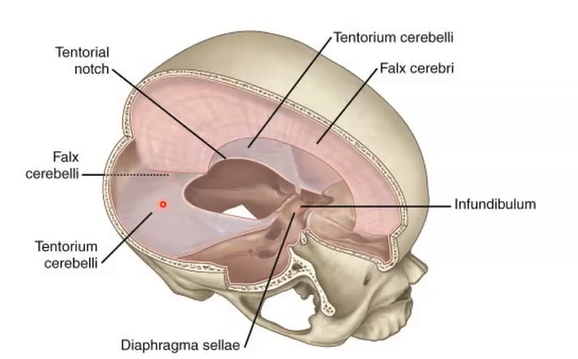
Falx Cerebri
Falx Cerebelli
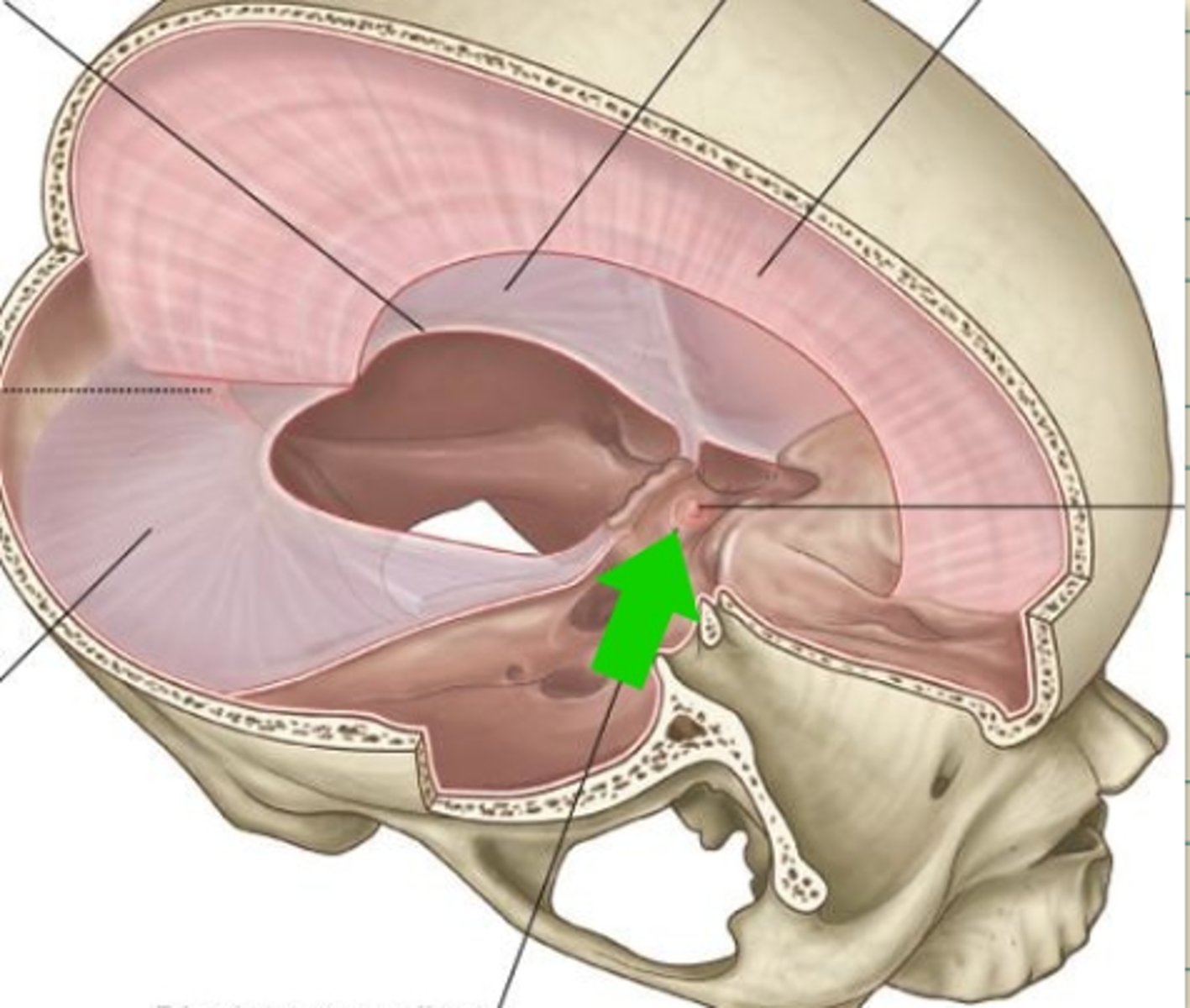
diaphragma sellae
tentorium cerebelli
How are most bones of the skull formed?
intramembranous ossification
direct conversion of mesenchymal cells -> Bone (no cartilage precursure)
- only capable of appositional growth
Fontanelles and its purpose
A soft membranous gap between of hyaline cartilage between the cranial bones of the calveria in the fetus and infant (also called "soft spots")
- allows movement and molding of head through birth canal during labor
- allows more rapid post-natal growth of brain
when does osteogenesis begin?
6-7 weeks gestation
When do the tables and diploe develop?
by the 4th year of life
What are the fontanelles
- Anterior (F1)
- Posterior (F2)
- Sphenoidal or anterolateral (F3) [paired]
- Mastoid or posterolateral (F4) [paired]
![<p>- Anterior (F1)<br>- Posterior (F2)<br>- Sphenoidal or anterolateral (F3) [paired]<br>- Mastoid or posterolateral (F4) [paired]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9ebdb15d-a92a-47ac-af67-c4d58072b6a6.png)
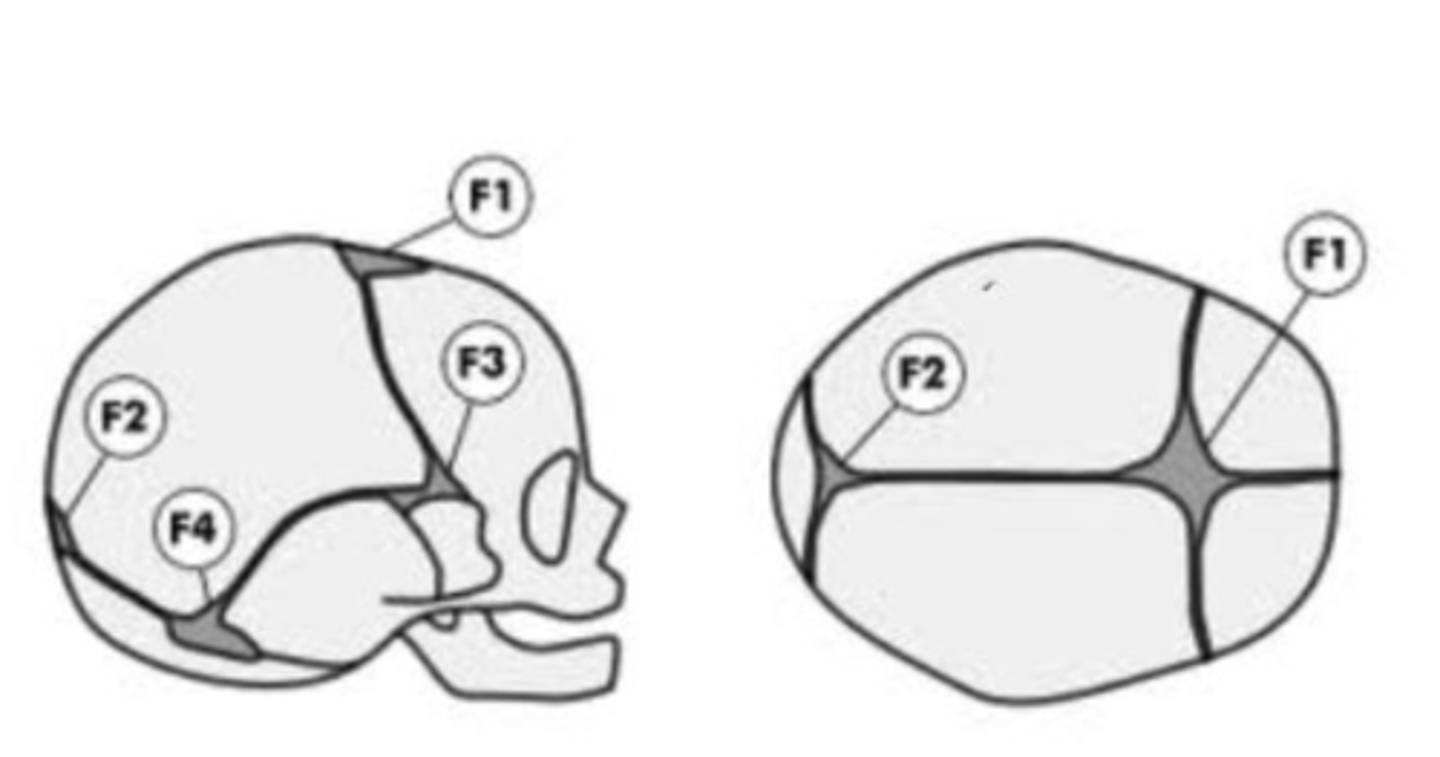
When does each Fontanelle close?
- Anterior (F1): closes 18-24 months last to close!
- Posterior (F2): closes 2-3 Months first to close!
- Sphenoidal or anterolateral (F3) [paired]: closes at 2-3 months
- Mastoid or posterolateral (F4) [paired]: closes by 12 months
What is an F1 suture in an infant called?
interfrontal suture
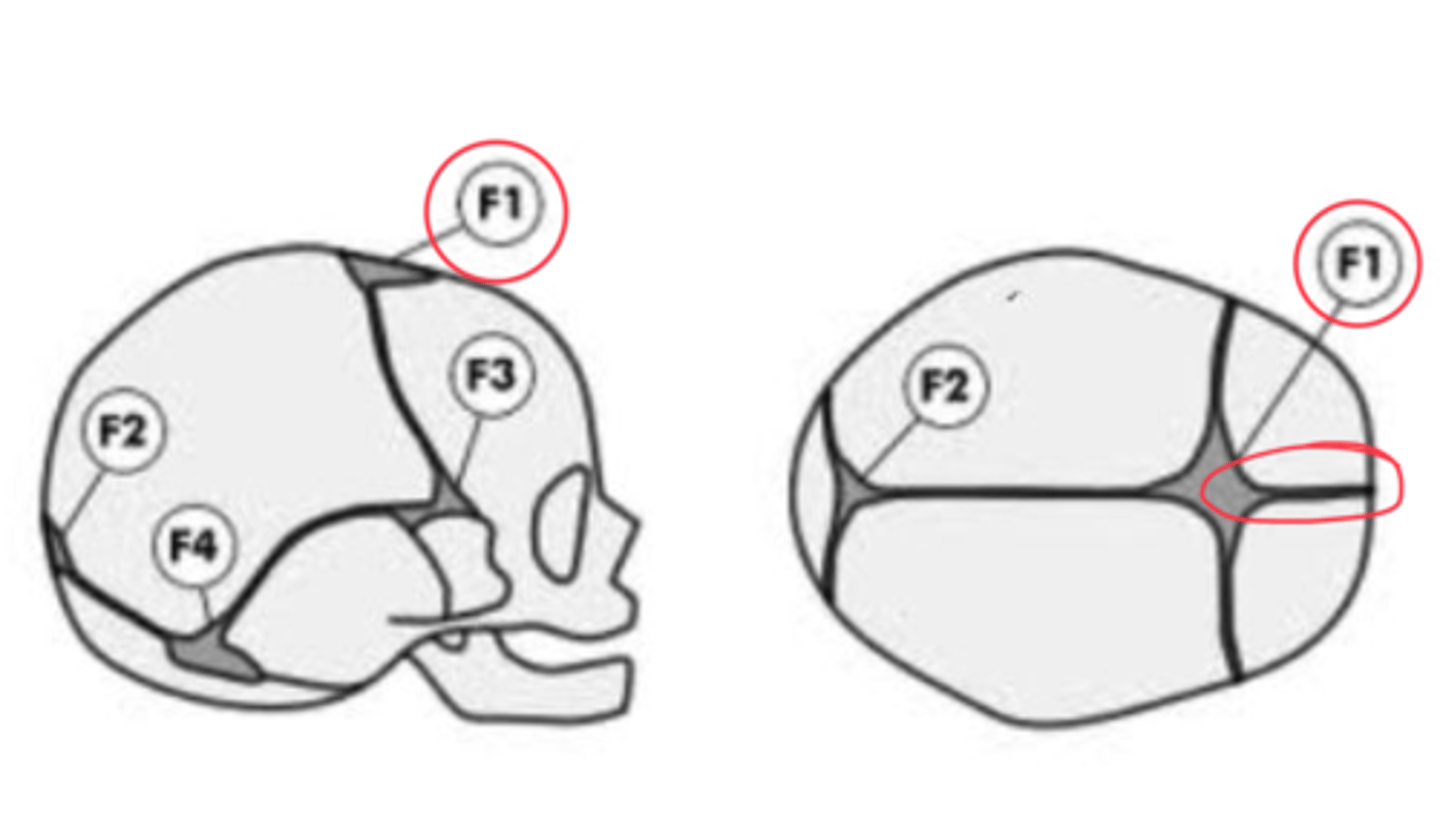
What is the F1 suture in adults?
what can it increase risk of?
Mesopic suture
can increase risk of fracture in that area
Views of the skull:
Norma verticalis
Norma dorsalis (occipitalis)
Norma lateralis
Norma frontalis
Norma basalis
Inside of skull
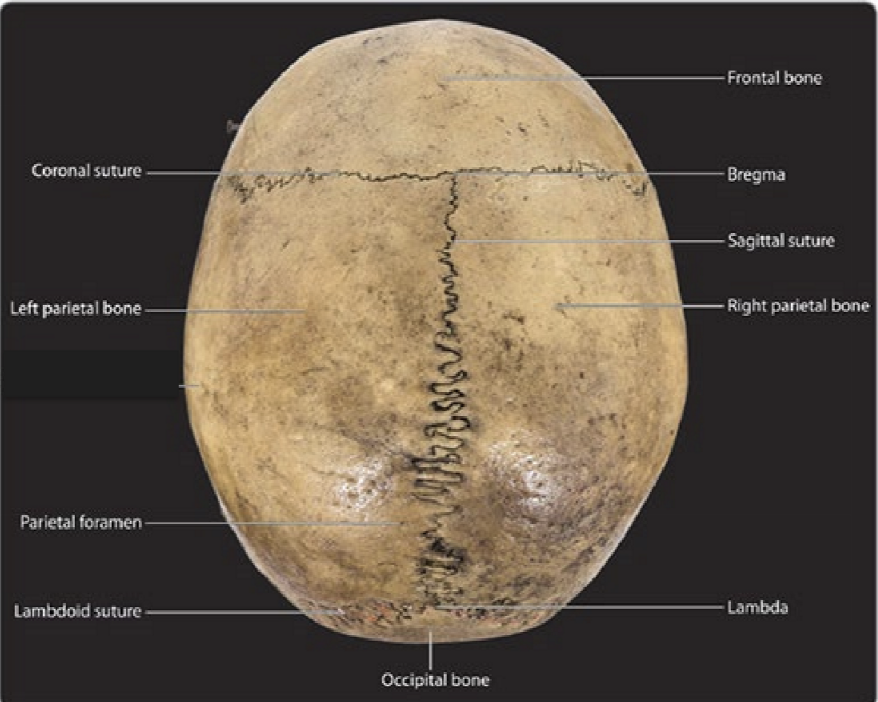
Structures seen from Norma verticalis
Bones visible: Frontal, 2 parietal, and occipital bone
Sutures: coronal, sagittal, lambdoid
Foramen: 2 parietal foramen
Craniometric points visible: bregma, lambda, and vertex (highest point, no sutures)
Structures seen from Norma Dorsalis (occipitalis)
Bones visible: 2 parietal bones, occipital bone, 2 temporal bones
Sutures: Sagittal, lambdoid, parietomastoid, occipitomastoid
Foramen: 2 parietal foramen
Craniometric points visible: lambda, asterion
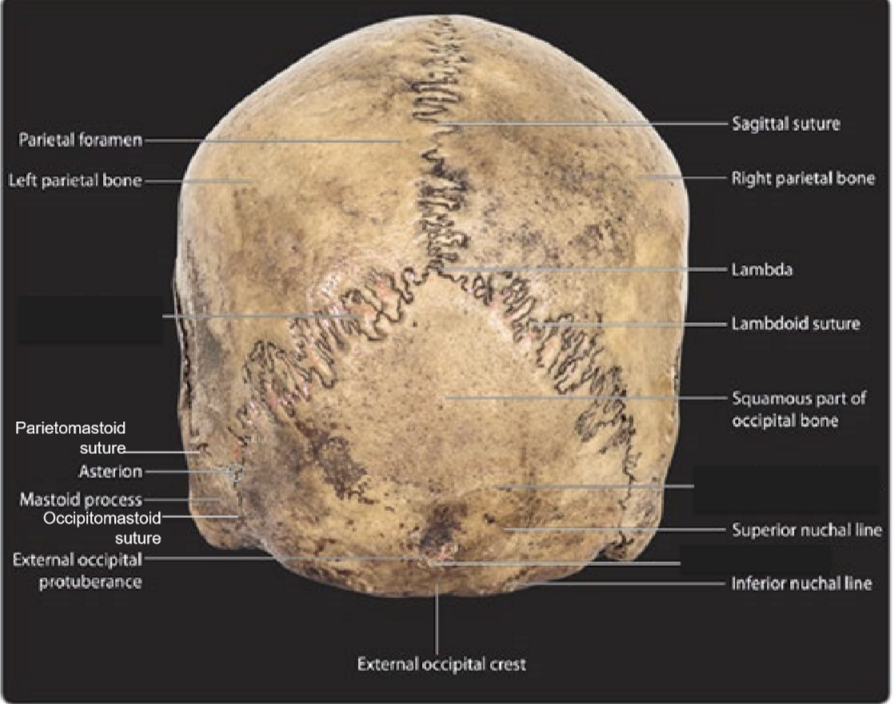
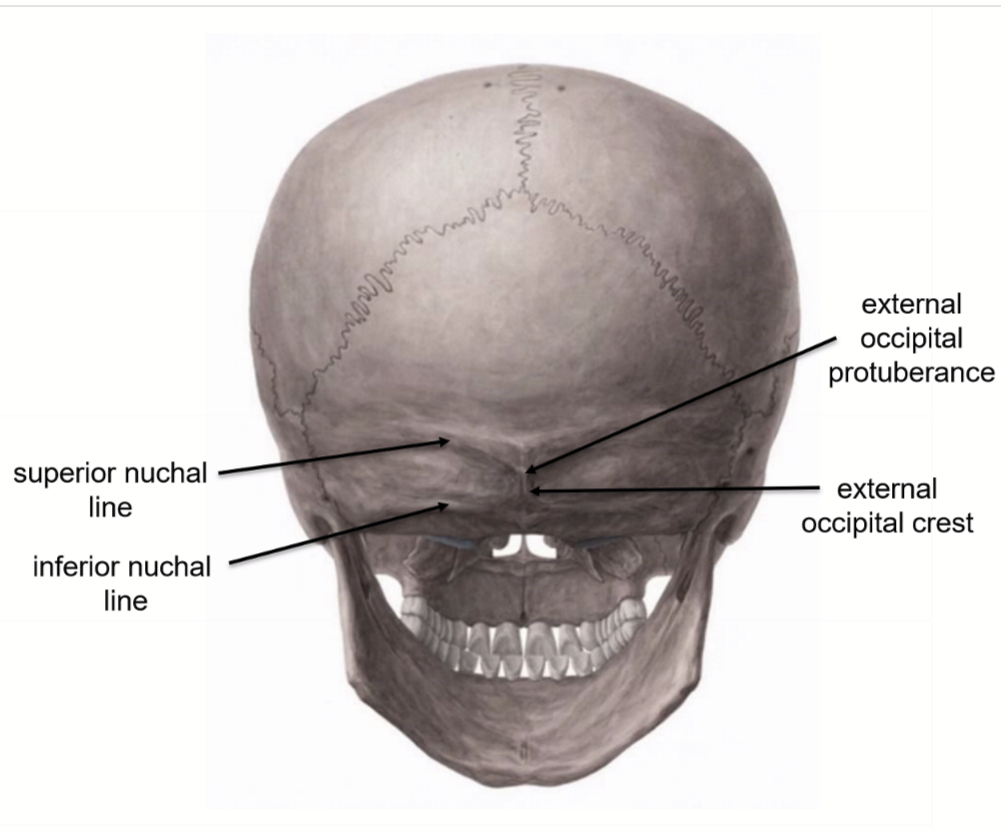
Other notable features seen from Norma Dorsalis (occipitalis)
superior nuchal line (trapezius, splenic capitis, and occipitalis muscle attach here)
inferior nuchal line (attachment site for 3 deep neck muscles)
external occipital crest
external occipital protuberance (marks junction of head and neck)
Bones visible from Norma Lateralis
frontal bone
2 parietal bones
2 temporal bones
occipital bone
2 zygomatic bones
2 maxillary bones
mandible
2 nasal bones
sphenoid
ethmoid
2 lacrimal bones
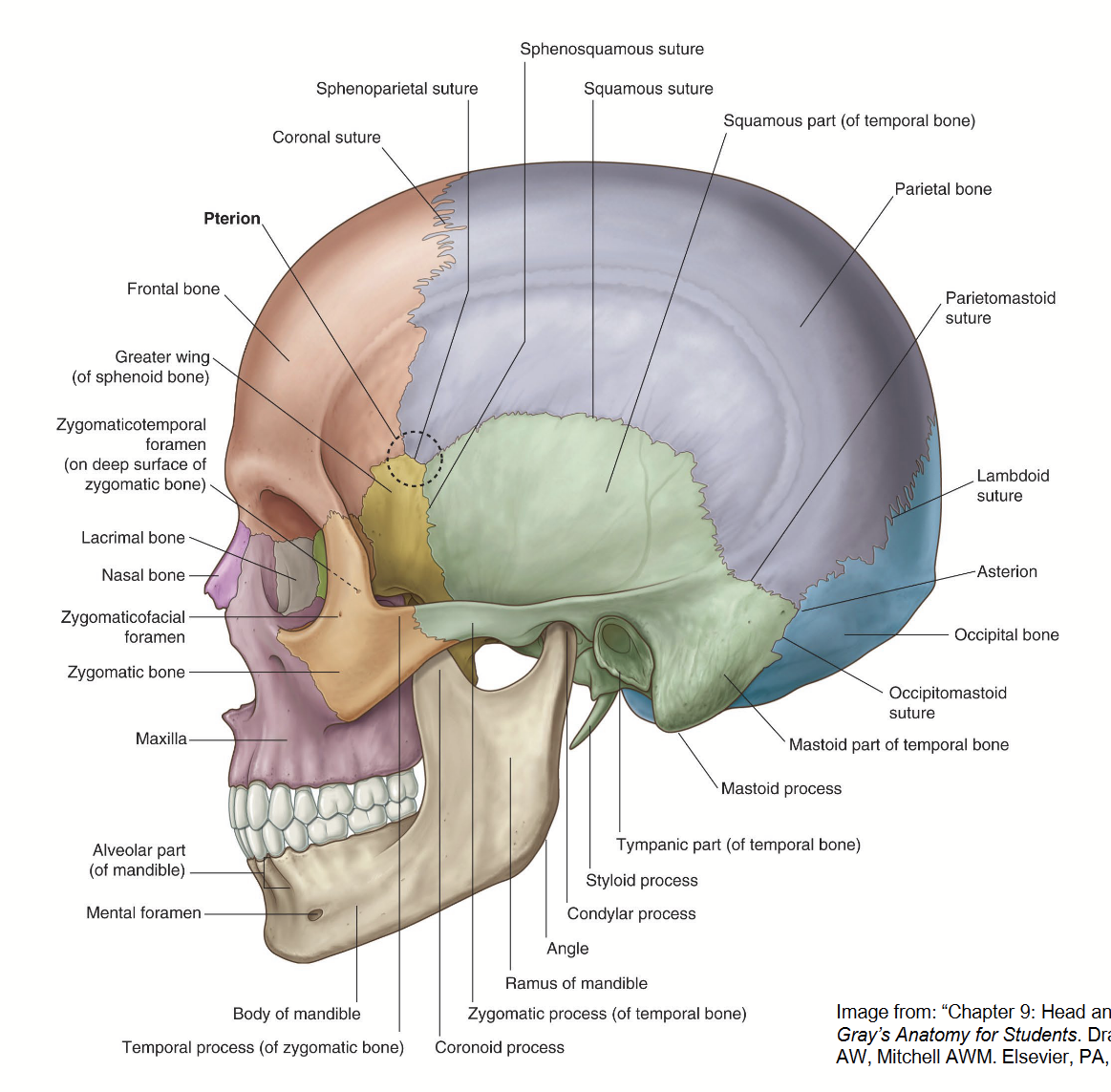
What is the pterion
Area in the temple region where five sutures join.
Sutures contain no diploe (only inner and outer table) = thinnest and weakest portion of the skull.
The 5 sutures that form the Pterion
coronal suture: joins frontal bone to sphenoid and parietal bones
sphenosquamous suture: joins sphenoid and temporal bones
squamous suture: joins temporal bone to sphenoid and parietal bones
sphenoparietal suture: joins sphenoid and parietal bones
sphenofrontal suture: joins sphenoid and frontal bones
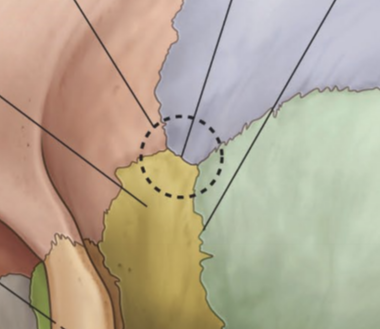
Parietal bone attachment sites for what muscle and where?
attachment sites for tempoarlis muscle at the superior temporal line and inferior temporal line
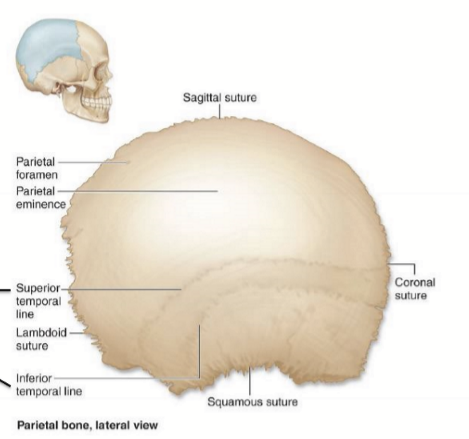
Portions of the temporal bone
squamous portion
mastoid portion
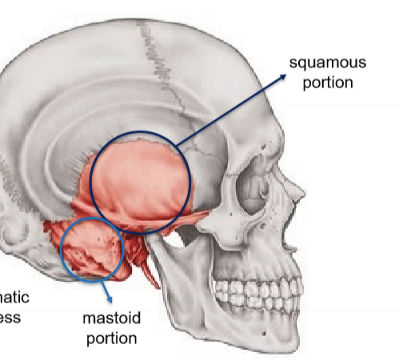
Structures found on temporal bone
external acoustic meatus
mastoid forament
mastoid process (attachment for sternocleidomastoid muscle)
styloid procces
mandibular fossa
zygomatic process
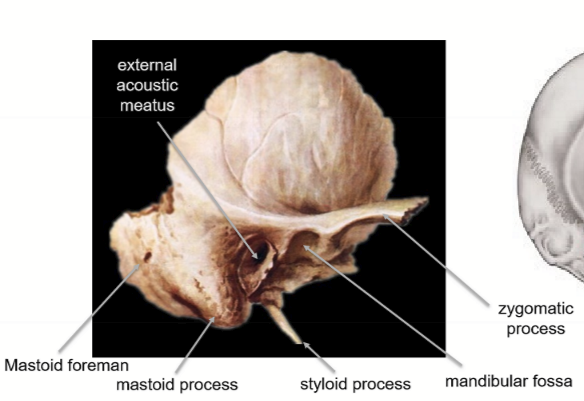
Temporal Bone Fossas
Temporal fossa
Infratemporal fossa
mandibular fossa
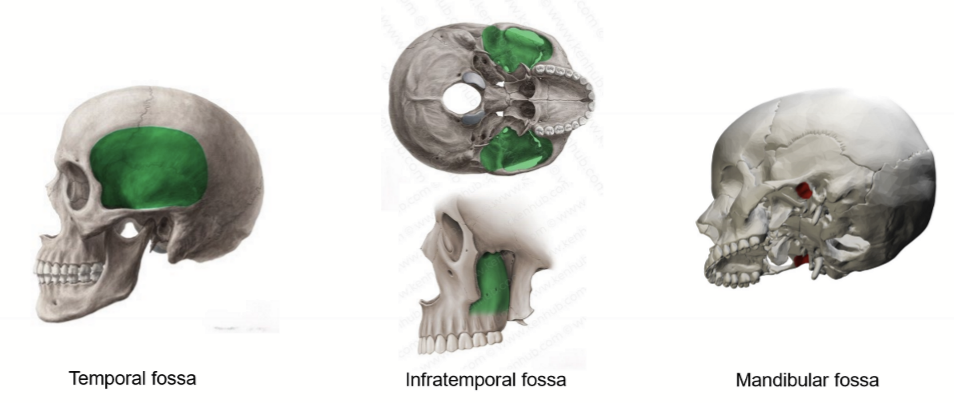
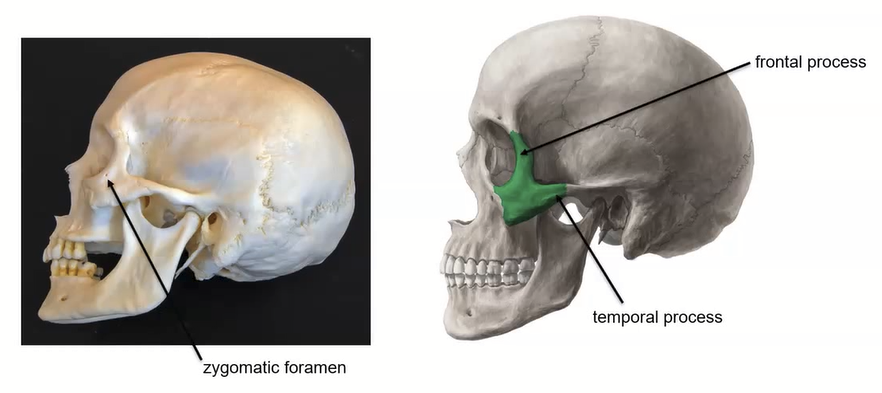
Zygomatic bone’s unique features
zygomatic foramen
frontal process
temporal process
Sutures seen from norma lateralis
coronal suture
lambdoid suture
squamous suture
parietomastoid suture
occipitomastoid suture
spehnosquaosal suture
sphenoparietal suture
sphenofrontal suture
sphenozygomatic suture
zygomaticontemporal suture
zygomaticonfrontal suture
zygomaticomaxillary suture
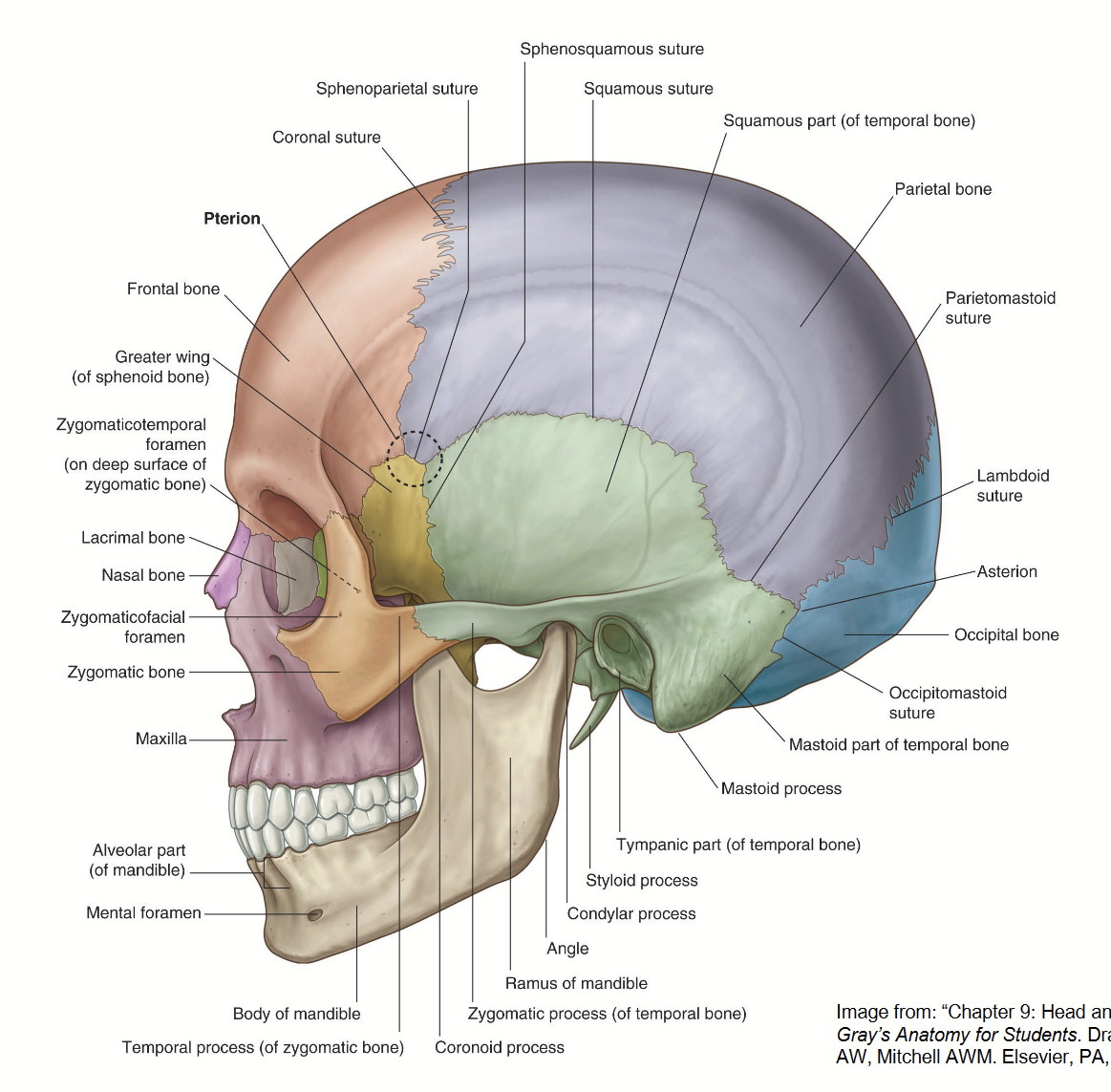
Norma Lateralis openings visible and other notable features
Openings:
eternal acoustic meatus
mental foramen
zygomatic foramen
Other notable features
temporal fossa
infratemporal fossa
zygomatic arch
asterion
pterion
What does the parietal foramen contain and what views can see it?
Emissary veins
Norma verticalis & norma dorsalis
What does the mental foramen contain and what views can see it?
Mental nerve
Norma Lateralis
What does the zygomatic foramen contain and what views can see it?
zygomatic nerve
Norma lateralis
What does the external acoustic meatus contain and what views can see it?
conducts sound waves from auricle to tympanic membrane
Norma lateralis
What is contained in the mandibular foramen and what makes this foramen unique?
It contains the mandibular nerve, but it is not “visible from any normal skull view”
Bones visible from Norma Frontalis
frontal bone
2 parietal bones
2 temporal bones
2 zygomatic bones
2 maxillary bones
mandible
2 nasal bones
spehnoid
ethomoid
2 lacrimal bones
vomer
2 inferior conchae
2 palatine bone - in orbit
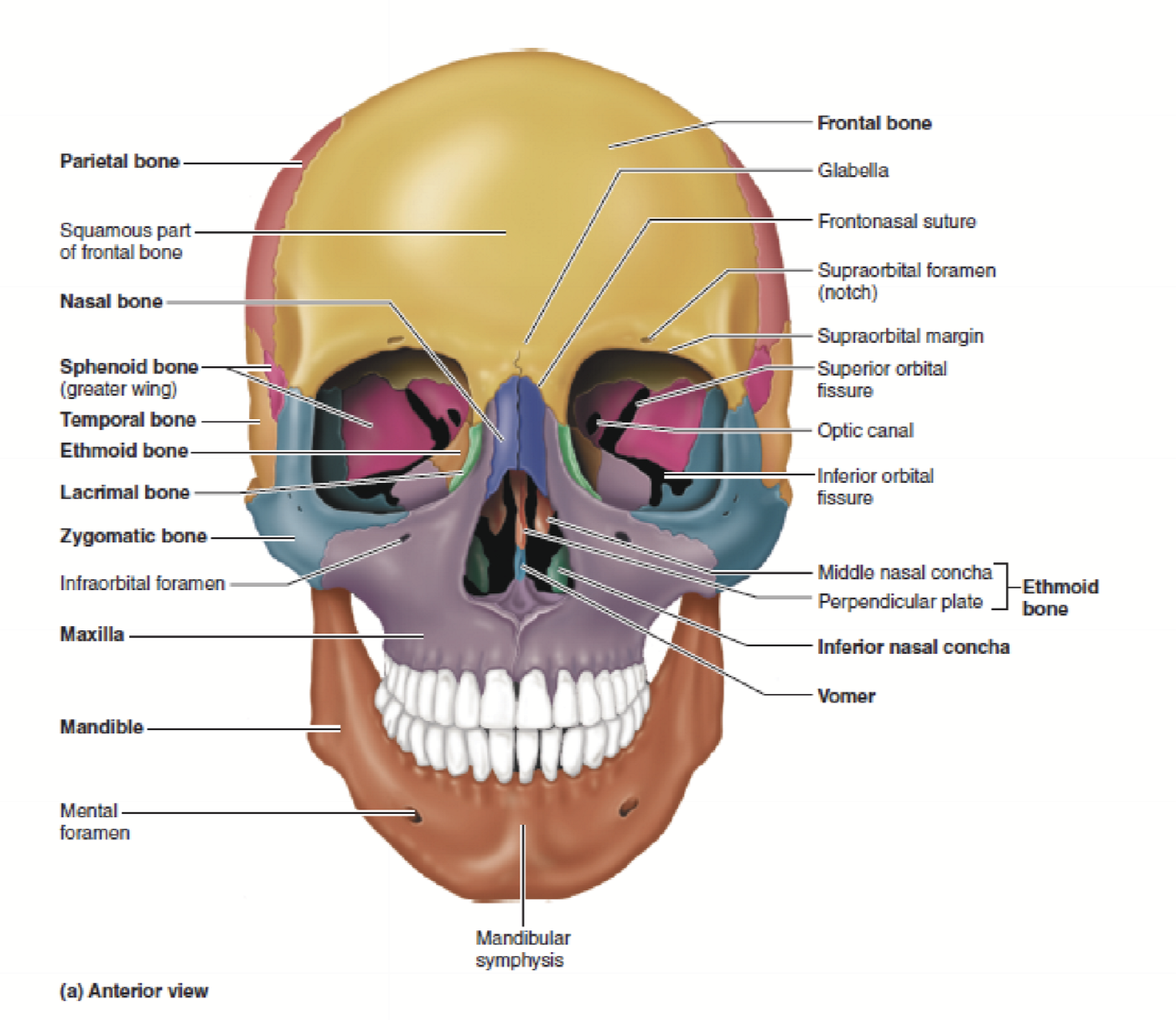
Bones that compose the lateral wall of orbit
greater wing of sphenoid
zygomatic bone
“the Great Z
Bones that compose the floor of orbit
Maxilla
Palatine
Zygomatic
“My Pal gets Z’s on the floor”
Bones that compose the medial wall of the orbit
Ethmoid = thinnest
lacrimal = thinner
maxillary
spheniod lesser wing
ELMS
Bones that compose the roof of the orbit
Frontal bone
lesser wing of sphenoid
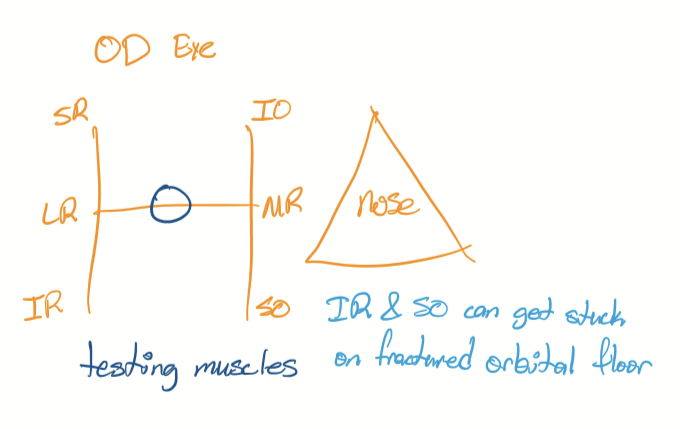
Innervation of eye muscles
CN3, CN 4, CN6
Mnemonic for CN innervation of orbit muscles
(LR6SO4)3 = Lateral Rectus CN6; Superior Oblique = CN4; all other muscles CN3
Orientation of CNs responsible for eye movement in certain directions (H chart thing)