prostaglandins, thromboxanes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
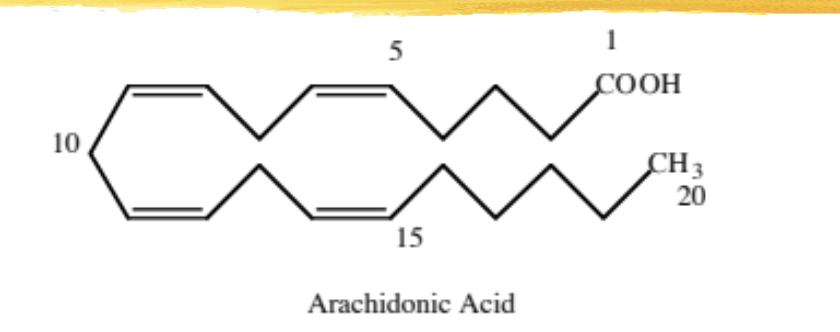
arachidonic acid (AA)
20 carbon poly-unsaturated fatty acid
precursor to the PG, TX, and leukotrienes
stored in cell’s lipid membrane as a phospholipid
can be metabolized once released by cyclooxygenase/lipoxygenase
phospholipase A2
lipase that regulates the release of AA
activation of this occurs in response to tissue damage, toxin exposure, and hormonal stimulation
glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone)
suppress phospholipase A2 activity
considered anti-inflammatory
how do we determine whether or not AA will be metabolized by cyclooxygenase and/or lipoxygenase?
dependent on cell/tissue type and the type of stimuli
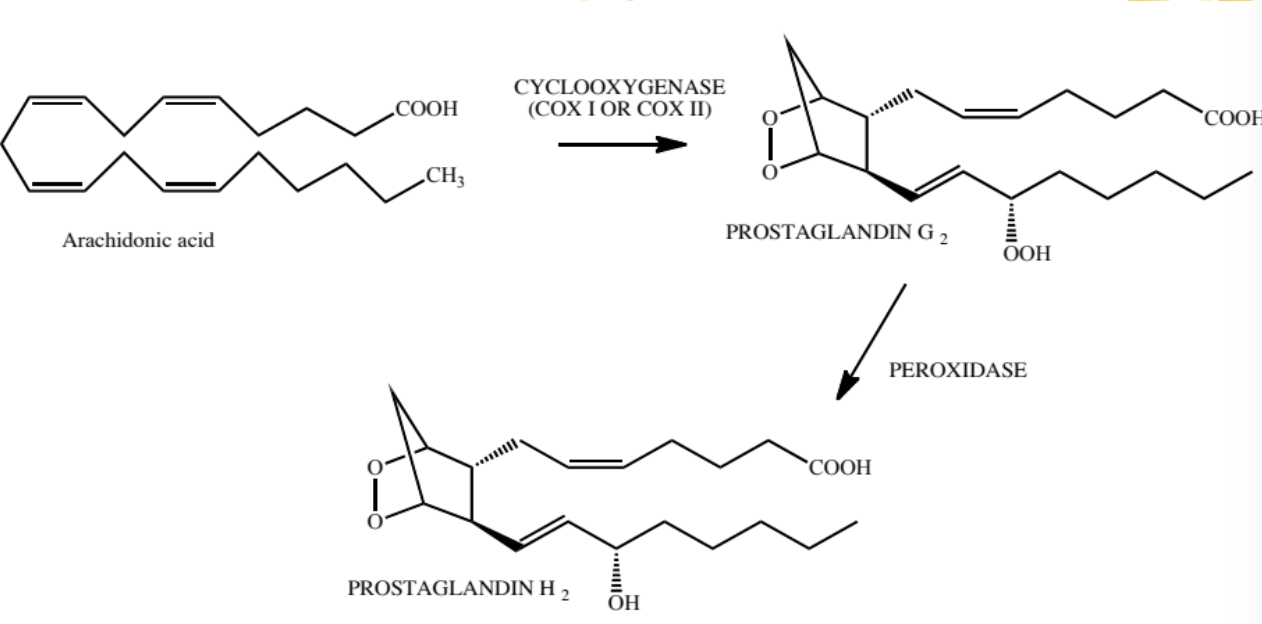
prostaglandin synthesis general process
prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) is converted by specific enzymes to each type of PG
the amount of each specific synthetase released varies from tissue to tissue
the specific type of prostaglandin produced is dependent on where PGH2 is produced
platelets have high concentrations of:
TXA synthetase
TXA2 is released and causes aggregation/vasoconstriction in response to vascular injury
vascular endothelial cells have high concentrations of:
PGI synthetase
PGI2 is produced by uninjured cells to control platelet aggregation/constriction
cyclooxygenase (COX) I
always present in all tissues that produce PG and TX
is involved in: gastric protection, platelet aggregation, inhibition of platelet aggregation (which is COX II mediated), vasoconstriction/dilation
COX II
inducible and present in inflammation
increased amounts are produced in inflammatory and immune cells in response to growth factors, tumor promotors, cytokines, and endotoxins
corticosteroids can inhibit its expression
it is also normally present in certain tissues
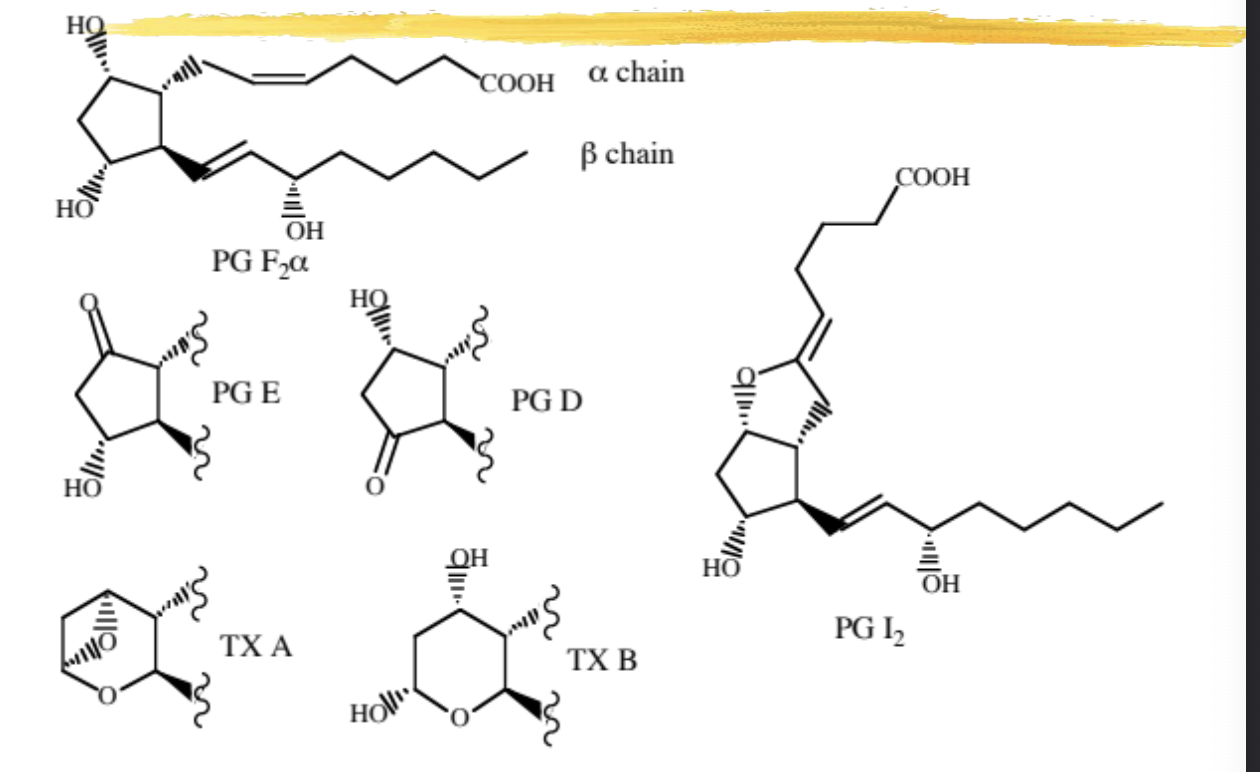
PG nomenclature characteristics
see image for nomenclature details
5,6 double bond is always Z/cis
13,14 double bond is always E/trans
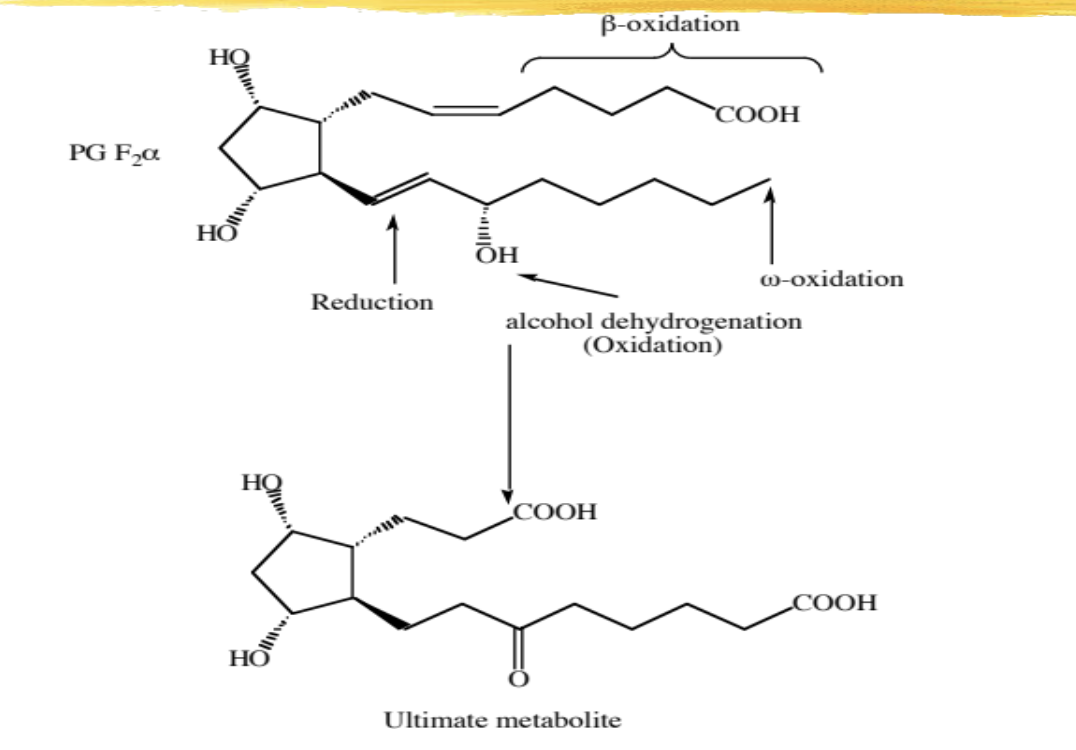
enzymatic metabolism and degradation of PG
see image for details
involves beta oxidation of one of the tails
reduction of the 13, 14 DB
changing of the 15 alcohol to a ketone
and addition of a COOH on the end of the second tail
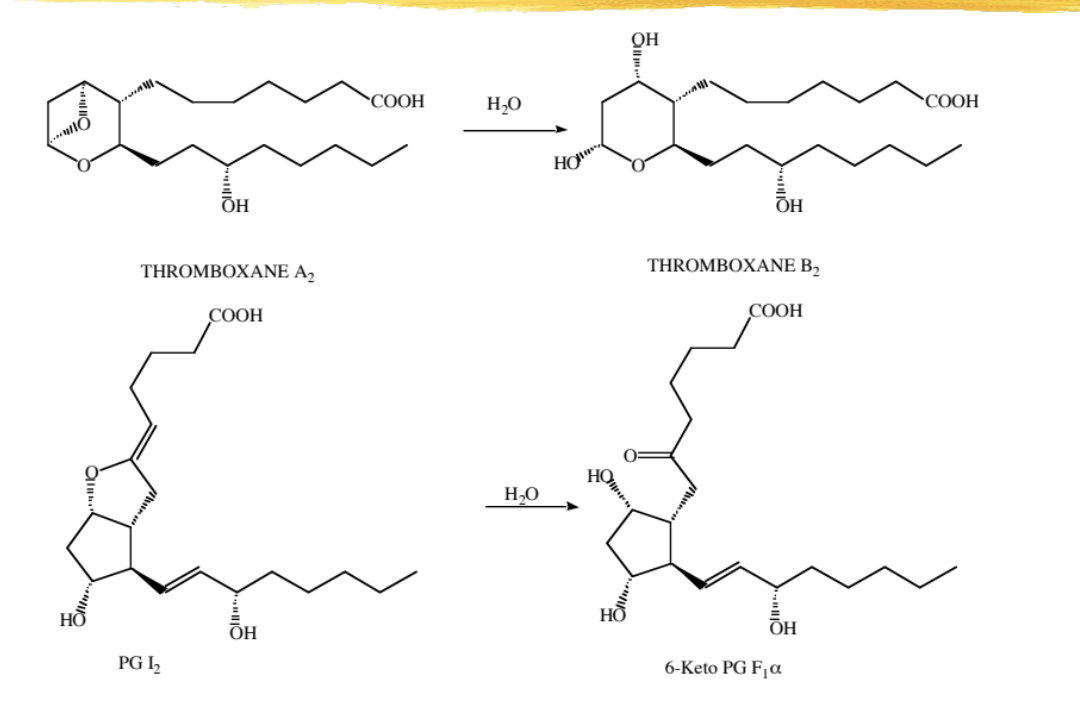
chemical metabolism and degradation of PG
see image for details
involves using water to reduce the epoxide to 2 alcohol groups in thromboxane A2 to B2
using natural PGs as drugs
natural PGs are very potent but:
susceptible to rapid degradation
short half life
effect is dependent on tissue
not orally active (due to degradation)
can cause NVD and cramping
generally applied/injected into the desired tissue
using modified PGs as drugs
chemical modification increases half life and ease of delivery
COOH → ester = increased lipophilicity
adding a phenyl/acetylene group increases lipophilicity and prevents oxidation
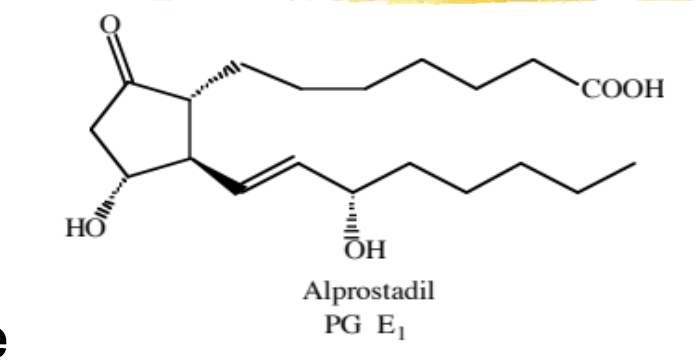
aprostadil
natural PG that is used to treat ED (urethral suppository) and ductus arterious-dependent congenital heart defects
ED: causes relaxation of arterial smooth muscle, increasing blood flow
heart defect: relaxation of ductus so that blood can continue to flow from the pulmonary vein to the aorta
ADME: short duration, ~80% first-pass metabolism
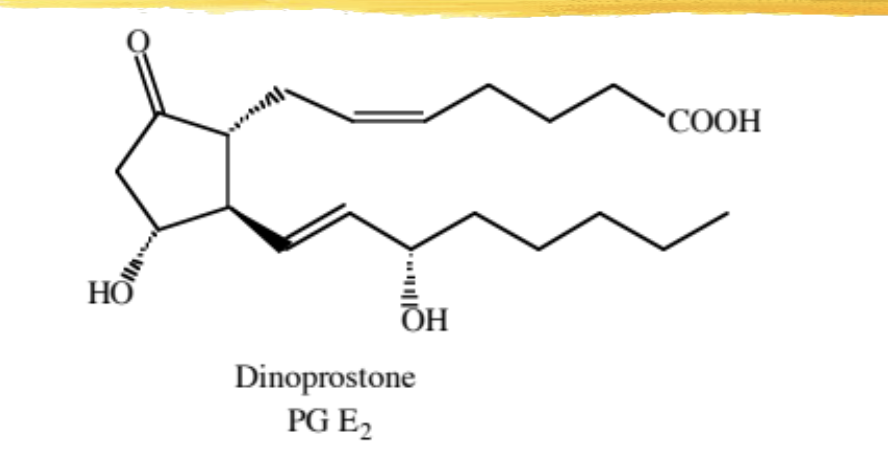
dinoprostone
natural PG that is used to cause cervical ripening and labor induction at or near term (vaginal suppository, endocervical gel), for 2nd trimester pregnancy termination, or for evacuation of uterine contents in fetal death
may take up to 17hrs to work
mechanism: causes uterine contractions
this is one reason why NSAIDs should not be used in pregnancy
ADME: 95% first pass through lungs, half life 2.5-5min, some systemic absorption, can cause n/v and increased body temp
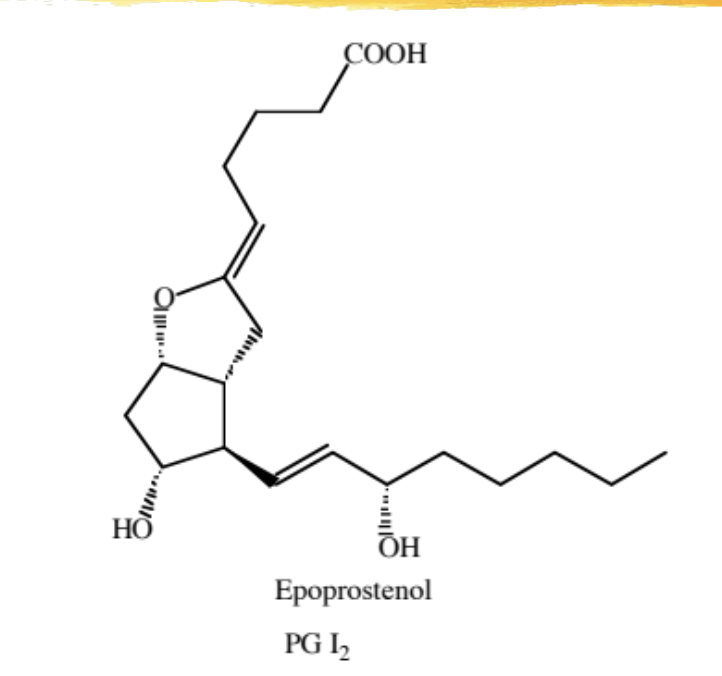
epoprostenol
natural PG used for primary pulmonary hypertension or scleroderma
mechanism: causes vasodilation of pulmonary and systemic vessel beds and inhibits platelet aggregation - directly opposes TXA2
ADME: 6min half life (continuous infusion required), inactivated through hydrolysis at physiological pH, effect dissipates 2-3min after end of infusion
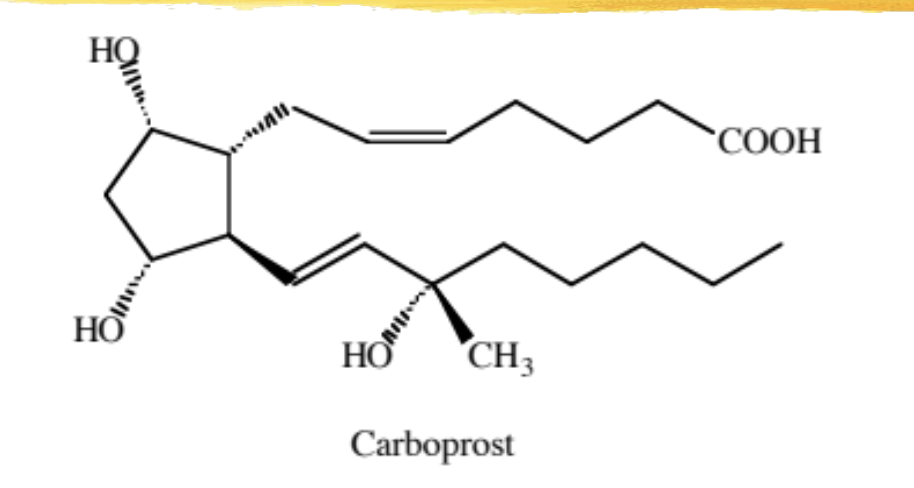
carboprost
15 methyl PGF2-alpha
modified PG used to treat postpartum bleeding that does not respond to conventional methods (IV oxytocin, uterine massage, IM ergot) or for 2nd trimester abortions
given IM due to 15-methyl 15-OH not converting to ketone
DOA is 4hrs
ADRs: n/v/d, bronchoconstriction, increased body temp
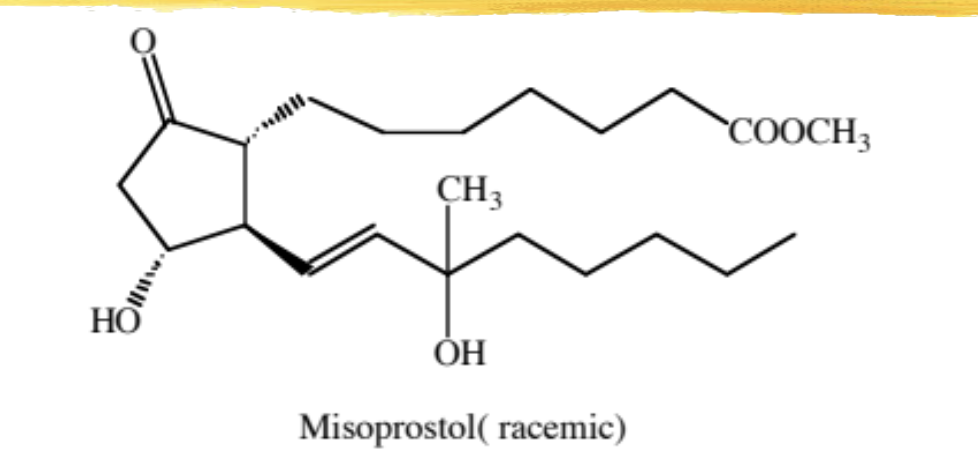
misoprostol
15 methyl PGE1 methyl ester
modified PG used to prevent NSAID-induced gastric ulcers in high risk populations (elderly, debilitating disease, history of gastric ulcers)
ADME: extensively absorbed, rapid hydrolysis to free acid (active form), oxidation of both chains and ring ketone reduction inactivates it, food/antacids decrease absorption, 80% excreted in urine. increased ½ life in renal impairment
mechanism: anti-secretory (decrease gastric acid) and mucosal protective. NSAIDs inhibit PG synthesis in gastric cells which can cause mucosal damage
WARNING: due to PGE2 and PGF2 similarity, it can induce abortions
ADRs: abdominal pain, n/v/d, Increased body temp
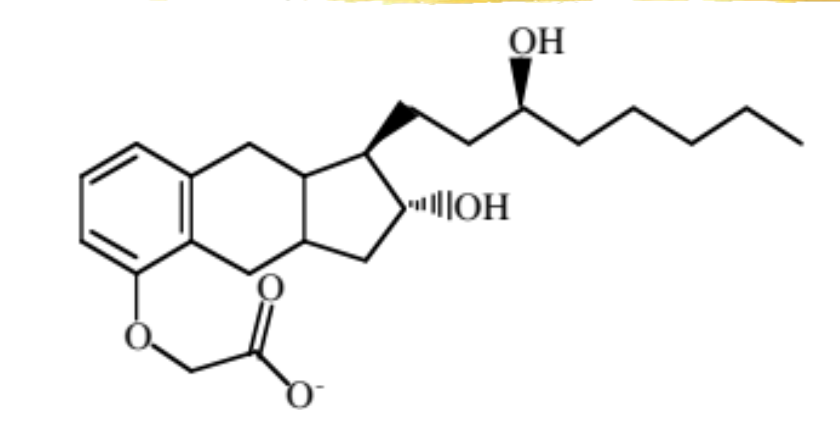
treprostinil
PGI2 analog
advantage: chemically stable and can be given SQ continuous infusion outpatient
used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH)
mechanism: causes vasodilation and inhibits platelet aggregation
ADME: 100% absorbed SQ, 91% protein bound, extensive CP450 metabolism but does not inhibit major enzymes, major route of elimination is in the urine as metabolites
ADR: infusion site pain/rxn, hypotension
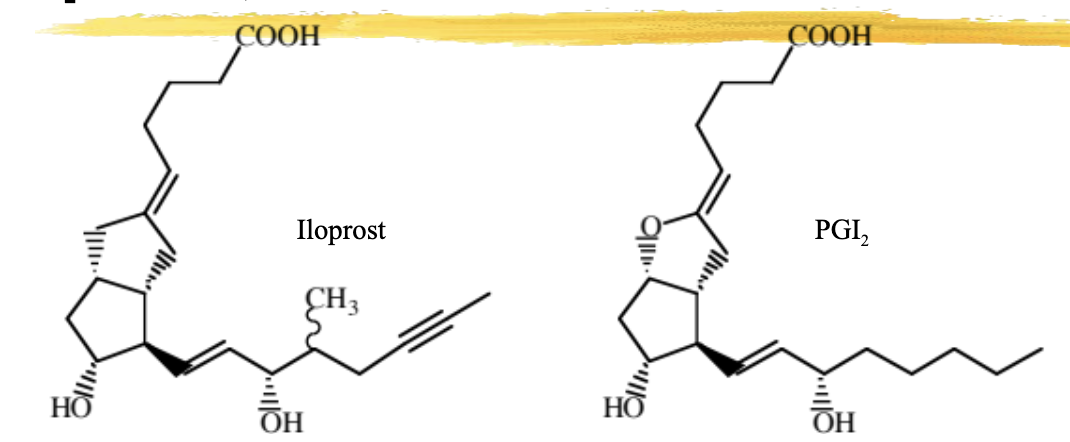
iloprost
PGI2 analog, but note no oxygen-containing ring = stable
16-methyl inhibits oxidation of OH
acetylene group increases lipid nature and inhibits oxidation
used for PAH
causes vasodilation and inhibits platelet aggregation
ADME: inhaled, 60% protein bound, metabolized by beta oxidation of CA chain, eliminated as free and conjugated metabolites in urine
ADR: hypotension
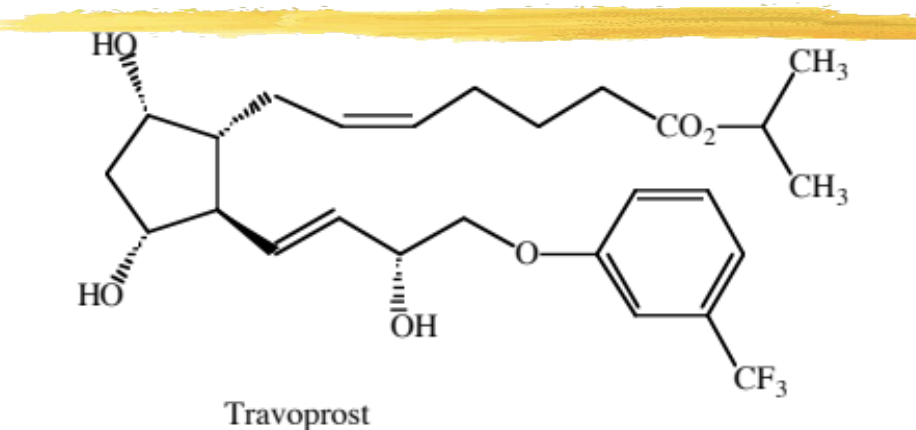
travoprost
F series modified PG ophthalmic analog with an isopropyl ester and aromatic ring
used to decrease IOP in pts with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension who are intolerant to other agents
MOA: selective PF receptor and increases outflow
ADME: absorbed across the cornea, hydrolyzed by esterase, metabolized by beta oxidation
ADR: well tolerated, eyelid rim, eyelashes and pigmented eye tissue may darken
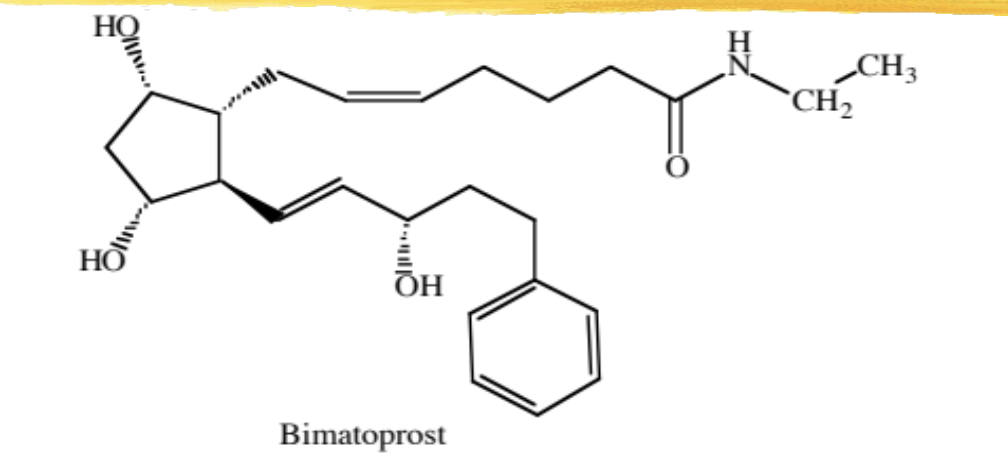
bimatoprost
F series modified PG analog with an amide and an aromatic ring
used to decrease IOP in pts with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension who are intolerant to other agents AND for eyelash browth
MOA: same as travoprost, but not a prodrug
ADME: absorbed across the cornea, redistribution leads to metabolism of inactive metabolites, parent and metabolites excreted via urine/feces
ADR: same as travoprost
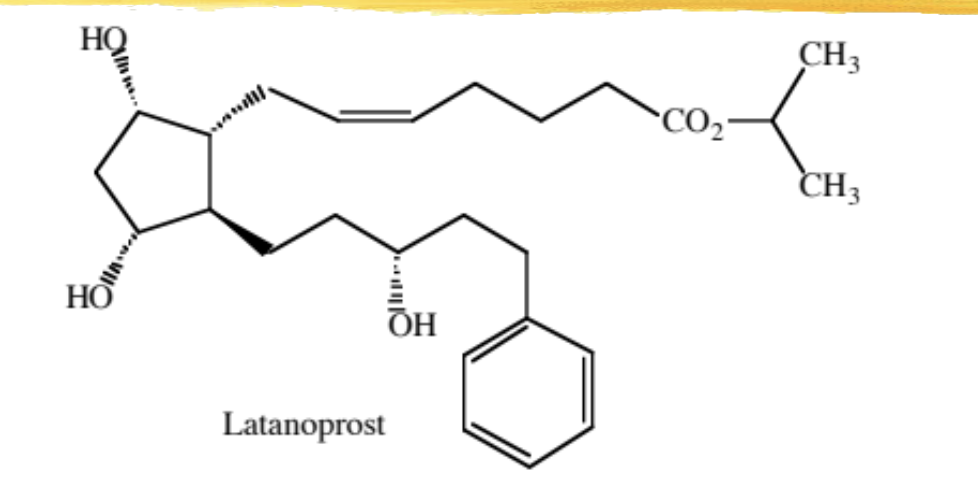
latanoprost
F series modified PG analog with a 13-14 DB isopropyl ester and an aromatic ring
use, MOA, and ADR same as travoprost
ADME: absorbed across cornea, ester hydrolyzed to free acid, eliminated in urine
no ketone metabolite observed
½ life: aqueous humor 4h, plasma 1h
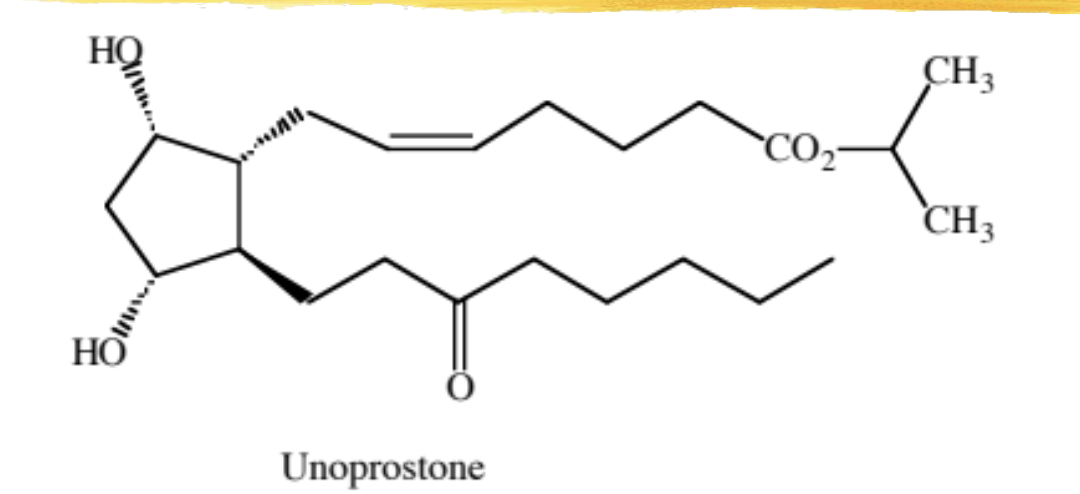
unoprostone
F series modified PG analog, no 13-14 DB or 15 ketone
uses, MOA, ADR same as others in the class
ADME: absorbed across cornea, hydrolyzed to free acid
low levels of free acid/ester in systemic circulation
excreted primarily unchanged
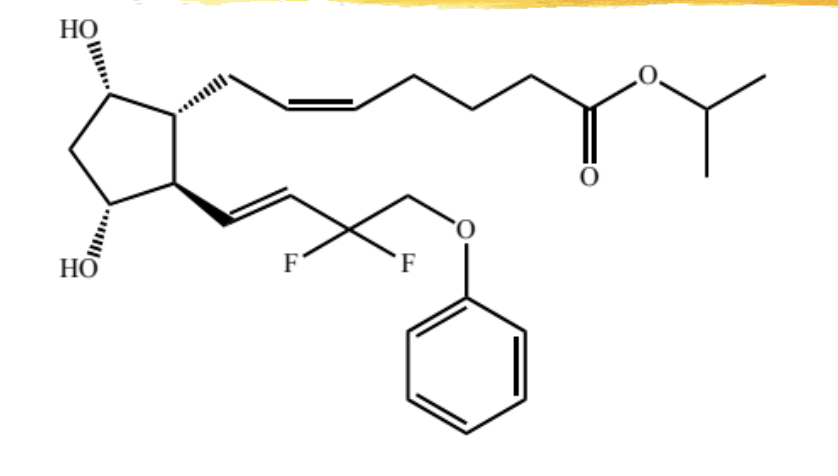
talfluprost
F series modified PG analog with a fluorine replacing the 15 OH
uses, MOA, ADR same as others in hte class
ADME: absorbed across cornea, hydrolyzed to free acid, low level of free acid/ester in circulation, metabolized in liver by beta oxidation and eliminated in urine