BSC2085L LESSON 11: Reflex Physiology and General Sensation
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
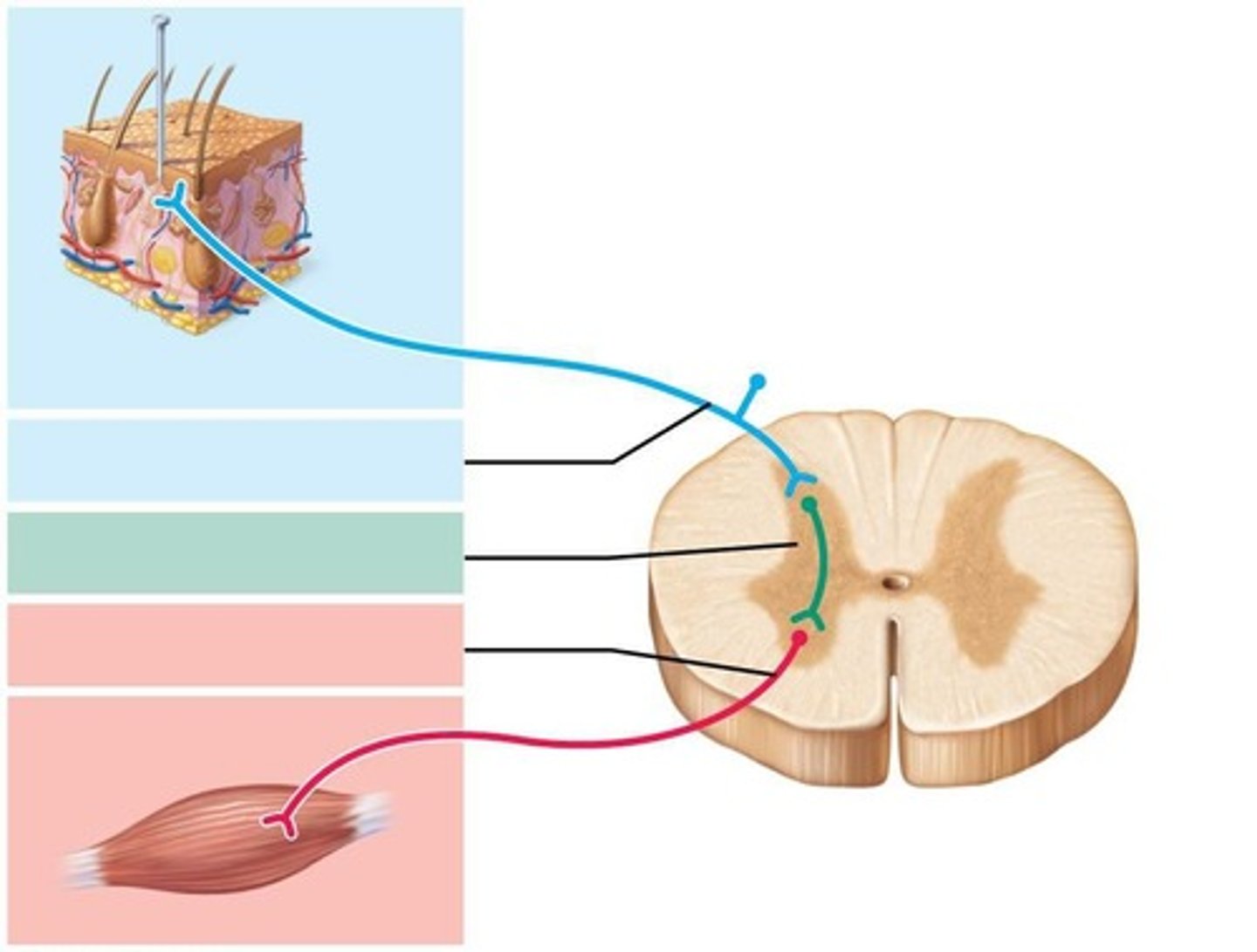
Reflex Arc
Mediated by neural paths (connections of neurons) to yield rapid involuntary muscle response to stimuli.
Autonomic Reflexes
Mediated through the autonomic nervous system (ANS) involving smooth muscles in digestion and glands in sweating.
Somatic Reflexes
Involve sensory stimulation that causes skeletal muscles to react, such as the withdrawal reflex from pain.
Receptor
Site of stimulus.
Sensory Neuron
Transmits afferent impulse to CNS
Integration Center
One or more synapses in the CNS.
Motor Neuron
Conducts efferent impulse to effector.
Effector
Muscle or glands that respond to impulses.
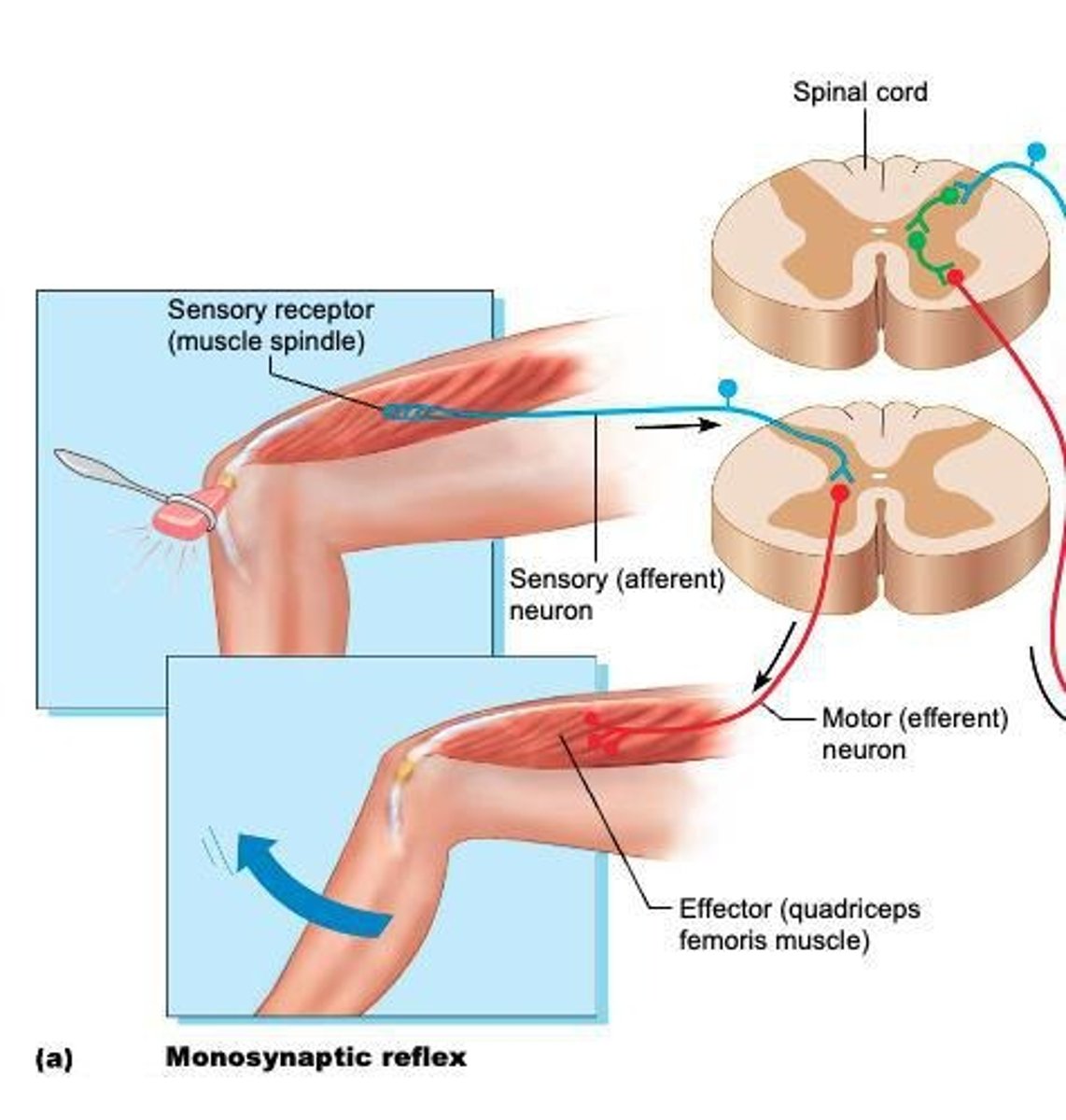
Monosynaptic Reflex Arc
Utilizes a 2 neuron (sensory and motor neurons) reflex arc with no interneuron, such as the knee-jerk reflex.
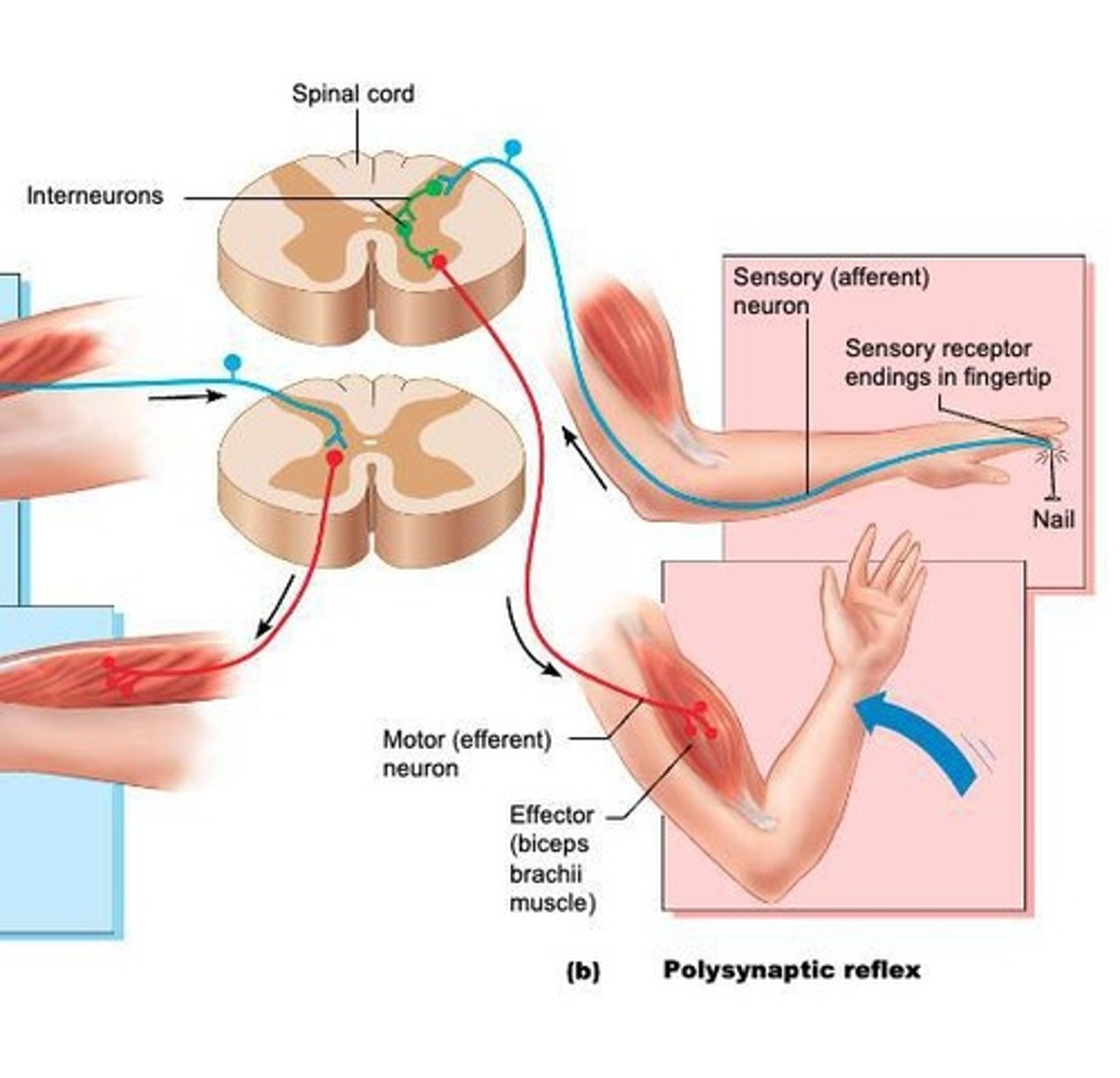
Polysynaptic Reflex Arc
Utilizes sensory and motor neurons connected by interneurons.
Stretch Reflex
Maintains posture/balance and locomotion; tendon stretch causes agonist muscle contraction and antagonistic relaxation.
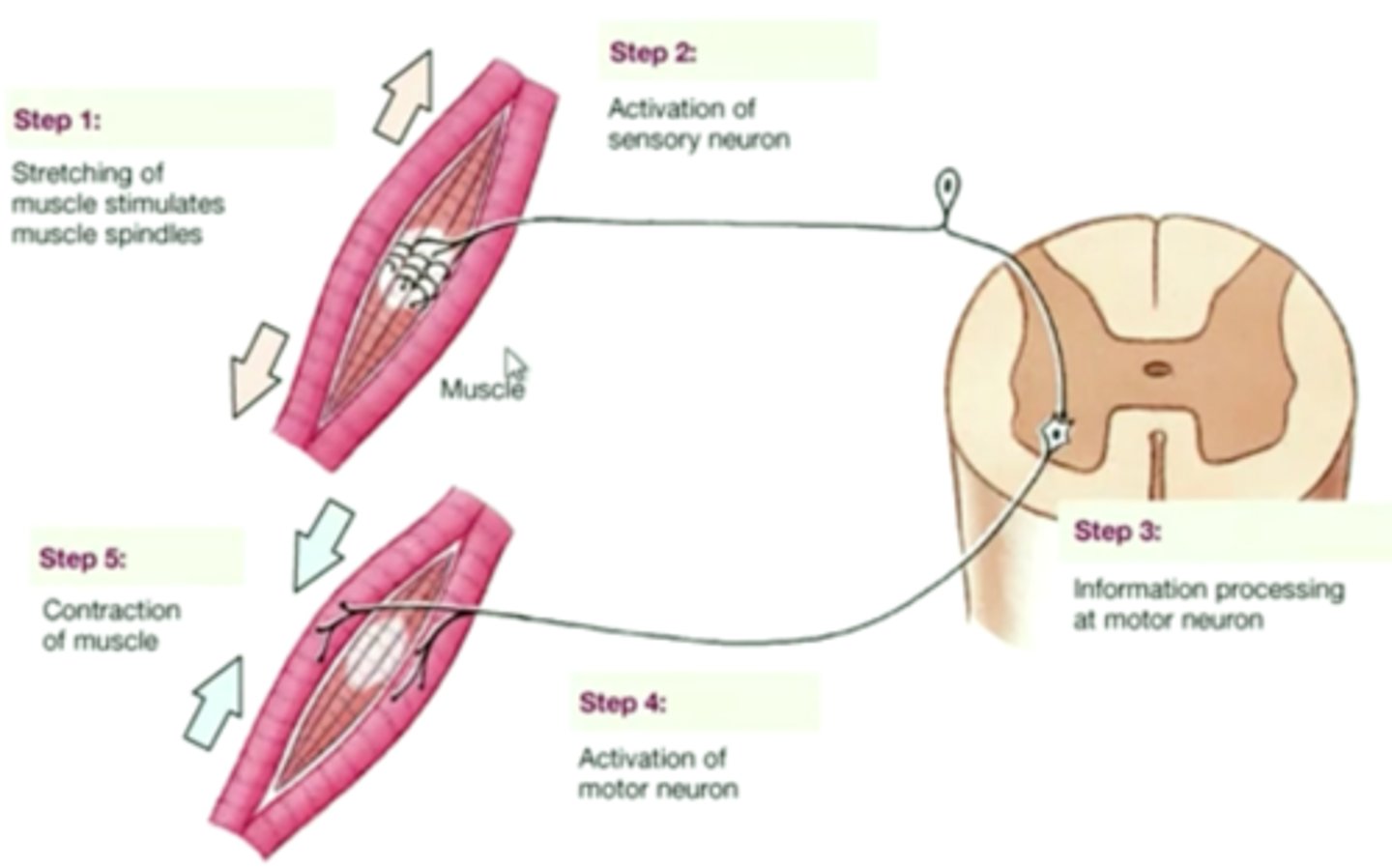
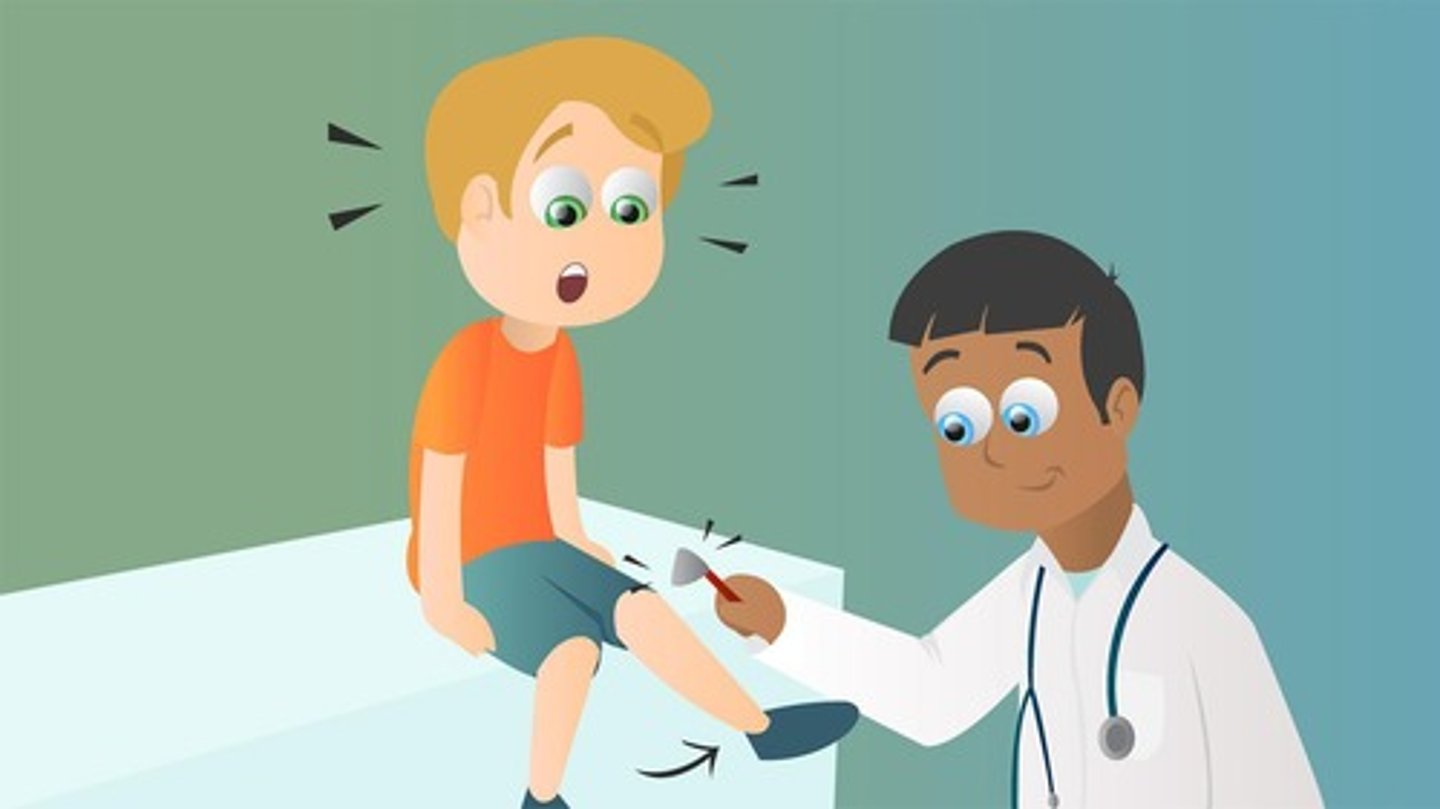
Patellar Reflex
Example of a stretch reflex, also known as the knee jerk reflex.

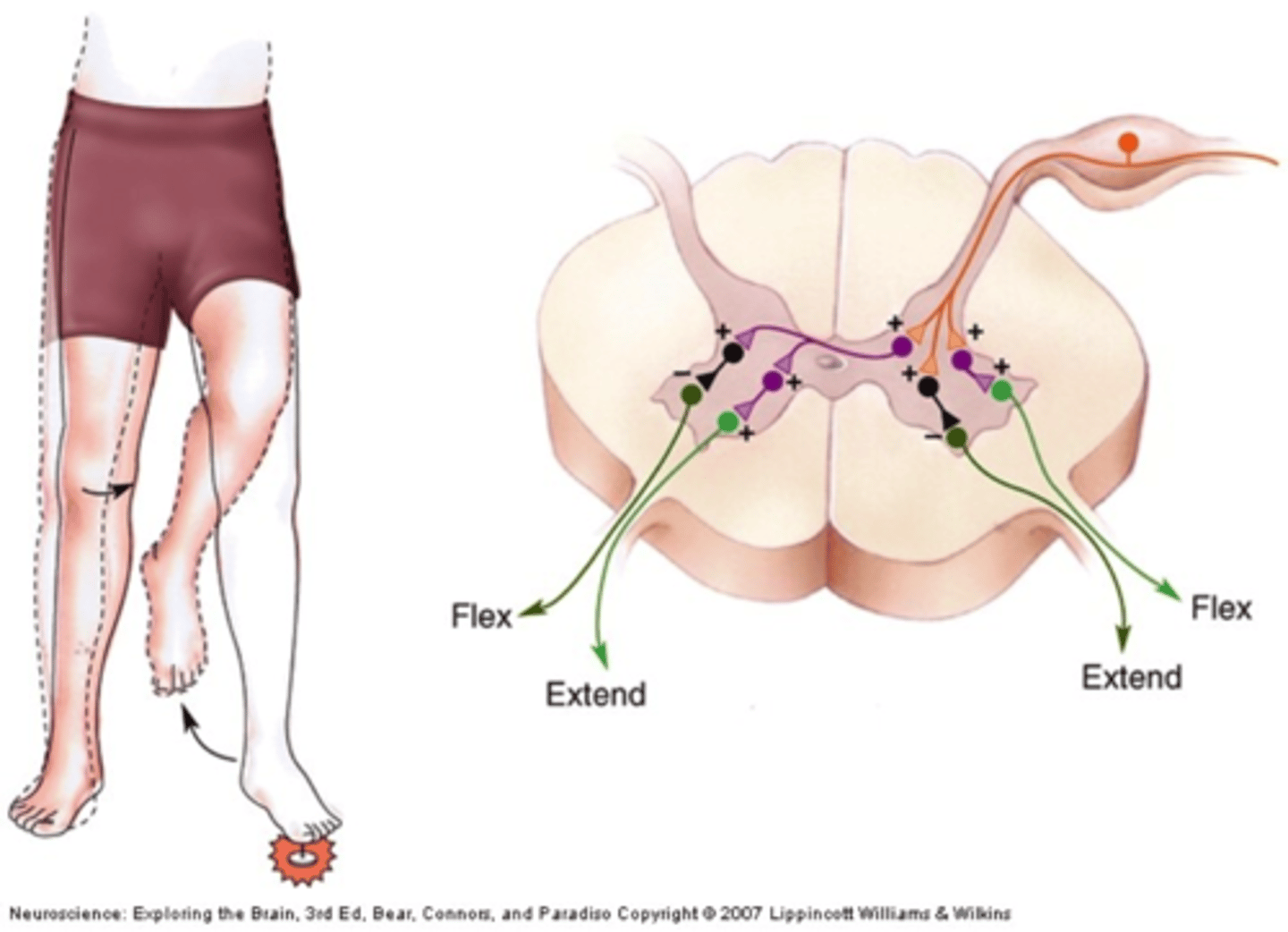
Crossed Extensor Reflex
Flexion of one limb followed by extension of the opposite limb.
Superficial Cord Reflex
Result from pain and temperature changes.
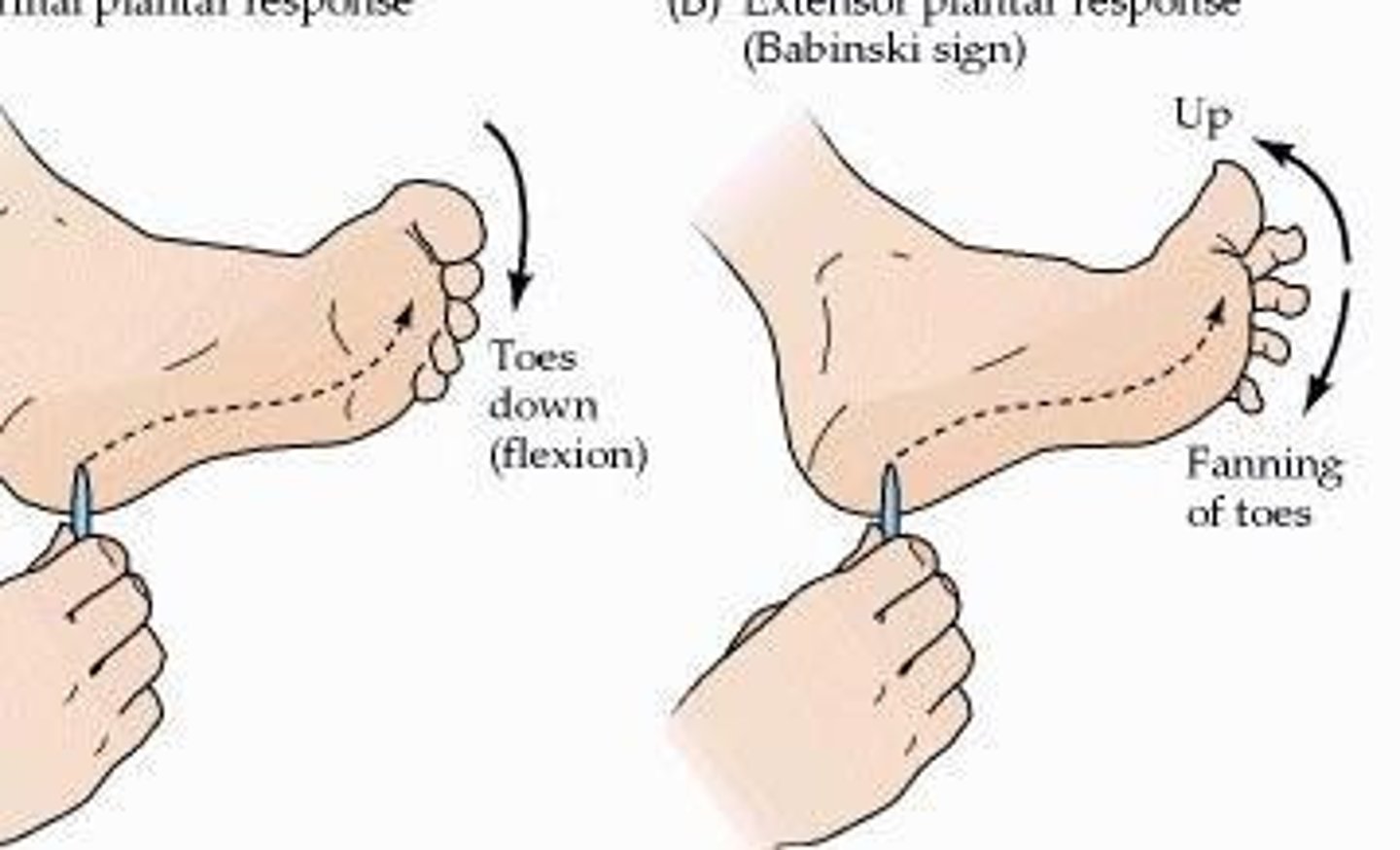
Plantar Reflex
Babinski's sign; abnormal response is flared toes, which may indicate ALS or other damage/disorder of CNS.
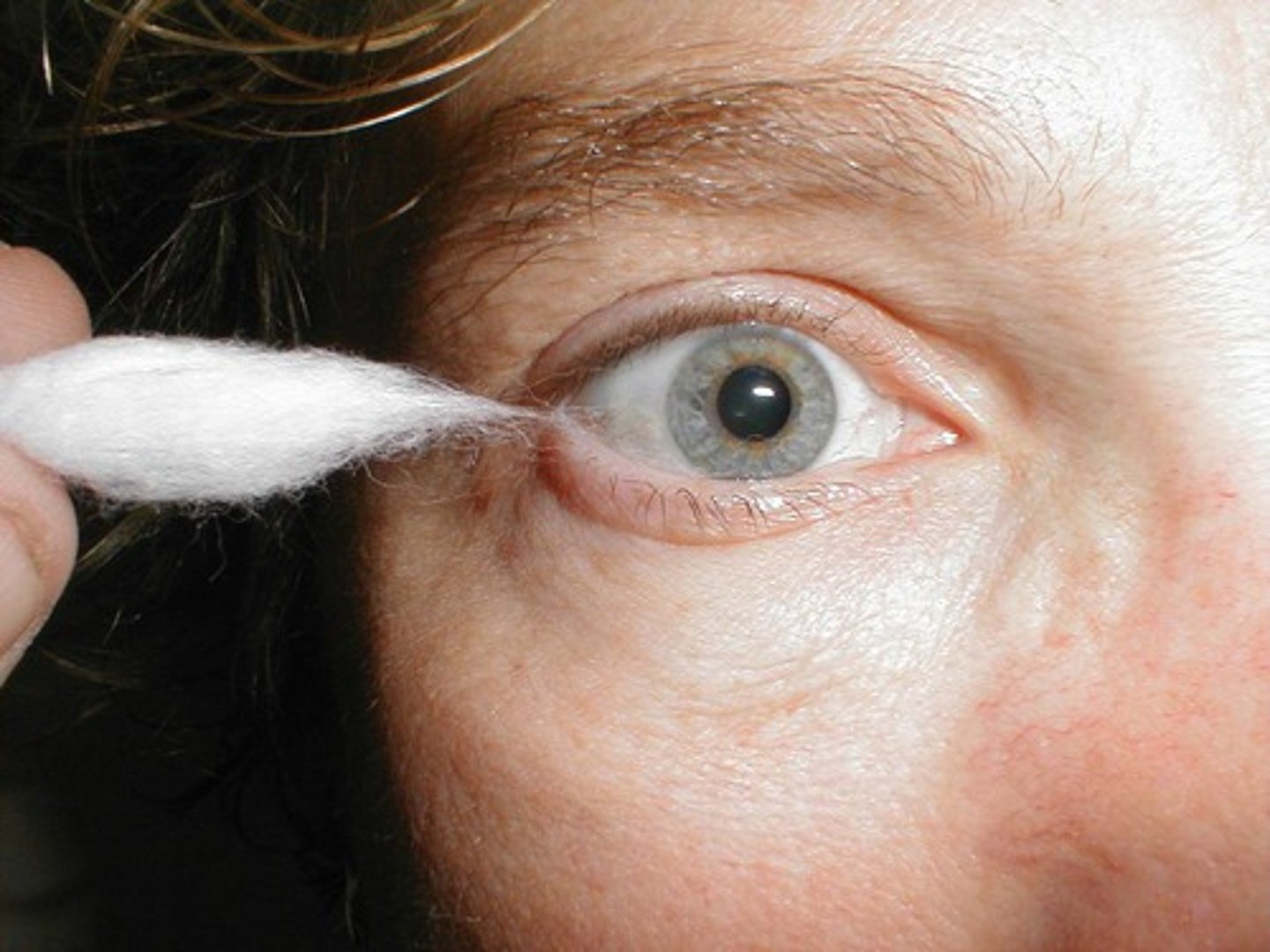
Corneal Reflex
A function of cranial nerve V (trigeminal); touching of the cornea causes blinking to occur.
Gag Reflex
A function of cranial nerves IX (glossopharyngeal) & X (vagus); touching of the uvula causes gag reflex.
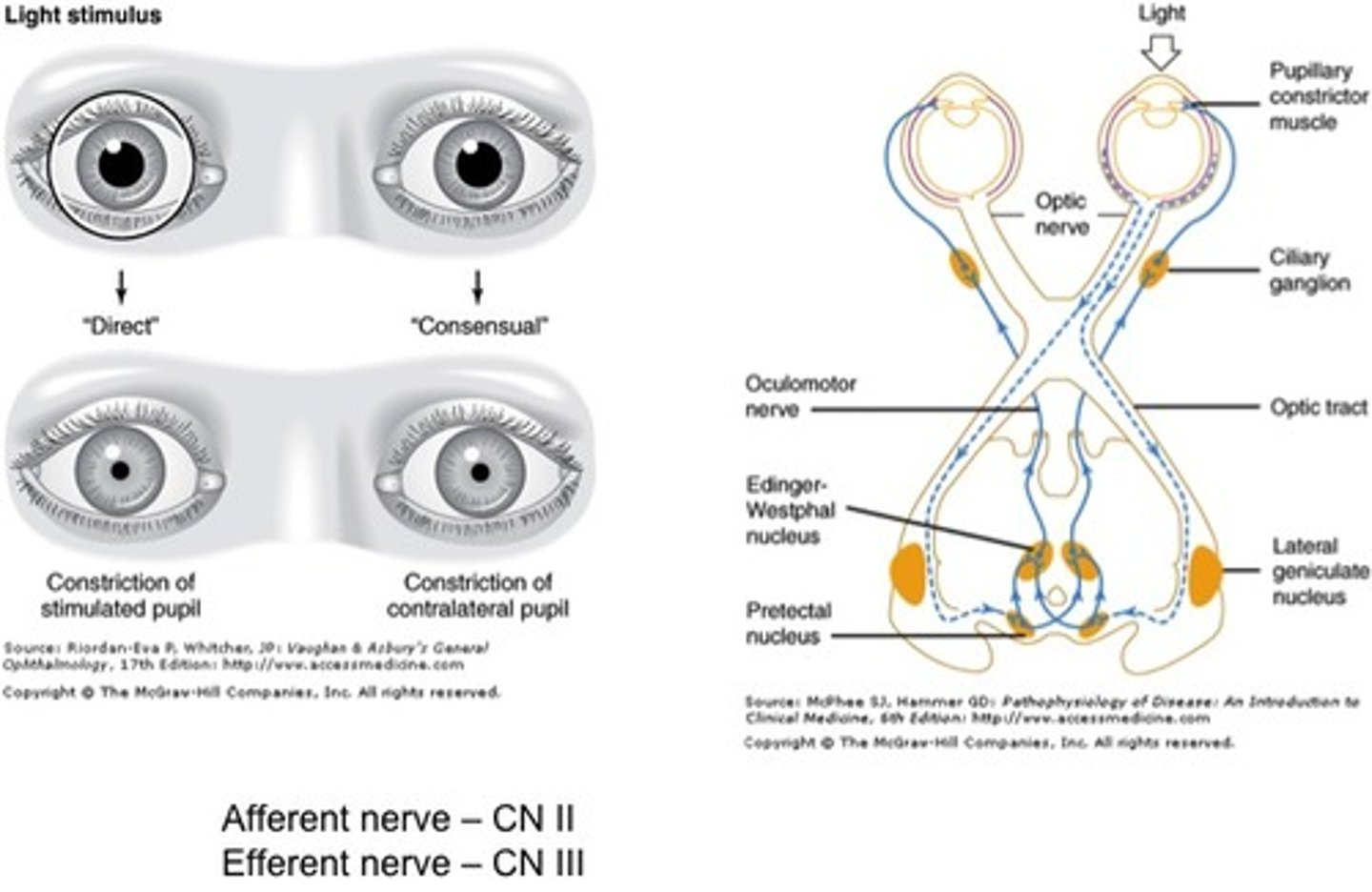
Pupillary Reflexes
Reflex caused by light stimulation of cranial nerve II (optic) causing iris constriction by cranial nerve III (oculomotor).
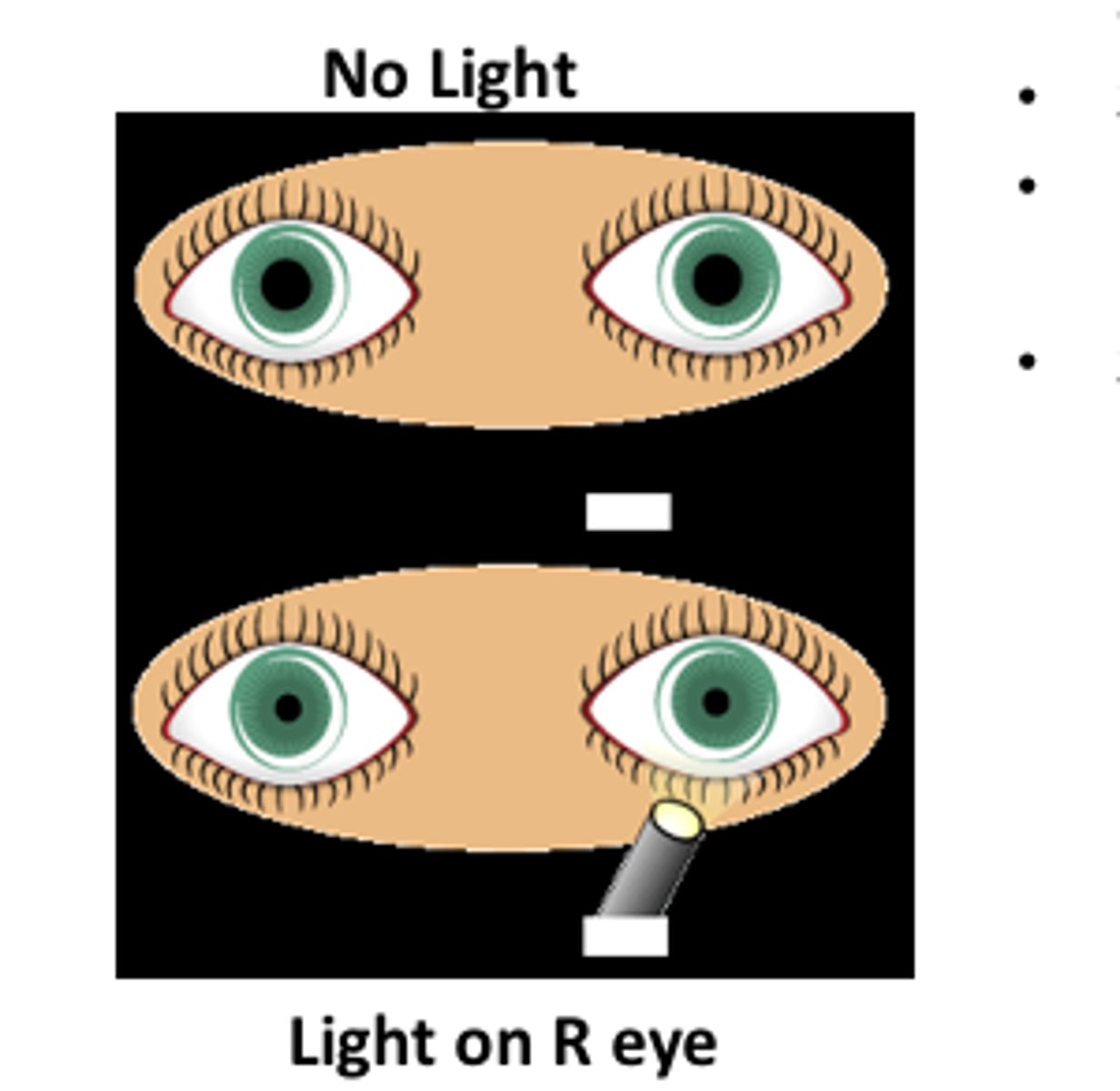
Pupillary Light Reflex
Pupil constricts due to light stimulus.
Consensual Reflex
Light stimulation of one eye causes pupil constriction in the contralateral (opposite side) eye.
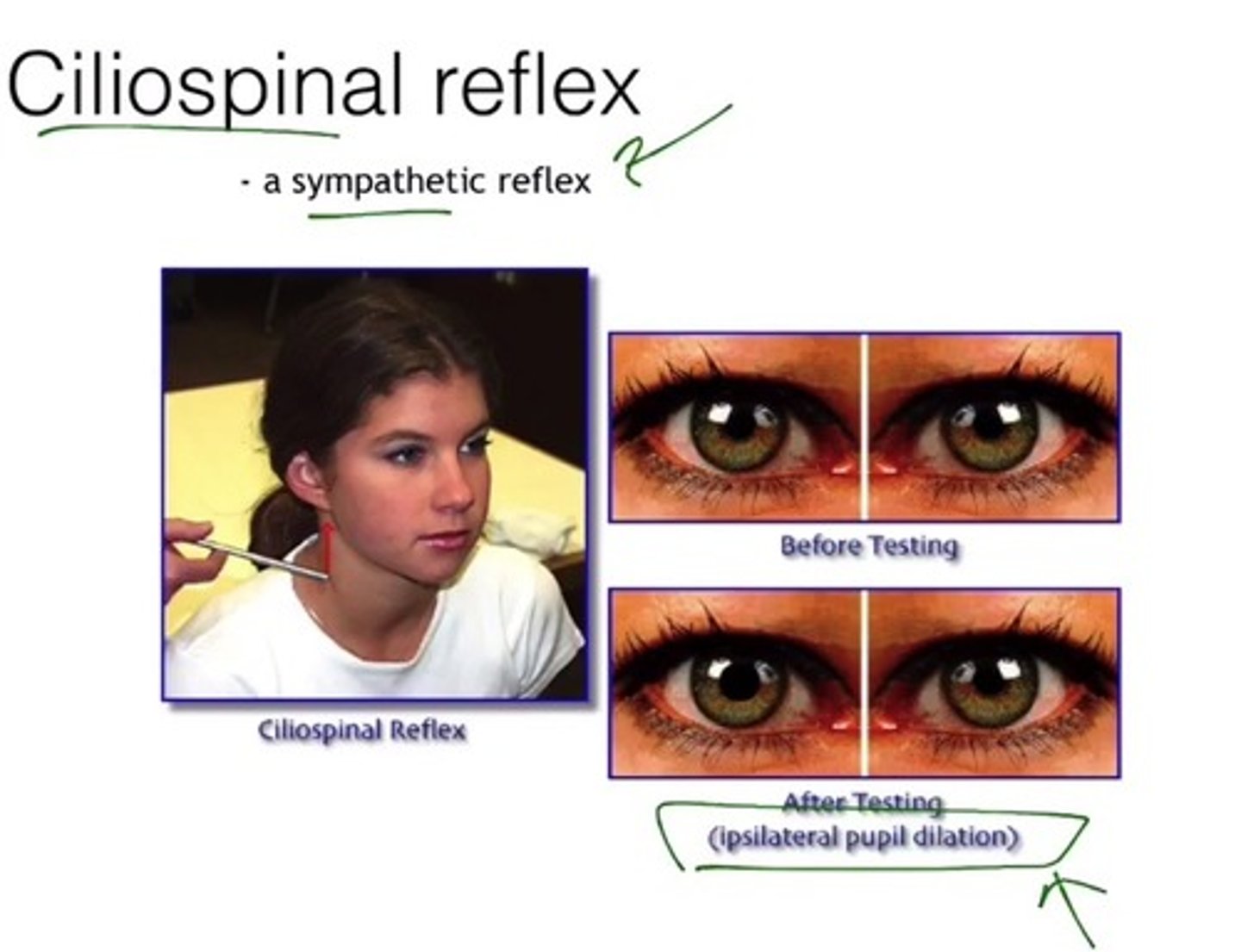
Ciliospinal Reflex
Stimulation (almost painful) of the back of the neck causes ipsilateral (same side) pupil dilation.
Salivary Reflex
Food odor detection causes salivation.
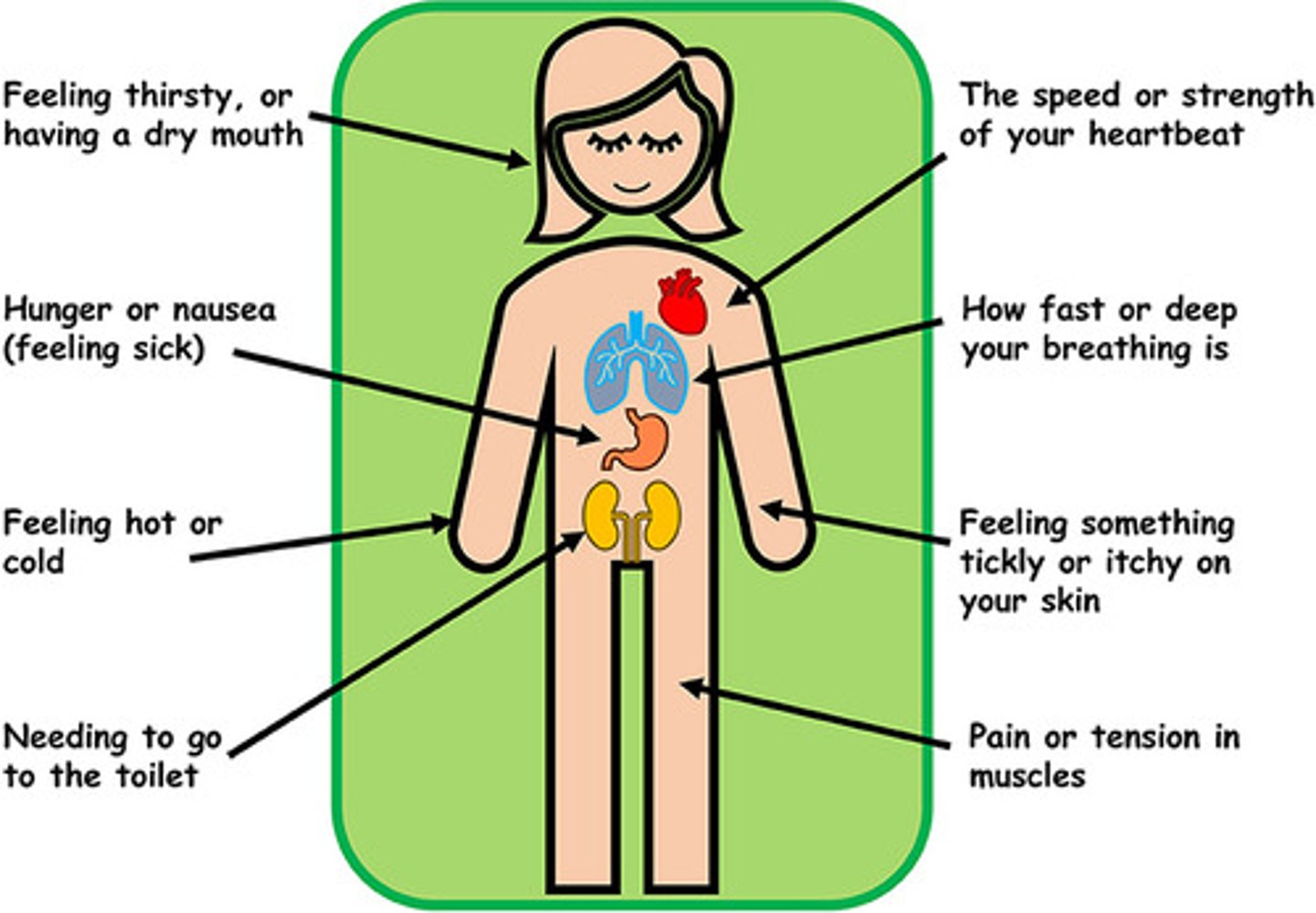
General Senses
General sensory receptors respond to touch, pressure, pain, heat, cold, stretch, vibration, & body position.
Special senses
Localized in groups; receptors for sight, hearing, equilibrium, smell, & taste.
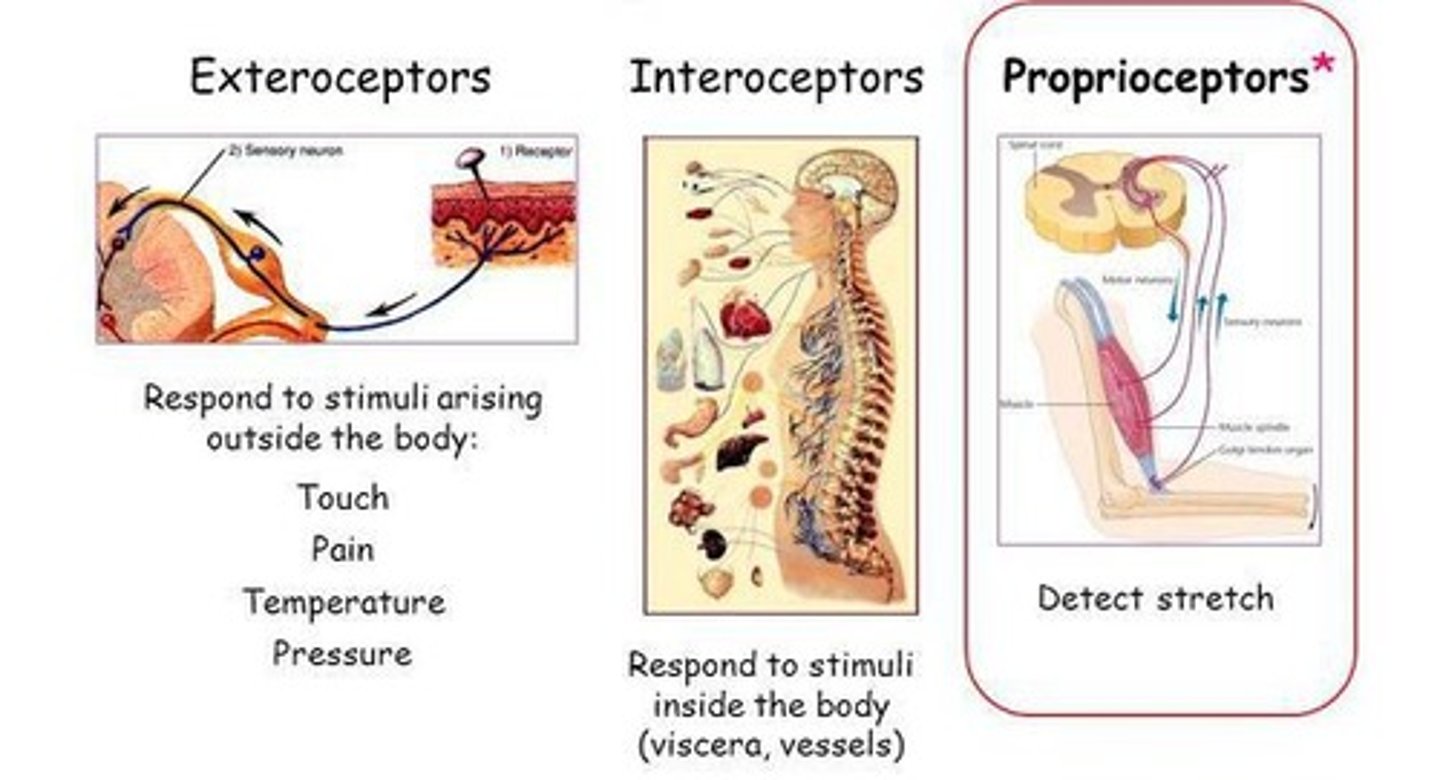
Exteroceptors
React to external stimuli.
Interoceptor/visceroceptor
React to internal stimuli.
Proprioceptor
Detects body/limb position.
Free/naked nerve endings
Detects light touch, pain, and temperature.
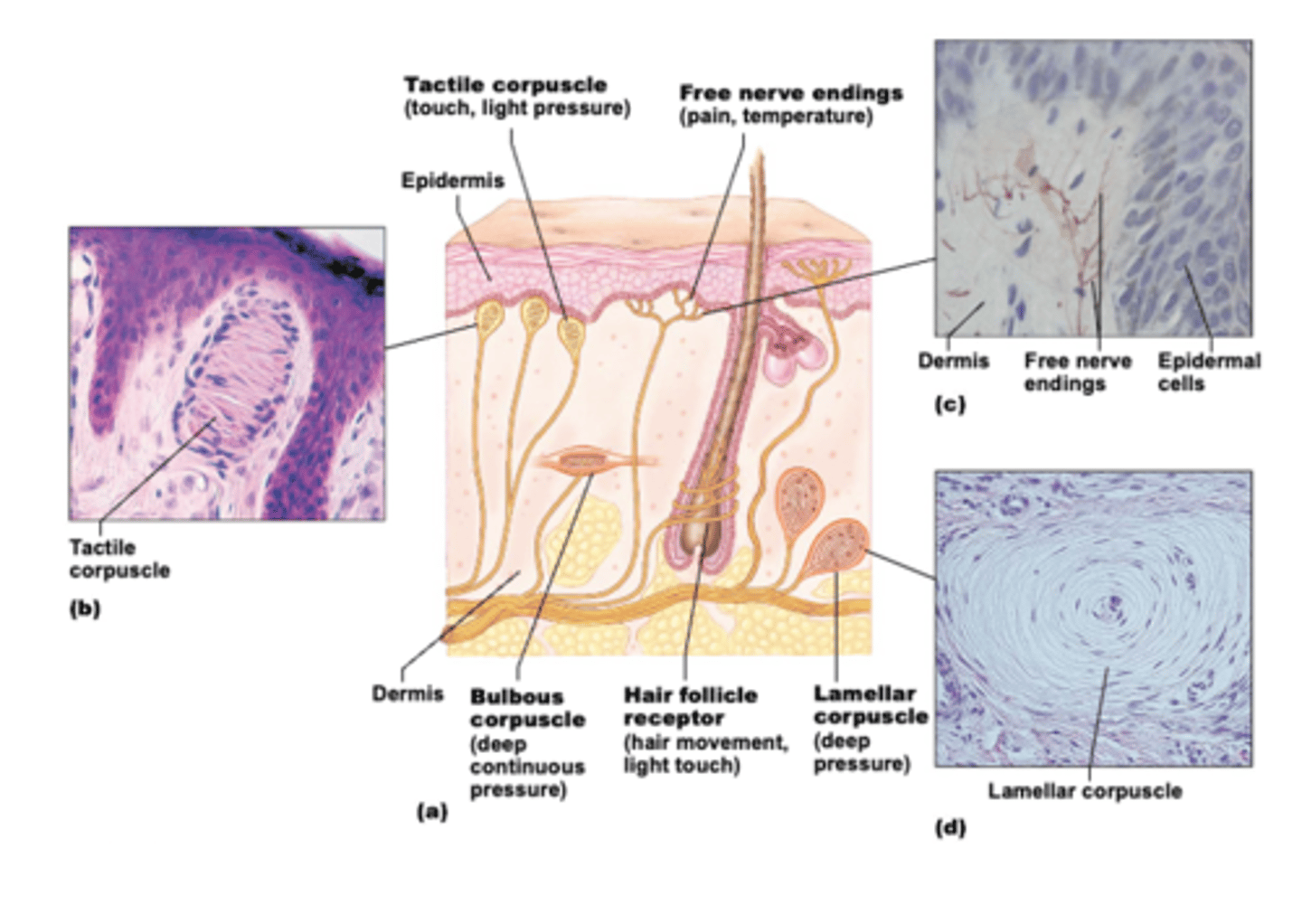
Hair follicle receptor
Detects light touch.
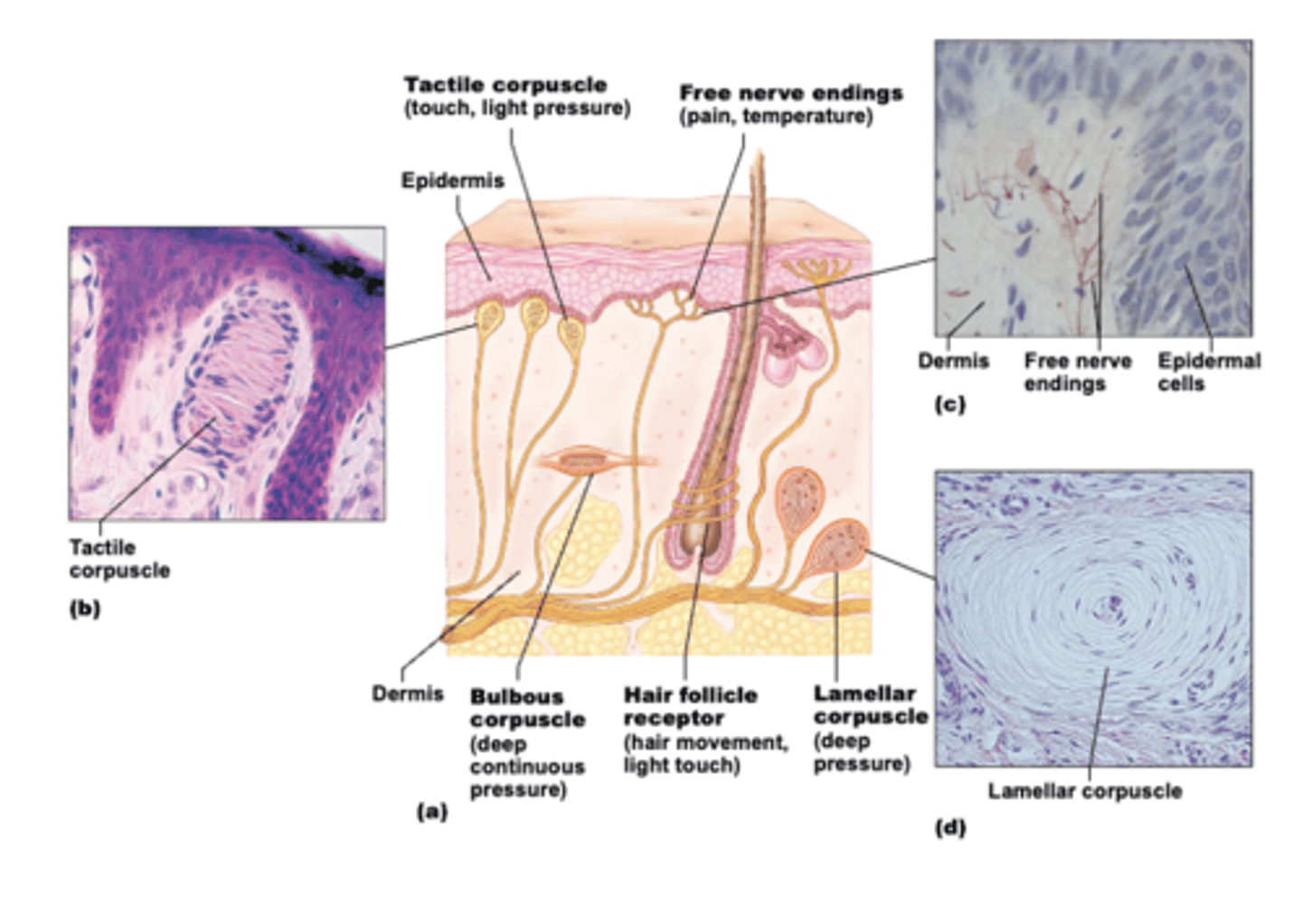
Tactile (Meissner's) corpuscle
Detects light touch and light pressure.
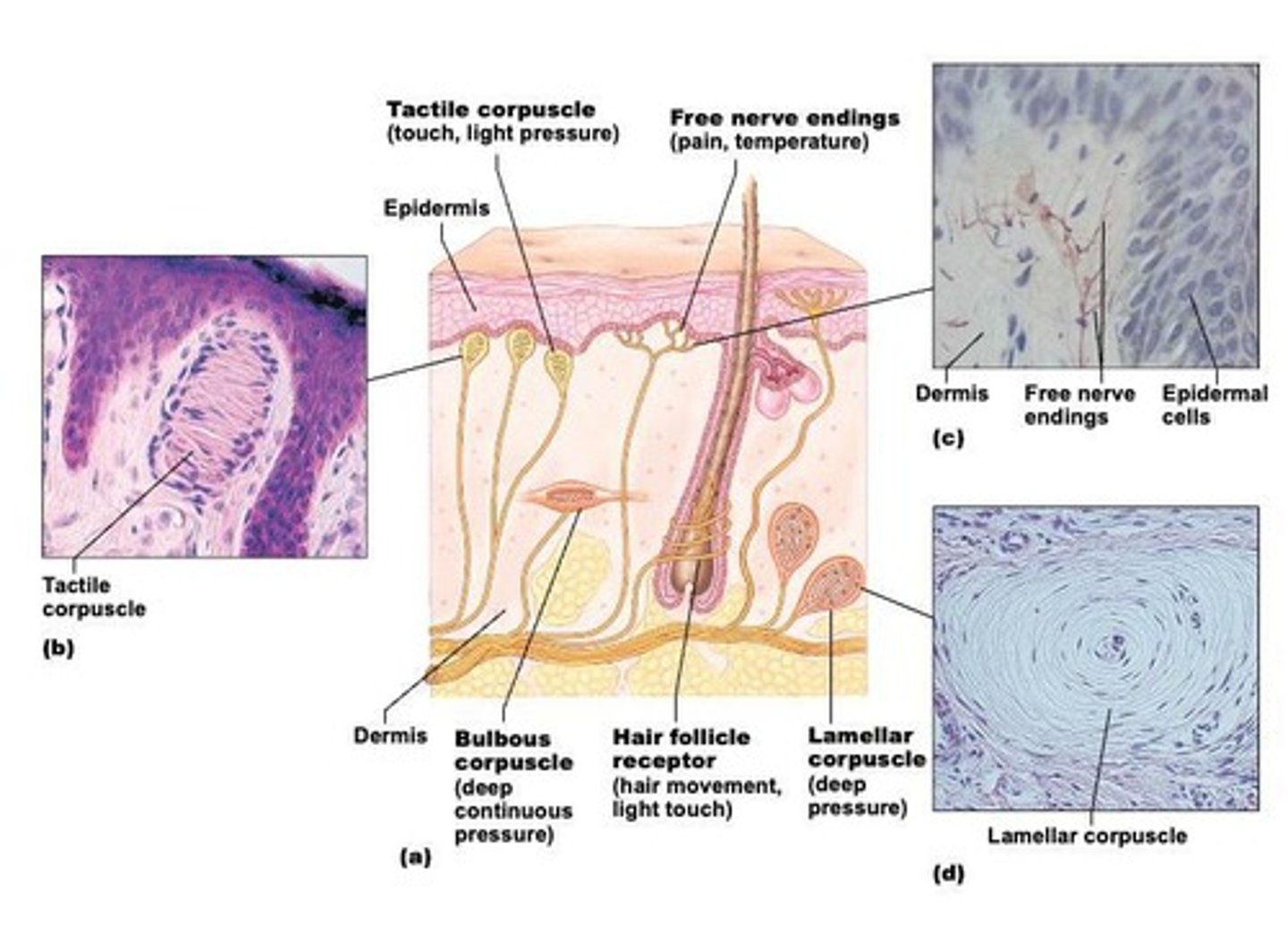
Bulbous (Ruffini's) corpuscle
Detects deep pressure/stretching.
Lamellar (Pacinian) corpuscle
Detects deep pressure/high frequency vibrations.
Qualities of cutaneous sensations
Touch, heat, cold, & pain.
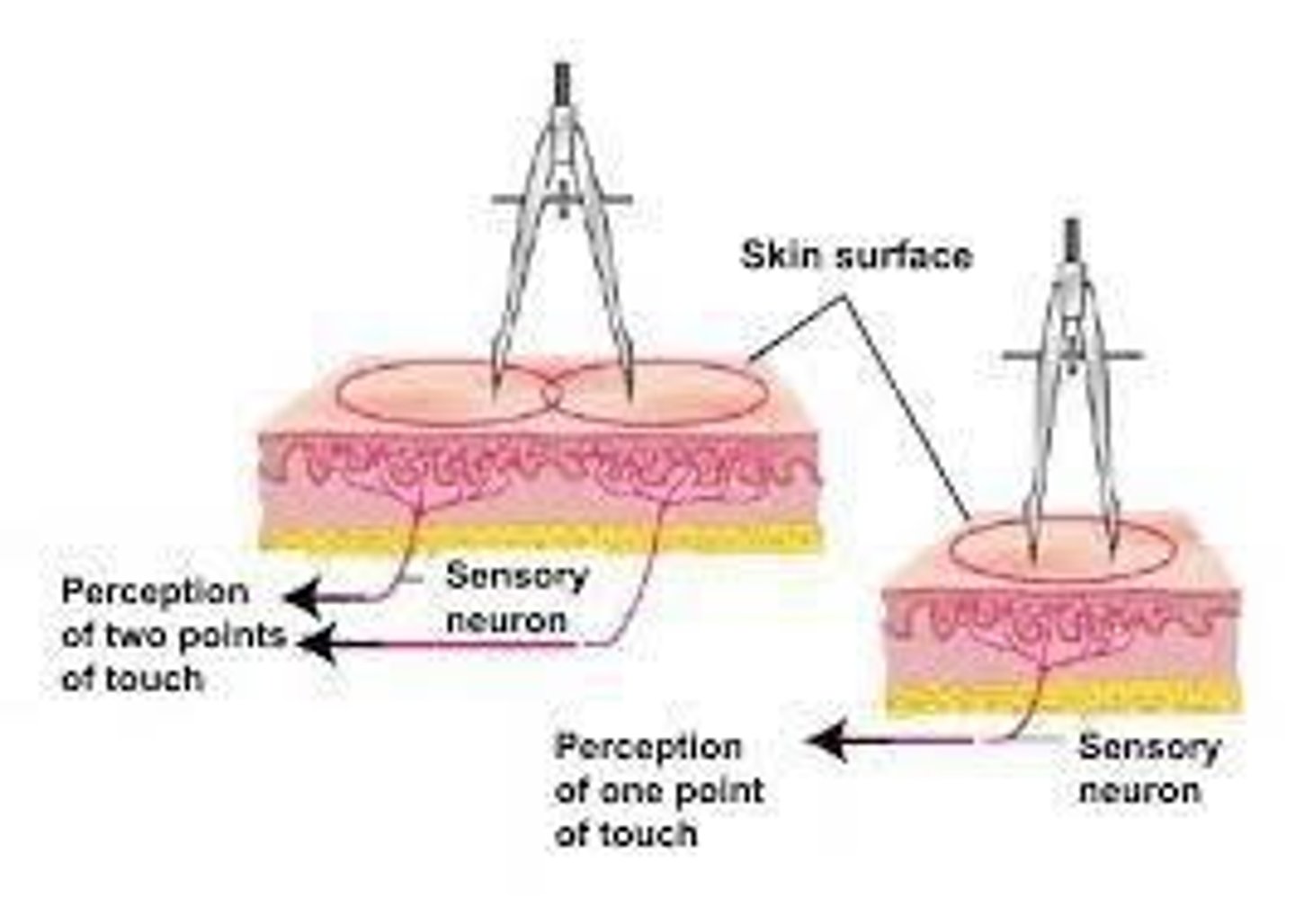
Two-point threshold
Smallest distance 2 points of contact can be perceived; closer on face than on back.
Tactile localization
Determining which point on skin has been stimulated.
Adaptation
Sensory receptor discharge from stimulus slows, causing the perception of stimulus to decrease.
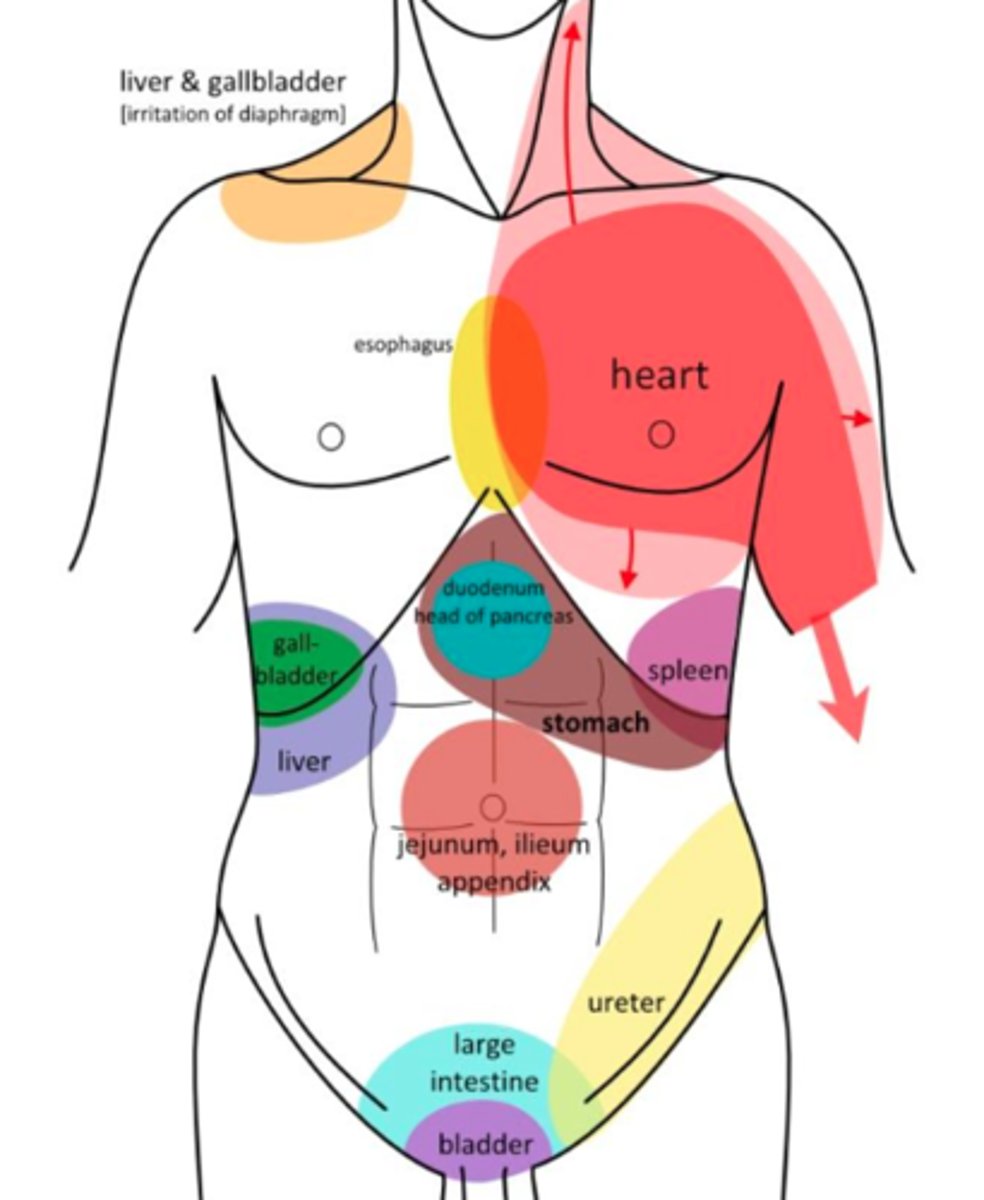
Referred pain
Perception of pain from one area of body when another area is actually receiving the noxious stimulus.