Module 10 W
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
You can use the culture characteristics of bacterial grwoth patterns in broth culture to learn about
Oxygen requirements
Hydrophobicity
Motility
Turbid
an evenly dispersed homogenous growth in a broth
sediment or pellets
cells that grow or sink to the bottom of the tube
pellicle
growth at the broth-air interface at the top of the broth tube
Obligate aerobe
grows only at the surface
microaerophilic
grows just below the surface
Facultative anaerobe
Grows throughout but greatest growth at the surface
aerotolerant anaerobe
grows with or without oxygen. Disperated equally throughout the medium
Obligate anaerobe
grows only at the bottom
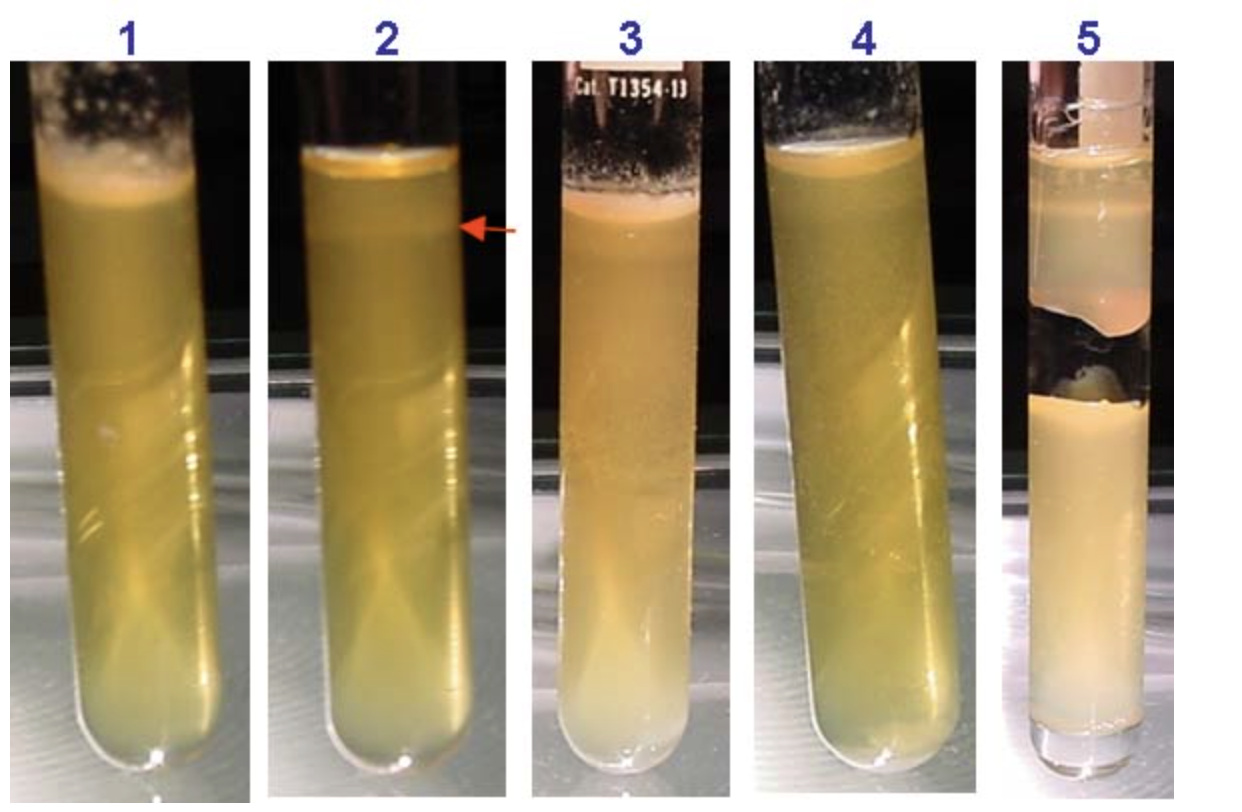
Say what type of grow each is
Obligate aerobe
Microaerophile
Facultative anaerobe
Aerotolerant anaerobe
Obligate anaerobe
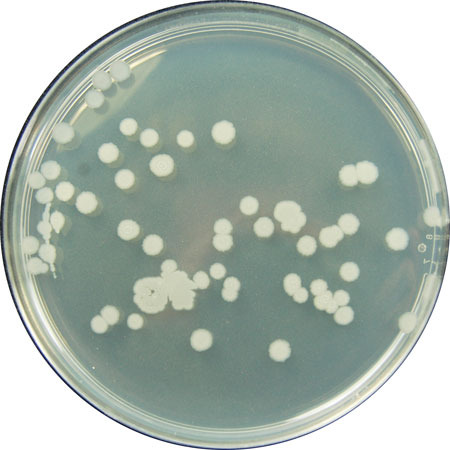
How may colonies vary
color, shape, elevation, and more
What can contaminate a bacteriology media
fungal growth
why is it unadvised to open the top if you suspect mold growing
it can release reproductive spores on the fungus which can be carried on for long distances on air currents
How does non-pigmented bacterial colonies look
translucent, tan, cream, or white in apperance
How do pigmented colonies appear?
red, golden yellow, or blue-green.
the colors in bacterial colonies can indicate
potential pathogens
Pigments can be
diffusible or non-diffusible
diffusible pigments
spread from colony into colony in surrounding agar medium
non diffusible pigment
stay within colonies
Say the following about bacillus subtilus
Growth Medium:
Pigment:
is it diffusible or not
Unique growth characteristics:
Oxygen characteristics:
Growth medium: Broth and Agar plate/slant
Pigment: Cream white (no pigment)
Diffusible/non-diffusible: N/A
Unique growth characteristics: Irregular
Oxygen characteristics: Aerobic and can form pellicle
Say the following about Staphylococcus epidermidis
Growth Medium:
Pigment:
is it diffusible:
Oxygen characteristics:
Growth Medium: Broth/Agar plate
Pigment: None (but can appear yellow)
is it diffusible: N/A
Oxygen characteristics: Faculative anaerobe
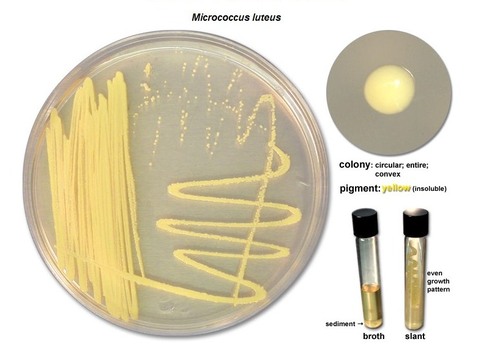
Say the following about: Micrococcus Luteus
Growth Medium:
Pigment:
is it diffusible:
Oxygen characteristics:
Growth Medium: Agar plate
Pigment: Yellow
is it diffusible: non-diffusible
Oxygen characteristics: Obligate aerobe
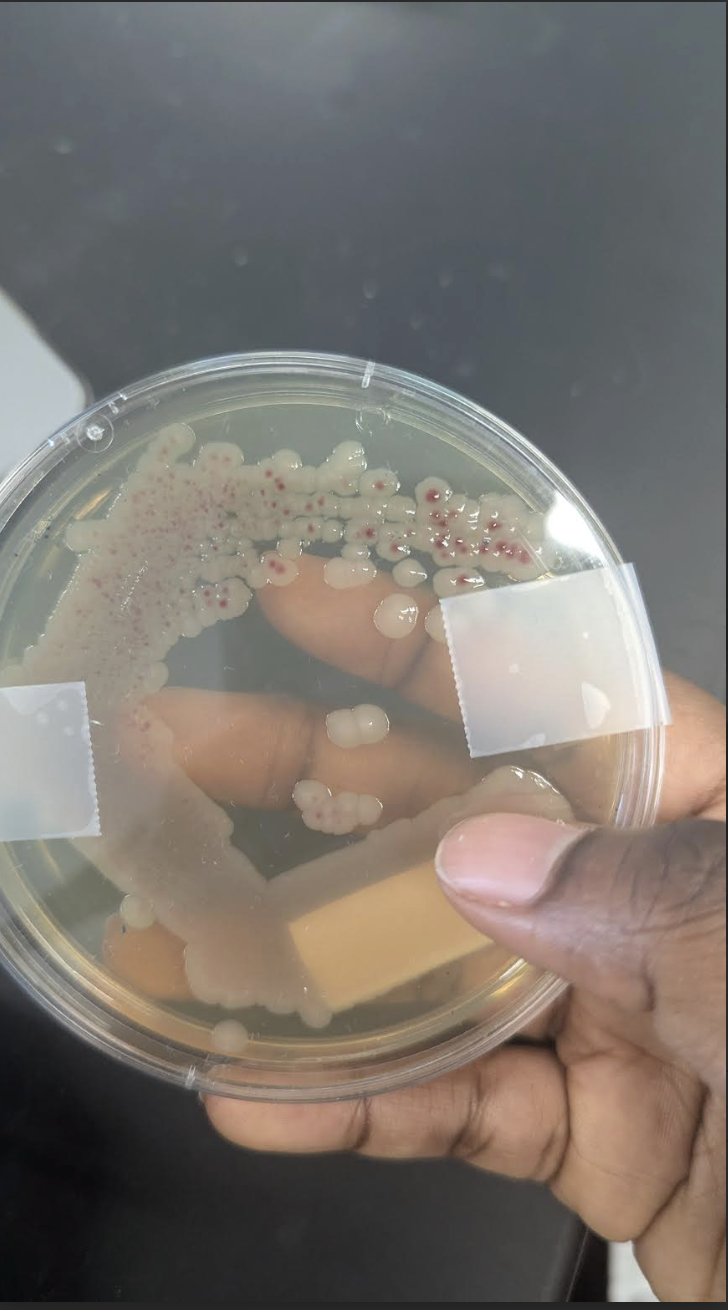
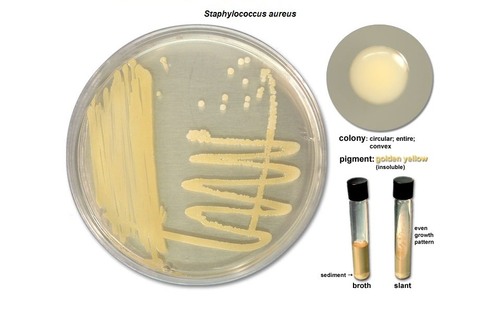
Say the following about: Serratia Marcescens
Growth Medium:
Pigment:
is it diffusible:
Oxygen characteristics:
Growth medium: Agar plates (25-30*C)
Pigment: Red (prodigiosin)
Is it diffusible: non diffusible
Oxygen characteristic: Facultative anaerobic
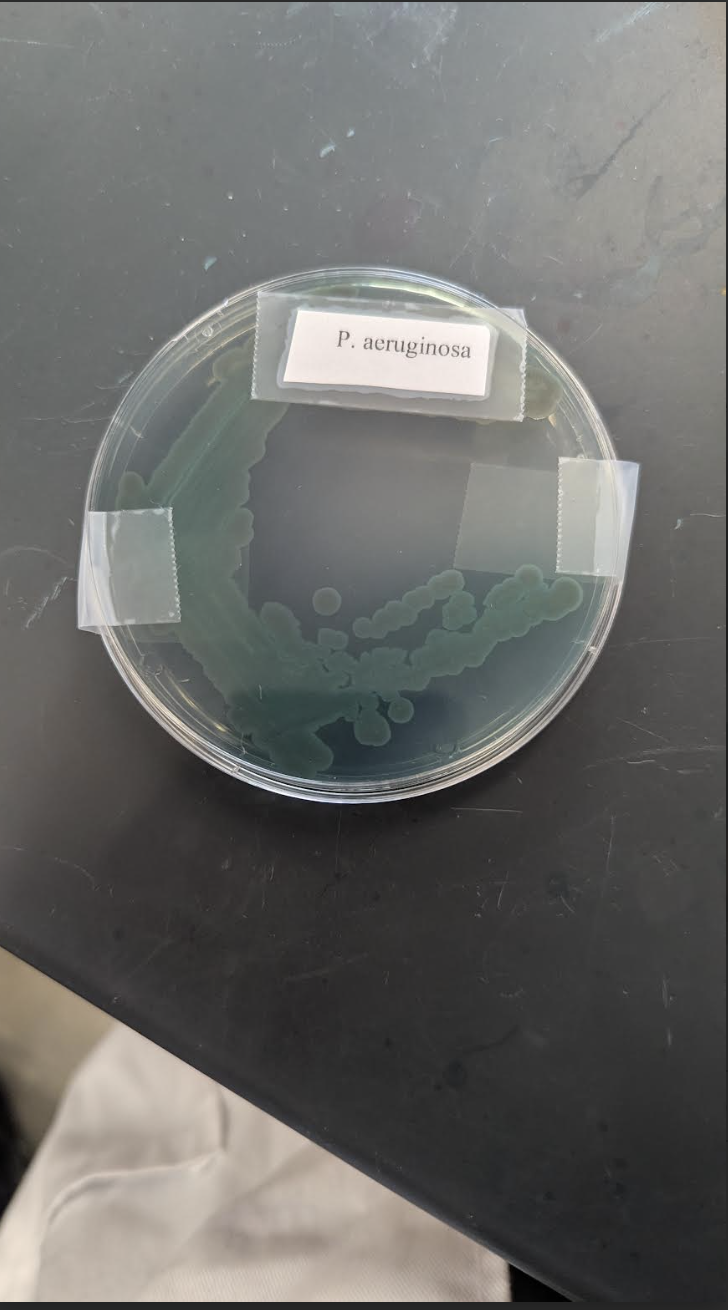

Say the following about: Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
Growth Medium:
Pigment:
is it diffusible:
Oxygen characteristics:
Growth medium: Agar plate/Slant
Pigment: green-blue pigment
Is it diffusible: Diffusible
Oxygen characteristic: Facultative anaerobe or aerobic. Fruity grape-like odor
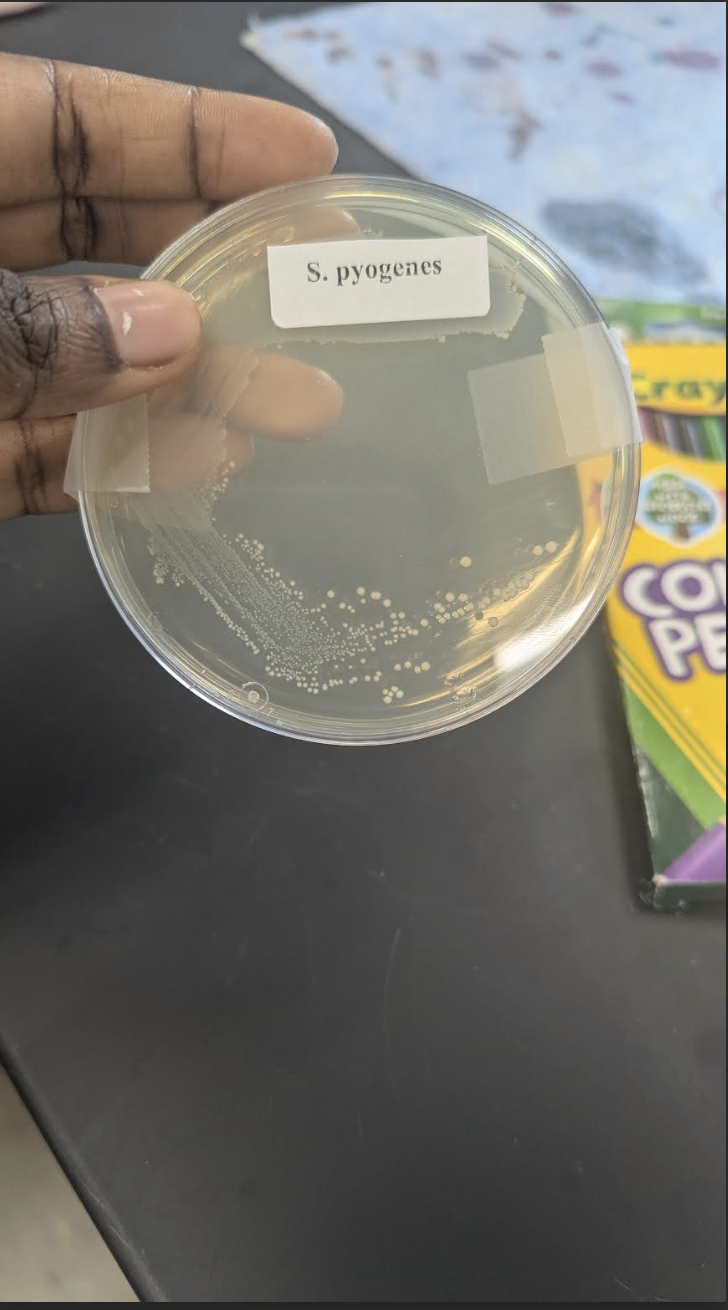

Say the following about: Group A streptococcus pyogenes
Growth Medium:
Pigment:
is it diffusible:
Oxygen characteristics:
Growth medium: agar or blood agar
Pigment: No pigment (but medium can be red)
is is it diffusible: N/A
Oxygen characteristics: Facultative anaerobic
What are the unique oders that microorganisms can produce
Pleasant grape like (pseudomonas aeruginosa)
Rotten egg smell of hydrogen sulfide
Sour smell of kitchen dish/sour milk from the growth of staphylococcus
Why do some colonies have a rotten egg smell of hydrogen sulfide
Produced when sulfate serves as a final electron acceptor in the electron transport system during anaerobic respiration
Two pathogenic bacteria that cause the most disease in humans are
streptococcus pyogenes and staphlycoccus aureus
What is pseudomonas aeruginosa
opportunistic pathogens that causes infections in health care settings
Where does pseudomonas aeruginosa grow in
Moist enviroments
What diseases can pseudomonas aeruginosa cause
Infection of burn victims because the primary skin barrier is destroyed (serous fluid produced)
Cystic fibrosis
blue-green pus of wounds
diseases caused by streptococcus pyogenes (name 3)
Streptococcal pharyngitis (strep throat)
Acute rheumatic fever and heart disease
Toxic shock syndrome
What is staphylococcus aureus known as
staph
diseases cause by staphylococcus aureus
foodborn intoxication
Cutaneous infections (impetigo, boils, wound infection)
Toxic shock syndrome, scalded skin syndrome
Bacteremia and metastatic infections
Mutualism
metabolic products that can be beneficial
parasitism
metabolic products that can be detrimental
What does the term hydrophobicity
the property of a substance to repel water and resist dissolving in it
Give two reasons why bacterial cells may grow only at the bottom of a broth tube, growth known as sediment or pellet
The bacterial is an obligate anaerobic organism
They are heavy/non-motile and sink
How are cell morphology and culture morphology differentiated from each other?
Cell morphology describes the shape and arrangement of individual bacterial cells under a microscope after staining while cultural morphology describes the appearance of a bacterial colony or culture growing on a solid or liquid media
Would you expect the same organism, grown for the same amount of time on the same agar plate medium to produce colonies of approximately the same size?
Not allows. Even though its the same organism/medium, the location and crowding affect colony size
If all colonies were well isolated, how would that affect the size of the colonies
colonies would be approximately the same size because each one has equal access to nutrients, space, and oxygen
What happens if the colonies are growing very close to one another?
Colonies would be smaller because they are competing for limited nutrients and oxygen
Would you expect to observe a difference in size, dependent upon where the bacterium is growing on the plate? Why or why not?
Yes colonies near the center or in crowded areas will usually be smaller due to higher competition and waste build up. Colonies at the edges tend to be larger since they have more access to fresh nutrients
When many colonies grow closely together, what gets ‘used up’ and what ‘builds up’ in the microenvironment around the bacteria?
gets sed up: Nutrients, oxygen, and space
Builds up: Waste products, toxins, and acidic byproducts of metabolism
Define morphology
The appearance and structure of a cell
What is a pellicle and what type of microorganism would grow as a pellicle
A pellicle are cells near the broth air interface. Microorganisms that are aerobic grow like this like bacillus
What would spreading growth on an agar slant signify about an organism
the motility of the organism
Give two examples of pigmented organisms
serratia marcescens
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
On the slant, bacillus subtilis often exhibits what type of growth
obligate aerobic
pinpoints (punctiform colonies) are indicative of what type of bacteria
Streptococcus
If you have a pure culture growing on an agar plate, which of the following would you expect to be true?
• Well-isolated colonies (CFUs) should be about the same size as colonies that are growing
very close together. (Yes or No)
• Well-isolated colonies (CFUs) should be larger than colonies that are growing very close
together. (Yes or No)
• Well-isolated colonies (CFUs) should be smaller than colonies that are growing very close
together. (Yes or No)
No
Yes
No
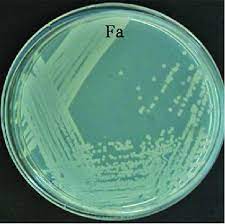
Pseudomonas fluorescens
pigment:
disease:
light bluish/greenish fluorescence stronger
Bloodstream and respiratory infection
Mycobacterium makes what in broth
pellicle