4.4.1 - financial sector
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
define financial market
a financial market is any exchange that facilitates the trading of financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, foreign exhcnage, insurance or commodities such as oil or gas
what are the key 5 roles of a financial market
to facilitate saving by households and business (secure place to save - store money - earn interest)
lend to businesses and individuals (financial market = intermediary between savers + borrowers)
facilitate the final exchange of goods and services - cash credit card contactless or foreign exchange
provide forward markets in currencies and commodities
to provide a market for equities
what are the three main types of financial markets
the money market - short term finance - up to 12 months - provided by commercial banks - provides short term gov borrowing to fund government budget deficit (fiscal)
the capital market - company shares or bonds are sold - long term 10 - 20 year loans - universities government and companies
foreign exchange market - currencies are traded - forward exchange or spot exchange
what is a forward market (currency)
a forward market in currency is a binding contract ( cant be broken ) in the foreign exchange market
locks in exchange rate for the buying and selling rate in the future
risk management technique + gives certainty - to guard against any changes in exhange rate
what is the forward market ( commodities )
it is a binding contract between buyers and sellers of a commodity
agreeing on a price of a commodity on a future date
binding means cant be broken
risk management technique and creates more certainty against changes in the price of the commodity
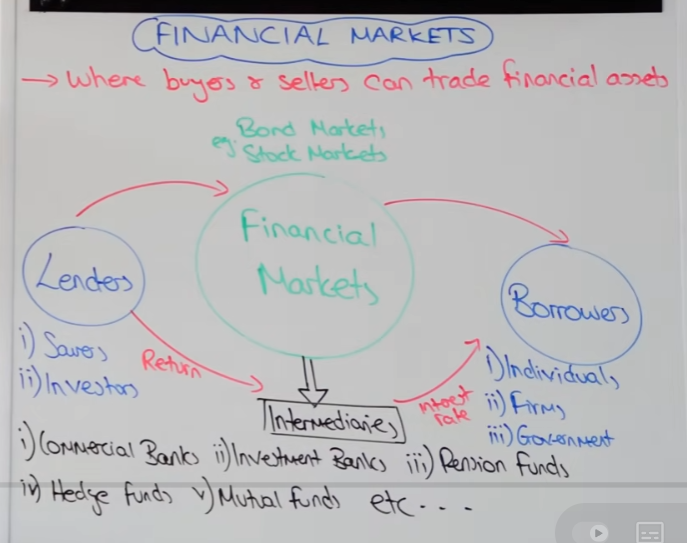
draw the link between financial markets and borrowers - describe it
commercial banks objective is to take lenders money, in a deposit, and return is payed
from savings, loans can be made and lent out to consumers and firms
they will charge a higher rate of interest to borrowers and reward savers with a lower rate of interest.
what are the characteristics of money
durability
portability
divisibility
acceptability
hard to counterfeit
valuable
what are the key functions of money
medium of exchange
store of value
unit of account
standard of deferred payment
what is market failure - and the types of market failure
market failure - occurs when a market fails to allocate recourses in an efficeint way, leading to a loss in economic and social welfare
externalities from financial instability
monopoly power in financial institution
market rigging/ collusion
speculative bubbles and irrational behaviour
moral hazard and attitudes to risk taking
asymmetric information + complexity
explain externalities from financial instability and give examples
third party effects by UK banks taking too much risk
tax payer - bail out cost - tax burden goes up
employees - higher unemployment rate
government - fiscal deficite
describe asymmetric information and give examples
one party holds more information then the other party
buyers and sellers of shares - insider information on stock
credit risk - banks knows more about the debtor
what is a moral hazard and examples of moral hazzard in the financial market
state bails out failing banks - this causes banks to be more risky as the state is likely to bail out
generous health insurance can lead to over prescription of drugs
describe market power and give examples
companies in the market act together ( collude ) to stop a market from acting as it should, in order to get an unfair advantge
illegal - stops market forces - supply and demand - harms rate of competition
e.g price fixing in the bond market
what is market power ( oligopoly/ monopoly ) and give examples
banking sector
high barriers to entry
unlikely to switch - habitual behaviour
what is speculative bubbles - give examples
a bubble exists when the market price is driven well above what it should bee - herd behaviour - market booms then busts
stages -
displacement stage - excitement grows
price boom - demand surges + limited ( inelastic supply )
euphoria - investors take advantage ( irrational exuberance )
profit taking stage - investors sell when prices are out of line with fundamentals
panic - herd mentality - desperate selling